【Linux】有名管道实现进程间通信——一个简单聊天程序
有名管道实现简单聊天程序
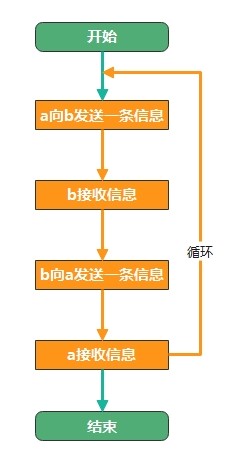
1. "你来我往"式简单聊天
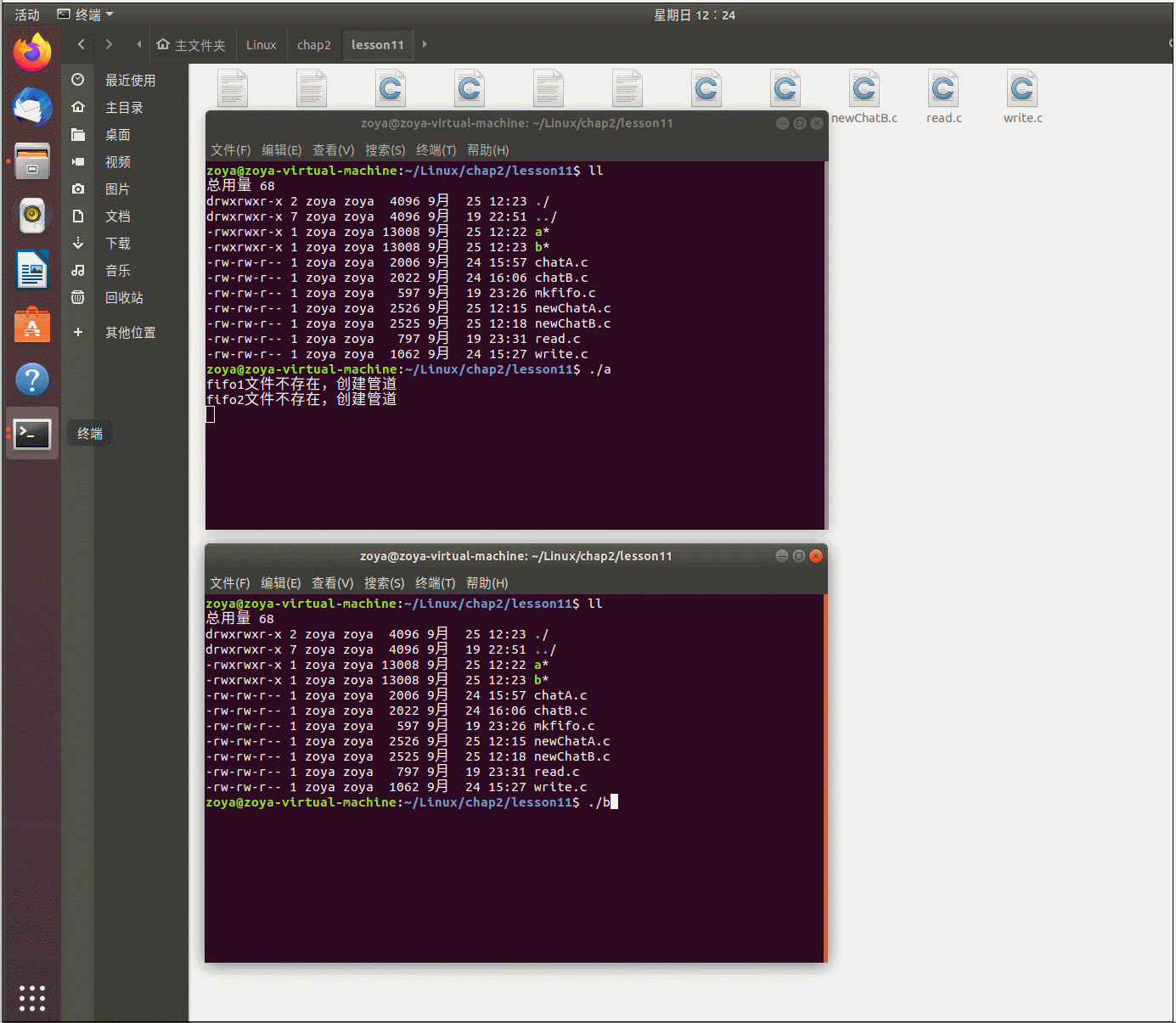