C#数组(Array)
原文:https://www.runoob.com/csharp/csharp-array.html
一、数组介绍
数组是一个存储相同类型元素的固定大小的顺序集合。数组是用来存储数据的集合,通常认为数组是一个同一类型变量的集合。
声明数组变量并不是声明 number0、number1、...、number99 一个个单独的变量,而是声明一个就像 numbers 这样的变量,然后使用 numbers[0]、numbers[1]、...、numbers[99] 来表示一个个单独的变量。数组中某个指定的元素是通过索引来访问的。
所有的数组都是由连续的内存位置组成的。最低的地址对应第一个元素,最高的地址对应最后一个元素。
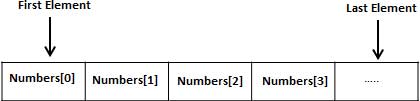
二、声明数组
在 C# 中声明一个数组,您可以使用下面的语法:
datatype[] arrayName;
其中:
- datatype 用于指定被存储在数组中的元素的类型。
- [ ] 指定数组的秩(维度)。秩指定数组的大小。
- arrayName 指定数组的名称。
例如:
double[] balance;
三、初始化数组
声明一个数组不会在内存中初始化数组。当初始化数组变量时,您可以赋值给数组。
数组是一个引用类型,所以您需要使用 new 关键字来创建数组的实例。
注意:数组必须指定长度,在没有给元素赋值前,所有的元素都会使用对应类型的默认值。
例如:
double[] balance = new double[10]; // 数组必须指定长度
四、赋值给数组
您可以通过使用索引号赋值给一个单独的数组元素,比如:
double[] balance = new double[10]; balance[0] = 4500.0;
您可以在声明数组的同时给数组赋值,比如:
double[] balance = { 2340.0, 4523.69, 3421.0};
您也可以创建并初始化一个数组,比如:
int [] marks = new int[5] { 99, 98, 92, 97, 95};
在上述情况下,你也可以省略数组的大小,比如:
int [] marks = new int[] { 99, 98, 92, 97, 95}; // 实际上也是定义了长度为5的数组
您也可以赋值一个数组变量到另一个目标数组变量中。在这种情况下,目标和源会指向相同的内存位置:
int [] marks = new int[] { 99, 98, 92, 97, 95}; int[] score = marks;
当您创建一个数组时,C# 编译器会根据数组类型隐式初始化每个数组元素为一个默认值。例如,int 数组的所有元素都会被初始化为 0。
五、访问数组元素
元素是通过带索引的数组名称来访问的。这是通过把元素的索引放置在数组名称后的方括号中来实现的。例如:
double salary = balance[9];
下面是一个实例,使用上面提到的三个概念,即声明、赋值、访问数组:
using System; namespace ArrayApplication { class MyArray { static void Main(string[] args) { int [] n = new int[10]; /* n 是一个带有 10 个整数的数组 */ int i,j; /* 初始化数组 n 中的元素 */ for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) { n[ i ] = i + 100; } /* 输出每个数组元素的值 */ for (j = 0; j < 10; j++ ) { Console.WriteLine("Element[{0}] = {1}", j, n[j]); } Console.ReadKey(); } } } /* 当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果: Element[0] = 100 Element[1] = 101 Element[2] = 102 Element[3] = 103 Element[4] = 104 Element[5] = 105 Element[6] = 106 Element[7] = 107 Element[8] = 108 Element[9] = 109 */
六、使用 foreach 循环
在前面的实例中,我们使用一个 for 循环来访问每个数组元素。您也可以使用一个 foreach 语句来遍历数组。
using System; namespace ArrayApplication { class MyArray { static void Main(string[] args) { int [] n = new int[10]; /* n 是一个带有 10 个整数的数组 */ /* 初始化数组 n 中的元素 */ for ( int i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) { n[i] = i + 100; } /* 输出每个数组元素的值 */ foreach (int j in n ) { int i = j-100; Console.WriteLine("Element[{0}] = {1}", i, j); } Console.ReadKey(); } } } /* 当上面的代码被编译和执行时,它会产生下列结果: Element[0] = 100 Element[1] = 101 Element[2] = 102 Element[3] = 103 Element[4] = 104 Element[5] = 105 Element[6] = 106 Element[7] = 107 Element[8] = 108 Element[9] = 109 */
七、数组进阶
1、多维数组
C# 支持多维数组。多维数组又称为矩形数组。
您可以声明一个 string 变量的二维数组,如下:
string [,] names;
或者,您可以声明一个 int 变量的三维数组,如下:
int [ , , ] m;
1.二维数组
多维数组最简单的形式是二维数组。一个二维数组,在本质上,是一个一维数组的列表。
一个二维数组可以被认为是一个带有 x 行和 y 列的表格。下面是一个二维数组,包含 3 行和 4 列:
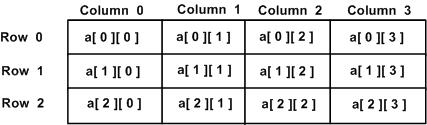
