Spring Boot 增加删除修改 批量
1.批量删除
a.自定义Repositoy中写
前台处理https://blog.csdn.net/yhflyl/article/details/81557670
首先前台先要获取所有的要删除数据的ID,并将ID拼接成字符串 例如: 2,3,4,5,然后通过GET请求返送到后台。
后台处理
控制器接收
/**
* @function 批量删除
* @param stu_id
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/del_stu")
@ResponseBody
public Msg batch_del_stu(@RequestParam("stu_id") String stu_id){
// 接收包含stuId的字符串,并将它分割成字符串数组
String[] stuList = stu_id.split(",");
// 将字符串数组转为List<Intger> 类型
List<Integer> LString = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(String str : stuList){
LString.add(new Integer(str));
}
// 调用service层的批量删除函数
studentsService.deleteBatch(LString);
return Msg.success().add("数组", LString);
}
service层
@Override
public void deleteBatch(List<Integer> stuList) {
// 第一种批量删除方法,是通过spring data中继承JpaRepository接口后,通过关键字拼接的方法进行删除,删除时候是通过ID一条一条删除的
// studentsRepository.deleteStudentsByStuIdIn(stuList);
// 第二种批量删除方法, 是通过自定义JPQL语句进行删除,使用的是 where stuId in ()的操作
studentsRepository.deleteBatch(stuList);
}
Repository接口层
public interface StudentsRepository extends Repository<Students, Integer>, JpaRepository<Students, Integer> {
/**
* @function 自定义JPQL
* @param ids
*/
// 注意更新和删除是需要加事务的, 并且要加上 @Modify的注解
@Modifying
@Transactional
@Query("delete from Students s where s.stuId in (?1)")
void deleteBatch(List<Integer> ids);
// 这个是通过spring data拼接关键字进行的操作
void deleteStudentsByStuIdIn(List<Integer> ids);
}
附加
@Modifying注解
1、在@Query注解中编写JPQL实现DELETE和UPDATE操作时候必须加上@Modifying注解,通知Spring Data这是一个delete或者updata操作
2、 updata和delete操作需要使用事务,此时需要定义service层,在service方法上添加事务操作
3、 注意JPQL不支持insert操作
@Query 如果在注解中添加 nativeQuery=true 是支持原生SQL查询
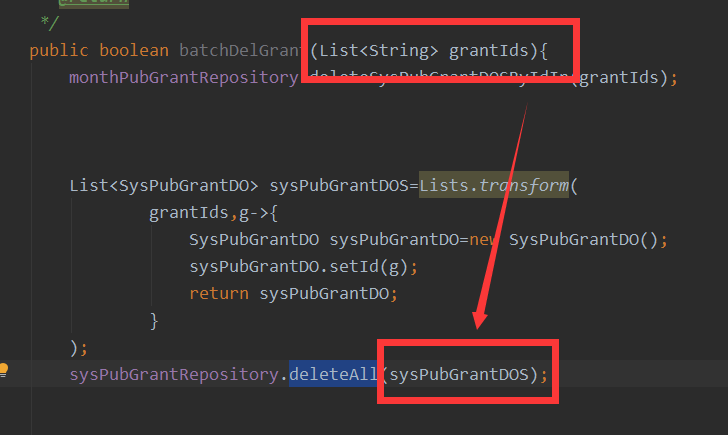
b.通过JpaRepository 或者CrudRepository 自带的
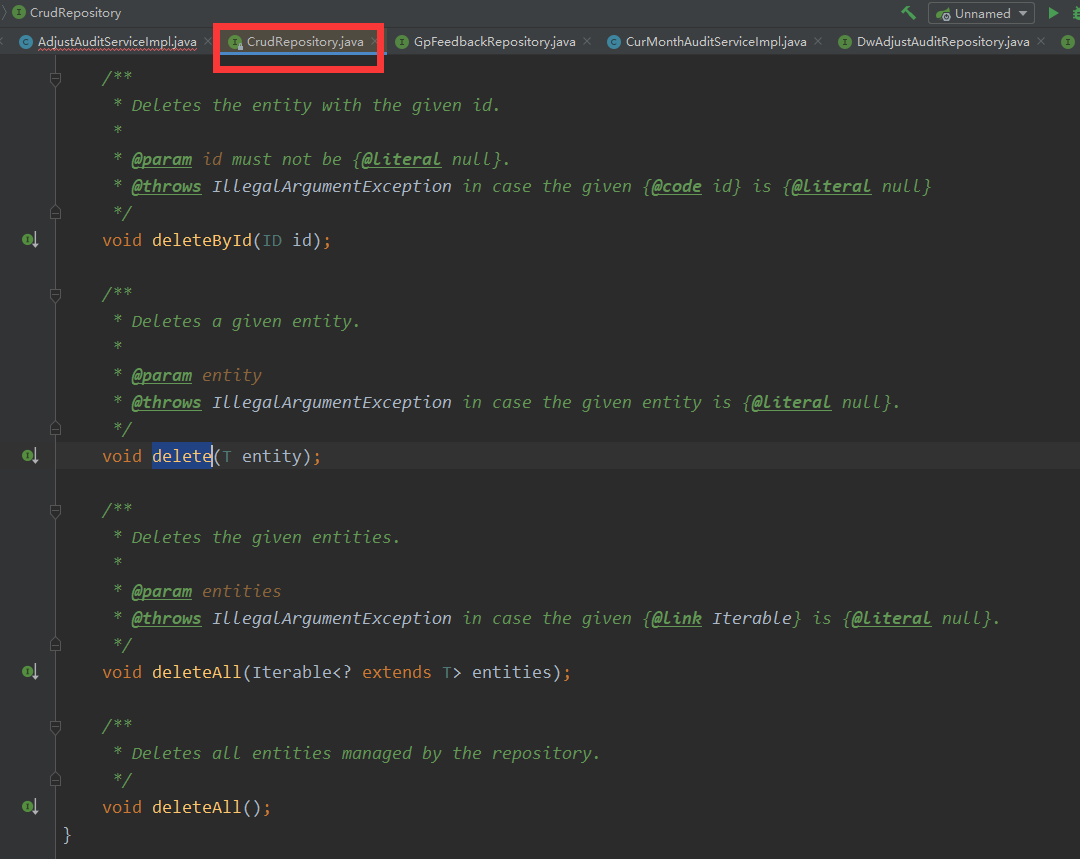
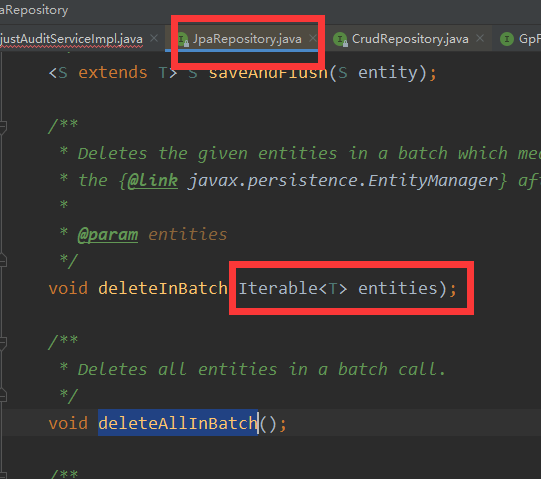
可以将前台的ids封装为entitys 使用这些自带的
如下
2.SpringDataJpa进行修改数据库操作有两种方式:
一、调用保存实体的方法
1、保存一个实体:repository.save(T entity)
2、保存多个实体:repository.save(Iterable<T> entitys)
3、保存一个实体并立即刷新更改:repository.saveAndFlush(T entity)
注意事项:保存对象时需要确定 PRIMARY KEY和唯一索引。否则会报出“Duplicate entry '1-2-0' for key”这样的错误。
修改对象时,也使用如上方法,但需要确定PRIMARY KEY,如果PRIMARY KEY不存在,则是添加操作。
二、@Query注解(写JPQL语句)
JPQL( Java 持久性查询语言)JPQL 和 SQL 的主要区别在于,前者处理JPA 实体、属性,后者直接在数据库空间内对表、列、行等关系数据进行处理。
JPQL解释:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33746131/article/details/56479226
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Modifying;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
Repositoryk中@Query写JPQL语句:@Query("JPQL语句")
例1 修改操作
@Modifying
@Transactional
@Query("update CityStationGoods csg set csg.isOnsale = ?2 where csg.id = ?1")
int updateOnSaleState(int id, Boolean isOnsale);
例2 使用参数下标
@Modifying
@Transactional
@Query("delete from GoodsActivity ga where ga.activityId = ?1")
void deleteByActivityId(Integer activityId);
例3 使用参数名
@Modifying
@Transactional
@Query("delete from GoodsActivity ga where ga.activityId = :id")
void deleteByActivityId(@Param(value = "id")Integer activityId);
Repositoryk中@Query写SQL语句:@Query(value="SQL语句",nativeQuery = true)
例1
@Query(value = "SELECT IFNULL(SUM(num),0) FROM shopping_cart WHERE member_id =?1", nativeQuery = true)
int getCartNum(Integer memberId);
注意事项:查询时不需要@Modifying注解。@Modifying:指示方法应被视为修改查询。
@Transactional注解:在update或delete时,需要事务提交。如果不写Transactional无法将修改后的操作保存到数据库中。该注解可以写在Service或Repository中。(本例因测试学习,写到了Repository中)
Spring Data Jpa 更新操作
第一步,通过Repository对象把实体根据ID查询出来
第二部,往查出来的实体对象进行set各个字段
第三步,通过Repository接口的save方法进行保存
保存和更新方式(已知两种)
- 第一种是通过@Query和@Modify注解进行更新,自己可在@Query注解的HQL或SQL片段中指定更新的字段
- 第二种是通过ById查询出来并进行设值,最后进行保存更新操作
3.新增:
看日志,JPA是先把所有的数据全查出来了,如果数据库有就更新,没有就新增。https://www.cnblogs.com/blog5277/p/10661096.html
saveall() save() 就可以
不能写insert 语句 jpa不支持