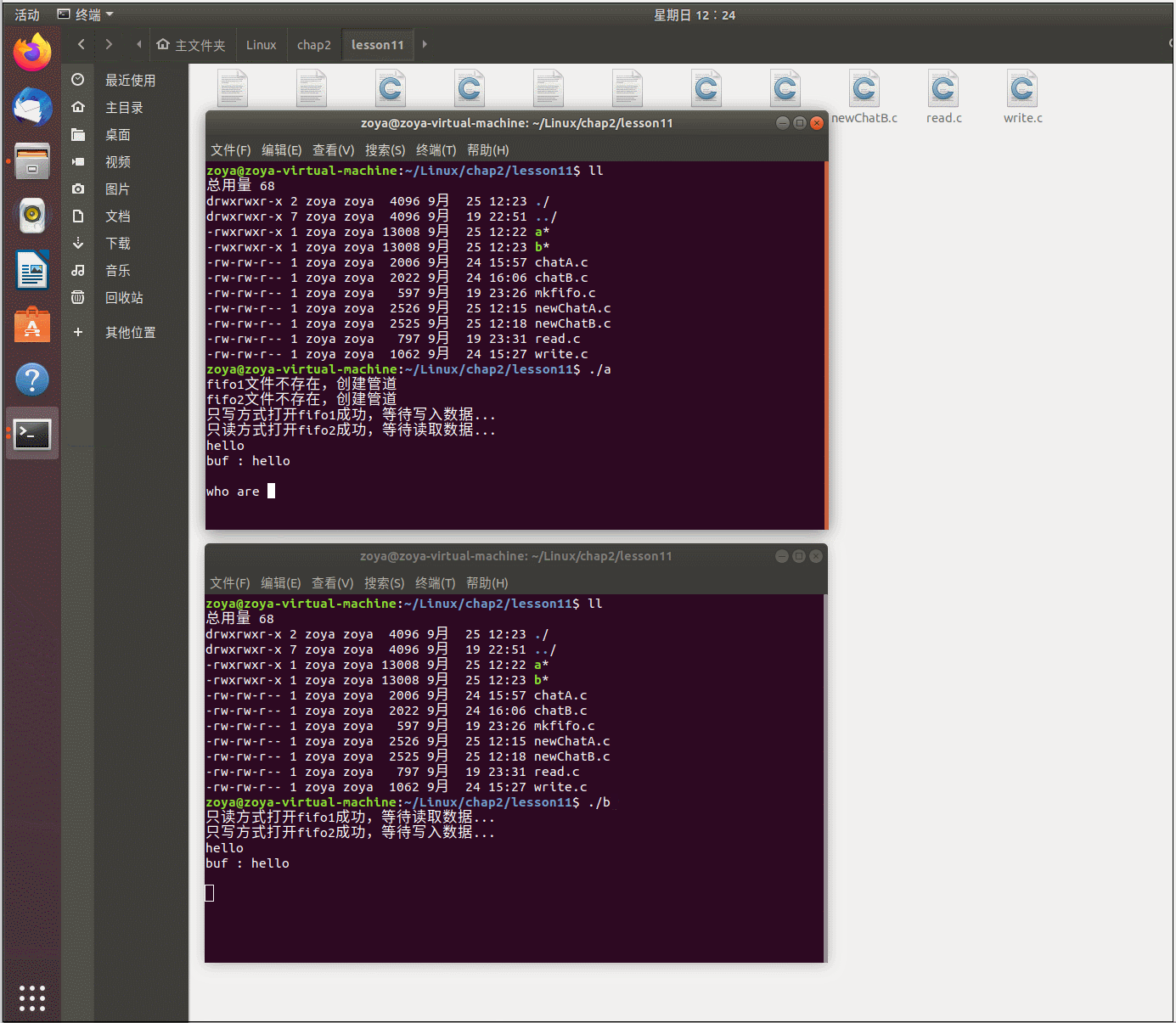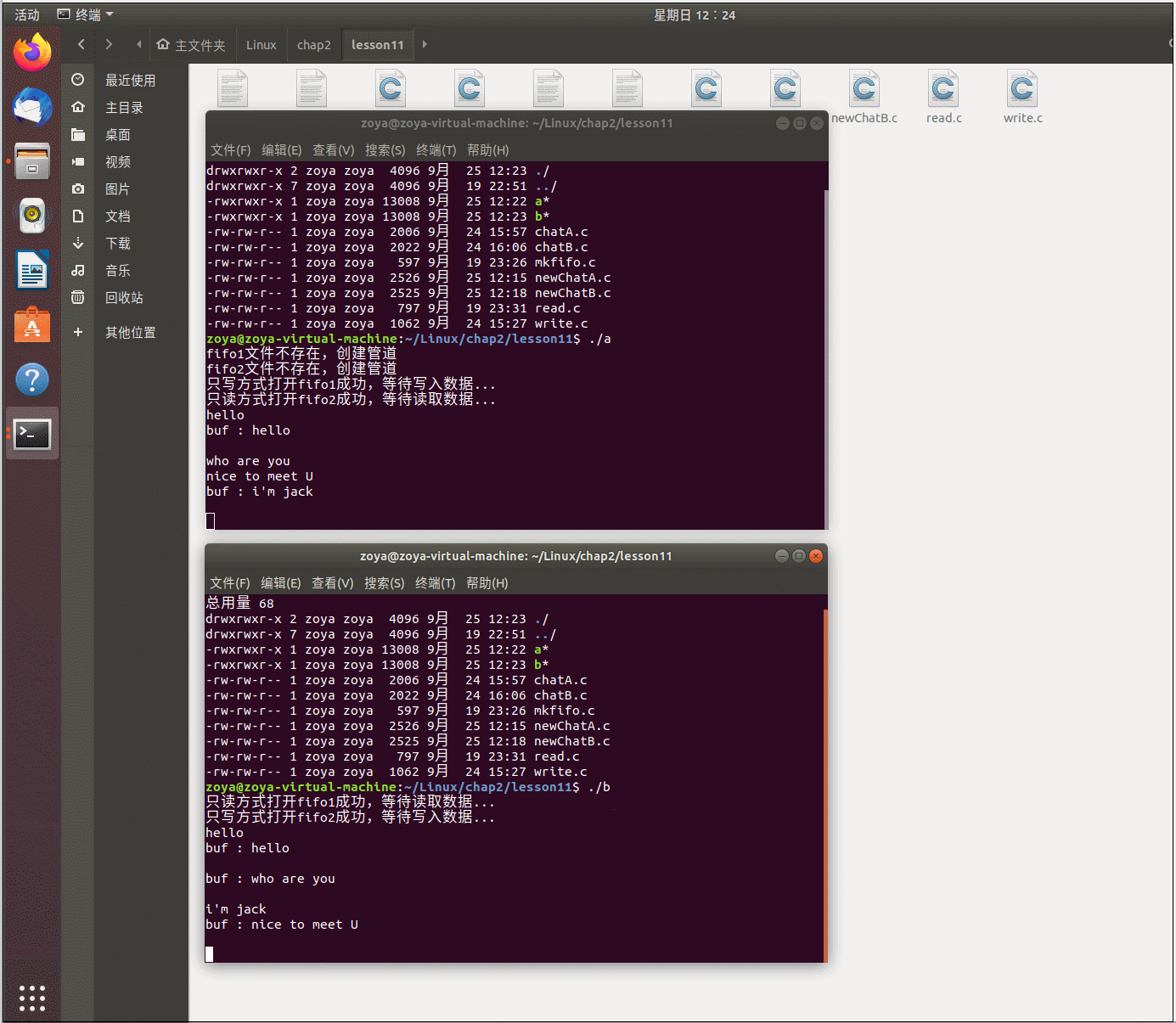