SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读
SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读 - RequestCondition体系
一般我们开发时,使用最多的还是@RequestMapping注解方式.
@RequestMapping(value = "/", param = "role=guest", consumes = "!application/json")
public void myHtmlService() {
// ...
}
台前的是RequestMapping ,正经干活的却是RequestCondition,根据配置的不同条件匹配request.
@RequestMapping注解,请看<SpringMVC源码解读 - HandlerMapping - RequestMappingHandlerMapping初始化>
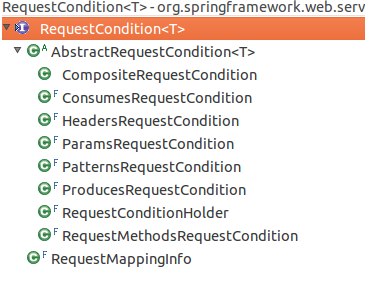
典型的接口+模板.一个接口ReqeustCondition,一个抽象类,定义基础,然后n多的具体实现.
实现中可以分为3类:基础实现,外观类和容器.
其中CompositeRequestCondition和RequestMappingInfo本身不带任何的匹配条件,只是用于包装其他的RequestCondition进行匹配
基础实现:
consumes对应request的提交内容类型content type,如application/json, text/html
headers 对应http request 的请求头
params对应http request parameter
Patterns对应url,就是注解value中的配置
produces指定返回的内容类型的content type,仅当request请求头中的(Accept)类型中包含该指定类型才返回
requestMethods对应 http method,如GET,POST,PUT,DELETE等
外观类:
RequestConditionHolder,用于不知道具体是RequestCondition哪个子类时.自定义的条件,使用的这个进行封装
容器:
CompositeRequestCondition封装基础实现,具体的匹配都委托给基础实现类.
RequestMappingInfo,对应@RequestMapping注解,一一对应注解内容与基础实现,使用时一一委托.
先来看看RequestCondition的接口定义
1 package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition;
2 /**
3 * The contract for request conditions.
4 */
5 public interface RequestCondition<T> {
6
7 /**
8 * 将不同的筛选条件合并
9 */
10 T combine(T other);
11
12 /**
13 * 根据request查找匹配到的筛选条件
14 */
15 T getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request);
16
17 /**
18 * 不同筛选条件比较,用于排序
19 */
20 int compareTo(T other, HttpServletRequest request);
21
22 }
23 }
老规矩,接下来得上抽象类AbstractRequestCondition
AbstractRequestCondition做的事不多,覆写equals,hashCode,toString.实现equals,hashCode,toString时预留模板方法getContent();实现toString时预留模板方法getToStringInfix().
1 package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition;
2 /**
3 * A base class for {@link RequestCondition} types providing implementations of
4 * {@link #equals(Object)}, {@link #hashCode()}, and {@link #toString()}.
5 *
6 * @author Rossen Stoyanchev
7 * @since 3.1
8 */
9 public abstract class AbstractRequestCondition<T extends AbstractRequestCondition<T>> implements RequestCondition<T> {
10
11 /**
12 * Return the discrete items a request condition is composed of.
13 * For example URL patterns, HTTP request methods, param expressions, etc.
14 * @return a collection of objects, never {@code null}
15 */
16 protected abstract Collection<?> getContent();
17
18 @Override
19 public boolean equals(Object o) {
20 if (this == o) {
21 return true;
22 }
23 if (o != null && getClass().equals(o.getClass())) {
24 AbstractRequestCondition<?> other = (AbstractRequestCondition<?>) o;
25 return getContent().equals(other.getContent());
26 }
27 return false;
28 }
29
30 @Override
31 public int hashCode() {
32 return getContent().hashCode();
33 }
34
35 @Override
36 public String toString() {
37 StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("[");
38 for (Iterator<?> iterator = getContent().iterator(); iterator.hasNext();) {
39 Object expression = iterator.next();
40 builder.append(expression.toString());
41 if (iterator.hasNext()) {
42 builder.append(getToStringInfix());
43 }
44 }
45 builder.append("]");
46 return builder.toString();
47 }
48
49 /**
50 * The notation to use when printing discrete items of content.
51 * For example " || " for URL patterns or " && " for param expressions.