因此,数组中的每个元素是使用形式为 a[ i , j ] 的元素名称来标识的,其中 a 是数组名称,i 和 j 是唯一标识 a 中每个元素的下标。
初始化二维数组
多维数组可以通过在括号内为每行指定值来进行初始化。下面是一个带有 3 行 4 列的数组。
int [,] a = new int [3,4] {
{0, 1, 2, 3} , /* 初始化索引号为 0 的行 */
{4, 5, 6, 7} , /* 初始化索引号为 1 的行 */
{8, 9, 10, 11} /* 初始化索引号为 2 的行 */
};
访问二维数组元素
二维数组中的元素是通过使用下标(即数组的行索引和列索引)来访问的。例如:
int val = a[2,3];
上面的语句将获取数组中第 3 行第 4 个元素。您可以通过上面的示意图来进行验证。让我们来看看下面的程序,我们将使用嵌套循环来处理二维数组:
using System; namespace ArrayApplication { class MyArray { static void Main(string[] args) { /* 一个带有 5 行 2 列的数组 */ int[,] a = new int[5, 2] {{0,0}, {1,2}, {2,4}, {3,6}, {4,8} }; int i, j; /* 输出数组中每个元素的值 */ // 方法一 Console.WriteLine("方法一"); for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) { for (j = 0; j < 2; j++) { Console.WriteLine("a[{0},{1}] = {2}", i, j, a[i,j]); } } // 方法二:C#中GetLength()函数,用来获取数组指定维数中的元素个数。 Console.WriteLine("方法二"); for (i = 0; i < a.GetLength(0); i++) { for (j = 0; j < a.GetLength(1); j++) { Console.WriteLine("a[{0},{1}] = {2}", i, j, a[i,j]); } } // 方法三:foreach Console.WriteLine("方法三"); foreach (int item in a) { Console.WriteLine("{0}", item); } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
C#中GetLength()函数,用来获取数组指定维数中的元素个数。
2、交错数组
交错数组是数组的数组。交错数组是一维数组。
用我们自己的话来解释就是:一维数组里面的每个元素都是数组类型,里面数组的长度不一定都要相同。
交错数组与二维数组的区别,可以直观的理解为交错数组每一行的长度是可以不一样的。
您可以声明一个带有 int 值的交错数组 scores,如下所示:
int [][] scores;
声明一个数组不会在内存中创建数组。创建上面的数组:
int[][] scores = new int[5][];
for (int i = 0; i < scores.Length; i++)
{
scores[i] = new int[4];
}
您可以初始化一个交错数组,如下所示:
int[][] scores = new int[2][]{new int[]{92,93,94},new int[]{85,66,87,88}};
其中,scores 是一个由两个整型数组组成的数组 -- scores[0] 是一个带有 3 个整数的数组,scores[1] 是一个带有 4 个整数的数组。
下面的实例演示了如何使用交错数组:
简单示例:
using System; namespace ArrayApplication { class MyArray { static void Main(string[] args) { /* 一个由 5 个整型数组组成的交错数组 */ int[][] a = new int[][]{ new int[]{0,0}, new int[]{1,2}, new int[]{2,4}, new int[]{3, 6}, new int[]{4, 8} }; int i, j; /* 输出数组中每个元素的值 */ for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) { for (j = 0; j < 2; j++) { Console.WriteLine("a[{0}][{1}] = {2}", i, j, a[i][j]); } } Console.ReadKey(); } } }
在 C# 语法中,交错数组使用两个中括号定义,但是,两个中括号很容易让人误以为它是二维数组,其实,它本质上是一维数组。
当交错数组里面数组长度不一样时,使用下面的方式去遍历:1.使用 for 搭配 Length 遍历;2.使用 foreach 嵌套遍历;
using System; namespace ArrayApplication { class MyArray { static void Main(string[] args) { // 声明一个交错数组 num,num 中有三个元素,分别是 num[0],num[1],num[2] 每个元素都是一个数组 int[][] num = new int[3][]; // 以下是声明交错数组的每一个元素的,每个数组的长度可以不同 num[0] = new int[] { 1, 2, 3 }; num[1] = new int[] { 4, 5, 6, 7 }; num[2] = new int[] { 8 }; /*遍历方式一:使用Length属性*/ for (int i = 0; i < num.Length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < num[i].Length; j++) { Console.WriteLine("num[{0},{1}]={2}", i, j, num[i][j]); } } /*遍历方式二:foreach 遍历交错数组*/ foreach (int[] tempArr in num) { foreach (int n in tempArr) { Console.WriteLine(n); } } Console.WriteLine(num.Rank);// 函数输出1,表示是一维数组。 } } }