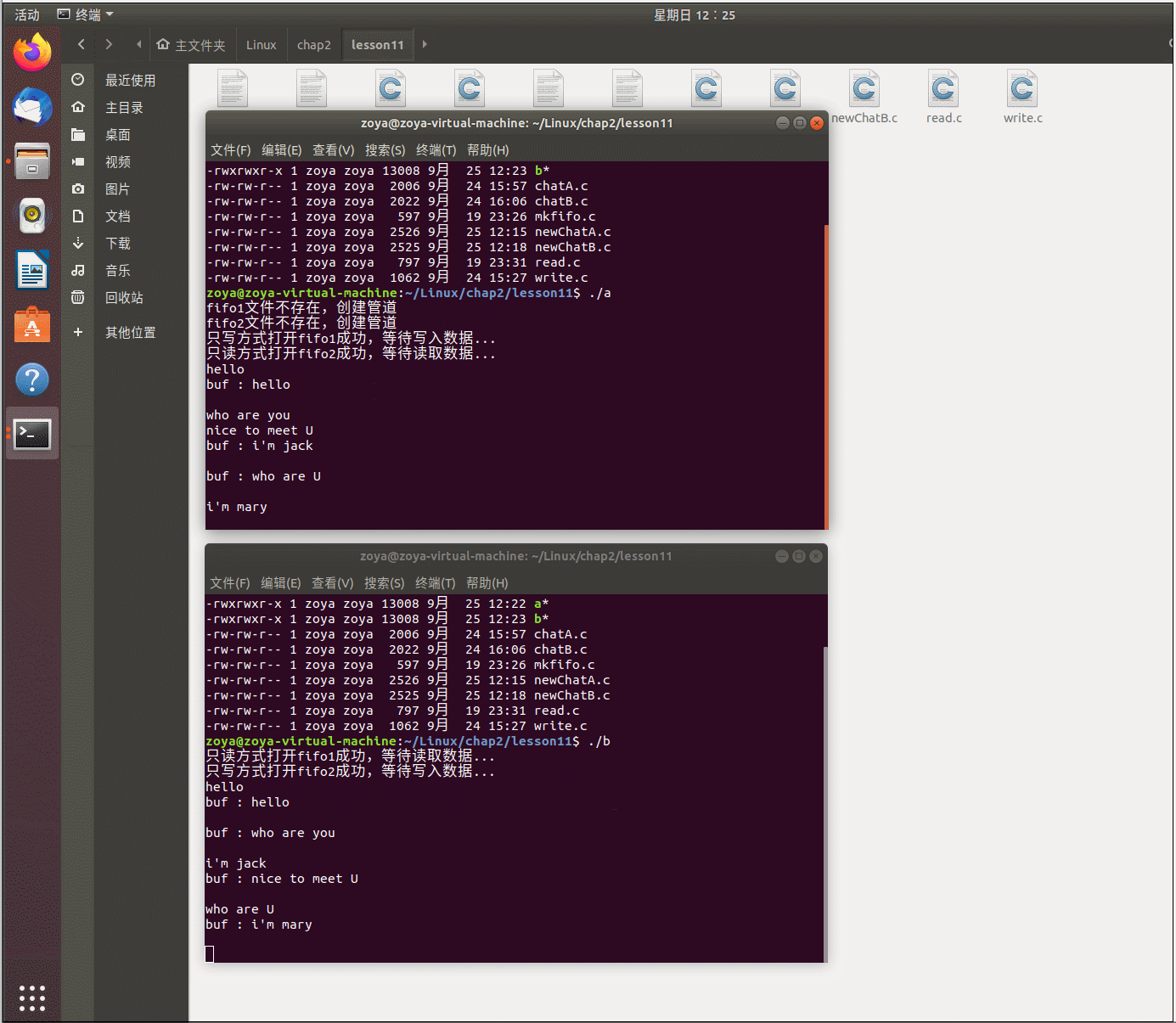
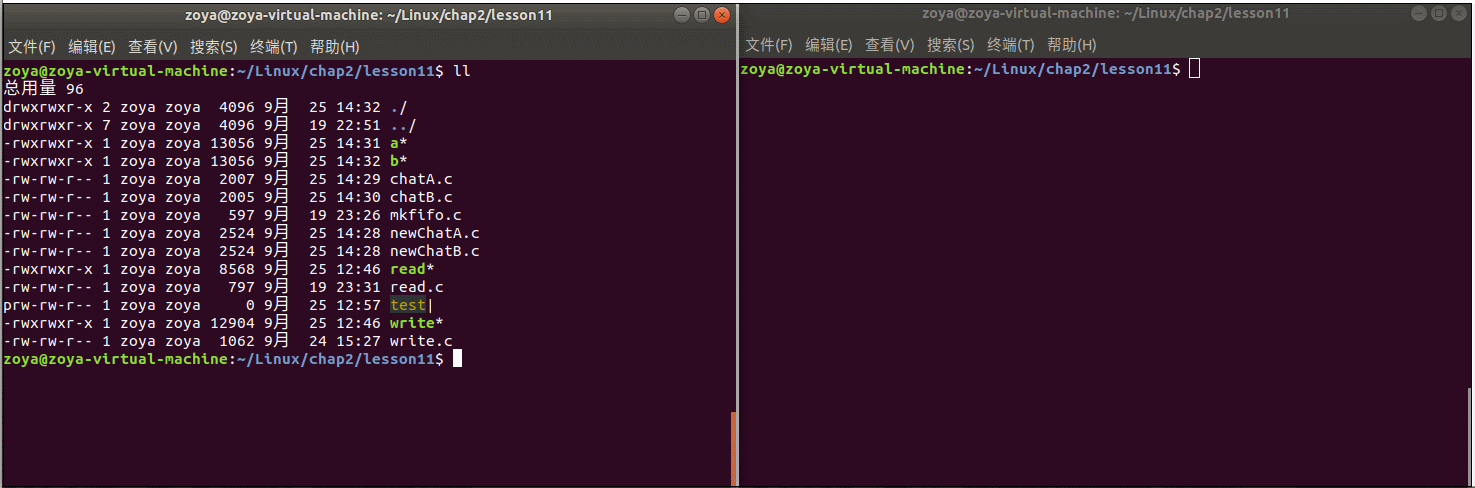