VueRouter小手册
一. 了解router
VueRouter 是Vue的插件,它可以通过根据地址栏动态的变换进而实现对不同路由组件进行切换。
比如:http:localhost:8080/path/123?username=xxx&password=xxx#route
在上面的url中,#后面部分我们称之为锚点,也称为hash值,而vue-route就是根据这个锚点去动态的在不同的组件之间切换。
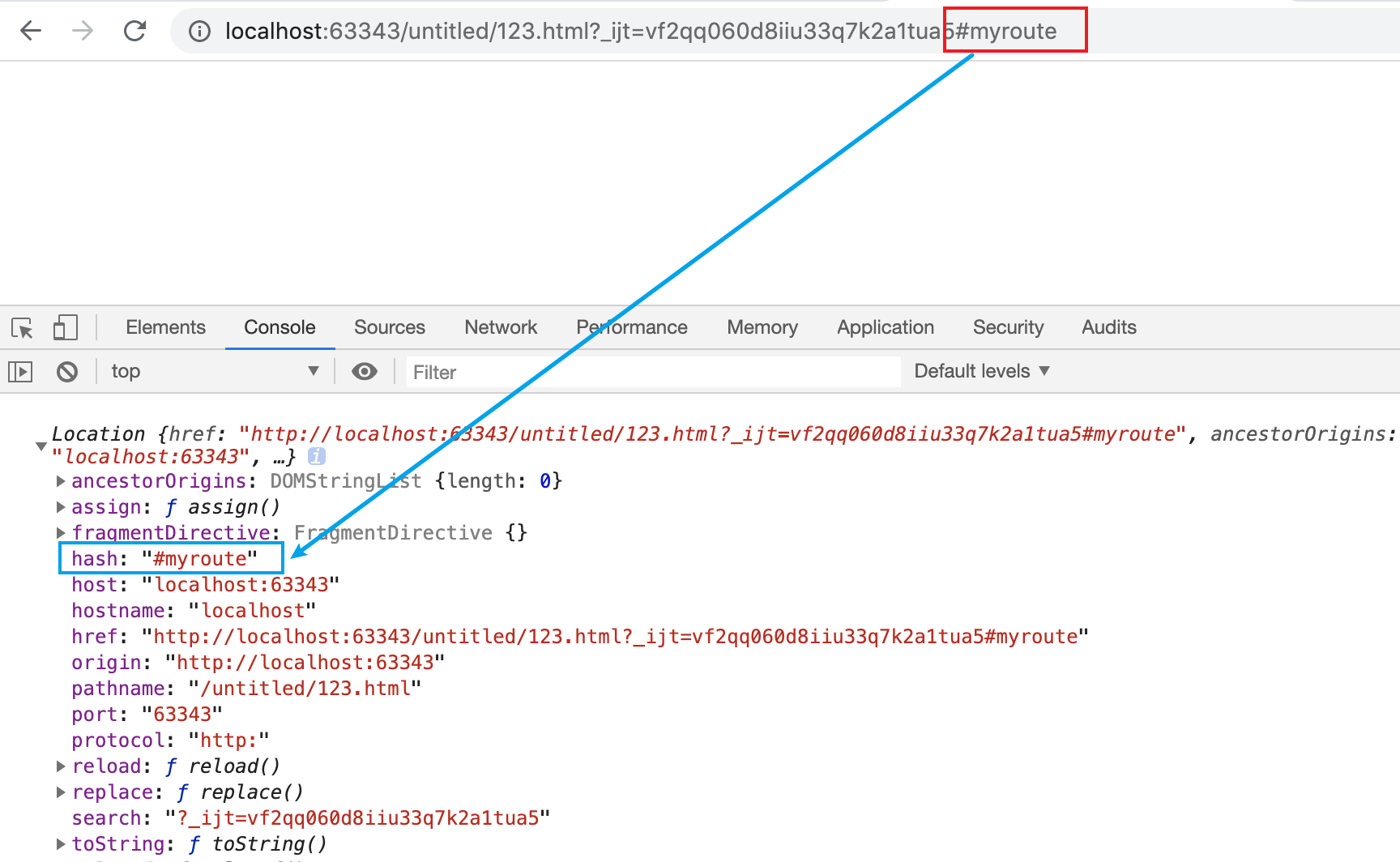
当然,url中的hash信息我们是可以通过js获取出来的,如下:
console.log(window.location)
在控制台上的输入如下:
我们在日常的开发中大多数情况下是在编写 xxx.vue, 然后这个vue文件中会如下的三部分。这其实就是一个vue 的模版/组件, 每个组件是有name或者是path的,那VueRouter实际上要解决的问题就是根据不同的锚点找到不同的组件, 这也就是所谓的路由分发。
路由分发就面临着几个问题:
- 传递参数
- 进行事件的处理和调用
路由底层的实现依赖了window.history对象
<template>
<div>
...
</div>
</template>
<script>
...
</script>
<style>
...
</style>
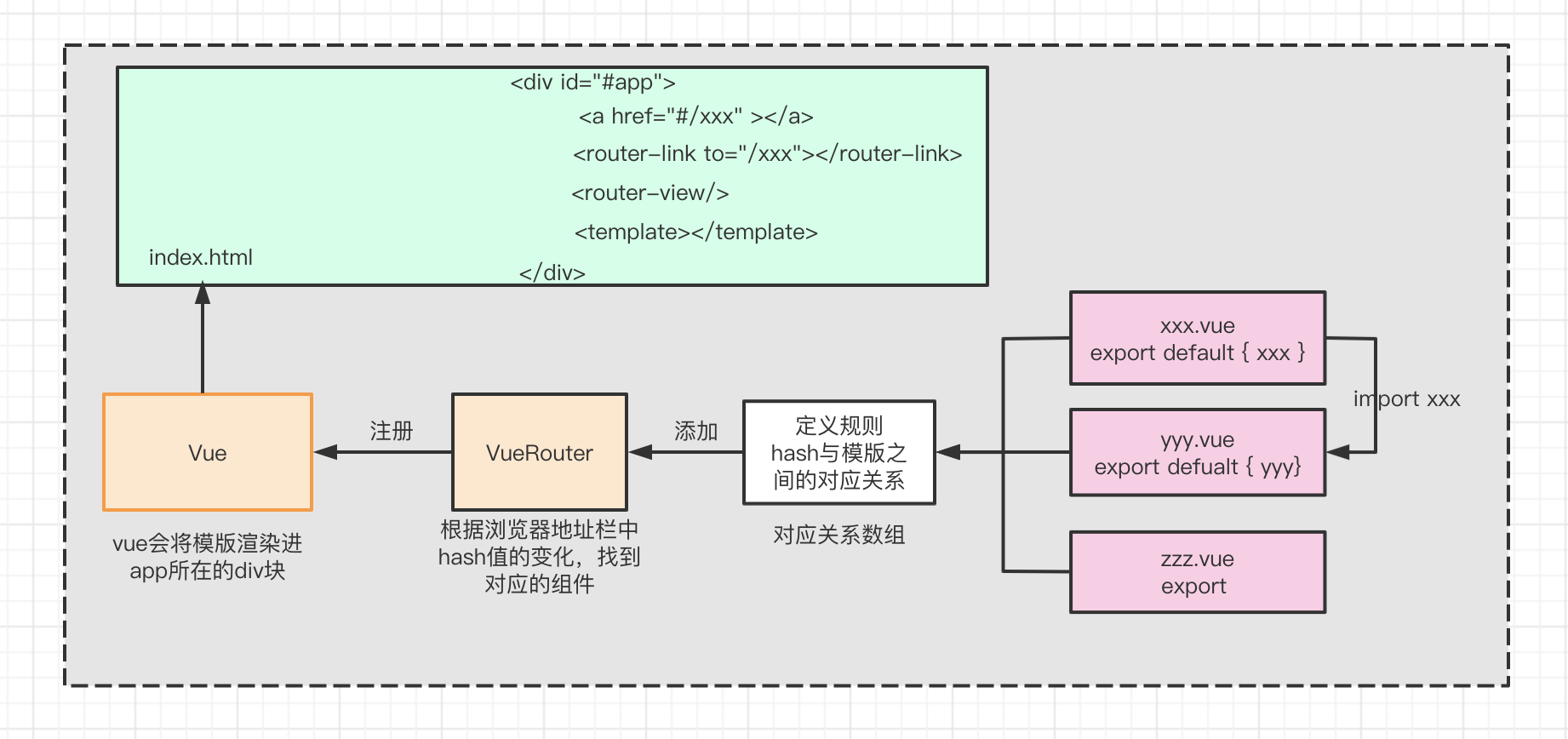
二. 工作流程
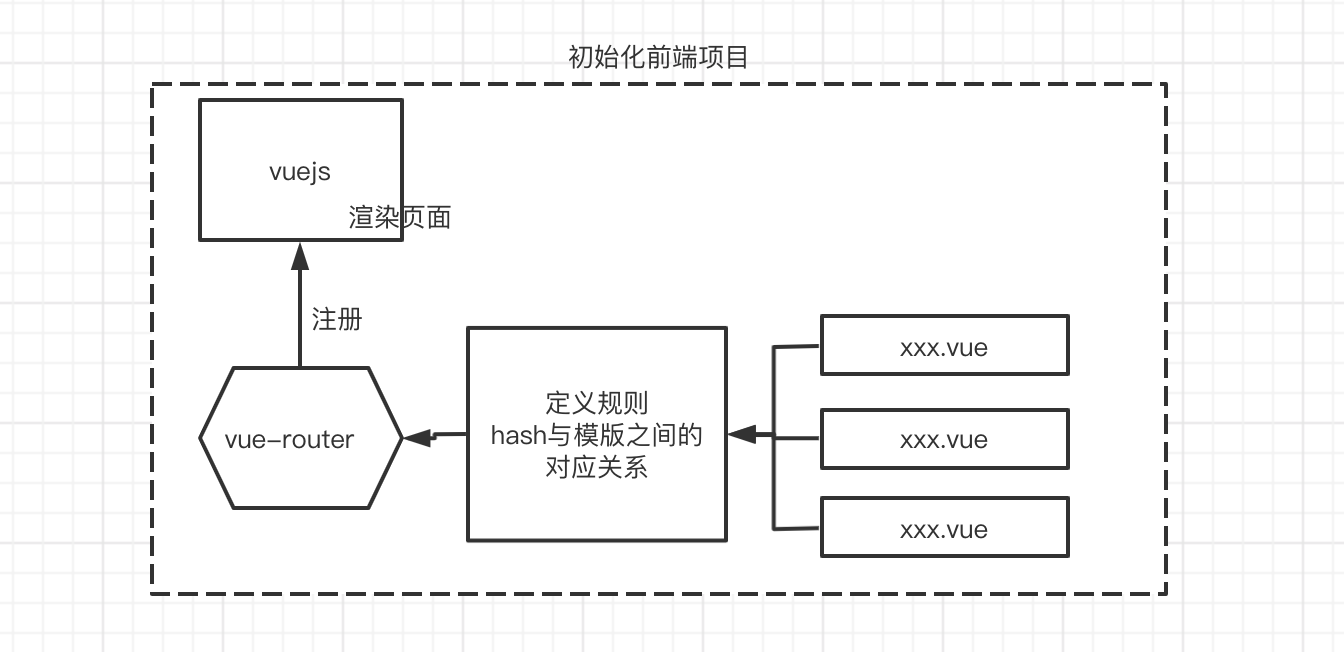
- 首先我们的初始化一个前端项目
- 下载vuejs,他是我们的核心
- 下载vue-router, router是vue的插件,因此我们要将下载好的vue-router注册进vue
- vue-router中定义规则。根据这个规则可以实现根据页面上的hash值找到对应的模版。
- 在页面中可以通过a标签定义转发的路由
- 通过
<router-view>对路由对应模版的内容进行占位
三. 简单的Demo
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script>
<style>
body {
background-color: #eee;
}
li {
list-style: none;
display: inline-block;
}
nav {
text-align: center;
}
a {
color: #333333;
text-decoration: none;
display: inline-block;
padding-left: 5px;
text-align: center;
}
.content {
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<nav>
<!--四种定义请求地址-->
<ul>
<li><a href="#/bar"> Bar </a></li>
<li><a href="#/about"> About </a></li>
<li><a href="#/">Home</a></li>
<li>
<router-link to="/notfound">Not Found</router-link>
</li>
<li>
<router-link to="/foo">Foo</router-link>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
<hr>
<div class="content">
<!--通过路由,组件最终被渲染的位置-->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</div>
</body>
<script>
// 创建模版
const NotFound = {template: `<p>Page not found</p>`}
const Home = {template: '<p>Home page</p>'}
const About = {template: '<p>About page</p>'}
const Foo = {template: '<div>foo</div>'}
const Bar = {template: '<div>bar</div>'}
// 将我们的模版和hash值进程绑定,封装成对象数组
const routes = [
{path: '/', component: Home},
{path: "/about", component: About},
{path: "/notfound", component: NotFound},
{path: "/foo", component: Foo},
{path: "/bar", component: Bar}
]
// new路由对象
const router = new VueRouter({
// 将存贮有 hash和组件的数组注册进路由器
routes
})
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
router, // ES6语法糖,相当于 router:router
data: {
title: "this is title"
}
})
</script>
</html>
实现的效果:点击nav中的标签,下面的内容会随着变化
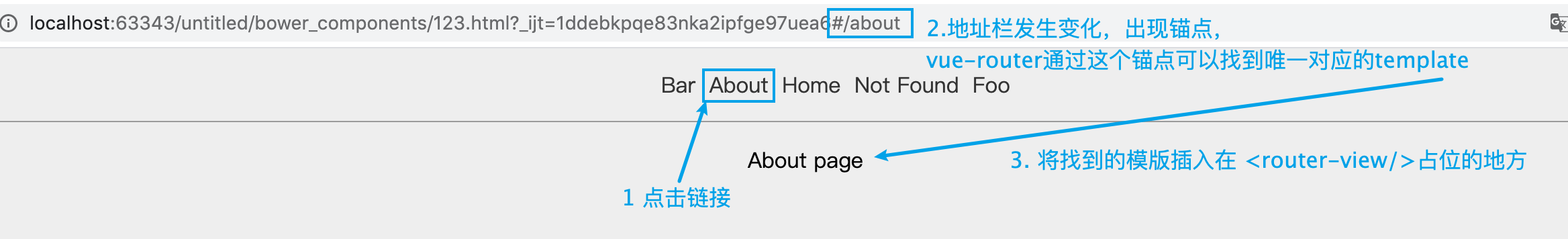