3、传递数组给函数
在 C# 中,您可以传递数组作为函数的参数。您可以通过指定不带索引的数组名称来给函数传递一个指向数组的指针。
using System; namespace ArrayApplication { class MyArray { double getAverage(int[] arr) { int i; double avg; int sum = 0; for (i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) { sum += arr[i]; } avg = (double)sum / arr.Length; return avg; } double getAverage2(int[] arr) { double avg; int sum = 0; foreach(int member in arr) { sum += member; } avg = (double)sum / arr.Length; return avg; } static void Main(string[] args) { MyArray app = new MyArray(); /* 一个带有 5 个元素的 int 数组 */ int [] balance = new int[]{1000, 2, 3, 17, 50}; double avg, avg2; /* 传递数组的指针作为参数 */ avg = app.getAverage(balance) ; avg2 = app.getAverage2(balance) ; /* 输出返回值 */ Console.WriteLine( "平均值是: {0} ", avg ); Console.WriteLine( "平均值2是: {0} ", avg2 ); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
传递交错数组(或者二维数组)作为参数:
using System; namespace ArrayApplication { class Program { public int getSum(int[][] array) { int sum = 0; foreach (int[] arr in array) foreach (int i in arr) sum += i; return sum; } static void Main(String[] args) { int[][] array = new int[3][]; array[0] = new int[] { 0, 1 }; array[1] = new int[] { 2, 3, 4 }; array[2] = new int[] { 5, 6, 7, 8 }; Program pro = new Program(); int sum = pro.getSum(array); // 交错数组作为参数 Console.WriteLine("{0}", sum); } } }
4、参数数组
有时,当声明一个方法时,您不能确定要传递给函数作为参数的参数数目。C# 参数数组解决了这个问题,参数数组通常用于传递未知数量的参数给函数。
在使用数组作为形参时,C# 提供了 params 关键字,使调用数组为形参的方法时,既可以传递数组实参,也可以传递一组数组元素。params 的使用格式为:
public 返回类型 方法名称( params 类型名称[] 数组名称 )
params 用法:
- 带 params 关键字的参数类型必须是一维数组,不能使用在多维数组上;
- 不允许和 ref、out 同时使用;
- 带 params 关键字的参数必须是最后一个参数,并且在方法声明中只允许一个 params 关键字。
- 不能仅使用 params 来使用重载方法。
- 没有 params 关键字的方法的优先级高于带有params关键字的方法的优先级
- C#中 params 相当于python中的 *args
using System; namespace MyParams { class MyParams { static void Test(int a, int b) { Console.WriteLine("a + b = {0}", a + b); } static void Test(params int[] list) { foreach(int i in list) { Console.Write("{0} ", i); } Console.WriteLine(); } static void Main(string[] args) { Test(1, 2); // 会调用第一个Test函数 Test(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); // 调用第二个Test函数:以形参同类型的值传入 int[] intList = new int[] {6, 7, 8}; Test(intList); // 调用第二个Test函数:以数组类型传入 Console.ReadLine(); } } }
结果:
a + b = 3
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8
5、Array 类
Array 类是 C# 中所有数组的基类,它是在 System 命名空间中定义。Array 类提供了各种用于数组的属性和方法。
1.Array 类的属性
下表列出了 Array 类中一些最常用的属性:
| 序号 | 属性 & 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | IsFixedSize 获取一个值,该值指示数组是否带有固定大小。 |
| 2 | IsReadOnly 获取一个值,该值指示数组是否只读。 |
| 3 | Length 获取一个 32 位整数,该值表示所有维度的数组中的元素总数。 |
| 4 | LongLength 获取一个 64 位整数,该值表示所有维度的数组中的元素总数。 |
| 5 | Rank 获取数组的秩(维度)。 |
如需了解 Array 类的完整的属性列表,请参阅微软的 C# 文档。
2.Array 类的方法
下表列出了 Array 类中一些最常用的方法:
| 方法 & 描述 |
|---|
