春秋杯冬季赛 2023
CF is Crypto Faker
一道白给的题,关键在于:
parameters = train.train(wild_phi, wild_e, n, r, phi0)
trained_phi = parameters[0]
trained_e = parameters[1]
这里给了真实的phi和e,再结合源码开头给的n,直接求d就可以解rsa了。
from Crypto.Util.number import *
n = 0x81c5f040bfaea676120cd62c36ba7afb303561504bbf8609afa3da60fb6202ca875b0bd2a06143ebcd16fa615557ff159d97909160d68e1938b3ecaf57709b3d2698476b6dd203811b6a2ec6a6e2a7e213ab719bcd3ab49bb864b10e9c78ea3f501c0e2213dfe431043bb6f0cc2e8d77bfb43869b843af1a99ae81b87811e101
phi = 0x81c5f040bfaea676120cd62c36ba7afb303561504bbf8609afa3da60fb6202ca875b0bd2a06143ebcd16fa615557ff159d97909160d68e1938b3ecaf57709b3bb712fdcba325655f111918472d4353a66854ccda50b63a1047278c15a4b39cde898d054db87092958c7c05f8fa566dcd969b1ff4b7d1935c375a4af3bfc341b0
e = 0x2c22193ad9abcca2f67552fc76dd07b3ef883f3d755c95119cdf82bb6a07c970fd37e582bb49250d8efaa29b8a59c82059165c654206a9d7261f6b45a90dc69
c1 = 0x29289e3d9275147b885b5061637564cbee3e4d9f48e52694e594f020e49da9b24d9246b2437fb2221fa86ca1a277f3fdd7ab5cad4738a02b66d47703ef816844a84c6c209c8251e8961c9ba2c791649e022627f86932d9700c3b1dc086e8b2747d0a5604955387a935464d3866dd4100b2f3d57603c728761d1d8ef7fdbdcbee
c2 = 0x2b0059f88454e0e36269c809b5d5b6b28e5bab3c87b20f9e55635239331100a0a582241e7a385034698b61ebf24b519e868617ff67974cc907cc61be38755737f9a6dbeb7890ff55550b1af1ecf635112fcaaa8b07a3972b3c6728cbcf2a3973a4d7bd92affec7e065e0ae83cd36858e6d983785a3668a8b82709d78a69796af
d = inverse(e,phi)
m1 = long_to_bytes(pow(c1,d,n)).decode()
m2 = long_to_bytes(pow(c2,d,n)).decode()
print(m1+m2)
not_wiener
e较大,d大约是n的0.273,小于0.292,考虑boneh_durfee,因为略微卡界,因此把m调到7才出:
from __future__ import print_function
import time
############################################
# Config
##########################################
"""
Setting debug to true will display more informations
about the lattice, the bounds, the vectors...
"""
debug = True
"""
Setting strict to true will stop the algorithm (and
return (-1, -1)) if we don't have a correct
upperbound on the determinant. Note that this
doesn't necesseraly mean that no solutions
will be found since the theoretical upperbound is
usualy far away from actual results. That is why
you should probably use `strict = False`
"""
strict = False
"""
This is experimental, but has provided remarkable results
so far. It tries to reduce the lattice as much as it can
while keeping its efficiency. I see no reason not to use
this option, but if things don't work, you should try
disabling it
"""
helpful_only = True
dimension_min = 7 # stop removing if lattice reaches that dimension
############################################
# Functions
##########################################
# display stats on helpful vectors
def helpful_vectors(BB, modulus):
nothelpful = 0
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
if BB[ii,ii] >= modulus:
nothelpful += 1
print(nothelpful, "/", BB.dimensions()[0], " vectors are not helpful")
# display matrix picture with 0 and X
def matrix_overview(BB, bound):
for ii in range(BB.dimensions()[0]):
a = ('%02d ' % ii)
for jj in range(BB.dimensions()[1]):
a += '0' if BB[ii,jj] == 0 else 'X'
if BB.dimensions()[0] < 60:
a += ' '
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
a += '~'
print(a)
# tries to remove unhelpful vectors
# we start at current = n-1 (last vector)
def remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, current):
# end of our recursive function
if current == -1 or BB.dimensions()[0] <= dimension_min:
return BB
# we start by checking from the end
for ii in range(current, -1, -1):
# if it is unhelpful:
if BB[ii, ii] >= bound:
affected_vectors = 0
affected_vector_index = 0
# let's check if it affects other vectors
for jj in range(ii + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# if another vector is affected:
# we increase the count
if BB[jj, ii] != 0:
affected_vectors += 1
affected_vector_index = jj
# level:0
# if no other vectors end up affected
# we remove it
if affected_vectors == 0:
print("* removing unhelpful vector", ii)
BB = BB.delete_columns([ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([ii])
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii-1)
return BB
# level:1
# if just one was affected we check
# if it is affecting someone else
elif affected_vectors == 1:
affected_deeper = True
for kk in range(affected_vector_index + 1, BB.dimensions()[0]):
# if it is affecting even one vector
# we give up on this one
if BB[kk, affected_vector_index] != 0:
affected_deeper = False
# remove both it if no other vector was affected and
# this helpful vector is not helpful enough
# compared to our unhelpful one
if affected_deeper and abs(bound - BB[affected_vector_index, affected_vector_index]) < abs(bound - BB[ii, ii]):
print("* removing unhelpful vectors", ii, "and", affected_vector_index)
BB = BB.delete_columns([affected_vector_index, ii])
BB = BB.delete_rows([affected_vector_index, ii])
monomials.pop(affected_vector_index)
monomials.pop(ii)
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, bound, ii-1)
return BB
# nothing happened
return BB
"""
Returns:
* 0,0 if it fails
* -1,-1 if `strict=true`, and determinant doesn't bound
* x0,y0 the solutions of `pol`
"""
def boneh_durfee(pol, modulus, mm, tt, XX, YY):
"""
Boneh and Durfee revisited by Herrmann and May
finds a solution if:
* d < N^delta
* |x| < e^delta
* |y| < e^0.5
whenever delta < 1 - sqrt(2)/2 ~ 0.292
"""
# substitution (Herrman and May)
PR.<u, x, y> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
Q = PR.quotient(x*y + 1 - u) # u = xy + 1
polZ = Q(pol).lift()
UU = XX*YY + 1
# x-shifts
gg = []
for kk in range(mm + 1):
for ii in range(mm - kk + 1):
xshift = x^ii * modulus^(mm - kk) * polZ(u, x, y)^kk
gg.append(xshift)
gg.sort()
# x-shifts list of monomials
monomials = []
for polynomial in gg:
for monomial in polynomial.monomials():
if monomial not in monomials:
monomials.append(monomial)
monomials.sort()
# y-shifts (selected by Herrman and May)
for jj in range(1, tt + 1):
for kk in range(floor(mm/tt) * jj, mm + 1):
yshift = y^jj * polZ(u, x, y)^kk * modulus^(mm - kk)
yshift = Q(yshift).lift()
gg.append(yshift) # substitution
# y-shifts list of monomials
for jj in range(1, tt + 1):
for kk in range(floor(mm/tt) * jj, mm + 1):
monomials.append(u^kk * y^jj)
# construct lattice B
nn = len(monomials)
BB = Matrix(ZZ, nn)
for ii in range(nn):
BB[ii, 0] = gg[ii](0, 0, 0)
for jj in range(1, ii + 1):
if monomials[jj] in gg[ii].monomials():
BB[ii, jj] = gg[ii].monomial_coefficient(monomials[jj]) * monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
# Prototype to reduce the lattice
if helpful_only:
# automatically remove
BB = remove_unhelpful(BB, monomials, modulus^mm, nn-1)
# reset dimension
nn = BB.dimensions()[0]
if nn == 0:
print("failure")
return 0,0
# check if vectors are helpful
if debug:
helpful_vectors(BB, modulus^mm)
# check if determinant is correctly bounded
det = BB.det()
bound = modulus^(mm*nn)
if det >= bound:
print("We do not have det < bound. Solutions might not be found.")
print("Try with highers m and t.")
if debug:
diff = (log(det) - log(bound)) / log(2)
print("size det(L) - size e^(m*n) = ", floor(diff))
if strict:
return -1, -1
else:
print("det(L) < e^(m*n) (good! If a solution exists < N^delta, it will be found)")
# display the lattice basis
if debug:
matrix_overview(BB, modulus^mm)
# LLL
if debug:
print("optimizing basis of the lattice via LLL, this can take a long time")
BB = BB.LLL()
if debug:
print("LLL is done!")
