cf 486B
Let's define logical OR as an operation on two logical values (i. e. values that belong to the set {0, 1}) that is equal to 1 if either or both of the logical values is set to 1, otherwise it is 0. We can define logicalOR of three or more logical values in the same manner:
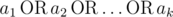 where
where 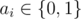 is equal to 1 if some ai = 1, otherwise it is equal to 0.
is equal to 1 if some ai = 1, otherwise it is equal to 0.
Nam has a matrix A consisting of m rows and n columns. The rows are numbered from 1 to m, columns are numbered from 1 to n. Element at row i (1 ≤ i ≤ m) and column j (1 ≤ j ≤ n) is denoted as Aij. All elements of A are either 0 or 1. From matrix A, Nam creates another matrix B of the same size using formula:
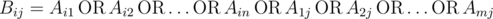 .
.
(Bij is OR of all elements in row i and column j of matrix A)
Nam gives you matrix B and challenges you to guess matrix A. Although Nam is smart, he could probably make a mistake while calculating matrix B, since size of A can be large.
The first line contains two integer m and n (1 ≤ m, n ≤ 100), number of rows and number of columns of matrices respectively.
The next m lines each contain n integers separated by spaces describing rows of matrix B (each element of B is either 0 or 1).
In the first line, print "NO" if Nam has made a mistake when calculating B, otherwise print "YES". If the first line is "YES", then also print m rows consisting of n integers representing matrix A that can produce given matrix B. If there are several solutions print any one.
2 2
1 0
0 0
NO
2 3
1 1 1
1 1 1
YES
1 1 1
1 1 1
2 3
0 1 0
1 1 1
YES
0 0 0
0 1 0
可以去死了,,,
A矩阵初始化全部赋值为1,然后 B矩阵为0的位置 直接 处理一遍A矩阵。注意当B矩阵元素为一时,需要判断一下A矩阵是否满足啊啊啊
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int a[110][110],b[110][110],n,m;
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i][j]);
b[i][j]=1;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]==0)
{
for(int k=1;k<=n;k++)
b[k][j]=0;
for(int k=1;k<=m;k++)
b[i][k]=0;
}
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
if(a[i][j]==1)
{
bool flag=0;
for(int k=1;k<=n;k++)
flag|=b[k][j];
for(int k=1;k<=m;k++)
flag|=b[i][k];
if(!flag)
{
printf("NO\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
printf("YES\n");
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<m;j++)
printf("%d ",b[i][j]);
printf("%d\n",b[i][m]);
}
return 0;
}