上面的例子是必须要理解的,不然真的就是仅仅知道有这么个效果,但是前因后果,以及对我们在做什么是不清楚的。大概的思路就是,我们首先创建组件,然后为每一个组件找一个唯一的hash值组成一个对象,多个组件+路由就可以形成一个数组,我们将这个数组注册进VueRouter对象,再把VueRouter对象以插件的形式注册进Vue对象。 此时环境就搭建好了。
我们再去点击这种连接时,浏览器的地址栏中就会出现#xxx 的锚点
<a href="#/">Home</a>
<router-link to="/notfound">Not Found</router-link>
流程如下:
四. 理解template和route的组合
通过如下的例子理解template和route是如何配合使用的, 我把理解写在代码中的注释上
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script>
<style>
body {
background-color: #eee;
}
li {
list-style: none;
display: inline-block;
}
nav {
text-align: center;
}
a {
color: #333333;
text-decoration: none;
display: inline-block;
padding-left: 5px;
text-align: center;
}
.content {
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<nav>
<!--四种定义请求地址-->
<ul>
<li><a href="#/bar"> 静态模版 </a></li>
<li><a href="#/dynamic"> 动态模版 </a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
<hr>
<div class="content">
<!--通过路由,组件最终被渲染的位置-->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</div>
</body>
<script>
// 静态模版,之所以叫他静态模版是因为我们可以直接看到它里面的数据全部是写死的,换句话说,这中静态模版除非我们真的仅仅是做一个展示页面,不需要和后端互动数据。除此之外,再无他用
const Bar = {template: '<div>bar</div>'}
// 动态模版
// 可以看到,这种模版其实就是我们在开发中大量自己编写的模版,一般他们都会被抽出去单独称为一个 xxx.vue的文件。在这里我们可以得心应手的编写和后端交互的逻辑,作为一个完整vue组件的它拥有包括vue组件生命周期在内的所有函数
// 第一个问题:这个动态组件是如何注册进Vue中的呢?
// 回答: 往下看看下面new Vue()部分的代码。将当前的动态组件注册在Vue的components部分即可。
// 第二个问题:如何找到这个动态组件并将其渲染在页面上的呢?
// 回答:首先来说,路由的跳转肯定是依赖于浏览器地址兰中 hash值的变化,所以我们得先通过a标签,或者router-link标签发送请求,让浏览器的地址栏hash值发生变化,具体的编码往上看。当地址栏中hash值发生变化后vue-router拿着变化的hash值去找对应的组件,找不到就报错,找到了就渲染
// 第三个问题:vue-router获取到hash值后,是和Vue对象的components中的注册信息的name比对,还是去跟vue-router中的path信息去比对? 还是去跟vue-router中的定义的name去比对呢?
// 回答:和vue-router中的path比对,命中后才算数
// 第四个问题:vue对象的components部分的name有什么用呢?
// 回答:能问这个问题,恐怕你是忘记了,组件需要映射成标签才能用,而这个name就是标签名,是可以自定义的
// 第五个问题:VueRouter中的路由对象中的name叫啥呢?
// 回答:首先这个router并不是必填项,如果有了那么,我们称其为具名路由
// 第六个问题:当我们把如下的部分单独抽取成单独的文件时,如果对外暴露这个组件呢?
// 回答:这个问题在下面通过一张图片直观的看出来。
const Home = {
template: '<div>{{title}}</div>',
data: function () {
return {
title: "this is a title"
}
},
methods: xxx ,
computed: xxx ,
}
// 将我们的模版和hash值进程绑定,封装成对象数组
const routes = [
{path: "/bar", component: Bar},
{path: "/dynamic", component: Home}
]
// new路由对象
const router = new VueRouter({
// 将存贮有 hash和组件的数组注册进路由器
routes
})
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
components:{
"dynamic":Home
},
router, // ES6语法糖,相当于 router:router
})
</script>
</html>
实现的效果如图:

如何将动态组件抽取出去?如何导入其他抽取出去的组件使用?