# transform vector i & j -> polynomials 1 & 2
if debug:
print("looking for independent vectors in the lattice")
found_polynomials = False
for pol1_idx in range(nn - 1):
for pol2_idx in range(pol1_idx + 1, nn):
# for i and j, create the two polynomials
PR.<w,z> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
pol1 = pol2 = 0
for jj in range(nn):
pol1 += monomials[jj](w*z+1,w,z) * BB[pol1_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
pol2 += monomials[jj](w*z+1,w,z) * BB[pol2_idx, jj] / monomials[jj](UU,XX,YY)
# resultant
PR.<q> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
rr = pol1.resultant(pol2)
# are these good polynomials?
if rr.is_zero() or rr.monomials() == [1]:
continue
else:
print("found them, using vectors", pol1_idx, "and", pol2_idx)
found_polynomials = True
break
if found_polynomials:
break
if not found_polynomials:
print("no independant vectors could be found. This should very rarely happen...")
return 0, 0
rr = rr(q, q)
# solutions
soly = rr.roots()
if len(soly) == 0:
print("Your prediction (delta) is too small")
return 0, 0
soly = soly[0][0]
ss = pol1(q, soly)
solx = ss.roots()[0][0]
#
return solx, soly
def example():
############################################
# How To Use This Script
##########################################
#
# The problem to solve (edit the following values)
#
# the modulus
N = 98871082998654651904594468693622517613869880791884929588100914778964766348914919202255397776583412976785216592924335179128220634848871563960167726280836726035489482233158897362166942091133366827965811201438682117312550600943385153640907629347663140487841016782054145413246763816202055243693289693996466579973
# the public exponent
e = 76794907644383980853714814867502708655721653834095293468287239735547303515225813724998992623067007382800348003887194379223500764768679311862929538017193078946067634221782978912767213553254272722105803768005680182504500278005295062173004098796746439445343896868825218704046110925243884449608326413259156482881
# the hypothesis on the private exponent (the theoretical maximum is 0.292)
delta = .274# this means that d < N^delta
#
# Lattice (tweak those values)
#
# you should tweak this (after a first run), (e.g. increment it until a solution is found)
m = 7 # size of the lattice (bigger the better/slower)
# you need to be a lattice master to tweak these
t = int((1-2*delta) * m) # optimization from Herrmann and May
X = 2*floor(N^delta) # this _might_ be too much
Y = floor(N^(1/2)) # correct if p, q are ~ same size
#
# Don't touch anything below
#
# Problem put in equation
P.<x,y> = PolynomialRing(ZZ)
A = int((N+1)/2)
pol = 1 + x * (A + y)
#
# Find the solutions!
#
# Checking bounds
if debug:
print("=== checking values ===")
print("* delta:", delta)
print("* delta < 0.292", delta < 0.292)
print("* size of e:", int(log(e)/log(2)))
print("* size of N:", int(log(N)/log(2)))
print("* m:", m, ", t:", t)
# boneh_durfee
if debug:
print("=== running algorithm ===")
start_time = time.time()
solx, soly = boneh_durfee(pol, e, m, t, X, Y)