| Clear 根据元素的类型,设置数组中某个范围的元素为零、为 false 或者为 null。 |
| Copy(Array, Array, Int32) 从数组的第一个元素开始复制某个范围的元素到另一个数组的第一个元素位置。长度由一个 32 位整数指定。 |
| CopyTo(Array, Int32) 从当前的一维数组中复制所有的元素到一个指定的一维数组的指定索引位置。索引由一个 32 位整数指定。 |
| Clone() 复制一个数组,但是需要进行强类型转换,因为返回值是object |
| GetLength 获取一个 32 位整数,该值表示指定维度的数组中的元素总数。 |
| GetLongLength 获取一个 64 位整数,该值表示指定维度的数组中的元素总数。 |
| GetLowerBound 获取数组中指定维度的下界。 |
| GetUpperBound 获取数组中指定维度的上界。 |
| GetType 获取当前实例的类型。从对象(Object)继承。 |
| SetValue(Object, Int32) 给一维数组中指定位置的元素设置值。索引由一个 32 位整数指定。 |
| GetValue(Int32) 获取一维数组中指定位置的值。索引由一个 32 位整数指定。 |
| Sort(Array) 使用数组的每个元素的 IComparable 实现来排序整个一维数组中的元素。 |
| Reverse(Array) 逆转整个一维数组中元素的顺序。 |
| IndexOf(Array, Object) 搜索指定的对象,返回整个一维数组中第一次出现的索引。 |
| ToString 返回一个表示当前对象的字符串。从对象(Object)继承。 |
如需了解 Array 类的完整的方法列表,请参阅微软的 C# 文档。
实例
下面的程序演示了 Array 类的一些方法的用法:
using System; namespace MyParams { class MyParams { static void PropertyTest() { int[] oneArr = new int[] {1, 2, 3}; int[,] twoArr = new int[,] {{4, 5, 6}, {6, 7, 9}}; Console.WriteLine("oneArr IsFixedSize: {0}", oneArr.IsFixedSize); // True Console.WriteLine("twoArr IsReadOnly: {0}", twoArr.IsReadOnly); // False // 获取所有维度的数组中的元素总数 Console.WriteLine("oneArr Length: {0}", oneArr.Length); // 3 Console.WriteLine("twoArr Length: {0}", twoArr.Length); // 6 Console.WriteLine("twoArr LongLength: {0}", twoArr.LongLength); // 6 // 数组维度 Console.WriteLine("oneArr Rank: {0}", oneArr.Rank); // 1 Console.WriteLine("twoArr Rank: {0}", twoArr.Rank); // 2 } /* Array.Clear()方法用于清除数组中的元素并将它们设置为其默认值 语法: Clear (Array arr, int index, int len); 在这里,arr是要清除其元素的数组,索引是要清除的元素的开始索引,而len是要清除的元素的计数。 */ static void ClearTest1() { Console.WriteLine("原始数组元素..."); int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 }; for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) { Console.Write("{0} ", arr[i]); } Console.WriteLine(); Console.WriteLine("Clear之后的数组元素..."); Array.Clear(arr, 4, 3); for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) { Console.Write("{0} ", arr[i]); } Console.WriteLine(); /* 结果 原始数组元素... 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Clear之后的数组元素... 1 2 3 4 0 0 0 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 */ } static void ClearTest2() { Console.WriteLine("二维数组原始元素..."); int[,] arr = new int[4,4] { {1, 2, 3, 4}, {5, 6, 7, 8}, {9, 10, 11, 12}, {13, 14, 15, 16} }; for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) { Console.Write("{0} ", arr[i,j]); } Console.WriteLine(); } Console.WriteLine(); Console.WriteLine("Clear之后的二维数组元素..."); Array.Clear(arr, 5, 9); for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) { Console.Write("{0} ", arr[i,j]); } Console.WriteLine(); } Console.WriteLine(); /* 结果 二维数组原始元素... 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 lear之后的二维数组元素... 