背景
自杀是一项公认的全球性的重大社会问题和公共卫生问题,严重影响社会和经济的发展。据世界卫生组织估计,每年全世界有大约78.6万人自杀,其比例约为每年每10万人中有10.7人,也就是说每隔40秒就有人自杀。据联合国新闻,世卫组织发布的“2019年全球自杀状况”报告中的最新估计显示,自杀仍是全球主要死因之一。高收入国家的自杀率最高,美洲是唯一一个自杀率上升的地区。根据近年来世界各国的自杀率,可以发现:自杀率在性别上的差异在各国之间非常明显,一般的自杀率会男性高于女性,目前男性自杀率最高的国家为前苏联解体后的立陶宛、俄罗斯联邦、拉托维亚和爱沙尼亚等国家(年自杀率>60/10万),而女性自杀率最高的国家依次为斯里兰卡、中国、匈牙利和爱沙尼亚等(年自杀率>14/10万)。而在部分非洲和拉丁美洲国家自杀率却非常低,如埃及、秘鲁等(年自杀率<1/10万)。国际上习惯上将年自杀率>20/10万的国家称为高自杀率国家,年自杀率<10/10万的国家称为低自杀率国家,李振涛说,在1993年以前的统计中,中国属于低自杀率国家。 根据世界卫生组织在2019年发布的报告,全球每40秒钟就有一个人自杀身亡,自杀已经成为导致人类死亡的主要原因之一。一些国家的自杀人数增长迅速,甚至达60%。中国93%有自杀行为的人没有看过心理医生,在每年8万自杀未遂者中,被进行心理评估的还不到1%。中国的自杀防御工作缺乏一个全国性的计划来协调,政府机构对这一问题的重视不够,缺乏财力支持,也缺乏有效的评估心理因素的工具,更缺少高素质的研究人。
数据集来源
本次分析基于Kaggle数据集对自杀行文进行分析,探索自杀行为影响因素,并对自杀因素进行可视化,直观的表现影响自杀率的行为,并使用logistic回归、决策树、随机森林三种机器学习算法建立自杀行为分类模型,评估自杀结果,预测自杀率。
1 import pandas as pd 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 import seaborn as sns 5 #import scikitplot as skplt 6 import sklearn as sk 7 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 8 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler 9 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']='SimHei' 10 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False 11 12 import warnings 13 warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
数据读取
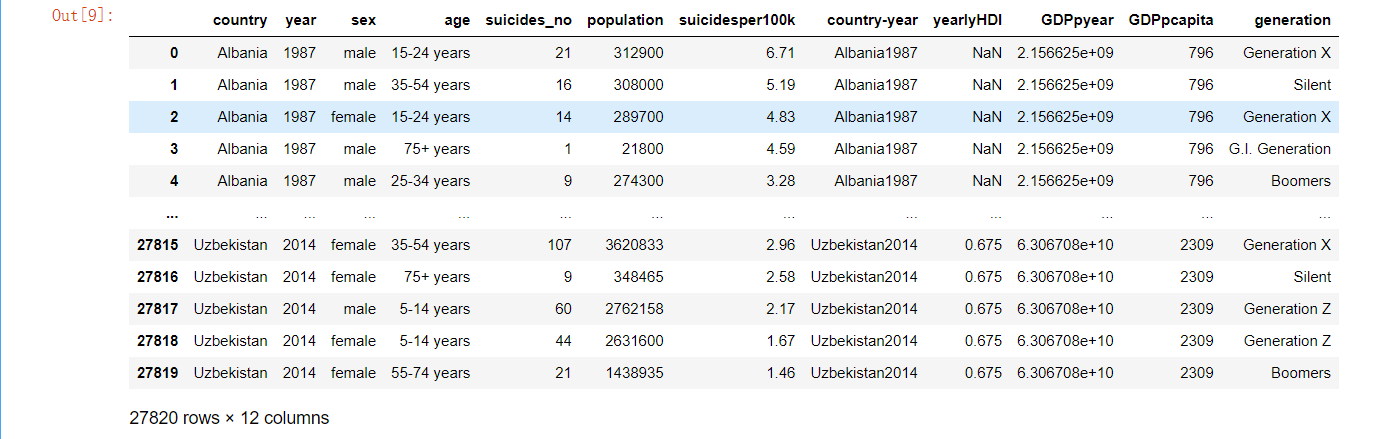
1 # 导入原始自杀数据集并重新命名列: 2 originaldata = pd.read_csv('./master.csv') 3 # 国家, 年份, 性别, 年龄, 自杀人数, 人口数量, 自杀人数/总人口*100000(自杀率), 4 # 国家-年份, 人类发展指数(用以衡量联合国各成员国经济社会发展水平的指标,是对传统的GNP指标挑战的结果。) 5 # 年度国内生产总值(衡量经济发展的指标), 年人均国内生产总值:国内生产总值/人口 , 世代 6 originaldata.columns = ['country', 'year', 'sex', 'age', 'suicides_no', 'population','suicidesper100k', 7 'country-year', 'yearlyHDI', 8 'GDPpyear', 'GDPpcapita', 'generation'] 9 10 originaldata.head()

1 originaldata.shape
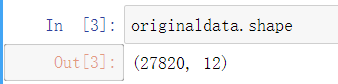
1 originaldata.info()
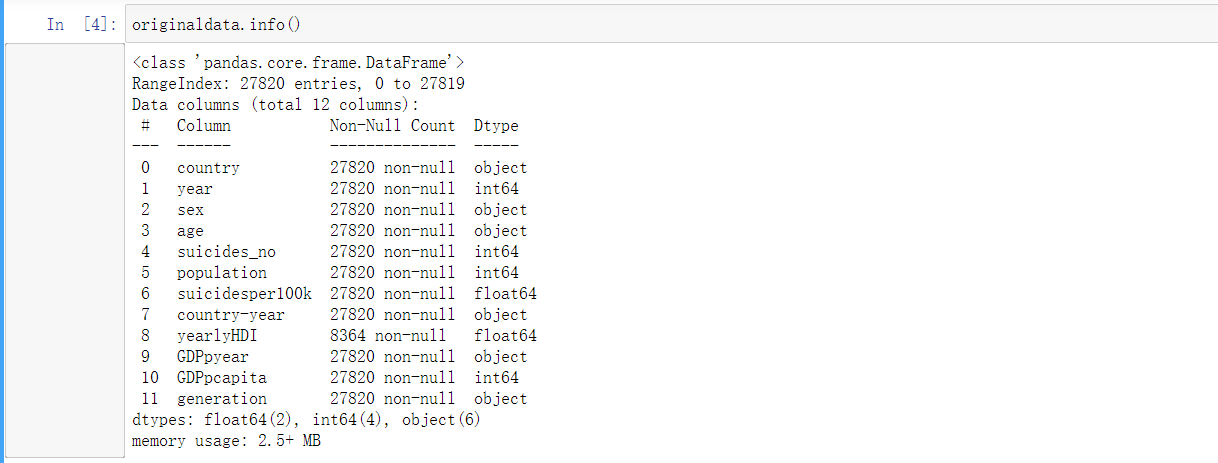
1 (originaldata=="male").sum()
1 a = 13910/27820 2 a

1 df3 = originaldata.groupby("country").agg({"country":"count"}) 2 df3.columns = ["count"] 3 df3

1 # 修复和清理原始数据 2 # 将 年度国内生产总值 数据中 ','分割去除掉(比如2,156,624,900),并且转换成float的数字类型 3 originaldata['GDPpyear'] = originaldata.apply(lambda x: float(x['GDPpyear'].replace(',', '')), axis=1) 4 originaldata['GDPpyear'].head(10) 5 6 # sex 转换为category类型 7 # Categoricals 是 pandas 的一种数据类型,对应着被统计的变量。Categoricals 是由固定的且有限数量的变量组成的。 8 originaldata.sex.astype('category')

1 df = originaldata.copy()#复制一份数据 2 df
1 df.suicidesper100k.mean() 2 df.suicidesper100k.std() 3 min(df.suicidesper100k) 4 max(df.suicidesper100k)

1 import seaborn as sns 2 sns.distplot(df.suicidesper100k) 3 plt.xticks(fontsize=10) 4 plt.yticks(fontsize=20) 5 plt.show()
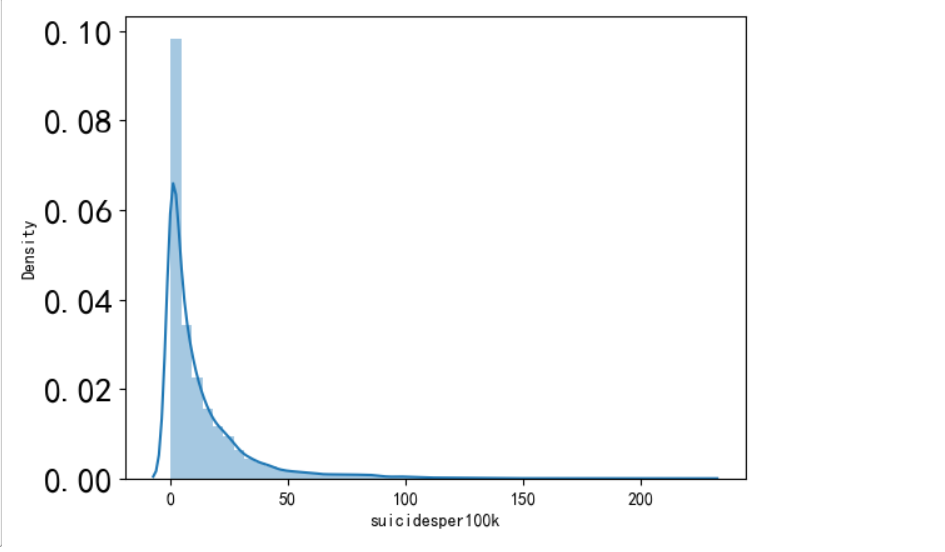
探索性分析
1 col = plt.cm.Spectral(np.linspace(0, 1, 20)) 2 3 plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) 4 agedistf = pd.DataFrame(df.groupby('sex').get_group('female').groupby('age').suicides_no.sum()) 5 agedistm = pd.DataFrame(df.groupby('sex').get_group('male').groupby('age').suicides_no.sum()) 6 plt.bar(agedistm.index, agedistm.suicides_no, color=col[18]) 7 plt.bar(agedistf.index, agedistf.suicides_no, color=col[8]) 8 plt.legend(['male', 'female'], fontsize=16) 9 plt.ylabel('Count', fontsize=14) 10 plt.xlabel('Suicides per 100K', fontsize=14) 11 plt.xticks(fontsize=10) 12 plt.yticks(fontsize=20) 13 plt.show()