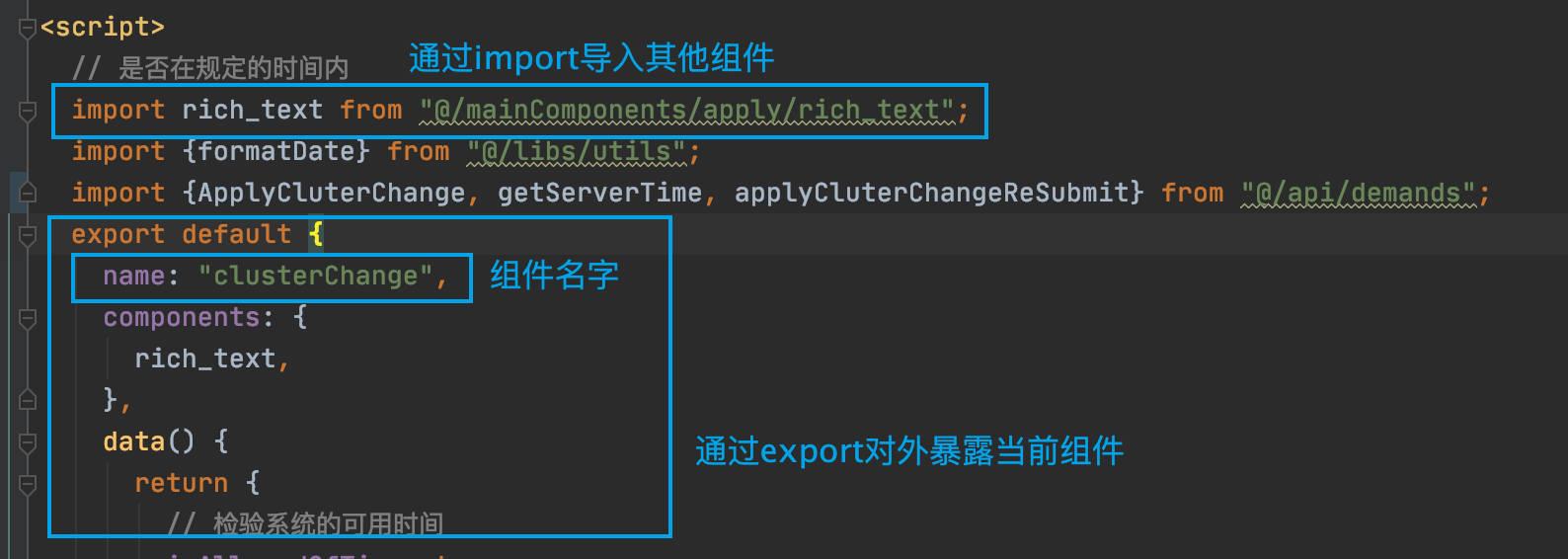
像上图中我们导入其他的组件后,注册进当前组件的 components部分,就是,通过这种方式vue可以将组件映射成标签。
其实现在就能小结一下,画一张不完整的图,来理解这个过程
五. Vue-Router-GoBack记录返回
Vue-Router-GoBack指的是路由的记录返回。比如我们依此点击路由: 从1 跳转到 2 跳转到 3 跳转到 4 ,goback就可以实现路由分别从 4 3 2 1会退回来。
vue-router-goback底层依赖的就是浏览器的内置对象 window.history
问题1: window.history的作用。
可以很直观的认为它里面会存储着浏览器地址栏中曾经访问过的地址
常用的api如下:
window.history.forword() // 前进
window.history.back() // 回退
当然这两个api能起作用的前提是,浏览器中确实存在历史记录才行。
问题2: vue-router-goback 如果实现回退呢?
如下:
// 一个{component + path}是一个路由对象
// 如下代码中的 this.$router即路由器对象,也就是多个路由对象的集合
window.history.length > 1 ? this.$router.go(-1) : this.$router.push("/")
六. Router-Link
不怕多嘴,因为必须得知道:路由的切换是根据浏览器地址栏url中的hash值而定的
在早期的vue中,通过设置a标签中的href属性以#/开头,来实现浏览器地址栏的变化
vue2.x后,router-link标签的诞生,就是为了替换掉a标签
看下router-link的源码如下:
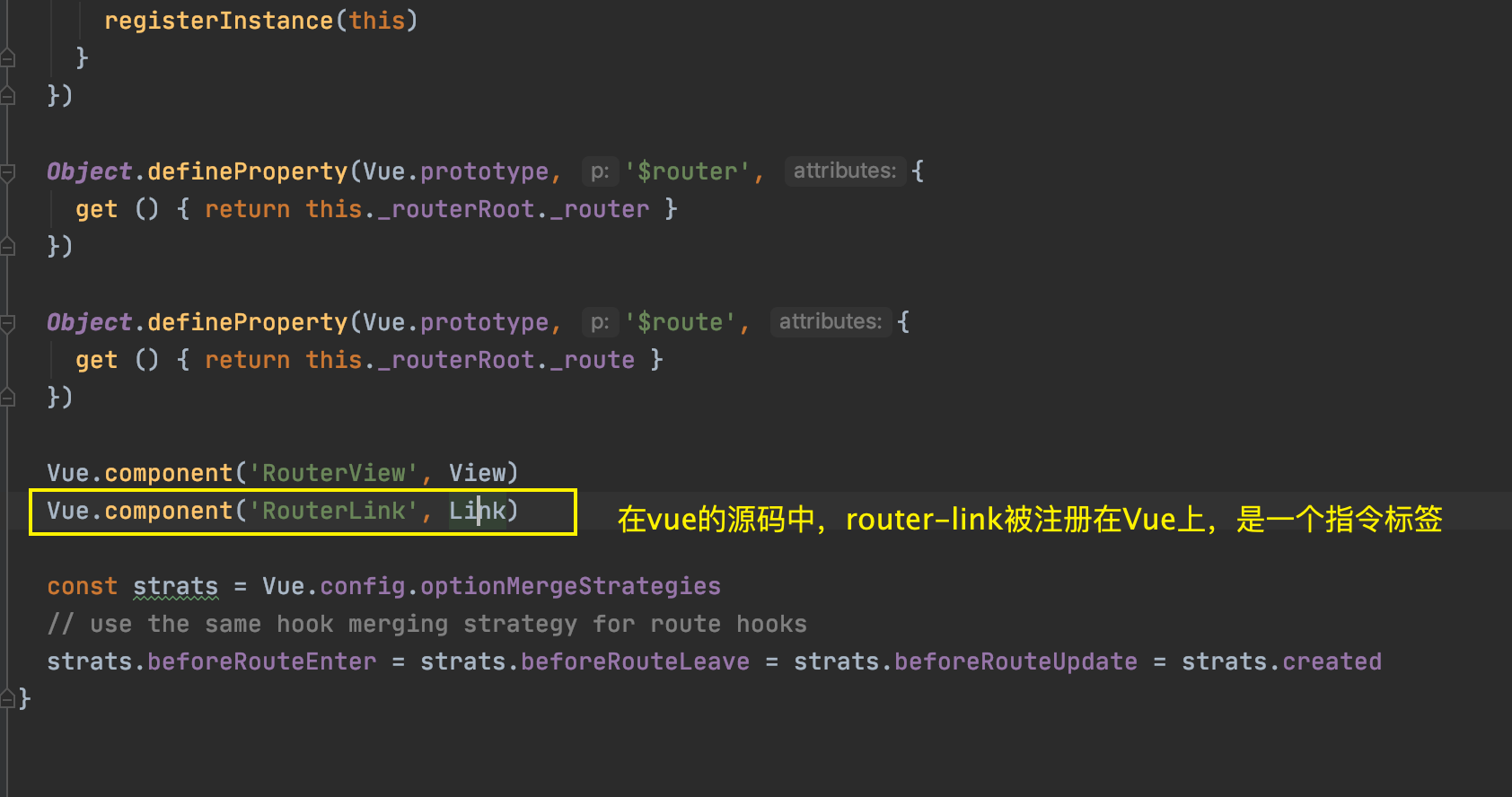
router-link以一个指令标签的方式被注册在vue上,name是RouterLink,实体是 Link
不知道大家有没有多想一下,因为如果是一个自定义的组件的话,我们想将其映射成标签,在html元素中使用,需要我们手动的将把它注册在vue组件的 components部分。 上面标黄色的部分,就是为什么我们可以直接使用类似下面的标签
<router-view> </router-view>
<router-link to=“/xxx/”> </router-link>
看看Link的详情
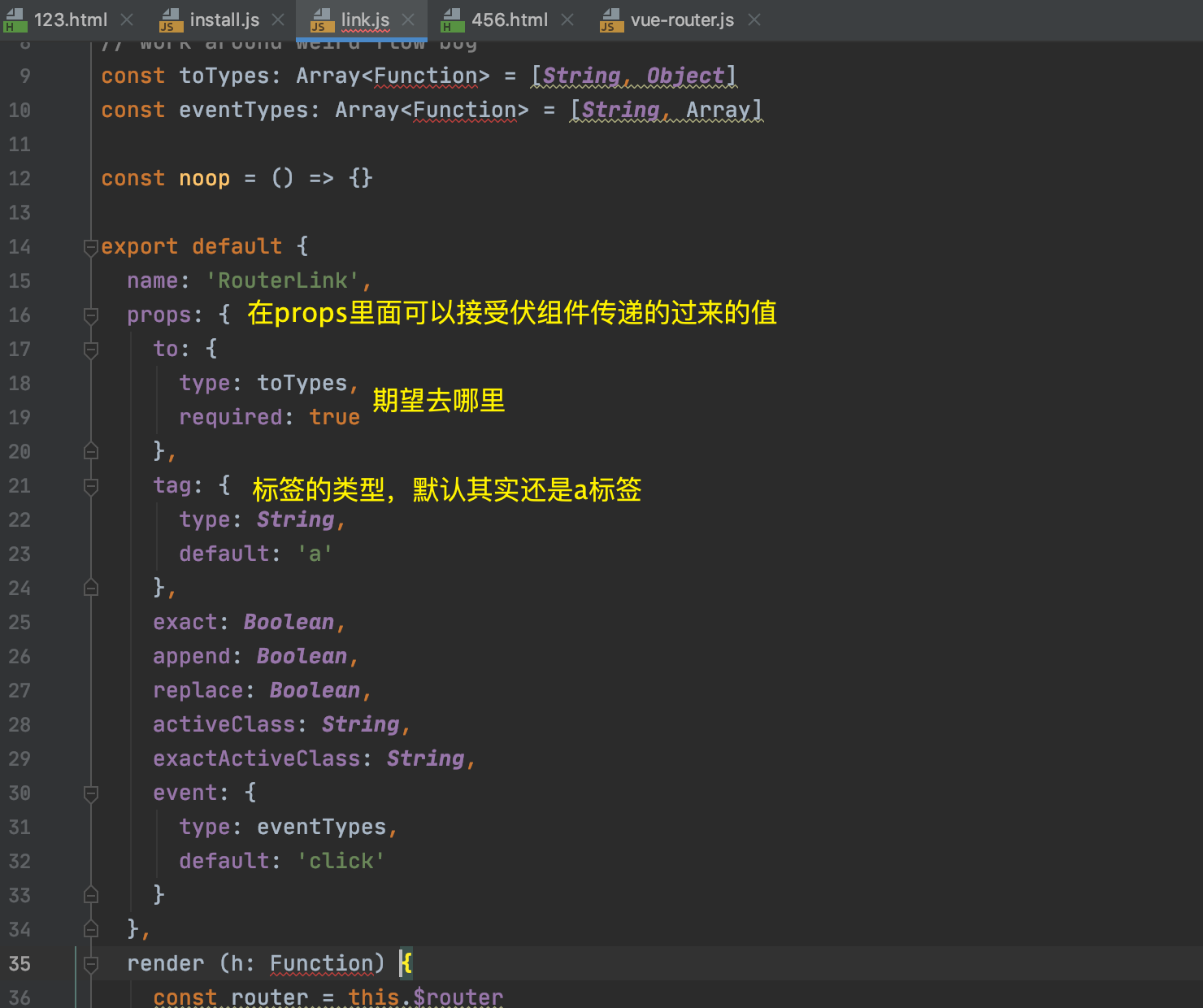
模拟实现router-link
<div>
<my-link to="/bar"> 自定义指令 </my-link>
</div>
<script>
// 自定义comonent
const myLink = {
props: [
'to'
],
template:"<a :href='\"#\"+to'><slot></slot></a>"
}
Vue.component("my-link", myLink)
...
</script>
七. 具名路由