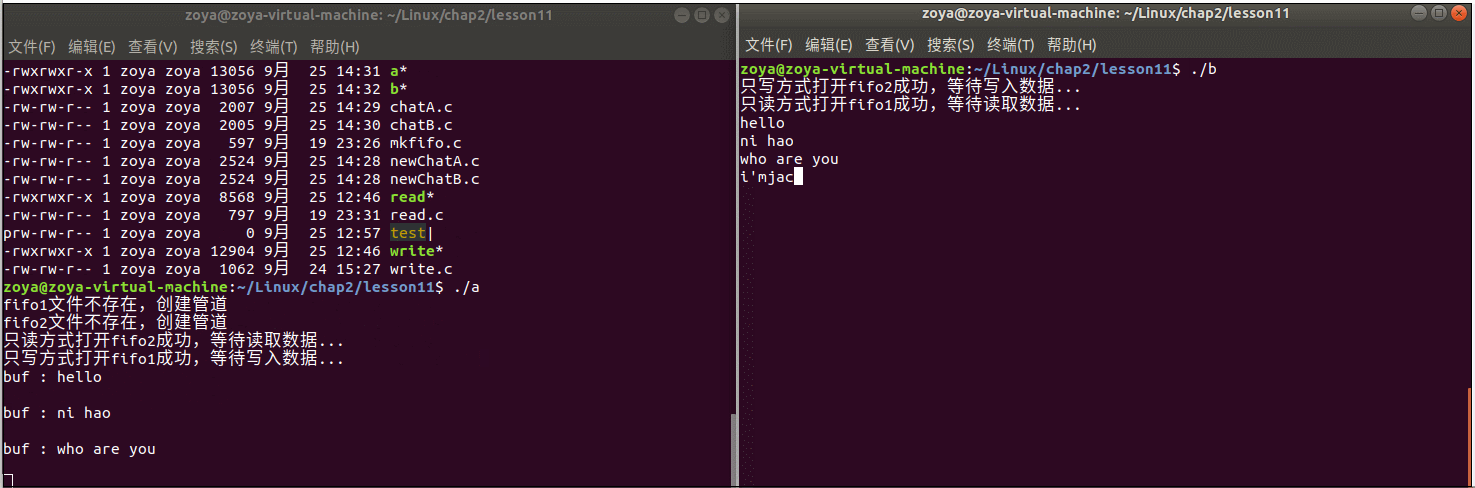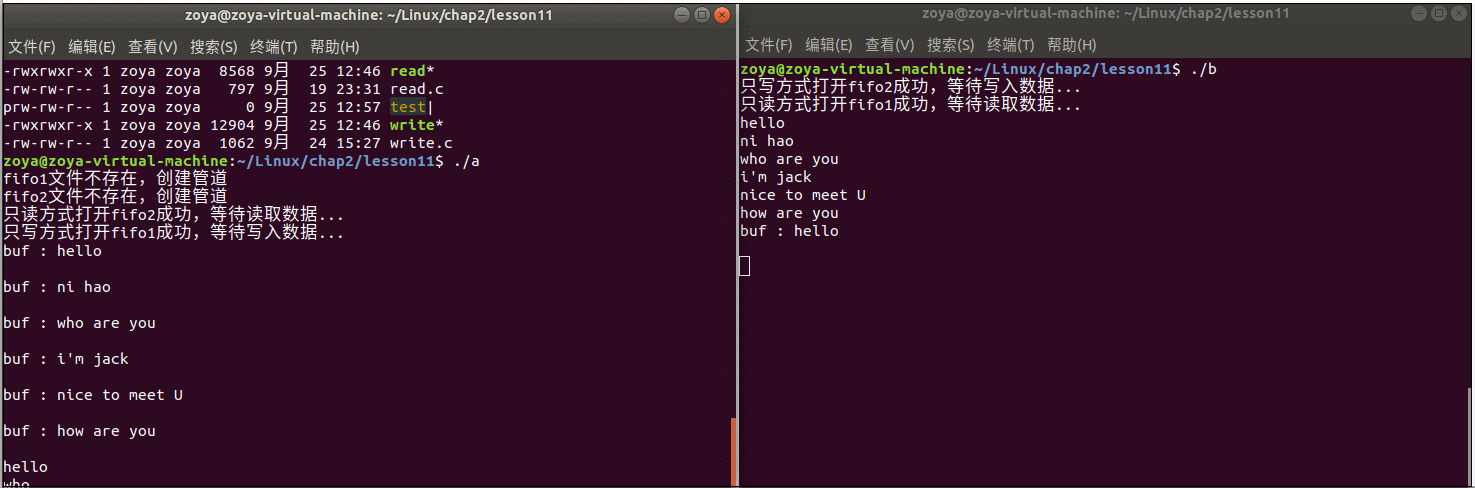