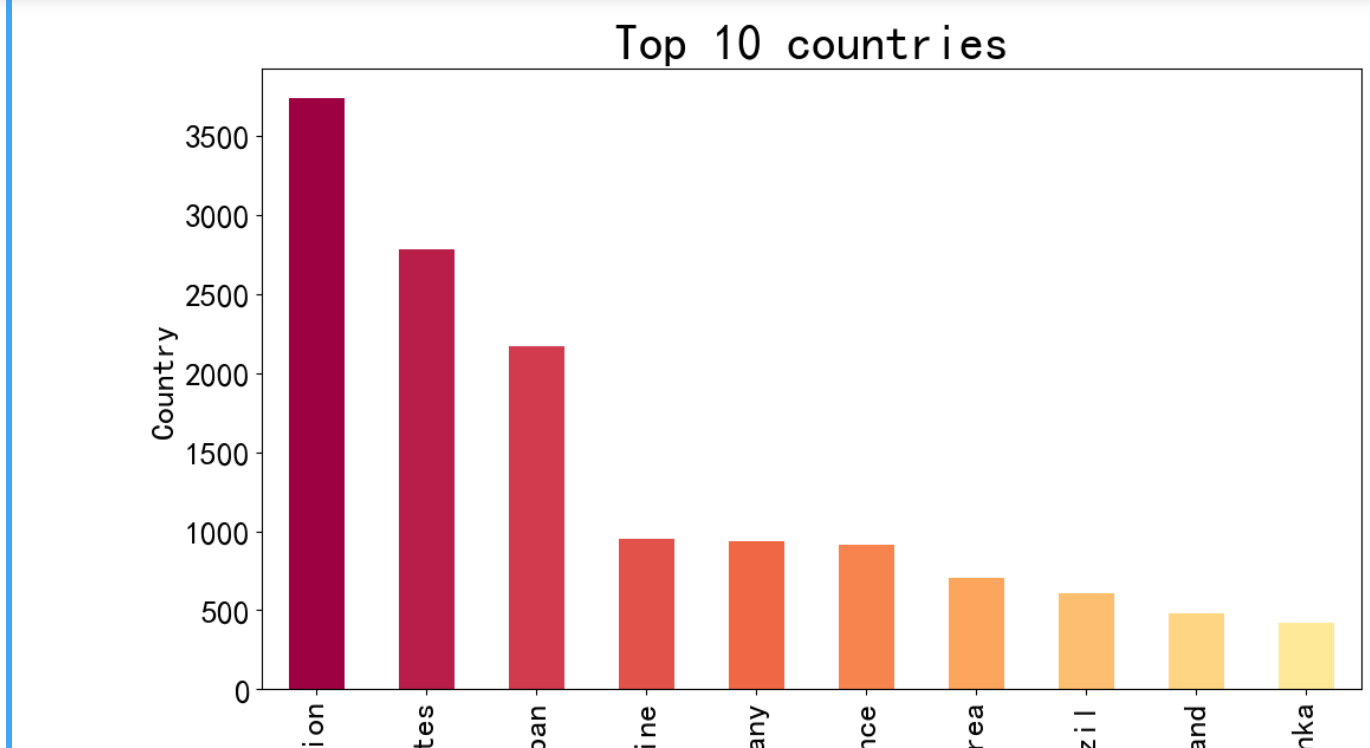
1 col = plt.cm.Spectral(np.linspace(0, 1, 22)) 2 plt.figure(figsize=(12, 15)) 3 4 plt.subplot(211) 5 #自杀率(放大1000倍)的平均值最高的前10个国家 6 df.groupby(['country']).suicidesper100k.mean().nlargest(10).plot(kind='bar', color=col, fontsize=20) 7 plt.xlabel('Average Suicides/100k', size=20) 8 plt.ylabel('Country', fontsize=20) 9 plt.title('Top 10 countries', fontsize=30) 10 11 plt.figure(figsize=(12, 15)) 12 plt.subplot(212) 13 #自杀人数的平均值最高的前10个国家 14 df.groupby(['country']).suicides_no.mean().nlargest(10).plot(kind='bar', color=col, fontsize=20) 15 plt.xlabel('Average Suicides_no', size=20) 16 plt.ylabel('Country', fontsize=20); 17 plt.title('Top 10 countries', fontsize=30) 18 plt.show()

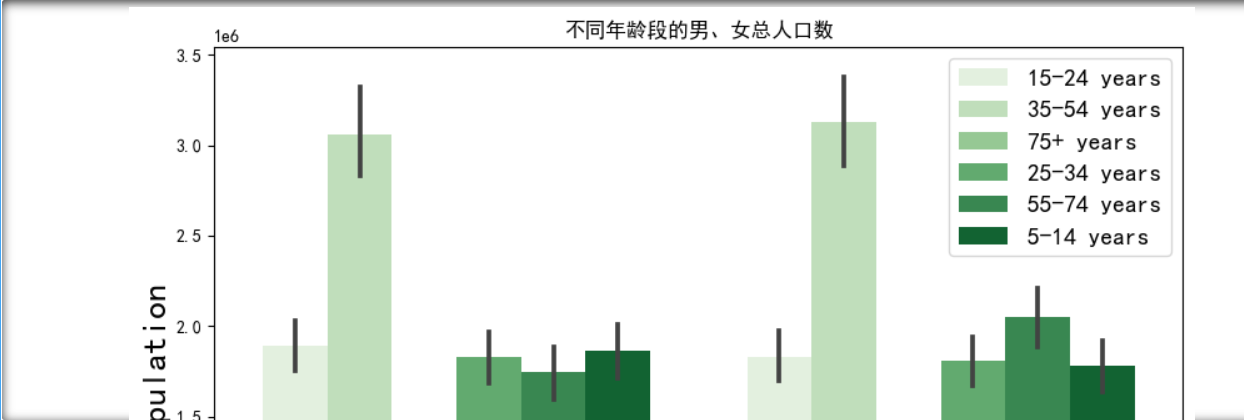
1 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 16)) 2 3 #总人口的各个年龄段的性别分布 4 plt.subplot(311) 5 sns.barplot(x='sex', y='population', hue='age', data=df, palette="Greens") #hue按年龄分组 6 plt.xticks(ha='right', fontsize=20) 7 plt.ylabel('Population', fontsize=20) 8 plt.xlabel('Sex', fontsize=20) 9 plt.title("不同年龄段的男、女总人口数") 10 plt.legend(fontsize=14, loc='best') 11 12 #自杀人数的各个年龄段的性别分布 13 plt.subplot(312) 14 sns.barplot(x='sex', y='suicides_no', hue='age', data=df, palette="Greens") 15 plt.xticks(ha='right', fontsize=20) 16 plt.ylabel('suicides incidences', fontsize=20) 17 plt.xlabel('Sex', fontsize=20) 18 plt.title("不同年龄段的男、女自杀人口数") 19 plt.legend(fontsize=14) 20 21 #自杀率(放大1000倍)的各个年龄段的性别分布 22 plt.subplot(313) 23 sns.barplot(x='sex', y='suicidesper100k', hue='age', data=df,palette="Greens") 24 plt.xticks(ha='right', fontsize=20); 25 plt.ylabel('suicidesper100k',fontsize=20); 26 plt.xlabel('Sex',fontsize=20); 27 plt.title("不同年龄段的男、女自杀率") 28 plt.legend(fontsize=14); 29 30 plt.subplots_adjust(top=1.2) 31 plt.show()
1 plt.figure(figsize=(12, 16)) 2 3 # 具体按性别和年份 来看 男女的自杀率 4 plt.subplot(311) 5 sns.lineplot(x='year', y='suicidesper100k', hue='sex', data=df, palette="hot") #hue按年龄分组 6 plt.xticks(ha='right', fontsize=20) 7 plt.ylabel('suicidesper100k', fontsize=20) 8 plt.xlabel('year', fontsize=20) 9 plt.legend(fontsize=14, loc='best') 10 plt.title("性别年份与自杀率关系图") 11 plt.show()

1 plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) 2 3 #选出year列并且去除重复的年份 4 year = originaldata.groupby('year').year.unique() 5 6 #各个年份的自杀人数汇总 7 #使用seaborn进行可视化,输入的数据必须为dataframe 8 totalpyear = pd.DataFrame(originaldata.groupby('year').suicides_no.sum()) 9 10 plt.plot(year.index[0:31], totalpyear[0:31], color=col[18]) #选取范围为[0:31] 1985年到2015年 11 plt.xlabel('year', fontsize=15) 12 plt.ylabel('Total number of suicides in the world', fontsize=15) 13 plt.show()

1 plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8)) 2 3 # 自杀率(放大1000倍)的分布情况,y轴为个数 4 plt.subplot(121) 5 plt.hist(df.suicidesper100k, bins=30, color=col[18]) #bins:条形数 6 plt.xlabel('Suicides per 100K of population', fontsize=25) 7 plt.xticks(rotation = 0, fontsize = 20) 8 plt.ylabel('count', fontsize=25) 9 plt.yticks( fontsize = 20) 10 11 # 年人均国内生产总值的分布情况,y轴为个数 12 plt.subplot(122) 13 plt.hist(df.GDPpcapita, bins=30, color=col[7]) 14 plt.xlabel('GDP', fontsize=25) 15 plt.xticks(rotation = 0,fontsize = 20) 16 plt.ylabel('count', fontsize=25) 17 plt.yticks(fontsize = 20) 18 plt.show()