# found a solution?
if solx > 0:
print("=== solution found ===")
if False:
print("x:", solx)
print("y:", soly)
d = int(pol(solx, soly) / e)
print("private key found:", d)
else:
print("=== no solution was found ===")
if debug:
print(("=== %s seconds ===" % (time.time() - start_time)))
if __name__ == "__main__":
example()
这样可以把a解出来,k1和k2满足线性关系,因此联立消元求出私钥即为flag。
from Crypto.Util.number import *
d = 1493519932573300884636712093929290985070801830526216141153447882450934993737739146621
print(d.bit_length())
n = 98871082998654651904594468693622517613869880791884929588100914778964766348914919202255397776583412976785216592924335179128220634848871563960167726280836726035489482233158897362166942091133366827965811201438682117312550600943385153640907629347663140487841016782054145413246763816202055243693289693996466579973
e = 76794907644383980853714814867502708655721653834095293468287239735547303515225813724998992623067007382800348003887194379223500764768679311862929538017193078946067634221782978912767213553254272722105803768005680182504500278005295062173004098796746439445343896868825218704046110925243884449608326413259156482881
c = 13847199761503953970544410090850216804358289955503229676987212195445226107828814170983735135692611175621170777484117542057117607579344112008580933900051471041224296342157618857321522682033260246480258856376097987259016643294843196752685340912823459403703609796624411954082410762846356541101561523204985391564
a = pow(c,d,n)
p= 161310487790785086482919800040790794252181955976860261806376528825054571226885460699399582301663712128659872558133023114896223014064381772944582265101778076462675402208451386747128794418362648706087358197370036248544508513485401475977401111270352593919906650855268709958151310928767086591887892397722958234379
q= 1115861146902610160756777713087325311747309309771
g= 61073566757714587321114447684333928353300944355112378054603585955730395524359123615359185275743626350773632555967063692889668342544616165017003197599818881844811647270423070958521148291118914198811187731689123176313367399492561288350530256722898205674043032421874788802819858438796795768177550638273020791962
y= 23678147495254433946472657196764372220306841739888385605070426528738230369489739339976134564575544246606937803367113623097260181789372915552172469427842482448570540429192377881186772226796452797182435452490307834205012154495575570994963829345053331967442452842152258650027916313982835119514473311305158299360
(h1, r1, s1) = 535874494834828755542711401117152397489711233142, 117859946800380767356190121030392492081340616512, 26966646740134065096660259687229179143947213779
(h2, r2, s2) = 236574518096866758760287021848258048065293279716, 863199000523521111517835459866422731857447792677, 517924607931342012033031470185302567344725962419
b= 17474742587088593627
A = (s2*a*r1-s1*r2)
B = -s2*b*s1+h2*s1-s2*a*h1
x = B * inverse(A,q) % q
print(long_to_bytes(x))
ez_ECC
一道脑洞题。
首先是给了个hint用rsa加密:
def RSA_reinforce(self,key: int):
p = my_own_prime(512)
q = my_own_prime(512)
n = p * q
leak = p + q
e = 16542764952
c = pow(key, e, n)
return (c, n, leak)
这里联立方程可以把p q求出来,然后发现e和p-1及q-1均不互素,那么考虑用子群+crt那个套路求解一下hint:
from Crypto.Util.number import *
import itertools
from tqdm import tqdm