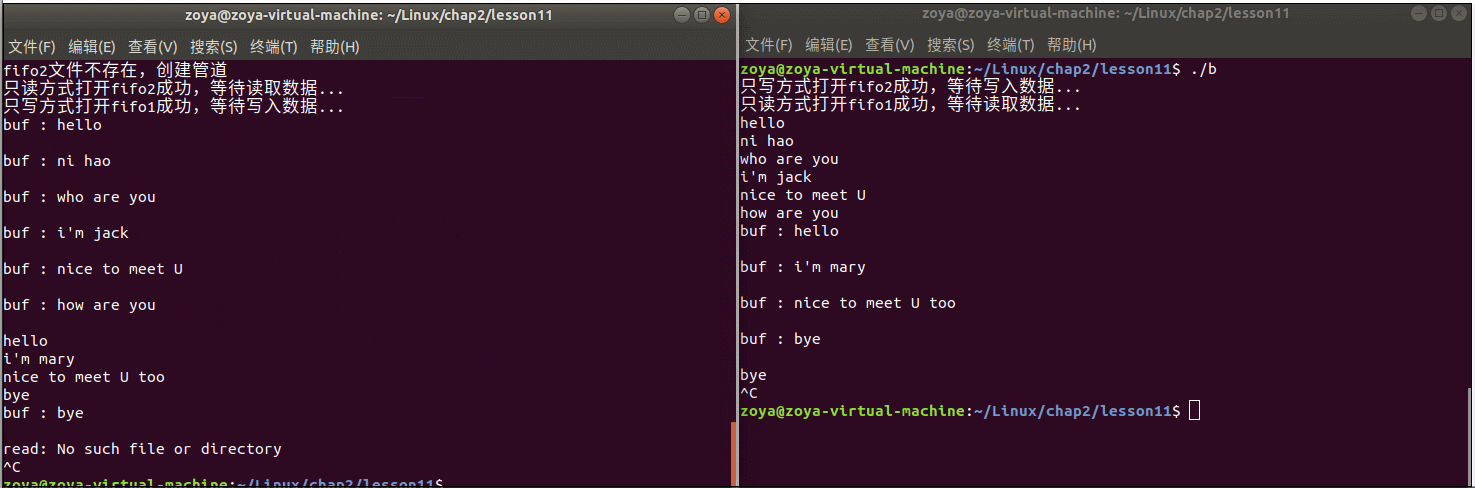
函数功能:简单聊天程序,两个程序a和b,a向b发送信息,b接收信息,b向a发送信息,a接收信息;...