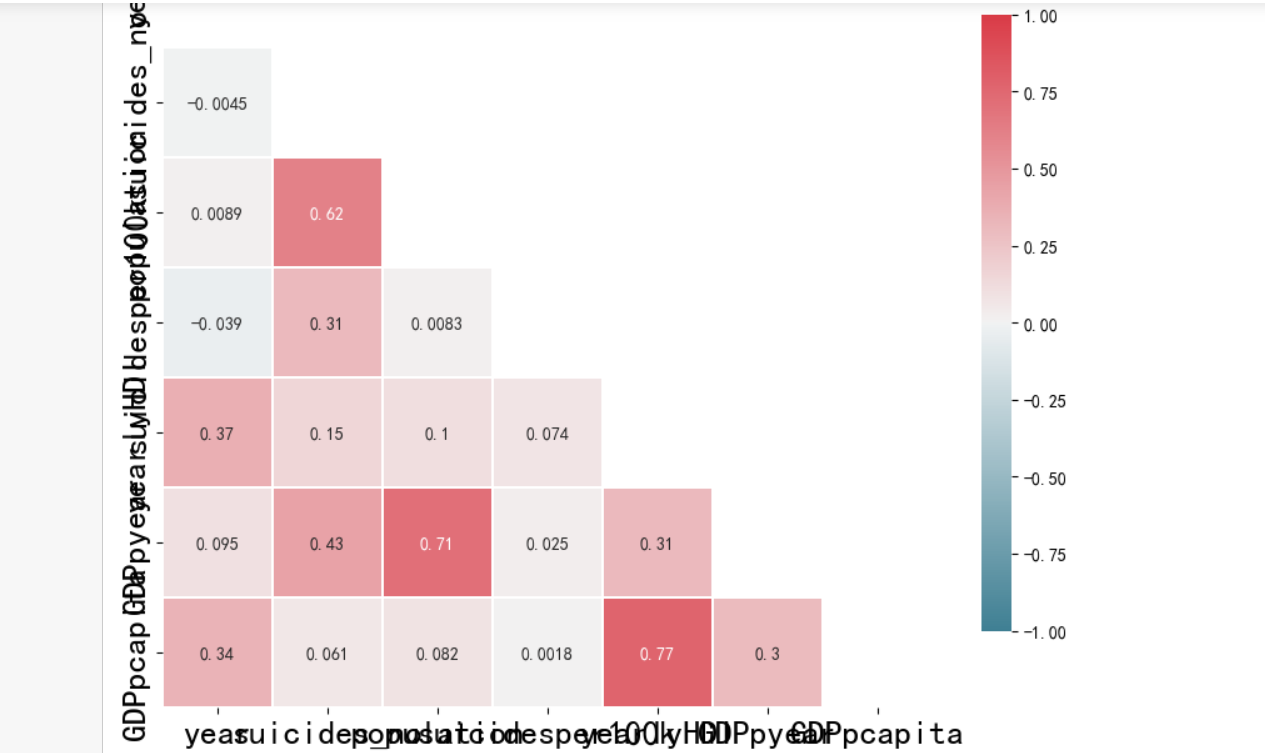
1 corr = df.corr() #相关系数矩阵,即给出了任意两个变量之间的相关系数 2 3 # 相关矩阵的上三角部分与下三角对称。因此,热图不需要显示整个矩阵。在下一步隐藏上三角形。 4 # 设置mask隐藏上三角 5 # np.zeros_like() 返回一个零数组,其形状和类型与给定的数组相同。 6 # 该 dtype=np.bool 参数会覆盖数据类型,因此我们的数组是一个布尔数组。 7 # np.triu_indices_from(mask) 返回数组上三角形的索引。 8 # 现在,我们将上三角形设置为True。 mask[np.triu_indices_from(mask)]= True 9 mask = np.zeros_like(corr, dtype=np.bool) 10 mask[np.triu_indices_from(mask)] = True 11 12 # 在Seaborn中创建热图 13 f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 8)) 14 # 生成自定义发散颜色图 15 cmap = sns.diverging_palette(220, 10, as_cmap=True) 16 17 # 绘制热图 18 # 数据为 corr 19 # vmax,vmin:分别是热力图的颜色取值最大和最小范围 20 # center:数据表取值有差异时,设置热力图的色彩中心对齐值;通过设置center值,可以调整生成的图像颜色的整体深浅 21 # square:设置热力图矩阵小块形状,默认值是False 22 # linewidths(矩阵小块的间隔), 23 # cbar_kws:热力图侧边绘制颜色刻度条时,相关字体设置,默认值是None 24 sns.heatmap(corr, mask=mask, cmap=cmap, vmax=1, vmin=-1, center=0, 25 square=True, linewidths=0.2, cbar_kws={"shrink": 0.8},annot=True) 26 plt.xticks(fontsize=20) 27 plt.yticks(fontsize=20) 28 plt.show()
数据预处理
1 #复制数据 2 total = df.copy() 3 # 对总人口用均值填充 4 total.population.fillna(total.population.mean(), inplace=True) 5 # 小于平均值的为低风险,大于平均值的为高风险 6 total['risk'] = np.where(total.suicidesper100k < total.suicidesper100k.mean(), 0, 1) 7 8 plt.figure(figsize=(16, 5)) 9 plt.subplot(121) 10 plt.hist(total.risk, color=col[8]) 11 plt.ylabel('counts', fontsize=20) 12 plt.xlabel('Suicide risk', fontsize=20) 13 plt.title("自杀高低风险数量") 14 15 plt.subplot(122) 16 sns.distplot(total.suicidesper100k[total.risk == 0], bins=10) 17 sns.distplot(total.suicidesper100k[total.risk == 1], bins=20) 18 plt.xlabel('Suicides', fontsize=20) 19 plt.title("自杀高低风险分布情况") 20 plt.show()
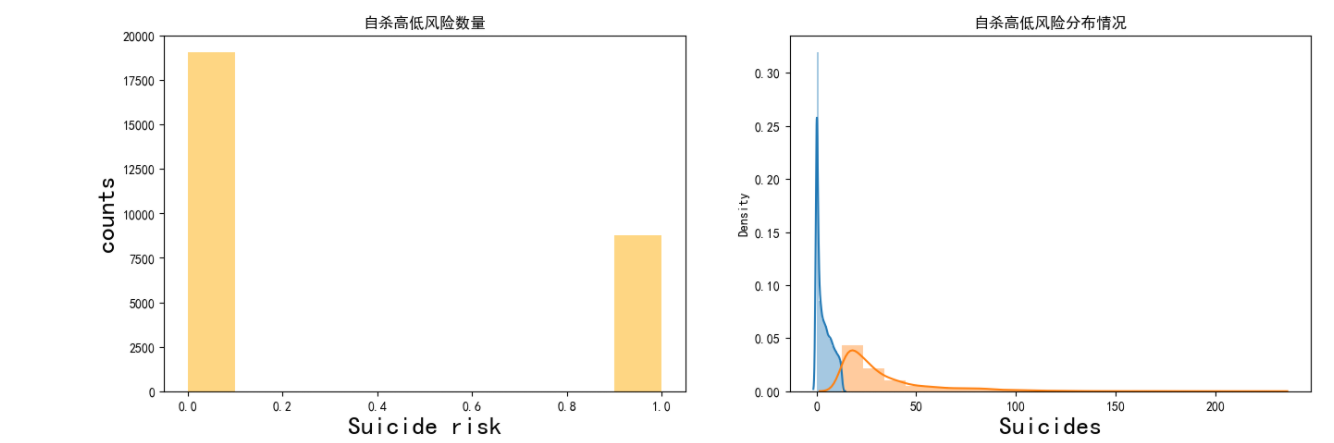
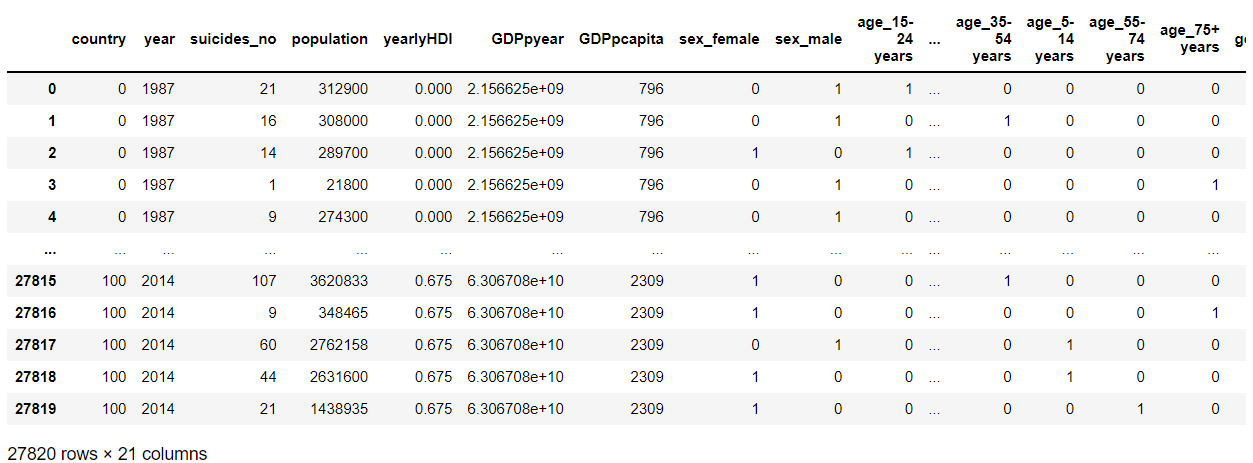
1 (total['risk']==1).sum() 2 (total['risk']==0).sum() 3 total.head(5) 4 total['yearlyHDI'].isnull().sum() 5 a = 19456/27820 6 a
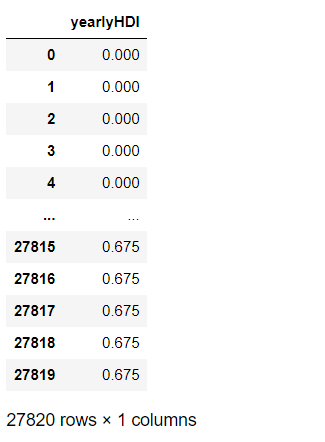
1 total['yearlyHDI'].describe() 2 total['yearlyHDI'].isnull().sum() 3 total
1 fill_1 = total['yearlyHDI'] 2 fill_1 = pd.DataFrame(fill_1) 3 fill_1
1 from scipy.interpolate import lagrange #导入拉格朗日函数 2 def ployinterp_column(s,n,k=2,result_type='broadcast'): # k=2表示用空值的前后两个数值来拟合曲线,从而预测空值 3 y = s[list(range(n+2-k,n+2)) + list(range(n+3,n+3-k))] # 取值,range函数返回一个左闭右开([left,right))的序列数 4 y = y[y.notnull()] # 取上一行中取出数值列表中的非空值,保证y的每行都有数值,便于拟合函数 5 return lagrange(y.index,list(y))(n) # 调用拉格朗日函数,并添加索引 6 for i in fill_1.columns: # 如果i在data的列名中,data.columns生成的是data的全部列名 7 for j in range(len(fill_1)): # len(data)返回了data的长度,若此长度为5,则range(5)会产生从0开始计数的整数列表 8 if (fill_1[i].isnull())[j]: # 如果data[i][j]为空,则调用函数ployinterp_column为其插值 9 fill_1[i][j] = ployinterp_column(fill_1[i],j,result_type='broadcast') 10 fill_1
1 # 对国家进行 标准化标签,将标签值统一转换成range(标签值个数-1)范围内 2 # 相当于fit(X).transform(X),意思就是先进行fit(),进行数据拟合,然后在进行transform() 进行标准化处理 3 4 from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder 5 le = LabelEncoder() 6 total.country = le.fit_transform(total.country) 7 total.country.unique() 8 9 # 为建立模型准备数据 10 X = total.drop(['suicidesper100k','risk','country-year'],axis = 1) 11 #用0进行填补 12 X['yearlyHDI'] = fill_1['yearlyHDI'] 13 y = total['risk'] 14 #对X进行独热编码处理 15 XS = pd.get_dummies(X)
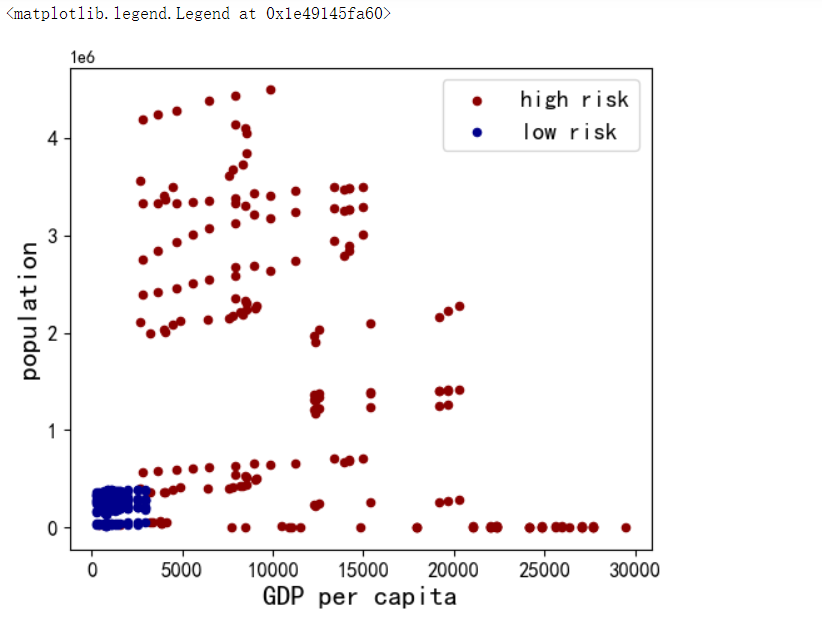
1 #GDP和人口的分布 2 ax1 = total[total['risk'] == 1][0:200].plot(kind='scatter', x='GDPpcapita', y='population', color='DarkRed', 3 label='high risk', figsize=(6, 5), fontsize=12) 4 total[total['risk'] == 0][0:200].plot(kind='scatter', x='GDPpcapita', y='population', color='DarkBlue', 5 label='low risk', ax=ax1) 6 7 plt.ylabel('population', fontsize=16) 8 plt.xlabel('GDP per capita', fontsize=16) 9 plt.legend(fontsize=14)
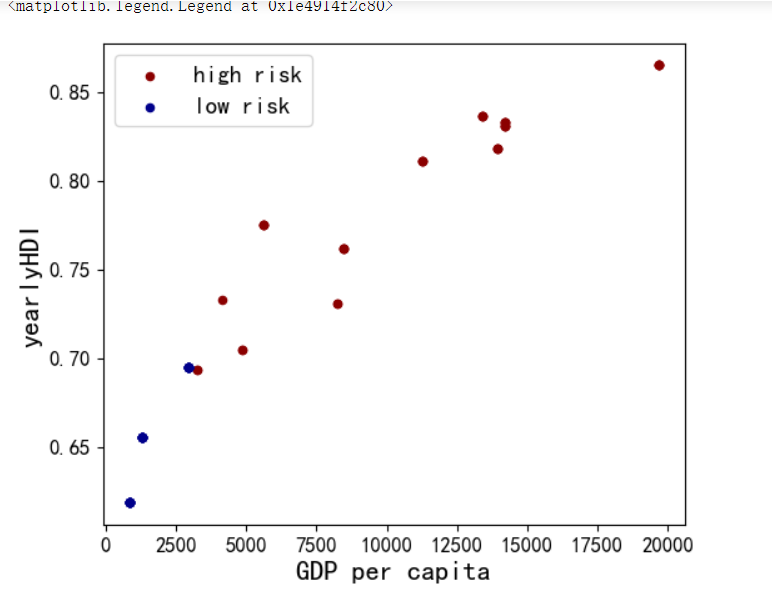
1 #GDP和人类发展指数的分布 2 ax1 = total[total['risk'] == 1][0:200].plot(kind='scatter', x='GDPpcapita', y='yearlyHDI', color='DarkRed', 3 label='high risk', figsize=(6, 5), fontsize=12) 4 total[total['risk'] == 0][0:200].plot(kind='scatter', x='GDPpcapita', y='yearlyHDI', color='DarkBlue', 5 label='low risk', ax=ax1) 6 7 plt.ylabel('yearlyHDI', fontsize=16) 8 plt.xlabel('GDP per capita', fontsize=16) 9 plt.legend(fontsize=14)
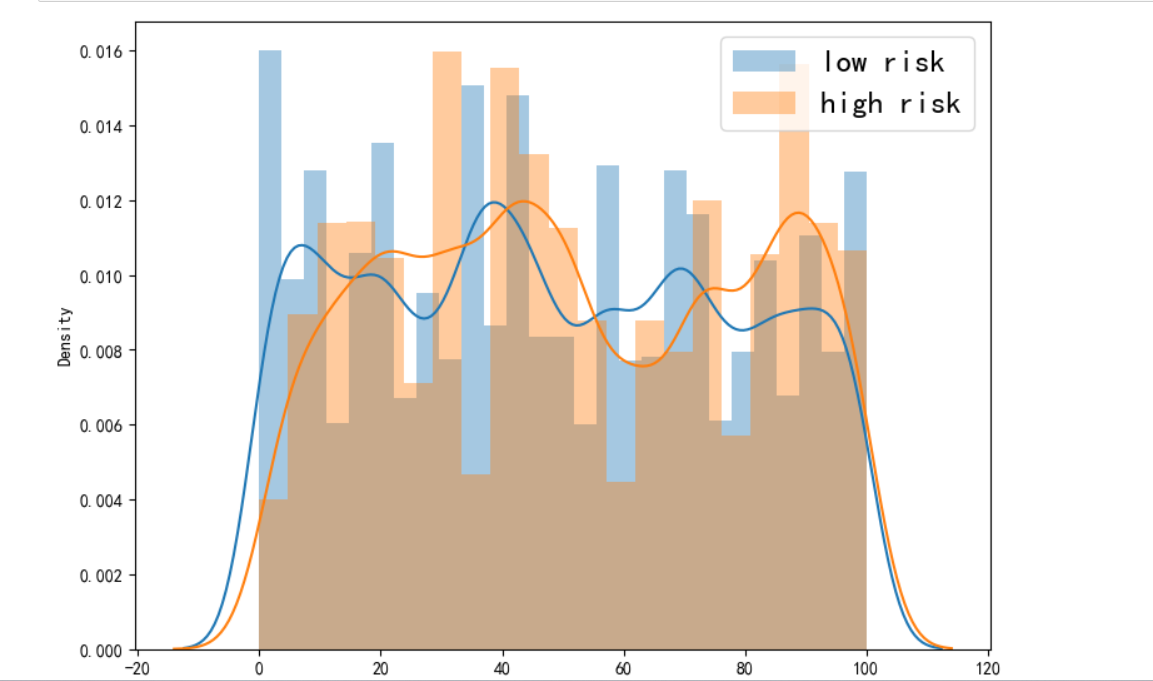
1 # 关于年份的高低自杀风险 2 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(30, 30)) 3 4 plt.subplot(4, 3, 1) 5 sns.distplot(total[total.columns[0]][total.risk == 0], label='low risk') 6 sns.distplot(total[total.columns[0]][total.risk == 1], label='high risk') 7 plt.legend(loc='best', fontsize=18) 8 plt.xlabel(total.columns[0], fontsize=18) 9 plt.show()
建模
1 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 2 # 将数据集拆分为训练集和测试集 3 # 首先将该数据3/4作为训练集,1/4作为测试集;再由训练集划分1/5作为验证集 4 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(XS, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=4) 5 X_train,X_valid,y_train,y_valid=train_test_split(X_train,y_train,test_size=0.2,random_state=4) 6 print('Train set:', X_train.shape, y_train.shape) 7 print('Test set:', X_test.shape, y_test.shape) 8 print('Test set:', X_valid.shape, y_valid.shape)