Hint = (12351774260625362799610458605055557349668978169954248709224197283033722650641969191523420968152180626844781310599988085824706330561484553939064653937267598659731237154241515349280967639128615784193195725170343153328247947729351564102666060302013802359410482179324719156651832539747622404434096773119440083329, 122908984806235457892414635852036332676574434804833208576141668077475917235411535511069143359388659946159724740722593181625712110278669227640297497485641848470391938438894136564046632275052354217712453952532772368082733299695485759213723305738760035793602060420638500827652832664161031815519780589765520132973, 22333858470427703056488469739724305644350178024239032705153649807913901449803887198889611591209527103787726531081225700412575986297091811550954958064297166)
c,n,leak = Hint
e = 16542764952
p = 12505332663944649833363705782585622154783535731134356705062751557012581621705445087053420721597737291635565932107641867441872588740363132435706587458477029
q = 9828525806483053223124763957138683489566642293104676000090898250901319828098442111836190869611789812152160598973583832970703397556728679115248370605820137
def get_oneroot(p, e):
while True:
Zp = Zmod(p)
g = Zp.random_element()
g = g^((p-1) // e)
for mult in divisors(e):
if (mult != e):
g2 = g^mult
if (g2 == 1):
break
else:
return g
def decrypt(p, c, e):
w = gcd(e, p-1)
e1, p1 = e // w, (p-1) // w
d = inverse_mod(e1, p1)
c1 = pow(c, d, p)
g, a, b = xgcd(p1, w)
g = get_oneroot(p, w)
m = pow(c1, b, p)
return [ZZ(m * g^i) for i in range(w)]
mp_list = decrypt(p, c, e)
print('Find root p OK')
mq_list = decrypt(q, c, e)
print('Find root q OK')
for mp, mq in itertools.product(mp_list, mq_list):
m = crt([mp, mq], [p, q])
msg = long_to_bytes(int(m))
try:
hint = msg.decode()
print(hint)
except:
continue
得到Anything greater than 2^15 is really that's too big
这里是个脑洞,暂时不知道怎么用,先看后边的签名过程。
做了250次密钥生成和dsa签名,每次签名是相互独立的,并且k值是由Dual ec生成的伪随机数,这个过程和2023年蓝帽杯的Dual ECDSA很像,但是本题的num1和num2很大没办法用bsgs求。
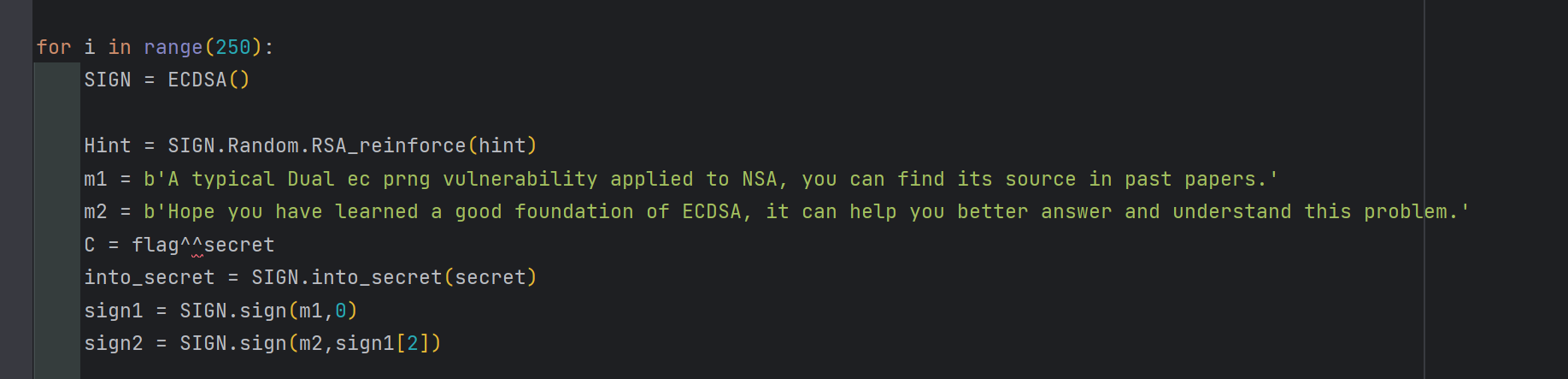
每次签名初始化ECDSA的时候,会第一次调用Dual ec,输出250比特作为私钥;然后会在SIGN.into_secret(secret)用曲线NIST384p对secret进行加密,该过程会调用第二次Dual ec,输出384比特作为ecc群的系数Key;后边就是两次对m1和m2的签名。
不难发现sign1和sign2是共用k的,那么可以求出私钥。
得到私钥,如果我们能够拿到Dual ec的后门的话,就可以预测ecc群的Key,把secret求出来。卡在这里很久,因为看起来这个后门是无法求到的。还是得回到hint上面来,猜测给了那么多组无关的dsa数据,应该有某一组是存在后门关系的,即,dQ = P。结合hint在2^15内进行爆破得到d。这里爆破用乘法比较慢,我是从前后两端同时开始爆的,其实用加法会快很多,可以参考糖醋小鸡块师傅的wp,学习了~
from tqdm import tqdm
import ecdsa
curves = ecdsa.curves
NIST256p = curves.NIST256p
NIST384p = curves.NIST384p
E=EllipticCurve(GF(int(NIST256p.curve.p())),[int(NIST256p.curve.a()), int(NIST256p.curve.b())])
P =
Q =
P = P[::-1][30:]
Q = Q[::-1][30:]
sign_bit = 0
for i,j in zip(P,Q):
p = E(i[0],i[1])
q = E(j[0],j[1])
for k in tqdm(range(2^15)):
if k*p==q or k*q==p:
print(p)
print(k)
sign_bit = 1
break
if sign_bit == 1:
break
P = (99376526638506705902714648195970871631891150648967956889439656483745513799077, 49286347987713888387330453808791204691290920954467279402308313223992253330920)
Q = (95979043517822469787247449840043678535429394578371796773017425344169131078878, 94108817998367868965643129518919867199519351407755146103464278196693149407197)
P = E(P)
Q = E(Q)
d = 32309
assert d * Q == P
拿到d之后解密做一轮预测+爆破seed的未知6比特即可:
from hashlib import *
import ecdsa
from Crypto.Util.number import *
from random import randint
import ecdsa
from math import ceil
from tqdm import tqdm
m1 = b'A typical Dual ec prng vulnerability applied to NSA, you can find its source in past papers.'
