EL技术
EL 表达式概述
EL(Express Lanuage)表达式可以嵌入在jsp页面内部,减少jsp脚本的编写,EL出现的目的是要替代jsp页面中脚本(java代码)的编写。
EL从域中取出数据(EL最重要的作用)
jsp脚本:<%=request.getAttribute(name)%>
EL表达式替代上面的脚本:${requestScope.name}
EL最主要的作用是获得四大域中的数据,格式${EL表达式}
EL获得pageContext域中的值:${pageScope.key};
EL获得request域中的值:${requestScope.key};
EL获得session域中的值:${sessionScope.key};
EL获得application域中的值:${applicationScope.key};
EL从四个域中获得某个值${key};
---同样是依次从pageContext域,request域,session域,application域中获取属性,在某个域中获取后将不在向后寻找
1)获得普通字符串
2)获得User对象的值
3)获得List<User>的值
<!-- 模拟域中的数据 -->
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("name", "pageContxt");
//存储字符串
request.setAttribute("name", "request");
//存储一个对象
Users user=new Users();
user.setId(1);
user.setUsername("lisi");
user.setPwd("123");
session.setAttribute("user", user);
//存储一个集合
List<Users> list=new ArrayList<Users>();
Users user1=new Users();
user1.setId(1);
user1.setUsername("wangwu");
user1.setPwd("123");
list.add(user1);
Users user2=new Users();
user2.setId(1);
user2.setUsername("zhaoliu");
user2.setPwd("123");
list.add(user2);
application.setAttribute("List", list);
%>
<hr>
<!-- 使用脚本取出域中的值 -->
<%=request.getAttribute("name") %>
<%Users u=(Users)session.getAttribute("user");
out.write(u.getUsername());
%>
<hr>
<!-- 使用EL表达式取出域中的值 -->
${requestScope.name}
${sessionScope.user.username}
${applicationScope.List[0].pwd}
<hr>
<!-- 使用el表达式 全域查找(会从最小的找,底层就是findAttribute()) -->
${name }
${user.username}
${List[0].pwd}
EL的内置对象11个
pageScope,requestScope,sessionScope,applicationScope
---- 获取JSP中域中的数据
param,paramValues - 接收参数.
相当于request.getParameter() request.getParameterValues()
header,headerValues - 获取请求头信息
相当于request.getHeader(name)
initParam - 获取全局初始化参数
相当于this.getServletContext().getInitParameter(name)
cookie - WEB开发中cookie
相当于request.getCookies()---cookie.getName()---cookie.getValue()
Form.html
<form action="/WEB02/form.jsp" method="get">
<input type="text" name="username">
<input type="text" name="password">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
Form.jsp
<!-- 获得表单的参数 -->
<%
request.getParameter("username");
//.....
%>
<!-- 使用EL获得参数 -->
${param.username }
${header["User-Agent"] }
${cookie.abc.value }
<!-- 通过el表达式获得request对象 -->
<%--${requestScope } --%>
${pageContext.request }
Cookie.jsp
<%
Cookie cookie=new Cookie("abc","zhangsan");
response.addCookie(cookie);
%>
Index.jsp
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/form.jsp" method="get">
<input type="text" name="username">
<input type="text" name="password">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
pageContext - WEB开发中的pageContext.
pageContext获得其他八大对象
${pageContext.request.contextPath}
EL执行表达式
例如:
${1+1}
${empty user}
${user==null?true:false}
JSTL技术
JSTL概述
JSTL(JSP Standard Tag Library),JSP标准标签库,可以嵌入在jsp页面中使用标签的形式完成业务逻辑等功能。jstl出现的目的同el一样也是要代替jsp页面中的脚本代码。JSTL标准标准标签库有5个子库,但随着发展,目前常使用的是他的核心库
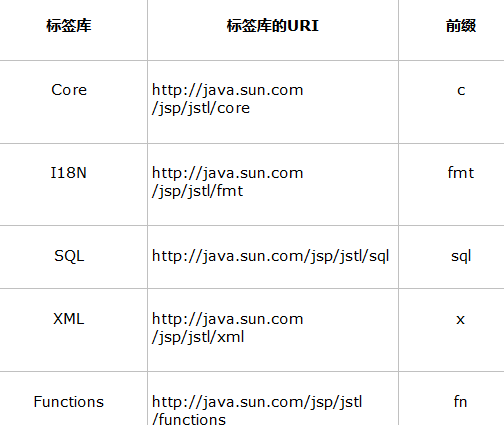
JSTL下载与导入
JSTL下载:
从Apache的网站下载JSTL的JAR包。进入“http://archive.apache.org/dist/jakarta/taglibs/standard/binaries/”网址下载 JSTL的安装包。jakarta-taglibs-standard-1.1.2.zip,然后将下载好的JSTL安装包 进行解压,此时,在lib目录下可以看到两个JAR文件,分别为jstl.jar和standard.jar。 其中,jstl.jar文件包含JSTL规范中定义的接口和相关类,standard.jar文件包含用于 实现JSTL的.class文件以及JSTL中5个标签库描述符文件(TLD)
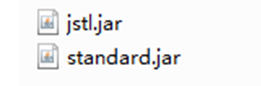
将两个jar包导入我们工程的lib中
使用jsp的taglib指令导入核心标签库
![]()
JSTL核心库的常用标签
1)<c:if test=””>标签
其中test是返回boolean的条件
<%request.setAttribute("count", 10); %>
<!--jstl标签经常会和el配合使用 -->
<!-- test代表的返回boolean的表达式 -->
<c:if test="${count==10 }">
xxxx
</c:if>
Index.jsp
<!-- 用户没有登陆 -->
<c:if test="${empty user }">
<a href="login.jsp">登陆</a>
<a href="register.jsp">注册</a>
</c:if>
<!-- 用户已经登陆 -->
<c:if test="${!empty user }">
<span>${user.name }</span>
<a href="#">退出</a>
</c:if>
Ceshi.jsp
<%
//模拟用户已经登录成功
User user=new User();
user.setId(100);
user.setName("张三");
user.setPwd("123");
session.setAttribute("user", user);
%>
2)<c:forEach>标签
使用方式有两种组合形式:
<!-- 模拟增强for productList---List<Product>
for(Product product:productList){
System.out.print(product.getName());
}
-->
<!-- items:一个集合或数组(从域中选) var:代表集合中的某一个元素 -->
<c:forEach items="${productList }" var="pro">
${pro.name }
</c:forEach>
<c:forEach items = "${map}" var="entry">
${entry.key }->${entry.value.name }<br>
</c:forEach>
示例:
1)遍历List<String>的值
2)遍历List<User>的值
3)遍历Map<String,String>的值
4)遍历Map<String,User>的值
5)遍历Map<User,Map<String,User>>的值
entry.key-----User
entry.value------List<String,User>