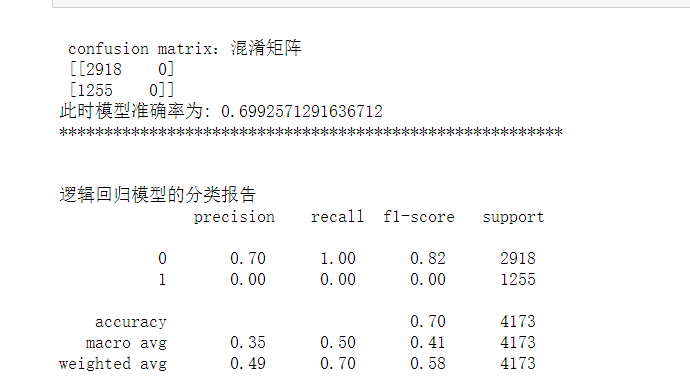
1 from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression 2 from sklearn.metrics import recall_score,accuracy_score 3 from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_fscore_support 4 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report 5 6 LR = LogisticRegression(C=0.001, solver='liblinear') 7 LR.fit(X_train, y_train) 8 9 # 预测类别:0还是1 10 yLRhat = LR.predict(X_valid) 11 12 # 预测 0或1的概率(例如 [0.54689436, 0.45310564] 预测出来为0) 13 yLRhat_prob = LR.predict_proba(X_valid) 14 15 cm = confusion_matrix(y_valid, yLRhat) 16 print('\n confusion matrix:混淆矩阵 \n', cm) 17 print('此时模型准确率为:',accuracy_score(y_valid, yLRhat)) 18 print('********************************************************') 19 print('\n') 20 print('逻辑回归模型的分类报告\n', classification_report(y_valid, yLRhat)) 21 #skplt.metrics.plot_confusion_matrix(y_valid,yLRhat,normalize=True)
1 X_train.head()
1 from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV 2 3 param={"tol":[1e-4, 1e-3,1e-2], "C":[0.4, 0.6, 0.8]} 4 grid = GridSearchCV(LogisticRegression(),param_grid=param, cv=5)#这里是5折交叉验证 5 grid.fit(X_train,y_train) 6 print(grid.best_params_) 7 print(grid.best_score_) 8 9 #得到最好的逻辑回归分类器 10 best_LR=grid.best_estimator_ 11 12 #进行训练、预测 13 best_LR.fit(X_train,y_train) 14 pred=best_LR.predict(X_valid) 15 16 cm = confusion_matrix(y_valid, pred) 17 print('\n confusion matrix:混淆矩阵 \n', cm) 18 print('最好的逻辑回归模型准确率为:',accuracy_score(y_valid, pred)) 19 print('********************************************************') 20 print('\n') 21 print('最好的逻辑回归模型的分类报告\n', classification_report(y_valid, pred))