还是这个例子:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<!-- <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script> -->
<script src="./vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="./vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script>
<style>
body {
background-color: #eee;
}
li {
list-style: none;
display: inline-block;
}
nav {
text-align: center;
}
a {
color: #333333;
text-decoration: none;
display: inline-block;
padding-left: 5px;
text-align: center;
}
.content {
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<nav>
<!--四种定义请求地址-->
<ul>
<li><a href="#/bar"> 静态模版 </a></li>
<li>
<router-link :to={name:'Dynamic'}> 动态模版</router-link>
</li>
<li>
<router-link v-bind:to={name:'Dynamic'}> 动态模版</router-link>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
<hr>
<div class="content">
<!--通过路由,组件最终被渲染的位置-->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</div>
</body>
<script>
// 静态模版
const Bar = {template: '<div>bar</div>'}
// 动态模版
const Home = {
template: '<div>{{title}}</div>',
data: function () {
return {
title: "this is a title"
}
}
}
// 将我们的模版和hash值进程绑定,封装成对象数组
const routes = [
{path: "/bar", component: Bar},
{path: "/dynamic",name: "Dynamic", component: Home}
]
// new路由对象
const router = new VueRouter({
// 将存贮有 hash和组件的数组注册进路由器
routes
})
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
components: {
"com-dynamic": Home
},
router, // ES6语法糖,相当于 router:router
})
</script>
</html>
具名路由就是说我们在创建一个route时,给他添加上name属性。
const routes = [
{
path: '/xxx',
component: xxx,
name: 'yyy'
},
]
然后我们在页面上使用这个路由时,可以route-link的to的动态数据绑定,将name传递给他。
// 这时一定要使用动态数据绑定
<router-link v-bind:to={name:'Dynamic'}> 动态模版</router-link>
// v-bind可以简写省略
<router-link :to={name:'Dynamic'}> 动态模版</router-link>
其实到这里具名路由到底是怎么回事就已经说完了,然后下面引出一个问题?
问:为什么一定得v-bind或者 :to这种动态数据类型绑定呢?
回答:
首先说,这个v-bind,它肯定是vue能识别的属性,它的作用就是:实现将model中的data单向的绑在在view上,当vue解析到这个v-bind属性时,知道这是个单向动态绑定,就不会使用后面的整体作为一个字符串去使用,而是去解析他,使用属性中的value作为路由值
其实你可以试一下,如果我们不使用动态数据绑定,vue肯定是不会解析{name:"xxx"} , 于是我们发出的请求就成了下面的样子。
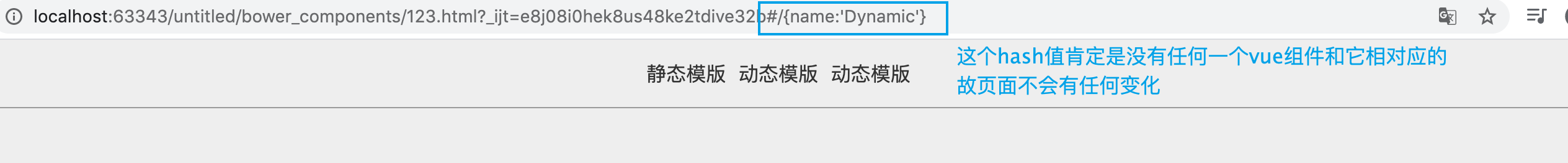
八. 路由激活状态 ActiveClass
参照下图:
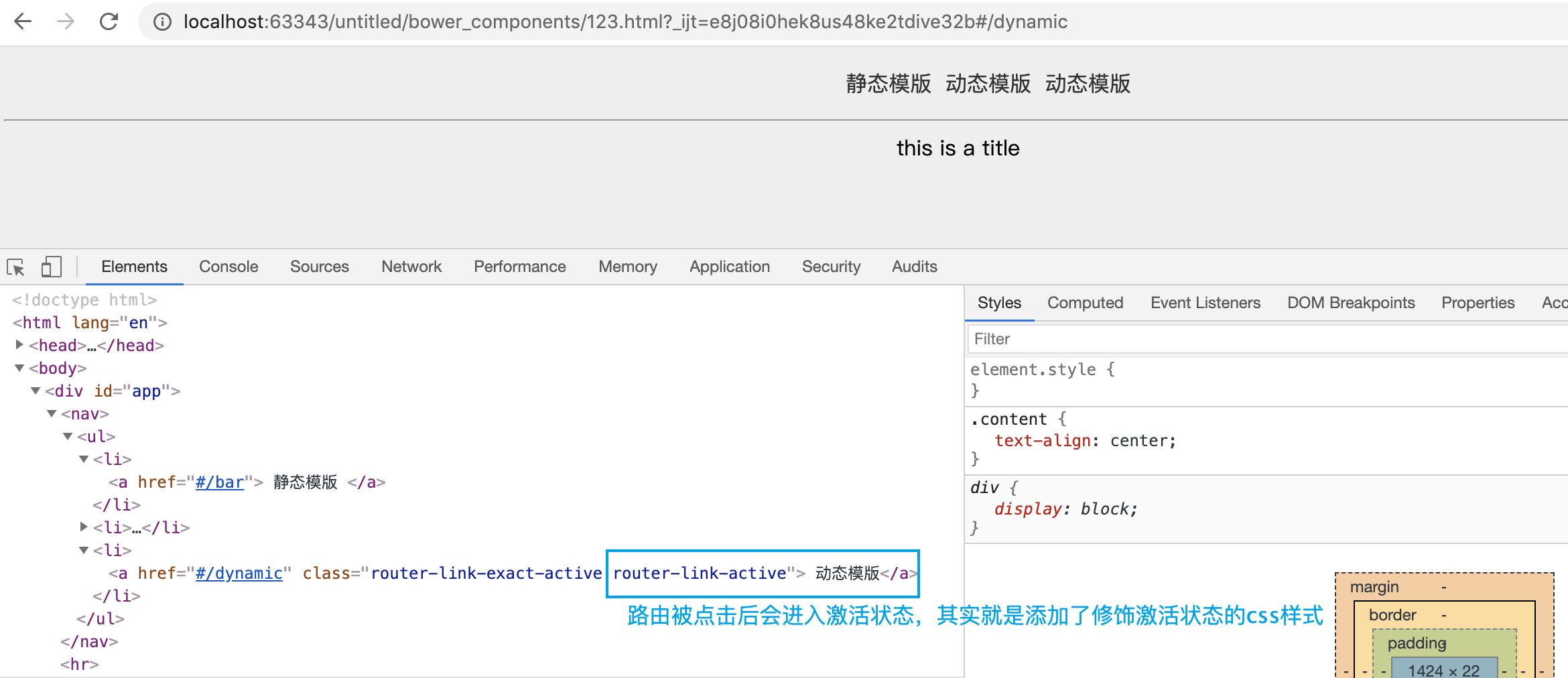
知道了这个属性叫啥,我们就可以进一步对齐进行覆盖,修饰。
比如:将激活状态的文字颜色改成红色
.router-link-active {
color: #E95659;
}
更进一步:可以进入到<router-link><router-link>标签的源码中。
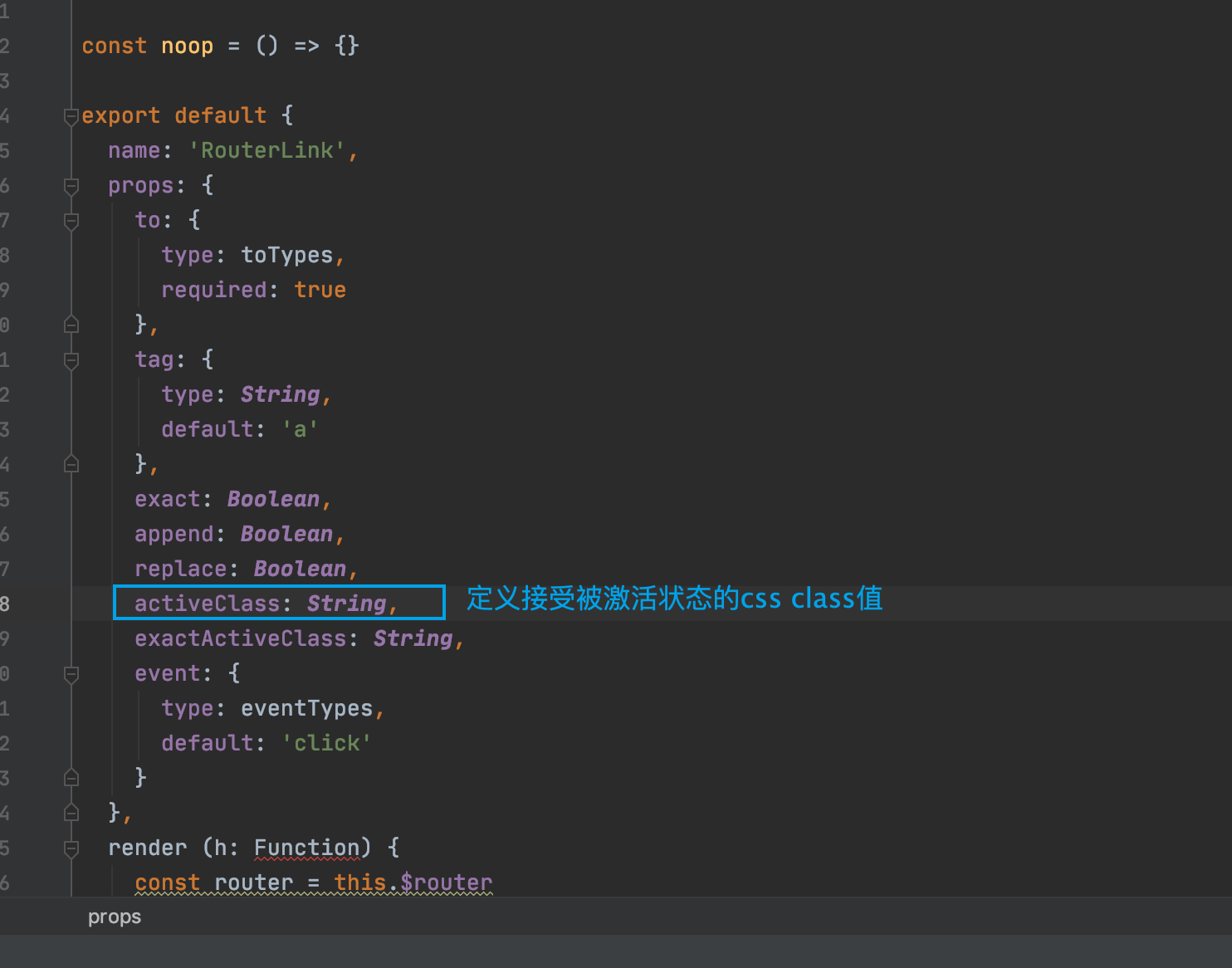
在props块中定义了上面蓝线圈出来的属性,既然在props里面说明它可以接受父组件(通过数据绑定,或者是路由传参)传递过来的值,谁是父组件呢? 这个问题和没问一样,在哪个vue标签中使用route-link标签,谁就是它的父组件呗
我们主要是看下这个叫activeClass的属性,然后它可以接受一个String类型的值。
多想一步,知道这个可以做什么呢? 其实就是意味着我们可以自定义 activeClass的name,换句话说,就是用我们自己定义的名字,替换掉它默认的名字 router-link-active
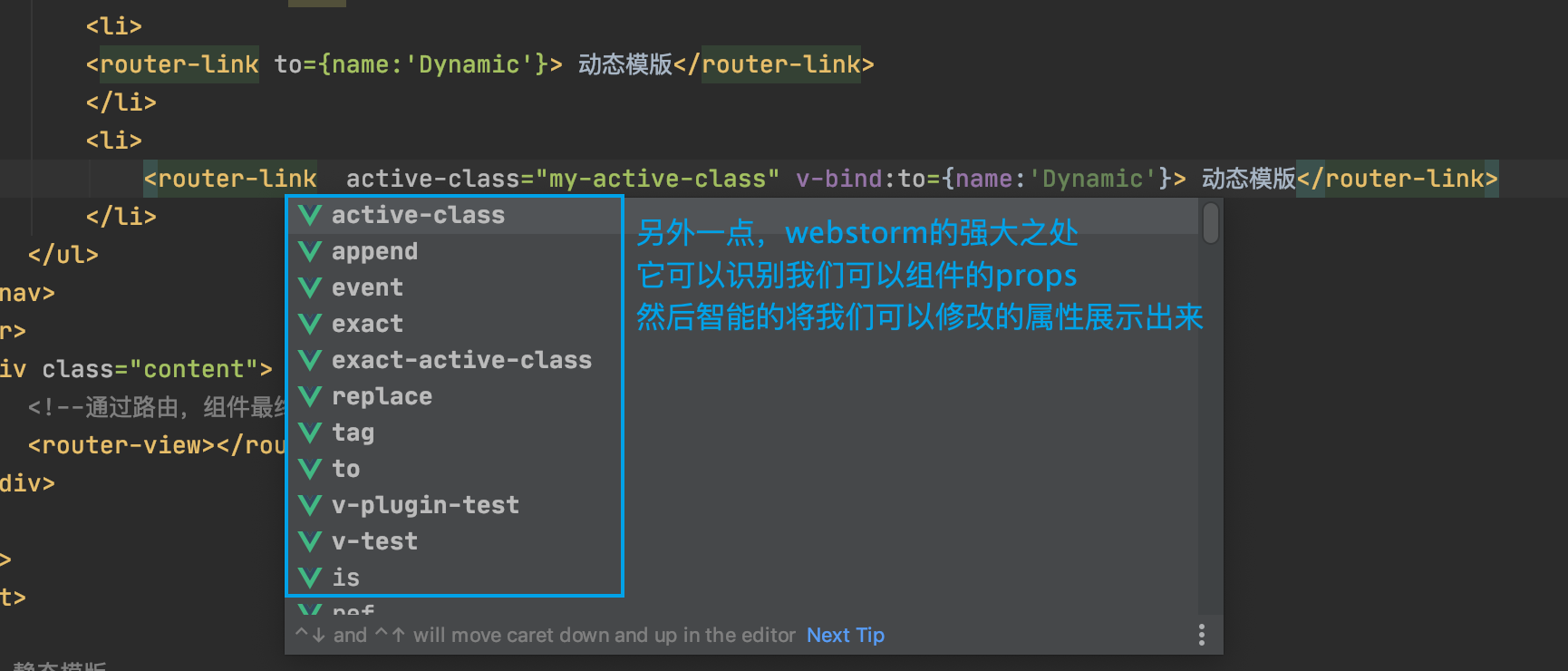
如下:
<router-link active-class="my-active-class" v-bind:to={name:'Dynamic'}>
动态模版
</router-link>
再补充一点:
九. 路由的重定向问题
路由的重定向问题解决了一个什么事呢?