源码参考:
chatA.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <string.h> int main() { char *fifo1 = "fifo1"; char *fifo2 = "fifo2"; // 1. 判断有名管道文件是否存在 int ret = access(fifo1, F_OK); if (ret == -1) { // 文件不存在,需要创建 printf("%s文件不存在,创建管道\n", fifo1); ret = mkfifo(fifo1, 0664); if (ret == -1) { perror("mkfifo"); exit(-1); // 退出 } } ret = access(fifo2, F_OK); if (ret == -1) { // 文件不存在,需要创建 printf("%s文件不存在,创建管道\n", fifo2); ret = mkfifo(fifo2, 0664); if (ret == -1) { perror("mkfifo"); exit(-1); // 退出 } } // 2. 以只写方式打开管道1 int fdw = open(fifo1, O_WRONLY); if (fdw == -1) { perror("open"); exit(-1); } printf("只写方式打开fifo1成功,等待写入数据...\n"); // 以只读方式打开管道2 int fdr = open(fifo2, O_RDONLY); if (fdr == -1) { perror("open"); exit(-1); } printf("只读方式打开fifo2成功,等待读取数据...\n"); // 3. 循环写读数据 char buf[256]; while (1) { memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); // 获取标准输入的数据,使用fgets()函数 fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin); // 写数据到fifo1 int len = write(fdw, buf, strlen(buf)); if (len == -1) { perror("write"); break; } // 读管道数据 memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); len = read(fdr, buf, sizeof(buf)); if (len <= 0) { perror("read"); break; } printf("buf : %s\n", buf); } // 关闭文件描述符 close(fdr); close(fdw); return 0; }
chatB.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <string.h> int main() { char *fifo1 = "fifo1"; char *fifo2 = "fifo2"; // 1. 判断有名管道文件是否存在 int ret = access(fifo1, F_OK); if (ret == -1) { // 文件不存在,需要创建 printf("%s文件不存在,创建管道\n", fifo1); ret = mkfifo(fifo1, 0664); if (ret == -1) { perror("mkfifo"); exit(-1); // 退出 } } ret = access(fifo2, F_OK); if (ret == -1) { // 文件不存在,需要创建 printf("%s文件不存在,创建管道\n", fifo2); ret = mkfifo(fifo2, 0664); if (ret == -1) { perror("mkfifo"); exit(-1); // 退出 } } // 2. 以只读方式打开管道1 int fdr = open(fifo1, O_RDONLY); if (fdr == -1) { perror("open"); exit(-1); } printf("只读方式打开fifo1成功,等待读取数据...\n"); // 以只写方式打开管道2 int fdw = open(fifo2, O_WRONLY); if (fdw == -1) { perror("open"); exit(-1); } printf("只写方式打开fifo2成功,等待写入数据...\n"); // 3. 循环读写数据 char buf[256]; while (1) { // 读管道数据 memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); int len = read(fdr, buf, sizeof(buf)); if (len <= 0) { perror("read"); break; } printf("buf : %s\n", buf); memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); // 获取标准输入的数据,使用fgets()函数 fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin); // 写数据到fifo1 len = write(fdw, buf, strlen(buf)); if (len == -1) { perror("write"); break; } } // 关闭文件描述符 close(fdr); close(fdw); return 0; }
程序运行:
2. "喋喋不休"式简单聊天
上面的程序不能实现一方一直给另一方发送信息,可以把读写功能分别放在不同的进程中,比如放在父子进程中分别对读写进行操作。
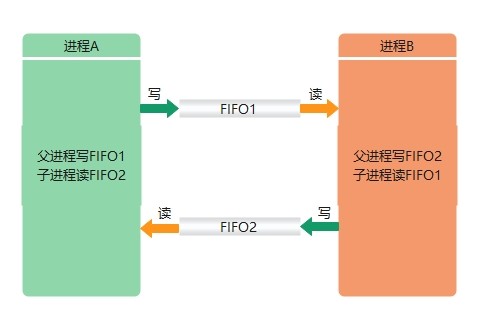
参考代码:
newChatA.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <string.h> int main() { // 1. 创建子进程 pid_t pid = fork(); if (pid > 0) { // 父进程, 写FIFO1 char *fifo1 = "fifo1"; // 2. 判断有名管道文件是否存在 int ret = access(fifo1, F_OK); if (ret == -1) { // 文件不存在,需要创建 printf("%s文件不存在,创建管道\n", fifo1); ret = mkfifo(fifo1, 0664); if (ret == -1) { perror("mkfifo"); exit(-1); // 退出 } } // 3. 以只写方式打开 FIFO1 int fdw = open(fifo1, O_WRONLY); if (fdw == -1) { perror("open"); exit(-1); } printf("只写方式打开fifo1成功,等待写入数据...\n"); // 4. 循环写入数据 char buf[256]; while (1) { memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); // 获取标准输入的数据,使用fgets()函数 fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin); // 写数据到fifo1 int len = write(fdw, buf, strlen(buf)); if (len == -1) { perror("write"); break; } } close(fdw); } else if (pid == 0) { // 子进程 读FIFO2 char *fifo2 = "fifo2"; int ret = access(fifo2, F_OK); if (ret == -1) { // 文件不存在,需要创建 printf("%s文件不存在,创建管道\n", fifo2); ret = mkfifo(fifo2, 0664); if (ret == -1) { perror("mkfifo"); exit(-1); // 退出 } } // 以只读方式打开 FIFO2 int fdr = open(fifo2, O_RDONLY); if (fdr == -1) { perror("open"); exit(-1); } printf("只读方式打开fifo2成功,等待读取数据...\n"); // 循环读数据 char buf[256]; while (1) { // 读管道数据 memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); int len = read(fdr, buf, sizeof(buf)); if (len <= 0) { perror("read"); break; } printf("buf : %s\n", buf); } close(fdr); } return 0; }
newChatB.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <string.h> int main() { // 1. 创建子进程 pid_t pid = fork(); if (pid > 0) { // 父进程, 写FIFO2 char *fifo2 = "fifo2"; // 2. 判断有名管道文件是否存在 int ret = access(fifo2, F_OK); if (ret == -1) { // 文件不存在,需要创建 printf("%s文件不存在,创建管道\n", fifo2); ret = mkfifo(fifo2, 0664); if (ret == -1) { perror("mkfifo"); exit(-1); // 退出 } } // 3. 以只写方式打开 FIFO2 int fdw = open(fifo2, O_WRONLY); if (fdw == -1) { perror("open"); exit(-1); } printf("只写方式打开fifo2成功,等待写入数据...\n"); // 4. 循环写入数据 char buf[256]; while (1) { memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); // 获取标准输入的数据,使用fgets()函数 fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), stdin); // 写数据到fifo1 int len = write(fdw, buf, strlen(buf)); if (len == -1) { perror("write"); break; } } close(fdw); } else if (pid == 0) { // 子进程 读FIFO1 char *fifo1 = "fifo1"; int ret = access(fifo1, F_OK); if (ret == -1) { // 文件不存在,需要创建 printf("%s文件不存在,创建管道\n", fifo1); ret = mkfifo(fifo1, 0664); if (ret == -1) { perror("mkfifo"); exit(-1); // 退出 } } // 以只读方式打开 FIFO1 int fdr = open(fifo1, O_RDONLY); if (fdr == -1) { perror("open"); exit(-1); } printf("只读方式打开fifo1成功,等待读取数据...\n"); // 循环读数据 char buf[256]; while (1) { // 读管道数据 memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); int len = read(fdr, buf, sizeof(buf)); if (len <= 0) { perror("read"); break; } printf("buf : %s\n", buf); } close(fdr); } return 0; }
程序运行:
如果您觉得阅读本文对您有帮助,请点一下“推荐”按钮,您的“推荐”将是我最大的写作动力!欢迎各位转载,但是未经作者本人同意,转载文章之后必须在文章页面明显位置给出作者和原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)