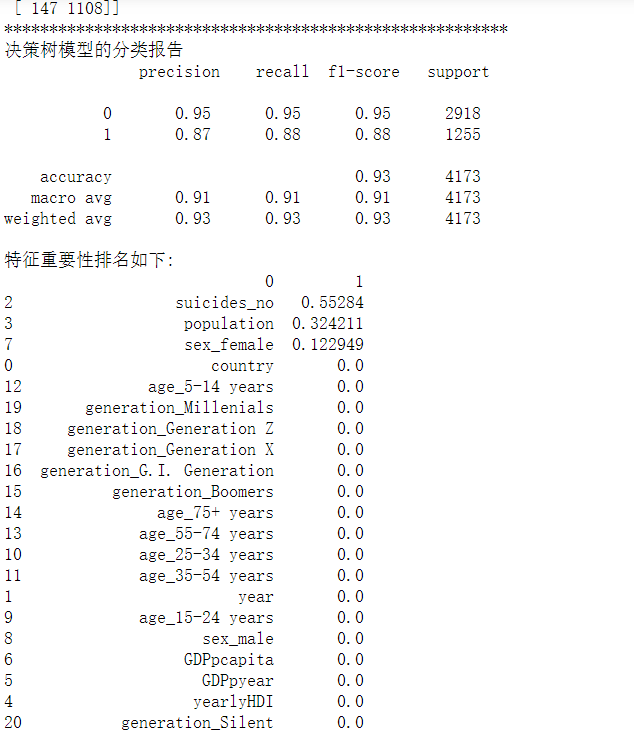
1 from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier 2 from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score 3 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report 4 5 # 决策树学习 6 # 函数为创建一个决策树模型 7 # criterion:gini或者entropy,前者是基尼系数,后者是信息熵。 8 # max_depth: int or None, optional (default=None) 设置决策随机森林中的决策树的最大深度,深度越大,越容易过拟合,推荐树的深度为:5-20之间。 9 # max_leaf_nodes: 通过限制最大叶子节点数,可以防止过拟合,默认是"None”,即不限制最大的叶子节点数。 10 DT = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion="entropy", max_depth=7, max_leaf_nodes=30) 11 DT.fit(X_train, y_train) 12 ydthat = DT.predict(X_valid) 13 14 print('***决策树模型***') 15 16 #决策树模型性能评估 17 print('验证集上的准确率:', DT.score(X_valid, y_valid)) 18 print('训练集上的准确率:', DT.score(X_train, y_train)) 19 20 # 混淆矩阵 21 print('CM\n', confusion_matrix(y_valid, ydthat)) 22 print('********************************************************') 23 24 print('决策树模型的分类报告\n', classification_report(y_valid, ydthat)) 25 26 DTfeat_importance = DT.feature_importances_ 27 DTfeat_importance = pd.DataFrame([X_train.columns, DT.feature_importances_]).T 28 29 # 特征重要性排序 30 print("特征重要性排名如下:") 31 print(DTfeat_importance.sort_values(by=1, ascending=False))
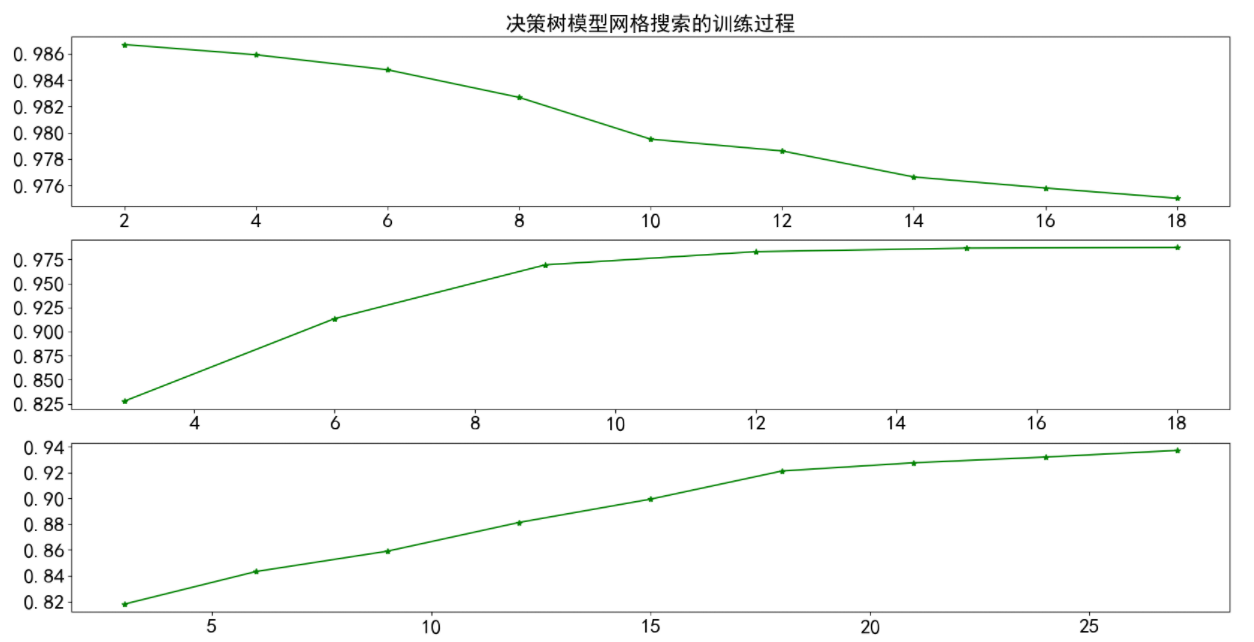
1 # 通过cv_results观察过程并做图 2 max_depth=np.arange(0,20,3) 3 max_leaf_nodes=np.arange(0,30,3) 4 min_samples_leaf =np.arange(0,20,2) 5 param1= {'criterion':['entropy'],'max_depth':max_depth} 6 param2= {'criterion':['entropy'],'min_samples_leaf':min_samples_leaf} 7 param3= {'criterion':['entropy'],'max_leaf_nodes':max_leaf_nodes} 8 9 10 clf1 = GridSearchCV(DecisionTreeClassifier(),param_grid=param1,cv=6) 11 clf1.fit(X_train,y_train) 12 13 clf2 = GridSearchCV(DecisionTreeClassifier(),param_grid=param2,cv=6) 14 clf2.fit(X_train,y_train) 15 16 17 clf3 = GridSearchCV(DecisionTreeClassifier(),param_grid=param3,cv=6) 18 clf3.fit(X_train,y_train)

1 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20,10), dpi=100) 2 ax = fig.add_subplot(311) 3 ax.plot(min_samples_leaf,clf2.cv_results_['mean_test_score'],'g*-',) 4 plt.title('决策树模型网格搜索的训练过程',fontsize=20) 5 plt.xticks(fontsize=20) 6 plt.yticks(fontsize=20) 7 8 ax = fig.add_subplot(312) 9 ax.plot(max_depth,clf1.cv_results_['mean_test_score'],'g*-') 10 plt.xticks(fontsize=20) 11 plt.yticks(fontsize=20) 12 ax = fig.add_subplot(313) 13 ax.plot(max_leaf_nodes,clf3.cv_results_['mean_test_score'],'g*-') 14 plt.xticks(fontsize=20) 15 plt.yticks(fontsize=20) 16 plt.show()
1 best_DT = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion="entropy", max_depth=15, max_leaf_nodes=25,min_samples_leaf=2) 2 best_DT.fit(X_train, y_train) 3 ydthat =best_DT.predict(X_valid) 4 5 print('***决策树模型***') 6 7 #决策树模型性能评估 8 print('验证集上的准确率:',best_DT.score(X_valid, y_valid)) 9 print('训练集上的准确率:',best_DT.score(X_train, y_train)) 10 11 # 混淆矩阵 12 print('CM\n', confusion_matrix(y_valid, ydthat)) 13 print('********************************************************') 14 15 print('决策树模型的分类报告\n', classification_report(y_valid, ydthat)) 16 17 DTfeat_importance = best_DT.feature_importances_ 18 DTfeat_importance = pd.DataFrame([X_train.columns, DT.feature_importances_]).T 19 20 # 特征重要性排序 21 print("特征重要性排名如下:") 22 print(DTfeat_importance.sort_values(by=1, ascending=False))