假设,用户在浏览器的地址栏中随意输入了一个地址
http://localhost:63343/bower_components/123.html?#/dynamic123123
这时,我们没有任何一个组件对应的hash值是dynamic123123
为了提高用户的体验,我们就可以这样处理:当用户输入一个不存在的hash值时我们将其重定向到指定的组件。
做法如下:
const routes = [
{path: "/bar", component: Bar},
{path: "/dynamic",name: "Dynamic", component: Home},
{path: "*", component: XXX}
]
如果用户输入的hash值可以在VueRouter中匹配到了相关的组件,直接渲染那个组件就好了。
如果用户输入的hash值没有匹配到任何hash,就会来到最后的*,这个*可以匹配任意hash,紧接着就可以将XXX组件呈现给用户
十. 路由的参数和动态路由
实现下面的demo,完成对路由参数的传递,动态路由的学习。

示例代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="./vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="./vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script>
<style>
body {
background-color: #eee;
}
li {
list-style: none;
/*display: inline-block;*/
}
nav {
text-align: center;
}
a {
color: #333333;
text-decoration: none;
/* display: inline-block;*/
padding-left: 5px;
text-align: center;
}
.content {
text-align: center;
}
.router-link-active {
color: #E95659;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<nav>
<ul>
<li v-for="student in students">
<span>{{student.id}} : {{student.name}}</span>
<router-link
:to='{"name":"stu",params:{"id":student.id,"name":student.name}}'>
查看详情
</router-link>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
<hr>
<div class="content">
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</div>
</body>
<script>
// 接受传递进来的参数
const Student = {
template: '<div><span>学号:{{student.id}}</span> <span>姓名:{{student.name}}</span> </div>',
computed: {
student: function f() {
var paramId = this.$route.params.id
var paramName = this.$route.params.name
return {
name: paramName,
id: paramId
}
}
},
// data 有如下两种写法
data: function () {
// data中要返回一个对象
return {
}
}
}
// 将我们的模版和hash值进程绑定,封装成对象数组
const routes = [
{path: "/student/:id/:name",name:'stu', component: Student},
]
// new路由对象
// router注册进VueRouter的过程中会产生一个 $router 对象,这个对象就是路由器对象, 通过this.$router可以获取到它,
// 而这个$router对象就叫做路由器对象,他是所有的$route对象的全集,它里面每一个单独的个体都是一个$route对象
// 这个$route对象就是一个单独的路由实例,包含path + component
// 同时我们可以在像路由传递参数, 传递的参数最终可以通过 this.$route.params.xxx 获取到, 这个xxx,我们传递的什么,这里就能获取到什么
const router = new VueRouter({
// 将存贮有 hash和组件的数组注册进路由器
routes
})
var app = new Vue({
router, // ES6语法糖,相当于 router:router
data: {
students: [
{id: 1, name: 'tom1'},
{id: 2, name: 'tom2'},
{id: 3, name: 'tom3'},
{id: 4, name: 'tom4'},
]
}
}).$mount("#app")
</script>
</html>
像这个需求肯定是很常见的需求,在业务方面的需求就是,前端通过ajax向后端发送请求,拉去学生的信息,拉去到的数据肯定会被存放在Vue中的Data对象中。 也就是上面的 students中。
基于vue组件化的设计风格,我们将展示学生详情的页面抽取出去做成一个vue的动态组件。
// 接受传递进来的参数
const Student = {
template: '<div><span>学号:{{student.id}}</span> <span>姓名:{{student.name}}</span> </div>',
computed: {
student: function f() {
var paramId = this.$route.params.id
var paramName = this.$route.params.name
return {
name: paramName,
id: paramId
}
}
},
// data 有如下两种写法
data: function () {
return {}
}
}
我们需要关心的就是,如何向通过路由向其他组件传递参数
推荐的做法是: <router-link></router-link> + 具名路由(给 route添加一个name属性)
<li v-for="student in students">
<span>{{student.id}} : {{student.name}}</span>
<router-link
:to='{"name":"stu",params{"id":student.id,"name":student.name}}'>
查看详情
</router-link>
</li>
其实到这里参数的传递就已经实现了,然后我们再捋一捋,参数的传递到底是怎么回事???
首先说的就是路由器对象,也就是 $router 对象。当我们把VueRouter注册进Vue时,就会产生一个 $router 对象。(其实就是上面代码中,我们new的VueRouter对象) 通过this.$router可以获取到,这个对象是一个集合,它里面有很多 $route 对象,$route对象就是 path+component对象的结合体。
其中每一个 $route 对象中都一个params属性,通过this.$route.params可以获取到,这个params属性中就存储着我们传递给他的所有的参数,也就是下图中黄色线圈出来的参数
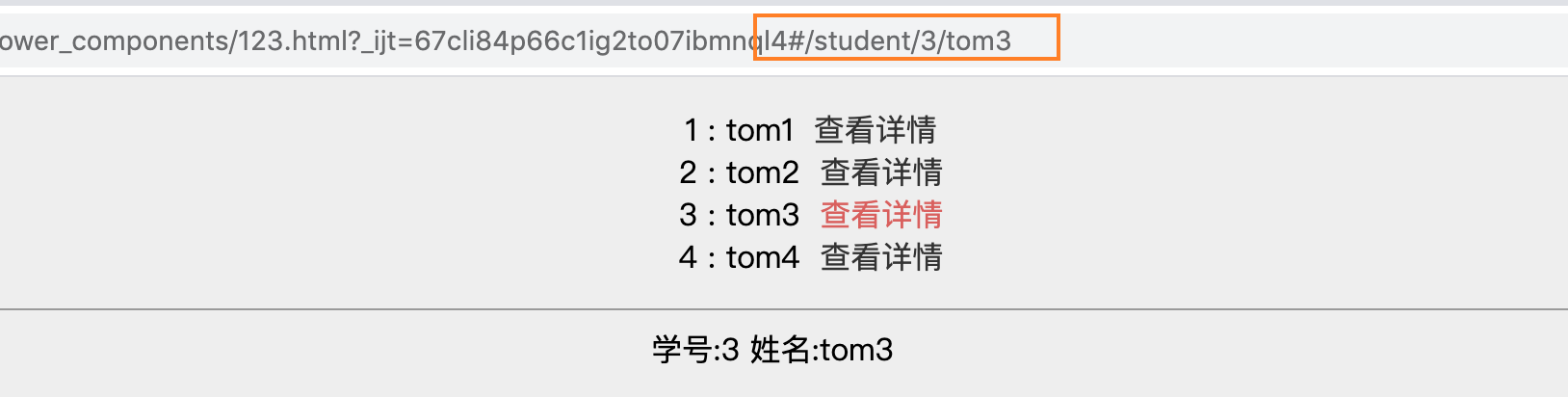
具体到那个参数我们通过this.$route.params.xxx 来获取,这个xxx,在Router中的path部分使用 :xxx 定义。
通过路由传递参数可以通过 this.$route.params获取出来,还可以通过像下面这样,使用props进行映射。然后能直接使用通过路由传递过来的参数。
// 接受传递进来的参数
const Student = {
template: '<div><span>学号:{{id}}</span> <span>姓名:{{name}}</span> </div>',
// 通过将props,将路由中 {path: "/student/:id/:name",name:'stu', component: Student},
// 将如上的id,name映射成下面的属性
props: [
"id", "name",
],
// data 有如下两种写法
data: function () {
// data中要返回一个对象
return {
}
}
}
props也会支持对象模式如下:
这种方式不会经常使用,因为它的props是我们硬编码上去的一个对象。它的值不能动态的改变。
const routes = [
{ path: "/student",
name:'stu',
component: Student,
props:{"id":"123","name":"tomcat"}
},
]
props支持函数式
// 将我们的模版和hash值进程绑定,封装成对象数组
const routes = [
{ path: "/student/:id/:name",
name:'stu',
component: Student,
props:function (router) {
console.log(router)
return router.params
}
},
]
其实你看这种函数的方式和方面直接写一个对象的模式相仿,这个函数必须把这个对象的params返回出去。否则组件中的props快中的属性是不能被附上值的。
通过函数的方式显然要更灵活一些,毕竟可以在中间做一些其他的操作
此外:console.log(router)打印结果如下:

十一. 编程式路由导航
问:编程式路由导航说啥意思呢?