m2 = b'Hope you have learned a good foundation of ECDSA, it can help you better answer and understand this problem.'
curves = ecdsa.curves
NIST256p = curves.NIST256p
NIST384p = curves.NIST384p
E=EllipticCurve(GF(int(NIST256p.curve.p())),[int(NIST256p.curve.a()), int(NIST256p.curve.b())])
class Random_EC():
def __init__(self,state = None,Gen_Curve = True):
if state == None:
self.state = getRandomNBitInteger(512)
else:
self.state = state
if Gen_Curve:
self.int_curve()
def int_curve(self,CURVE = None):
self.P = P
self.Q = Q
def int_getkey(self):
# To get the right random key
t = int((self.state * self.Q).xy()[0])
self.int_updade()
# print(len(bin(t))-2)
return t%(2**250)
def RSA_reinforce(self,key: int):
p = my_own_prime(512)
q = my_own_prime(512)
n = p * q
leak = p + q
e = 16542764952
c = pow(key, e, n)
return (c, n, leak)
def int_updade(self):
self.state = int((self.state * self.P).xy()[0])
def Random_key(self, n:int):
out = 0
number = ceil(n/250)
for i in range(number):
out = (out<<250) + self.int_getkey()
return out % (2^n)
C = 28370462154406144789913243909256020527531135264361458510233553021695306448248185548876492600895007348961847185821989
Hint = (12351774260625362799610458605055557349668978169954248709224197283033722650641969191523420968152180626844781310599988085824706330561484553939064653937267598659731237154241515349280967639128615784193195725170343153328247947729351564102666060302013802359410482179324719156651832539747622404434096773119440083329, 122908984806235457892414635852036332676574434804833208576141668077475917235411535511069143359388659946159724740722593181625712110278669227640297497485641848470391938438894136564046632275052354217712453952532772368082733299695485759213723305738760035793602060420638500827652832664161031815519780589765520132973, 22333858470427703056488469739724305644350178024239032705153649807913901449803887198889611591209527103787726531081225700412575986297091811550954958064297166)
pub_key = (23063531651133054044852146745751828065565652508316078757465526964945889829041322577333868291426745685755660447945768, 38213774544479557349161813523787259744626407961805163166366401345392394160489749007540120063131112167181615738936602)
P = E(99376526638506705902714648195970871631891150648967956889439656483745513799077, 49286347987713888387330453808791204691290920954467279402308313223992253330920)
Q = E(95979043517822469787247449840043678535429394578371796773017425344169131078878, 94108817998367868965643129518919867199519351407755146103464278196693149407197)
r1,s1 = (32594514971850903210957109229029032596013744664454613348001968983388557886022626485537652491952756966982681985873826, 33822531453262141722363336331985371357432586409495680846477948429687072595338746861106767975593900234281162130620713)
r2,s2 = (32594514971850903210957109229029032596013744664454613348001968983388557886022626485537652491952756966982681985873826, 30963116078493244587396392437563800584802728459796510243236725881496588593849796130551914519859427419450232539678279)
e1 = int(sha256(m1).hexdigest(), 16)
e2 = int(sha256(m2).hexdigest(), 16)
order = 39402006196394479212279040100143613805079739270465446667946905279627659399113263569398956308152294913554433653942643
pri = (s2*e1-s1*e2)*ZZ(inverse(s1*r2-s2*r1,order)) %order
E1 = EllipticCurve(GF(int(NIST384p.curve.p())),[int(NIST384p.curve.a()), int(NIST384p.curve.b())])
FF = E1(12219467168510963191933866108724307399115854676119007622103880230537250338471252977689989738440080704914043187805666 , 15140655916234412794356873631237108843402057349206472869810848889771783263614142207164313273971781373595696054566462)
d = 32309
rand1 = pri
assert d*Q==P
for l in tqdm(range(2^6)):
try:
seed = rand1+(l<<250)
Q0 = E.lift_x(seed)
except:
continue
state = ZZ((d*Q0).xy()[0])
R = Random_EC(state)
res = R.Random_key(384)
F = ZZ(inverse(int(res),order))*FF
assert int(res)*F==FF
if b'flag' in (long_to_bytes(int(F.xy()[0])^^C)):
print(long_to_bytes(int(F.xy()[0])^^C))
break


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号