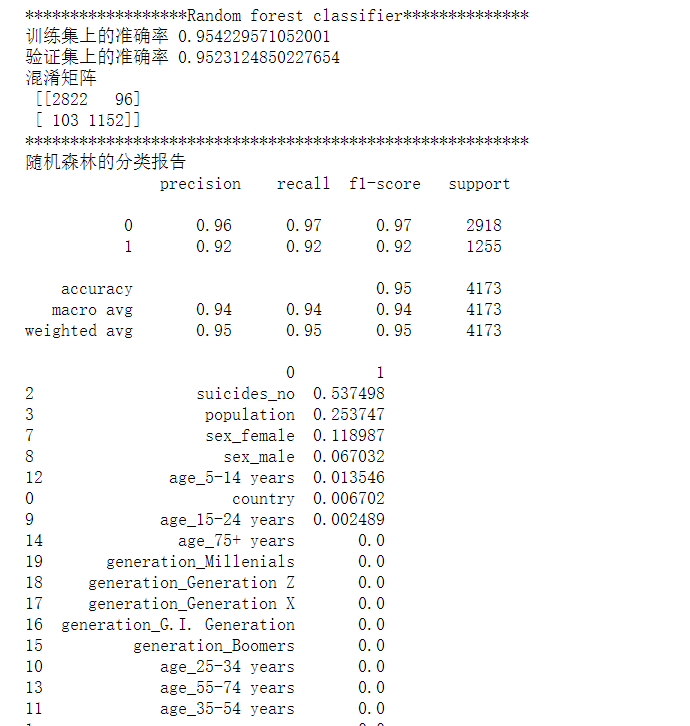
1 # 随机森林可以视为多颗决策树的集成,鲁棒性更强,泛化能力更好,不易产生过拟合现象。但是噪声比较大的情况下会过拟合。 2 3 from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier 4 5 random_forest = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=20, max_depth=10, min_samples_split=2, min_samples_leaf=5, 6 max_leaf_nodes=20, max_features=len(X_train.columns)) 7 8 random_forest.fit(X_train, y_train) 9 10 yrfhat = random_forest.predict(X_valid) 11 feat_importance = random_forest.feature_importances_ 12 rffeat_importance = pd.DataFrame([X_train.columns, random_forest.feature_importances_]).T 13 14 print('******************Random forest classifier**************') 15 print('训练集上的准确率', random_forest.score(X_train, y_train)) 16 print('验证集上的准确率', random_forest.score(X_valid,y_valid)) 17 print('混淆矩阵\n', confusion_matrix(y_valid, yrfhat)) 18 print('********************************************************') 19 print('随机森林的分类报告\n', classification_report(y_valid, yrfhat)) 20 print(rffeat_importance.sort_values(by=1, ascending=False))
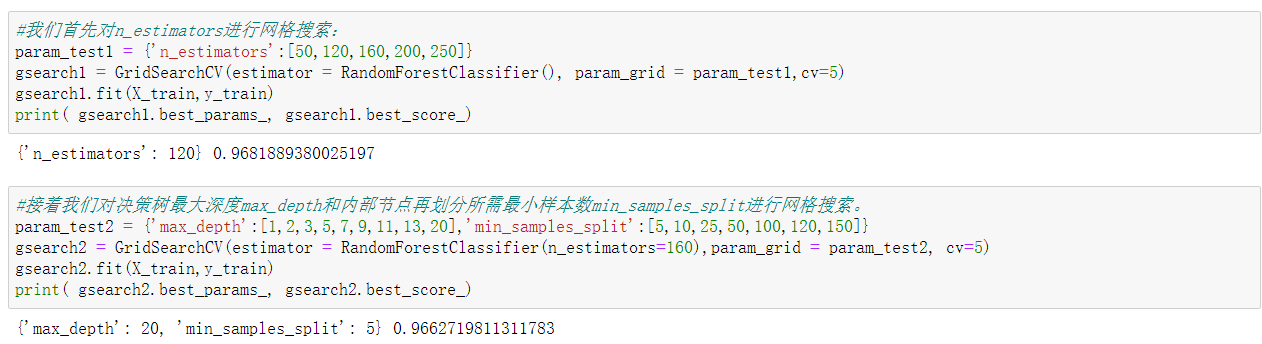
1 #我们首先对n_estimators进行网格搜索: 2 param_test1 = {'n_estimators':[50,120,160,200,250]} 3 gsearch1 = GridSearchCV(estimator = RandomForestClassifier(), param_grid = param_test1,cv=5) 4 gsearch1.fit(X_train,y_train) 5 print( gsearch1.best_params_, gsearch1.best_score_) 6 #接着我们对决策树最大深度max_depth和内部节点再划分所需最小样本数min_samples_split进行网格搜索。 7 param_test2 = {'max_depth':[1,2,3,5,7,9,11,13,20],'min_samples_split':[5,10,25,50,100,120,150]} 8 gsearch2 = GridSearchCV(estimator = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=160),param_grid = param_test2, cv=5) 9 gsearch2.fit(X_train,y_train) 10 print( gsearch2.best_params_, gsearch2.best_score_)
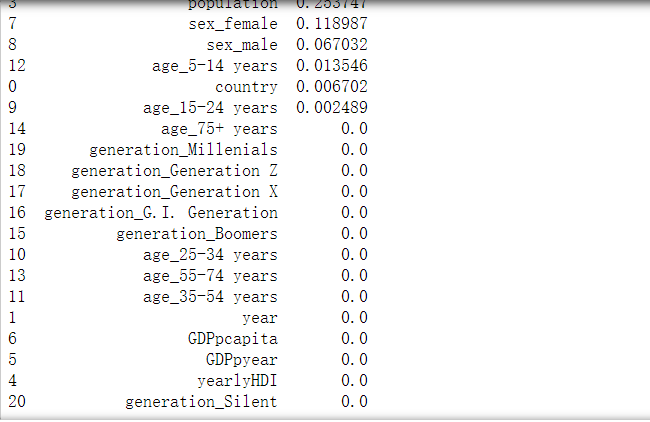
1 #最好的随机森林模型 2 best_rf=RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=160, max_depth=20, min_samples_split=5) 3 4 best_rf .fit(X_train, y_train) 5 6 yrfhat = best_rf .predict(X_valid) 7 feat_importance = best_rf.feature_importances_ 8 rffeat_importance = pd.DataFrame([X_train.columns, random_forest.feature_importances_]).T 9 10 print('******************随机森林模型**************') 11 print('训练集上的准确率',best_rf.score(X_train, y_train)) 12 print('验证集上的准确率',best_rf.score(X_valid,y_valid)) 13 print('混淆矩阵\n', confusion_matrix(y_valid, yrfhat)) 14 print('********************************************************') 15 print('最好的随机森林模型的分类报告\n', classification_report(y_valid, yrfhat)) 16 print(rffeat_importance.sort_values(by=1, ascending=False))