答:
就是用写代码的方式控制路由的跳转,前面的我们实现路由的跳转不是使用a标签就是使用 vue-link标签实现。这种方式配合css样式可以装饰成按钮,以用户可见的状态存在。
那么编程式路由导航,其实说的是通过使用 诸如 this.$router.push(xxx)的方式去实现路由的跳转,通常我们将其放置在事件的回调里面,由我们代码中逻辑去控制该不该进行路由的跳转。
本质上,声明式路由导航和编程式路由导航是一样的
再看一下这个router.push(location, onComplete?, onAbort?)方法。
这里的router === this.$router
为什么说他们相等呢? this就是vm对象,之所以他们相等,是因为我们在下面创建Vue时,使用router给Vue的router赋值了。
const router = new VueRouter({
// 将存贮有 hash和组件的数组注册进路由器
routes : [
{path: "/student/:id/:name",name:'stu', component: Student},
]
})
var app = new Vue({
router, // ES6语法糖,相当于 router:router
data: {
students: [
{id: 1, name: 'tom1'},
]
}
}).$mount("#app")
使用 router.push 方法。这个方法会向 history 栈添加一个新的记录,所以,当用户点击浏览器后退按钮时,则回到之前的 URL。
push方法常见的使用方式有如下几种:
// 字符串
// 下面两种方式是等价的,都是根据path进行路由的切换
router.push('home') === router.push({ path: 'home' })
// 根据路由名称进行跳转,如这个user,她是路由的名称
// 注意这个name指的的在组件注册进VueRouter中时给的那个名字
// {path:"xxx",name:"yyy",component:ZZZ}
// -- name,而不是在组件中定义中export的name
// -- params 是将要传递给路由的参数对象集合
router.push({ name: 'user', params: { userId: '123' }})
// 带查询参数,变成 /register?plan=private
router.push({ path: 'register', query: { plan: 'private' }})
//也可以直接这样
router.push("/register?plan=private")
问:向params传参和向query传参的区别是什么???
-
比如我们这么写:
this.$router.push({name:'user',params:{userID:'123'}})最终的再url地址栏上的表现是:
xxx/user/123 -
如果我们这么写:
this.$router.push({pash:'register',query:{plan:'private'}})最终在地址栏上的表现上:
xxx/register?plan=private
但是无论我们选择使用哪些方式,最终在我们都可以通过this.$route.params将其获取出来。
最后补充和this.$router.push相似的还有replace,表示替换。
十二. 命名视图
问:什么是命名视图?
具名路由指的是我们可以为<router-view>标签指定具体的名字,梳理一下思路,前面我们通过a标签或者是<router-link>标签进行页面路由的跳转时,通常会留一个没有名字的<router-view> 占位,vue会自动根据当前浏览器地址栏上的hash值找到相对应的模版,然后渲染上去。
也就是说,<router-view> 本质上就是一个占位符。也就是组件最终被渲染的位置。
那么命名视图其实就是为<router-view>标签指定好具体的名字,让他仅仅为hash的路由组件占位。
问:这样做有什么好处呢?
好处肯定是有的,如果我们这样做,那么原生的html代码就让我们抽取成vue的组件了。
问:命名视图常用在什么场景中?
显然易见,如果我们将其用在布局和组件的拆分上,我们的代码将会很优雅。
举个例子: 如下代码是中规中矩的html代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="./vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="./vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script>
<style>
* ,#app{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
a {
color: #333333;
text-decoration: none;
/* display: inline-block;*/
padding-left: 5px;
text-align: center;
}
div {
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
.header {
height: 50px;
background-color: #EEEEEE;
}
.banner {
background-color: aqua;
float: left;
margin-right: 5px;
height: 300px;
width: 29%;
}
.content {
background-color: yellow;
float: right;
height: 300px;
width: 70%;
}
.footer {
height: 50px;
background-color: #E95659;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<div class="header"></div>
<div style="overflow: hidden">
<div class="banner"></div>
<div class="content"></div>
</div>
<div class="footer"></div>
</div>
</body>
<script>
</script>
</html>
最终的渲染图:
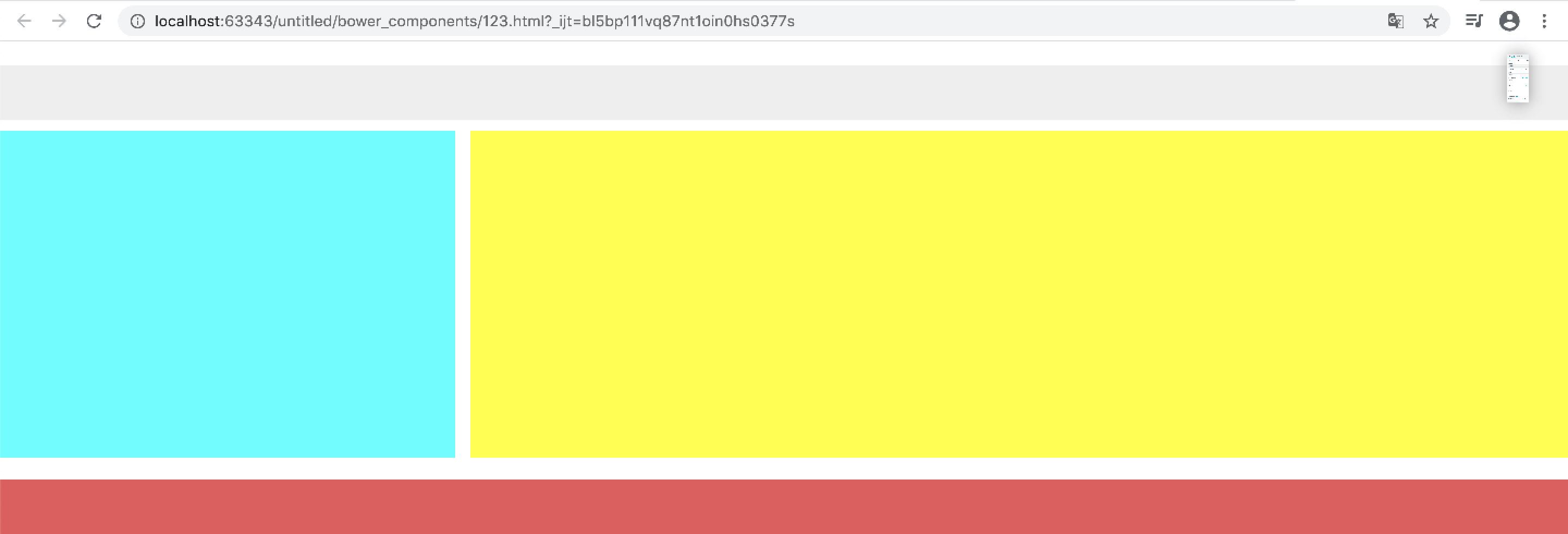
然后通过命名视图,优化代码如下:
可以看到,上面代码中的html代码全部被抽取出去换成了vue组件,取而代之的是具名视图组件<router-view name="xxx"> (具名视图只会为特定名称的组件占位)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="./vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="./vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script>
<style>
*, #app {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
a {
color: #333333;
text-decoration: none;
padding-left: 5px;
text-align: center;
}
div {
margin-bottom: 10px;
}
.header {
height: 50px;
background-color: #EEEEEE;
}
.banner {
background-color: aqua;
float: left;
margin-right: 5px;
height: 300px;
width: 29%;
}
.content {
background-color: yellow;
float: right;
height: 300px;
width: 70%;
}
.footer {
height: 50px;
background-color: #E95659;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<router-view class="view header" name="one">123</router-view>
<div style="overflow: hidden">
<router-view class="view banner" name="two"></router-view>
<router-view class="view " name="three"></router-view>
</div>
<router-view class="view footer" name="four">456</router-view>
</div>
</body>
<script>
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
components: {
one: {
template: "<div >header</div>"
},
two: {
template: "<div class='header'>header</div>"
},
three: {
template: "<div class='content'>content</div>"
},
four: {
template: "<div>footer</div>"
}
}
}
]
})
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
router,
data: {
title: "this is title"
}
})
</script>
</html>
效果图:
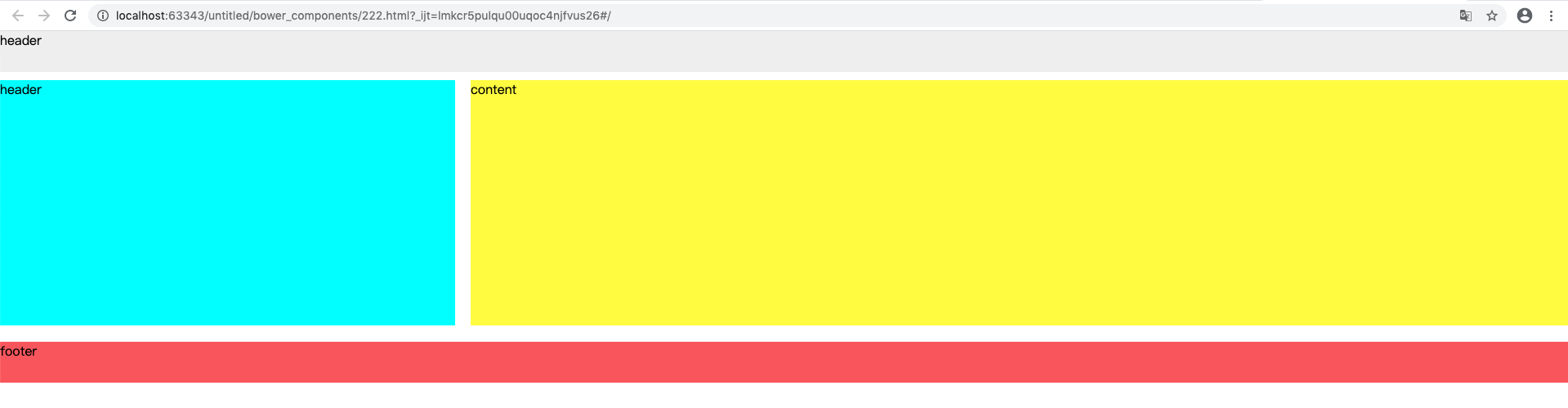
问: <router-view class="view xxx" name="yyy"> 中的xxx和yyy是什么?
