了解Flask
了解Flask
什么是Flask
Flask 是一个微框架(Micro framework),所谓微框架,它就是很轻量级的,作者划分出了Flask应该负责什么(请求路由、处理请求、返回响应)、不应该负责什么(数据库抽象、表单验证)。它倡导地是不要重复造轮子,结合社区优秀的库,使得Flask更加灵活、定制性更强。
Flask如何处理请求
Flask run起来
先写一个简单的Flask应用(main.py)
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def index():
return 'Hello World'
app.run("127.0.0.1", 80, debug=True)
执行测试
> python main.py
> curl http://127.0.0.1:80
Hello World
分析源码
查看一下app.run()函数源码
def run(self, host=None, port=None, debug=None, load_dotenv=True, **options):
...
from werkzeug.serving import run_simple
try:
run_simple(host, port, self, **options)
finally:
self._got_first_request = False
核心逻辑是执行run_simple函数,并且第三个参数self是Flask对象
看一下Flask类的实现
class Flask:
def wsgi_app(self, environ, start_response):
# 将请求信息包装为一个ctx对象
ctx = self.request_context(environ)
error = None
try:
try:
# ctx压栈
ctx.push()
# 分发 处理
response = self.full_dispatch_request()
except Exception as e:
error = e
response = self.handle_exception(e)
except: # noqa: B001
error = sys.exc_info()[1]
raise
return response(environ, start_response)
finally:
if self.should_ignore_error(error):
error = None
# ctx 出栈
ctx.auto_pop(error)
def __call__(self, environ, start_response):
return self.wsgi_app(environ, start_response)
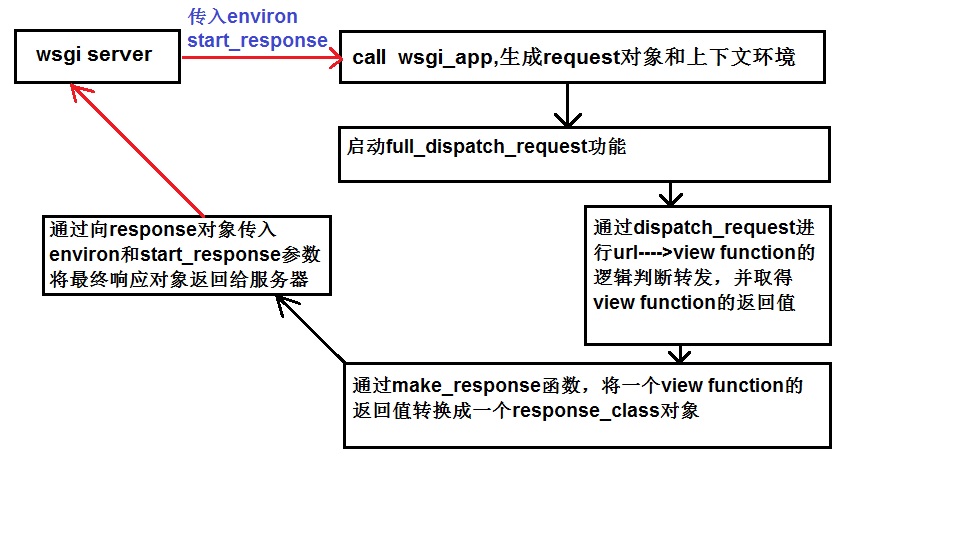
当请求到来时,程序在调用app时,由于实现了__call__函数,则通过该函数调用了wsgi_app()函数
具体分析wsgi_app函数:
- 生成request请求对象和请求上下文(封装在request_context函数里)
- 将生成的请求上下文(本次请求的环境)push入栈,存储。
- 请求进入预处理(例如before_request),错误处理及请求转发到响应的过程(full_dispatch_request函数)
Local类
Local类是用werkzeug库实现的一个用于类存储数据的类,它支持多线程安全存储。
使用原理
使用__storage__(dict类型)存储数据,但是通过获取到的线程id作为标识来进行隔离,让每个线程读写自己线程的数据
__storage__的结构是这样的
{
"线程id1": {"stack": [ctx,]},
"线程id2": {"stack": []},
}
实际源码
from thread import get_ident
class Local(object):
__slots__ = ("__storage__", "__ident_func__")
def __init__(self):
object.__setattr__(self, "__storage__", {})
object.__setattr__(self, "__ident_func__", get_ident)
def __getattr__(self, name):
# 重写了该方法,首先获取当前线程id,然后去读取该线程id下的数据
try:
return self.__storage__[self.__ident_func__()][name]
except KeyError:
raise AttributeError(name)
def __setattr__(self, name, value):
# 重写了该方法,首先获取当前线程id,然后去写入该线程id下的数据
ident = self.__ident_func__()
storage = self.__storage__
try:
storage[ident][name] = value
except KeyError:
storage[ident] = {name: value}
def __delattr__(self, name):
# 重写了该方法,首先获取当前线程id,然后去删除该线程id下的数据
try:
del self.__storage__[self.__ident_func__()][name]
except KeyError:
raise AttributeError(name)
LocalStack类
LocalStack是基于Local类实现的栈类,所以它支持线程安全。
实际源码
class LocalStack(object):
def __init__(self):
self._local = Local()
def push(self, obj):
"""Pushes a new item to the stack"""
rv = getattr(self._local, "stack", None)
if rv is None:
self._local.stack = rv = []
rv.append(obj)
return rv
def pop(self):
"""Removes the topmost item from the stack, will return the
old value or `None` if the stack was already empty.
"""
stack = getattr(self._local, "stack", None)
if stack is None:
return None
elif len(stack) == 1:
release_local(self._local)
return stack[-1]
else:
return stack.pop()
@property
def top(self):
try:
return self._local.stack[-1]
except (AttributeError, IndexError):
return None
1.LocalStack在init中创建了一个Local对象,此时storage是一个空字典
2.当调用push时,即传入线程或进程对象时,先判断是否已存在,否则新创建一个空间(列表,作为栈),入栈
3.当调用top时,返回栈顶元素
4.调用pop时若栈中只剩一个元素,则取出后删除该栈空间,否则pop栈顶元素