全代码附上
1 import pandas as pd 2 import numpy as np 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 import seaborn as sns 5 #import scikitplot as skplt 6 import sklearn as sk 7 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 8 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler 9 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']='SimHei' 10 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False 11 12 import warnings 13 warnings.filterwarnings("ignore") 14 # 导入原始自杀数据集并重新命名列: 15 originaldata = pd.read_csv('./master.csv') 16 # 国家, 年份, 性别, 年龄, 自杀人数, 人口数量, 自杀人数/总人口*100000(自杀率), 17 # 国家-年份, 人类发展指数(用以衡量联合国各成员国经济社会发展水平的指标,是对传统的GNP指标挑战的结果。) 18 # 年度国内生产总值(衡量经济发展的指标), 年人均国内生产总值:国内生产总值/人口 , 世代 19 originaldata.columns = ['country', 'year', 'sex', 'age', 'suicides_no', 'population','suicidesper100k', 20 'country-year', 'yearlyHDI', 21 'GDPpyear', 'GDPpcapita', 'generation'] 22 23 originaldata.head() 24 originaldata.shape 25 originaldata.info() 26 (originaldata=="male").sum() 27 a = 13910/27820 28 a 29 df3 = originaldata.groupby("country").agg({"country":"count"}) 30 df3.columns = ["count"] 31 df3 32 # 修复和清理原始数据 33 # 将 年度国内生产总值 数据中 ','分割去除掉(比如2,156,624,900),并且转换成float的数字类型 34 originaldata['GDPpyear'] = originaldata.apply(lambda x: float(x['GDPpyear'].replace(',', '')), axis=1) 35 originaldata['GDPpyear'].head(10) 36 37 # sex 转换为category类型 38 # Categoricals 是 pandas 的一种数据类型,对应着被统计的变量。Categoricals 是由固定的且有限数量的变量组成的。 39 originaldata.sex.astype('category') 40 df = originaldata.copy()#复制一份数据 41 df 42 df.suicidesper100k.mean() 43 df.suicidesper100k.std() 44 min(df.suicidesper100k) 45 max(df.suicidesper100k) 46 import seaborn as sns 47 sns.distplot(df.suicidesper100k) 48 plt.xticks(fontsize=10) 49 plt.yticks(fontsize=20) 50 plt.show() 51 df.suicidesper100k.isnull().sum() 52 col = plt.cm.Spectral(np.linspace(0, 1, 20)) 53 54 plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) 55 agedistf = pd.DataFrame(df.groupby('sex').get_group('female').groupby('age').suicides_no.sum()) 56 agedistm = pd.DataFrame(df.groupby('sex').get_group('male').groupby('age').suicides_no.sum()) 57 plt.bar(agedistm.index, agedistm.suicides_no, color=col[18]) 58 plt.bar(agedistf.index, agedistf.suicides_no, color=col[8]) 59 plt.legend(['male', 'female'], fontsize=16) 60 plt.ylabel('Count', fontsize=14) 61 plt.xlabel('Suicides per 100K', fontsize=14) 62 plt.xticks(fontsize=10) 63 plt.yticks(fontsize=20) 64 plt.show() 65 col = plt.cm.Spectral(np.linspace(0, 1, 22)) 66 plt.figure(figsize=(12, 15)) 67 68 plt.subplot(211) 69 #自杀率(放大1000倍)的平均值最高的前10个国家 70 df.groupby(['country']).suicidesper100k.mean().nlargest(10).plot(kind='bar', color=col, fontsize=20) 71 plt.xlabel('Average Suicides/100k', size=20) 72 plt.ylabel('Country', fontsize=20) 73 plt.title('Top 10 countries', fontsize=30) 74 75 plt.figure(figsize=(12, 15)) 76 plt.subplot(212) 77 #自杀人数的平均值最高的前10个国家 78 df.groupby(['country']).suicides_no.mean().nlargest(10).plot(kind='bar', color=col, fontsize=20) 79 plt.xlabel('Average Suicides_no', size=20) 80 plt.ylabel('Country', fontsize=20); 81 plt.title('Top 10 countries', fontsize=30) 82 plt.show() 83 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 16)) 84 85 #总人口的各个年龄段的性别分布 86 plt.subplot(311) 87 sns.barplot(x='sex', y='population', hue='age', data=df, palette="Greens") #hue按年龄分组 88 plt.xticks(ha='right', fontsize=20) 89 plt.ylabel('Population', fontsize=20) 90 plt.xlabel('Sex', fontsize=20) 91 plt.title("不同年龄段的男、女总人口数") 92 plt.legend(fontsize=14, loc='best') 93 94 #自杀人数的各个年龄段的性别分布 95 plt.subplot(312) 96 sns.barplot(x='sex', y='suicides_no', hue='age', data=df, palette="Greens") 97 plt.xticks(ha='right', fontsize=20) 98 plt.ylabel('suicides incidences', fontsize=20) 99 plt.xlabel('Sex', fontsize=20) 100 plt.title("不同年龄段的男、女自杀人口数") 101 plt.legend(fontsize=14) 102 103 #自杀率(放大1000倍)的各个年龄段的性别分布 104 plt.subplot(313) 105 sns.barplot(x='sex', y='suicidesper100k', hue='age', data=df,palette="Greens") 106 plt.xticks(ha='right', fontsize=20); 107 plt.ylabel('suicidesper100k',fontsize=20); 108 plt.xlabel('Sex',fontsize=20); 109 plt.title("不同年龄段的男、女自杀率") 110 plt.legend(fontsize=14); 111 112 plt.subplots_adjust(top=1.2) 113 plt.show() 114 plt.figure(figsize=(12, 16)) 115 116 # 具体按性别和年份 来看 男女的自杀率 117 plt.subplot(311) 118 sns.lineplot(x='year', y='suicidesper100k', hue='sex', data=df, palette="hot") #hue按年龄分组 119 plt.xticks(ha='right', fontsize=20) 120 plt.ylabel('suicidesper100k', fontsize=20) 121 plt.xlabel('year', fontsize=20) 122 plt.legend(fontsize=14, loc='best') 123 plt.title("性别年份与自杀率关系图") 124 plt.show() 125 plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6)) 126 127 #选出year列并且去除重复的年份 128 year = originaldata.groupby('year').year.unique() 129 130 #各个年份的自杀人数汇总 131 #使用seaborn进行可视化,输入的数据必须为dataframe 132 totalpyear = pd.DataFrame(originaldata.groupby('year').suicides_no.sum()) 133 134 plt.plot(year.index[0:31], totalpyear[0:31], color=col[18]) #选取范围为[0:31] 1985年到2015年 135 plt.xlabel('year', fontsize=15) 136 plt.ylabel('Total number of suicides in the world', fontsize=15) 137 plt.show() 138 plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8)) 139 140 # 自杀率(放大1000倍)的分布情况,y轴为个数 141 plt.subplot(121) 142 plt.hist(df.suicidesper100k, bins=30, color=col[18]) #bins:条形数 143 plt.xlabel('Suicides per 100K of population', fontsize=25) 144 plt.xticks(rotation = 0, fontsize = 20) 145 plt.ylabel('count', fontsize=25) 146 plt.yticks( fontsize = 20) 147 148 # 年人均国内生产总值的分布情况,y轴为个数 149 plt.subplot(122) 150 plt.hist(df.GDPpcapita, bins=30, color=col[7]) 151 plt.xlabel('GDP', fontsize=25) 152 plt.xticks(rotation = 0,fontsize = 20) 153 plt.ylabel('count', fontsize=25) 154 plt.yticks(fontsize = 20) 155 plt.show() 156 corr = df.corr() #相关系数矩阵,即给出了任意两个变量之间的相关系数 157 158 # 相关矩阵的上三角部分与下三角对称。因此,热图不需要显示整个矩阵。在下一步隐藏上三角形。 159 # 设置mask隐藏上三角 160 # np.zeros_like() 返回一个零数组,其形状和类型与给定的数组相同。 161 # 该 dtype=np.bool 参数会覆盖数据类型,因此我们的数组是一个布尔数组。 162 # np.triu_indices_from(mask) 返回数组上三角形的索引。 163 # 现在,我们将上三角形设置为True。 mask[np.triu_indices_from(mask)]= True 164 mask = np.zeros_like(corr, dtype=np.bool) 165 mask[np.triu_indices_from(mask)] = True 166 167 # 在Seaborn中创建热图 168 f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 8)) 169 # 生成自定义发散颜色图 170 cmap = sns.diverging_palette(220, 10, as_cmap=True) 171 172 # 绘制热图 173 # 数据为 corr 174 # vmax,vmin:分别是热力图的颜色取值最大和最小范围 175 # center:数据表取值有差异时,设置热力图的色彩中心对齐值;通过设置center值,可以调整生成的图像颜色的整体深浅 176 # square:设置热力图矩阵小块形状,默认值是False 177 # linewidths(矩阵小块的间隔), 178 # cbar_kws:热力图侧边绘制颜色刻度条时,相关字体设置,默认值是None 179 sns.heatmap(corr, mask=mask, cmap=cmap, vmax=1, vmin=-1, center=0, 180 square=True, linewidths=0.2, cbar_kws={"shrink": 0.8},annot=True) 181 plt.xticks(fontsize=20) 182 plt.yticks(fontsize=20) 183 plt.show() 184 #复制数据 185 total = df.copy() 186 # 对总人口用均值填充 187 total.population.fillna(total.population.mean(), inplace=True) 188 # 小于平均值的为低风险,大于平均值的为高风险 189 total['risk'] = np.where(total.suicidesper100k < total.suicidesper100k.mean(), 0, 1) 190 191 plt.figure(figsize=(16, 5)) 192 plt.subplot(121) 193 plt.hist(total.risk, color=col[8]) 194 plt.ylabel('counts', fontsize=20) 195 plt.xlabel('Suicide risk', fontsize=20) 196 plt.title("自杀高低风险数量") 197 198 plt.subplot(122) 199 sns.distplot(total.suicidesper100k[total.risk == 0], bins=10) 200 sns.distplot(total.suicidesper100k[total.risk == 1], bins=20) 201 plt.xlabel('Suicides', fontsize=20) 202 plt.title("自杀高低风险分布情况") 203 plt.show() 204 (total['risk']==1).sum() 205 (total['risk']==0).sum() 206 total.head(5) 207 total['yearlyHDI'].isnull().sum() 208 a = 19456/27820 209 a 210 total['yearlyHDI'].describe() 211 total['yearlyHDI'].isnull().sum() 212 total 213 fill_1 = total['yearlyHDI'] 214 fill_1 = pd.DataFrame(fill_1) 215 fill_1 216 from scipy.interpolate import lagrange #导入拉格朗日函数 217 def ployinterp_column(s,n,k=2,result_type='broadcast'): # k=2表示用空值的前后两个数值来拟合曲线,从而预测空值 218 y = s[list(range(n+2-k,n+2)) + list(range(n+3,n+3-k))] # 取值,range函数返回一个左闭右开([left,right))的序列数 219 y = y[y.notnull()] # 取上一行中取出数值列表中的非空值,保证y的每行都有数值,便于拟合函数 220 return lagrange(y.index,list(y))(n) # 调用拉格朗日函数,并添加索引 221 for i in fill_1.columns: # 如果i在data的列名中,data.columns生成的是data的全部列名 222 for j in range(len(fill_1)): # len(data)返回了data的长度,若此长度为5,则range(5)会产生从0开始计数的整数列表 223 if (fill_1[i].isnull())[j]: # 如果data[i][j]为空,则调用函数ployinterp_column为其插值 224 fill_1[i][j] = ployinterp_column(fill_1[i],j,result_type='broadcast') 225 fill_1 226 # 对国家进行 标准化标签,将标签值统一转换成range(标签值个数-1)范围内 227 # 相当于fit(X).transform(X),意思就是先进行fit(),进行数据拟合,然后在进行transform() 进行标准化处理 228 229 from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder 230 le = LabelEncoder() 231 total.country = le.fit_transform(total.country) 232 total.country.unique() 233 234 # 为建立模型准备数据 235 X = total.drop(['suicidesper100k','risk','country-year'],axis = 1) 236 #用0进行填补 237 X['yearlyHDI'] = fill_1['yearlyHDI'] 238 y = total['risk'] 239 #对X进行独热编码处理 240 XS = pd.get_dummies(X) 241 #GDP和人口的分布 242 ax1 = total[total['risk'] == 1][0:200].plot(kind='scatter', x='GDPpcapita', y='population', color='DarkRed', 243 label='high risk', figsize=(6, 5), fontsize=12) 