二分图最大分配
二分图是一个无向图,分为x,y两部分,x部中的点与y中的点往往会存在多条无向边,若x1与y2之间存在一条边,那么x1与y2可以“分配”,当然每个点部止局限于只有一条边,可以有多条,所以又有多种分配方法,为达到让这个二分图中分配数量最大,即使x1与y2可以“分配”也只是暂时的,因为要为其他点“让步”,举个例子:
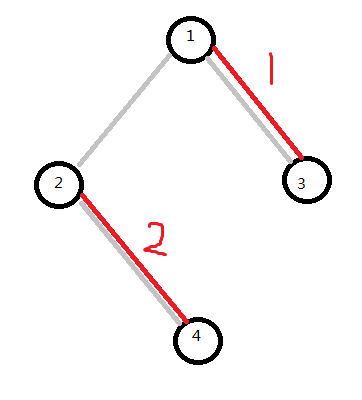 图中,点1到点2有一条边,点1到点3有一条边,点2到点4有一条边
图中,点1到点2有一条边,点1到点3有一条边,点2到点4有一条边
就“择近原则”,点1可以首先和点2“分配”,但点3发现自己只有点1可以“分配”,于是就向点1提出要求“分配”,可是点1已经被“分配过了”,于是点1就去找点2商量问它可不可以找另一个点“分配”,点2就去询问点4能否“分配”,发现点4还没有被“分配”,也就是说点2可以找另一个点分配,于是返回true,不和点1“分配”了,和点4分配,点1得到true便与点3“分配”了
细心的人可能会发现,如果像开始那样:点1与点2分配,那么只有1个“分配组”,而经过这一系列算法(匈牙利算法)而拓展路线(增广路)便有2个“分配组”,这就称为二分图最大分配

1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 int m; 6 int n; 7 int x,y; 8 int ans; 9 int match[210]; //记录分配目标 10 int put[110][3]; //输出 11 bool book[210]; //记录剪枝 12 bool way[210][210]; //记录无向图的边 13 inline int read() //快速读入 14 { 15 int sign=1,num=0; 16 char ch=getchar(); 17 while(!isdigit(ch)){if(ch=='-')sign=-1;ch=getchar();} 18 while(isdigit(ch)){num=num*10+(ch-'0');ch=getchar();} 19 return sign*num; 20 } 21 void init() //读入函数 22 { 23 m=read(); 24 n=read(); 25 while(x!=-1&&y!=-1) 26 { 27 x=read(); //无向边存两次 28 y=read(); 29 way[x][y]=true; 30 way[y][x]=true; 31 } 32 } 33 bool dfs(int x) 34 { 35 for(int y=m+n;y>0;--y) 36 { 37 if(way[x][y]&&book[y]==false) //枚举点x的边 38 { 39 book[y]=true; //记录点y已被查找(并非分配) 40 if(match[y]==0||dfs(match[y])) //若y没有被分配或与y分配的人还有"退"的余地 41 { 42 match[x]=y; //储存分配目标 43 match[y]=x; 44 return true; 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 return false; 49 } 50 int main() //看代码建议从mian函数看起 51 { 52 init(); 53 for(int i=1;i<=m+n;++i) //枚举点 54 { 55 memset(book,false,sizeof(book)); 56 dfs(i); 57 } 58 for(int i=1;i<=m+n;++i) 59 if(match[i]!=0&&match[match[i]]!=0) //防止重复输出 60 { 61 put[++ans][1]=i; 62 put[ans][2]=match[i]; 63 match[match[i]]=0; 64 } 65 if(ans==0) //特判 66 { 67 puts("No Solution!"); 68 return 0; 69 } 70 printf("%d",ans); 71 for(int i=1;i<=ans;++i) 72 printf("\n%d %d",put[i][1],put[i][2]); 73 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号