1 2 3 4 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 15 16 */ } /* Copy(Array, Array, Int32) 从数组的第一个元素开始复制某个范围的元素到另一个数组中(从第一个元素开始) */ static void CopyTest() { int[] num1 = new int[] {1,2,3,4,5}; int[] num2 = new int[4] {6,6,6,6}; Array.Copy(num1, num2, 3); foreach(int i in num2) { Console.Write("{0} ", i); } Console.WriteLine(); /* 结果 1 2 3 6 */ } /* CopyTo(Array, Int32) 从当前的一维数组中复制所有的元素到一个指定的一维数组的指定索引位置 与Copy的区别是 Copy只能从源数组的第一个元素开始复制到目标数组,目标数组也是从第一个元素开始接收 CopyTo是把源数组的所有元素,复制到目标数组,目标数组从指定的索引开始 */ static void CopyToTest() { int[] num1 = new int[] {1,2,3}; int[] num2 = new int[6]; num1.CopyTo(num2, 2); foreach(int i in num2) { Console.Write("{0} ", i); } Console.WriteLine(); /* 结果 0 0 1 2 3 0 */ } /* Array.Clone方法: Array的浅表副本仅复制Array的元素,无论他们是引用类型还是值类型,但是不负责这些引用所引用的对象。 新Array中的引用与原始Array的引用指向相同的对象。 Clone 需要使用强制类型转换,原因在于Clone()返回的类型为Object */ static void CloneTest() { int[,] intArr1 = {{1, 2, 3},{4,5,6}}; int[,] intArr2 = (int [,])intArr1.Clone(); // 需要使用强制类型转换,原因在于Clone()返回的类型为Object for (int i = 0; i < intArr2.GetLength(0); i++) { for (int j = 0; j < intArr2.GetLength(1); j++) Console.Write("{0} ", intArr2[i,j]); Console.WriteLine(); } Console.WriteLine(); /* 结果 1 2 3 4 5 6 */ } /* GetLength(rank): 获取一个 32 位整数,该值表示指定维度的数组中的元素总数。 GetLongLength(rank): 获取一个 64 位整数,该值表示指定维度的数组中的元素总数 */ static void GetLengthTest() { int[,] arr3 = new int[3,4]; Console.WriteLine("GetLength: {0}", arr3.GetLength(0)); // 获取数组第一个维度的长度 Console.WriteLine("GetLongLength: {0}", arr3.GetLongLength(1)); // 获取数组第二个维度的长度 Console.WriteLine(); /* 结果 GetLength: 3 GetLongLength: 4 */ } /* GetLowerBound(rank): 获取数组中指定维度的下界。 GetUpperBound(rank): 获取数组中指定维度的上界。 */ static void GetBoundTest() { int[,] arr4 = new int[3,4] { {1,2,3,4}, {5,6,7,8}, {9,10,11,12}, }; Console.WriteLine("这是{0}维数组", arr4.Rank); // 这是2维数组 for(int i = arr4.GetLowerBound(0); i <= arr4.GetUpperBound(0); i++) { // arr4.GetLowerBound(0);其中的0表示取第一维的下限,一般数组索引是0开始,为0 // 同理 arr4.GetUpperBound(0);其中的0表示取第一维的上限,在本例中是3行4列的数组,所以为2 for(int j = arr4.GetLowerBound(1); j <= arr4.GetUpperBound(1); j++) { // arr4.GetLowerBound(1);其中的1表示取第二维的下限,一般数组索引是0开始,为0 // arr4.GetUpperBound(1);其中的1表示取第二维的上限,在本例中是3行4列的数组,所以为3 // 遍历数组的元素 Console.Write(arr4[i,j]); } } } /* GetType: 获取当前实例的类型。从对象(Object)继承。 Type类,用来包含类型的特性。对于程序中的每一个类型,都会有一个包含这个类型的信息的Type类的对象,类型信息包含数据,属性和方法等信息。 有两种方法可以生成Type类的对象:一种是Typeof(类名),一种是对象调用GetType()函数,如: Type tp = typeof(int); double db = 3.14; Type dbTp = db.GetType(); */ static void GetTypeTest() { object[] values = { (int) 100, (long) 17111}; // 定义一个含两种类型的数组 foreach (object value in values) { Type tp = value.GetType(); // 获取每个元素的类型 if (tp.Equals(typeof(int))) Console.WriteLine("{0} 是整型", value); else Console.WriteLine("{0} 不是整型", value); } /* 结果 100 是整型 17111 不是整型 */ } /* GetValue(Int32, ...) 支持一维数组,多维数组 SetValue(Object, Int32, ...) 