244 total[total['risk'] == 0][0:200].plot(kind='scatter', x='GDPpcapita', y='population', color='DarkBlue', 245 label='low risk', ax=ax1) 246 247 plt.ylabel('population', fontsize=16) 248 plt.xlabel('GDP per capita', fontsize=16) 249 plt.legend(fontsize=14) 250 #GDP和人类发展指数的分布 251 ax1 = total[total['risk'] == 1][0:200].plot(kind='scatter', x='GDPpcapita', y='yearlyHDI', color='DarkRed', 252 label='high risk', figsize=(6, 5), fontsize=12) 253 total[total['risk'] == 0][0:200].plot(kind='scatter', x='GDPpcapita', y='yearlyHDI', color='DarkBlue', 254 label='low risk', ax=ax1) 255 256 plt.ylabel('yearlyHDI', fontsize=16) 257 plt.xlabel('GDP per capita', fontsize=16) 258 plt.legend(fontsize=14) 259 # 关于年份的高低自杀风险 260 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(30, 30)) 261 262 plt.subplot(4, 3, 1) 263 sns.distplot(total[total.columns[0]][total.risk == 0], label='low risk') 264 sns.distplot(total[total.columns[0]][total.risk == 1], label='high risk') 265 plt.legend(loc='best', fontsize=18) 266 plt.xlabel(total.columns[0], fontsize=18) 267 plt.show() 268 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split 269 # 将数据集拆分为训练集和测试集 270 # 首先将该数据3/4作为训练集,1/4作为测试集;再由训练集划分1/5作为验证集 271 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(XS, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=4) 272 X_train,X_valid,y_train,y_valid=train_test_split(X_train,y_train,test_size=0.2,random_state=4) 273 print('Train set:', X_train.shape, y_train.shape) 274 print('Test set:', X_test.shape, y_test.shape) 275 print('Test set:', X_valid.shape, y_valid.shape) 276 from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression 277 from sklearn.metrics import recall_score,accuracy_score 278 from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_fscore_support 279 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report 280 281 LR = LogisticRegression(C=0.001, solver='liblinear') 282 LR.fit(X_train, y_train) 283 284 # 预测类别:0还是1 285 yLRhat = LR.predict(X_valid) 286 287 # 预测 0或1的概率(例如 [0.54689436, 0.45310564] 预测出来为0) 288 yLRhat_prob = LR.predict_proba(X_valid) 289 290 cm = confusion_matrix(y_valid, yLRhat) 291 print('\n confusion matrix:混淆矩阵 \n', cm) 292 print('此时模型准确率为:',accuracy_score(y_valid, yLRhat)) 293 print('********************************************************') 294 print('\n') 295 print('逻辑回归模型的分类报告\n', classification_report(y_valid, yLRhat)) 296 #skplt.metrics.plot_confusion_matrix(y_valid,yLRhat,normalize=True) 297 X_train.head() 298 from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV 299 300 param={"tol":[1e-4, 1e-3,1e-2], "C":[0.4, 0.6, 0.8]} 301 grid = GridSearchCV(LogisticRegression(),param_grid=param, cv=5)#这里是5折交叉验证 302 grid.fit(X_train,y_train) 303 print(grid.best_params_) 304 print(grid.best_score_) 305 306 #得到最好的逻辑回归分类器 307 best_LR=grid.best_estimator_ 308 309 #进行训练、预测 310 best_LR.fit(X_train,y_train) 311 pred=best_LR.predict(X_valid) 312 313 cm = confusion_matrix(y_valid, pred) 314 print('\n confusion matrix:混淆矩阵 \n', cm) 315 print('最好的逻辑回归模型准确率为:',accuracy_score(y_valid, pred)) 316 print('********************************************************') 317 print('\n') 318 print('最好的逻辑回归模型的分类报告\n', classification_report(y_valid, pred)) 319 from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier 320 from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score 321 from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report 322 323 # 决策树学习 324 # 函数为创建一个决策树模型 325 # criterion:gini或者entropy,前者是基尼系数,后者是信息熵。 326 # max_depth: int or None, optional (default=None) 设置决策随机森林中的决策树的最大深度,深度越大,越容易过拟合,推荐树的深度为:5-20之间。 327 # max_leaf_nodes: 通过限制最大叶子节点数,可以防止过拟合,默认是"None”,即不限制最大的叶子节点数。 328 DT = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion="entropy", max_depth=7, max_leaf_nodes=30) 329 DT.fit(X_train, y_train) 330 ydthat = DT.predict(X_valid) 331 332 print('***决策树模型***') 333 334 #决策树模型性能评估 335 print('验证集上的准确率:', DT.score(X_valid, y_valid)) 336 print('训练集上的准确率:', DT.score(X_train, y_train)) 337 338 # 混淆矩阵 339 print('CM\n', confusion_matrix(y_valid, ydthat)) 340 print('********************************************************') 341 342 print('决策树模型的分类报告\n', classification_report(y_valid, ydthat)) 343 344 DTfeat_importance = DT.feature_importances_ 345 DTfeat_importance = pd.DataFrame([X_train.columns, DT.feature_importances_]).T 346 347 # 特征重要性排序 348 print("特征重要性排名如下:") 349 print(DTfeat_importance.sort_values(by=1, ascending=False)) 350 # 通过cv_results观察过程并做图 351 max_depth=np.arange(0,20,3) 352 max_leaf_nodes=np.arange(0,30,3) 353 min_samples_leaf =np.arange(0,20,2) 354 param1= {'criterion':['entropy'],'max_depth':max_depth} 355 param2= {'criterion':['entropy'],'min_samples_leaf':min_samples_leaf} 356 param3= {'criterion':['entropy'],'max_leaf_nodes':max_leaf_nodes} 357 358 359 clf1 = GridSearchCV(DecisionTreeClassifier(),param_grid=param1,cv=6) 360 clf1.fit(X_train,y_train) 361 362 clf2 = GridSearchCV(DecisionTreeClassifier(),param_grid=param2,cv=6) 363 clf2.fit(X_train,y_train) 364 365 366 clf3 = GridSearchCV(DecisionTreeClassifier(),param_grid=param3,cv=6) 367 clf3.fit(X_train,y_train) 368 369 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20,10), dpi=100) 370 ax = fig.add_subplot(311) 371 ax.plot(min_samples_leaf,clf2.cv_results_['mean_test_score'],'g*-',) 372 plt.title('决策树模型网格搜索的训练过程',fontsize=20) 373 plt.xticks(fontsize=20) 374 plt.yticks(fontsize=20) 375 376 ax = fig.add_subplot(312) 377 ax.plot(max_depth,clf1.cv_results_['mean_test_score'],'g*-') 378 plt.xticks(fontsize=20) 379 plt.yticks(fontsize=20) 380 ax = fig.add_subplot(313) 381 ax.plot(max_leaf_nodes,clf3.cv_results_['mean_test_score'],'g*-') 382 plt.xticks(fontsize=20) 383 plt.yticks(fontsize=20) 384 plt.show() 385 best_DT = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion="entropy", max_depth=15, max_leaf_nodes=25,min_samples_leaf=2) 386 best_DT.fit(X_train, y_train) 387 ydthat =best_DT.predict(X_valid) 388 389 print('***决策树模型***') 390 391 #决策树模型性能评估 392 print('验证集上的准确率:',best_DT.score(X_valid, y_valid)) 393 print('训练集上的准确率:',best_DT.score(X_train, y_train)) 394 395 # 混淆矩阵 396 print('CM\n', confusion_matrix(y_valid, ydthat)) 397 print('********************************************************') 398 399 print('决策树模型的分类报告\n', classification_report(y_valid, ydthat)) 400 401 DTfeat_importance = best_DT.feature_importances_ 402 DTfeat_importance = pd.DataFrame([X_train.columns, DT.feature_importances_]).T 403 404 # 特征重要性排序 405 print("特征重要性排名如下:") 406 print(DTfeat_importance.sort_values(by=1, ascending=False)) 407 # 随机森林可以视为多颗决策树的集成,鲁棒性更强,泛化能力更好,不易产生过拟合现象。但是噪声比较大的情况下会过拟合。 408 409 from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier 410 411 random_forest = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=20, max_depth=10, min_samples_split=2, min_samples_leaf=5, 412 max_leaf_nodes=20, max_features=len(X_train.columns)) 413 414 random_forest.fit(X_train, y_train) 415 416 yrfhat = random_forest.predict(X_valid) 417 feat_importance = random_forest.feature_importances_ 418 rffeat_importance = pd.DataFrame([X_train.columns, random_forest.feature_importances_]).T 419 420 print('******************Random forest classifier**************') 421 print('训练集上的准确率', random_forest.score(X_train, y_train)) 422 print('验证集上的准确率', random_forest.score(X_valid,y_valid)) 423 print('混淆矩阵\n', confusion_matrix(y_valid, yrfhat)) 424 print('********************************************************') 425 print('随机森林的分类报告\n', classification_report(y_valid, yrfhat)) 426 print(rffeat_importance.sort_values(by=1, ascending=False)) 427 #我们首先对n_estimators进行网格搜索: 428 param_test1 = {'n_estimators':[50,120,160,200,250]} 429 gsearch1 = GridSearchCV(estimator = RandomForestClassifier(), param_grid = param_test1,cv=5) 430 gsearch1.fit(X_train,y_train) 431 print( gsearch1.best_params_, gsearch1.best_score_) 432 #接着我们对决策树最大深度max_depth和内部节点再划分所需最小样本数min_samples_split进行网格搜索。 433 param_test2 = {'max_depth':[1,2,3,5,7,9,11,13,20],'min_samples_split':[5,10,25,50,100,120,150]} 434 gsearch2 = GridSearchCV(estimator = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=160),param_grid = param_test2, cv=5) 435 gsearch2.fit(X_train,y_train) 436 print( gsearch2.best_params_, gsearch2.best_score_) 437 #最好的随机森林模型 438 best_rf=RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=160, max_depth=20, min_samples_split=5) 439 440 best_rf .fit(X_train, y_train) 441 442 yrfhat = best_rf .predict(X_valid) 443 feat_importance = best_rf.feature_importances_ 444 rffeat_importance = pd.DataFrame([X_train.columns, random_forest.feature_importances_]).T 445 446 print('******************随机森林模型**************') 447 print('训练集上的准确率',best_rf.score(X_train, y_train)) 448 print('验证集上的准确率',best_rf.score(X_valid,y_valid)) 449 print('混淆矩阵\n', confusion_matrix(y_valid, yrfhat)) 450 print('********************************************************') 451 print('最好的随机森林模型的分类报告\n', classification_report(y_valid, yrfhat)) 452 print(rffeat_importance.sort_values(by=1, ascending=False))



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号