52 */
53 protected abstract String getToStringInfix();
54
55 }
接下来得看具体实现了,捏不到软柿子,用ParamsRequestCondition简单说明下子类吧
// ParamsRequestCondition
1 // 保存解析出来的param匹配条件 2 private final Set<ParamExpression> expressions;
ParamExpression其实很简单,看父类AbstractNameValueExpression很清楚
// AbstractNameValueExpression
1 package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition;
2 abstract class AbstractNameValueExpression<T> implements NameValueExpression<T> {
3 // 参数的名字
4 protected final String name;
5 // 参数的值
6 protected final T value;
7 // 参数的匹配规则,是= 还是!=
8 protected final boolean isNegated;
9 }
到这里我们就可以看懂,使用ParamExpression保存param参数,这样可以任意多个.
combine的实现也就水到渠成,直接把expression拼接到一个集合里就行:
1 package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition;
2 public final class ParamsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ParamsRequestCondition> {
3 /**
4 * Returns a new instance with the union of the param expressions
5 * from "this" and the "other" instance.
6 */
7 public ParamsRequestCondition combine(ParamsRequestCondition other) {
8 Set<ParamExpression> set = new LinkedHashSet<ParamExpression>(this.expressions);
9 set.addAll(other.expressions);
10 return new ParamsRequestCondition(set);
11 }
12 }
getMatchingCondition时,只要有一个不符合就判定条件不匹配
1 package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition;
2 public final class ParamsRequestCondition extends AbstractRequestCondition<ParamsRequestCondition> {
3 /**
4 * Returns "this" instance if the request matches all param expressions;
5 * or {@code null} otherwise.
6 */
7 public ParamsRequestCondition getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
8 for (ParamExpression expression : expressions) {
9 if (!expression.match(request)) {
10 return null;
11 }
12 }
13 return this;
14 }
15 }
这边的match方法比较有意思,可以看下
1 package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition;
2 abstract class AbstractNameValueExpression<T> implements NameValueExpression<T> {
3 public final boolean match(HttpServletRequest request) {
4 boolean isMatch;
5 if (this.value != null) {
6 isMatch = matchValue(request);
7 }
8 else { // 没有value时,只要匹配name就好
9 isMatch = matchName(request);
10 }
11 return isNegated ? !isMatch : isMatch; // 这边需要看仔细,=与!=的处理
12 }
13
14 protected abstract boolean matchName(HttpServletRequest request);
15
16 protected abstract boolean matchValue(HttpServletRequest request);
17 }
ParamExpression中给出matchName与matchValue的实现.
ParamExpression这里又是接口+抽象实现+模板方法设计模式,偷个懒,暂时不去关心各层抽象的什么.
compareTo根据匹配条件的多少来判定顺序
// ParamsRequestCondition
1 public int compareTo(ParamsRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {
2 return other.expressions.size() - this.expressions.size();
3 }
记得还留有两个模板方法
getContent直接返回记录param的expressions
getToStringInfix则使用&&
// ParamsRequestCondition
1 @Override
2 protected Collection<ParamExpression> getContent() {
3 return expressions;
4 }
5
6 @Override
7 protected String getToStringInfix() {
8 return " && ";
9 }
再看看是如何解析param的
// ParamsRequestCondition
1 /**
2 * Create a new instance from the given param expressions.
3 * @param params expressions with syntax defined in {@link RequestMapping#params()};
4 * if 0, the condition will match to every request.
5 */
6 public ParamsRequestCondition(String... params) {
7 this(parseExpressions(params));
8 }
9
10 private static Collection<ParamExpression> parseExpressions(String... params) {
11 Set<ParamExpression> expressions = new LinkedHashSet<ParamExpression>();
12 if (params != null) {
13 for (String param : params) {
14 expressions.add(new ParamExpression(param));
15 }
16 }
17 return expressions;
18 }
核心的代码还是在AbstractNameValueExpression
// AbstractNameValueExpression
逻辑不复杂,代码看着有点烦,是不是应该听Martin Fowler在<重构>中的建议,来个extract method?
1 AbstractNameValueExpression(String expression) {
2 int separator = expression.indexOf('=');
3 if (separator == -1) {
4 this.isNegated = expression.startsWith("!");
5 this.name = isNegated ? expression.substring(1) : expression;
6 this.value = null;
7 }
8 else {
9 this.isNegated = (separator > 0) && (expression.charAt(separator - 1) == '!');
10 this.name = isNegated ? expression.substring(0, separator - 1) : expression.substring(0, separator);
11 this.value = parseValue(expression.substring(separator + 1));
12 }
13 }
RequestCondition的解读未完,待续:
SpringMVC源码解读 - RequestMapping注解实现解读 - ConsumesRequestCondition



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号