支持一维数组,多维数组,第一个参数是需要设置的值,后面参数是对应的索引位置 */ static void ValueTest() { /* 一维数组 */ string[] arr1 = new string[3]; // 设置值 arr1.SetValue("One", 0); arr1.SetValue("Two", 1); arr1.SetValue("Three", 2); //获取值 for (int i = arr1.GetLowerBound(0); i <= arr1.GetUpperBound(0); i++) { Console.WriteLine(arr1.GetValue(i)); } Console.WriteLine(); /* 二维数组 */ string[,] arr2 = new string[2,2]; // 设置值 arr2[0,0] = "python"; arr2[0,1] = "java"; arr2.SetValue("C#", 1, 0); // 两种方式都可以赋值 arr2.SetValue("C++", 1, 1); //获取值 for (int i = arr2.GetLowerBound(0); i <= arr2.GetUpperBound(0); i++) { for (int j = arr2.GetLowerBound(1); j <= arr2.GetUpperBound(1); j++) Console.WriteLine(arr2.GetValue(i, j)); } /* 结果 One Two Three python java C# C++ */ } /* IndexOf(Array array, Object value, Int32 startIndex, Int32 count) 此处只支持一维数组 */ static void IndexOfTest() { /* 一维数组 */ string[] arr = new string[] {"hello", "hi", "ff", "six", "old six", "age"}; Console.WriteLine(Array.IndexOf(arr, "hello")); // 0 Console.WriteLine(Array.IndexOf(arr, "old six")); // 4 Console.WriteLine(Array.IndexOf(arr, "niu pi")); // -1 Console.WriteLine(Array.IndexOf(arr, "ff", 2, 3)); // 从索引2开始,查找3个(ff,six,old six),结果:2 Console.WriteLine(Array.IndexOf(arr, "ff", 1, 1)); // 从索引1开始,查找1个(hi),结果:-1 Console.WriteLine(Array.IndexOf(arr, "ff", 1)); // 从索引1开始,查找后面所有,结果:2 } /* Sort(Array):使用数组的每个元素的 IComparable 实现来排序整个一维数组中的元素。 Reverse(Array):逆转整个一维数组中元素的顺序。 两个函数都只是支持一维数组 */ static void SortationTest() { int[] list = { 34, 72, 13, 44, 25, 30, 10 }; Console.Write("原始数组: "); foreach (int i in list) { Console.Write(i + " "); } Console.WriteLine(); // 逆转数组 Array.Reverse(list); Console.Write("逆转数组: "); foreach (int i in list) { Console.Write(i + " "); } Console.WriteLine(); // 排序数组 Array.Sort(list); Console.Write("排序数组: "); foreach (int i in list) { Console.Write(i + " "); } Console.WriteLine(); /* 结果: 原始数组: 34 72 13 44 25 30 10 逆转数组: 10 30 25 44 13 72 34 排序数组: 10 13 25 30 34 44 72 */ } /* ToString: 返回一个表示当前对象的字符串。从对象(Object)继承。 */ static void ToStringTest() { int[] list = { 34, 72, 13, 44, 25, 30, 10 }; string[] list2 = { "a", "b" }; Console.WriteLine("{0}",list.ToString()); // System.Int32[] Console.WriteLine("{0}",list2.ToString()); // System.String[] Console.WriteLine("{0}",list2[0].ToString()); // a } static void Main(string[] args) { PropertyTest(); ClearTest1(); ClearTest2(); CopyTest(); CopyToTest(); CloneTest(); GetLengthTest(); GetBoundTest(); GetTypeTest(); ValueTest(); IndexOfTest(); SortationTest(); ToStringTest(); } } }
静态方法:即使用Array类调用的
- Array.Clear
- Array.Copy -- 支持多维数组
- Array.IndexOf -- 只支持一维数组
- Array.Sort -- 只支持一维数组
- Array.Reverse -- 只支持一维数组
非静态方法:即Array的对象去调用的
- arrObj.CopyTo -- 仅支持一维数组
- arrObj.Clone
- arrObj.GetLength
- arrObj.GetLongLength
- arrObj.GetLowerBound
- arrObj.GetUpperBound
- arrObj.GetType
- arrObj.GetValue
- arrObj.SetValue
- arrObj.ToString


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号