xxx:是为当前组件绑定class属性,当然也可以不这样指定,可以在具体的vue组件中去添加css样式
yyy:就是命名视图中的名,它和components中的各个组件名一一对应。
十三. 嵌套路由
看如下的demo
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="./vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="./vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
nav {
height: 60px;
background-color: #eee;
}
li {
list-style: none;
display: inline-block;
padding-left: 10px;
line-height: 60px;
}
nav a {
text-decoration: none;
color: black;
padding-left: 10px;
padding-right: 10px;
}
nav a:hover {
display: inline-block;
color: #ffffff;
background-color: #444444;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<nav>
<router-view></router-view>
</nav>
</div>
</body>
<script>
const navComponent = {
template: `<div>
<div>
<ul>
<li><a href="#/index">首页</a></li>
<li><a href="#">文章</a></li>
<li><a href="#">友情链接</a></li>
<li><a href="#">点我关注</a></li>
</ul>
</div>
<div>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</div>`,
name: "nav"
}
const indexComponent = {
template: `<div> this is 首页 --> index</div>`
}
const router = new VueRouter({
// todo 如果说路由没有加载出来,也不报错,八成是VueRouter的这个属性名被写错了
routes: [
{
path: "/",
component: navComponent,
children: [
{
path: "/index",
component: indexComponent
}
]
},
]
})
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
router: router,
data: {}
})
</script>
</html>
最终实现的效果就是:当我们点击首页时,在nav标签的下面渲染出首页组件的子组件。
效果图:
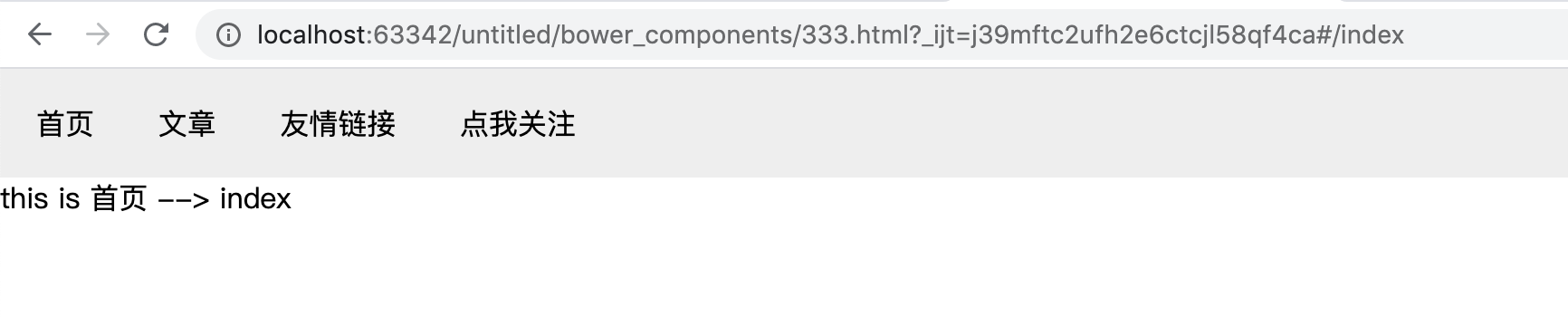
说一下需要注意的地方:像下面样通过children块为当前路由注册子路由。
const router = new VueRouter({
// todo 如果说路由没有加载出来,也不报错,八成是VueRouter下面这个属性名被写错了
routes: [
{
path: "/",
component: navComponent,
children: [
{
path: "/index",
component: indexComponent
}
]
},
]
})
十四. params和query
首先:
第一:VueRouter根据浏览器地址栏中的hash值去匹配并渲染组件
第二:url中的含有:网络协议+端口+params+query
params+query相当于是hash
比如这个:
http://localhost:63342/untitled#/index/12?id=10&name=tom
params : /index/12
query : ?id=10&name=tom
-
params参数的传递其实在上文中第十节路由参数传递模块已经说了多几种情况了,这里不再重复说
-
那么query模式传递的参数一般怎么处理呢?
参考如下代码:?id=1&name=tom的信息被封装进了router的query部分
const indexComponent = { template: `<div> id:{{id}} name:{{name}}</div>`, props:["id","name"] } const router = new VueRouter({ // todo 如果说路由没有加载出来,也不报错,八成是VueRouter的这个属性名被写错了 routes: [ { path: "/", component: navComponent, children: [ { path: "/index", component: indexComponent, props:function (router) { console.log(router) return router.query } } ] }, ] })router的打印结果如图:
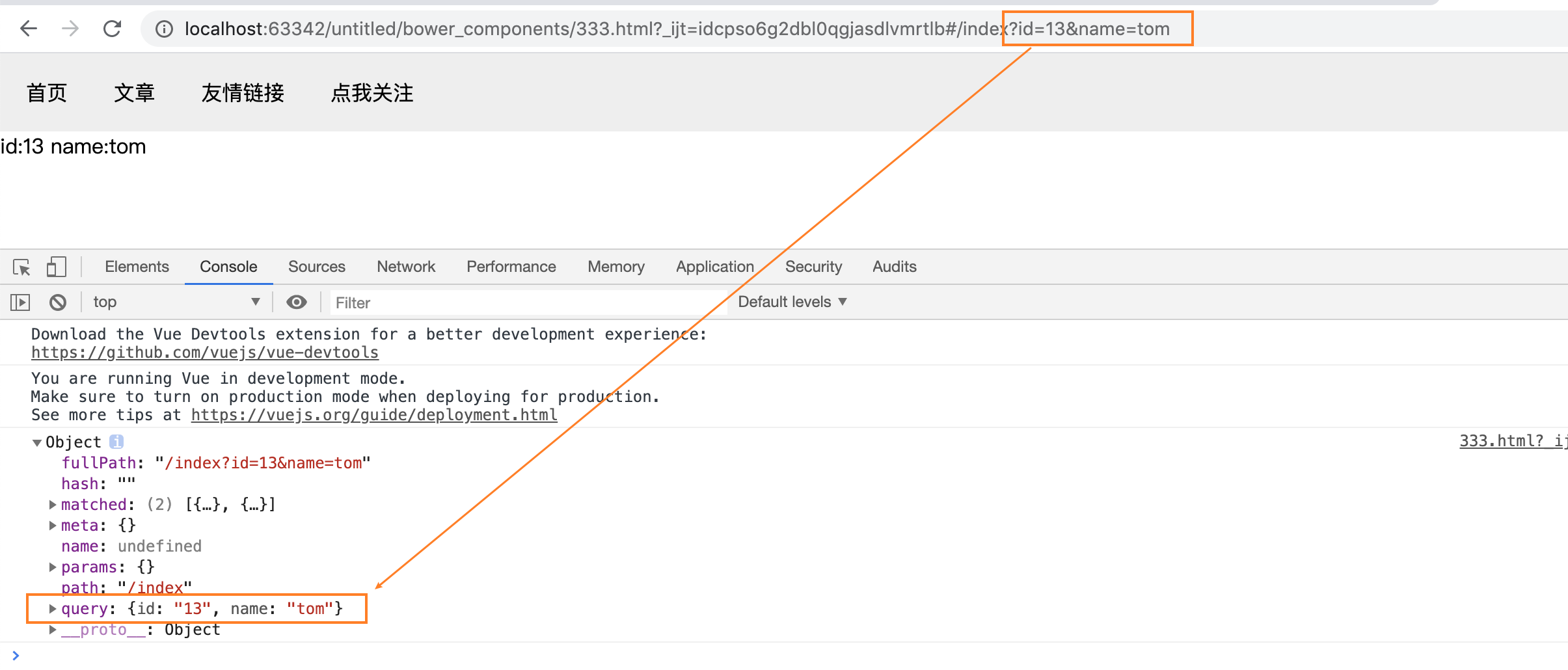
当然,它和params的用户几乎是相同的
总结一下,其实就是url中的path部分和参数部分,会被分别封装进route对象的不同属性中。这仅仅是为了可以实现两种参数的区分,最终的目的都是为了可以传递参数。以及实现路由的跳转
十五. 导航守卫
导航守卫也被称作路由钩子函数,他们指的都是router对象中的回调函数,他们会在路由所处的不同状态被回调
如下是简单的demo
为每个路由单独写回调
const router = new VueRouter({
// todo 如果说路由没有加载出来,也不报错,八成是VueRouter的这个属性名被写错了
routes: [
{
path: "/",
component: navComponent,
children: [
{
path: "/index",
component: indexComponent,
props:function (router) {
console.log(router)
return router.query
},
beforeEnter:function (to,from,next) {
console.log("to: ",to)
console.log("form: ",from)
// next是一个函数
console.log("next: ",next)
// next(true) 表示进行路由的跳转
// next(false) 表示不进行路由的跳转
}
}
]
},
]
})
当发生路由跳转时,beforeEnter会被回调,查看控制台的打印结果:
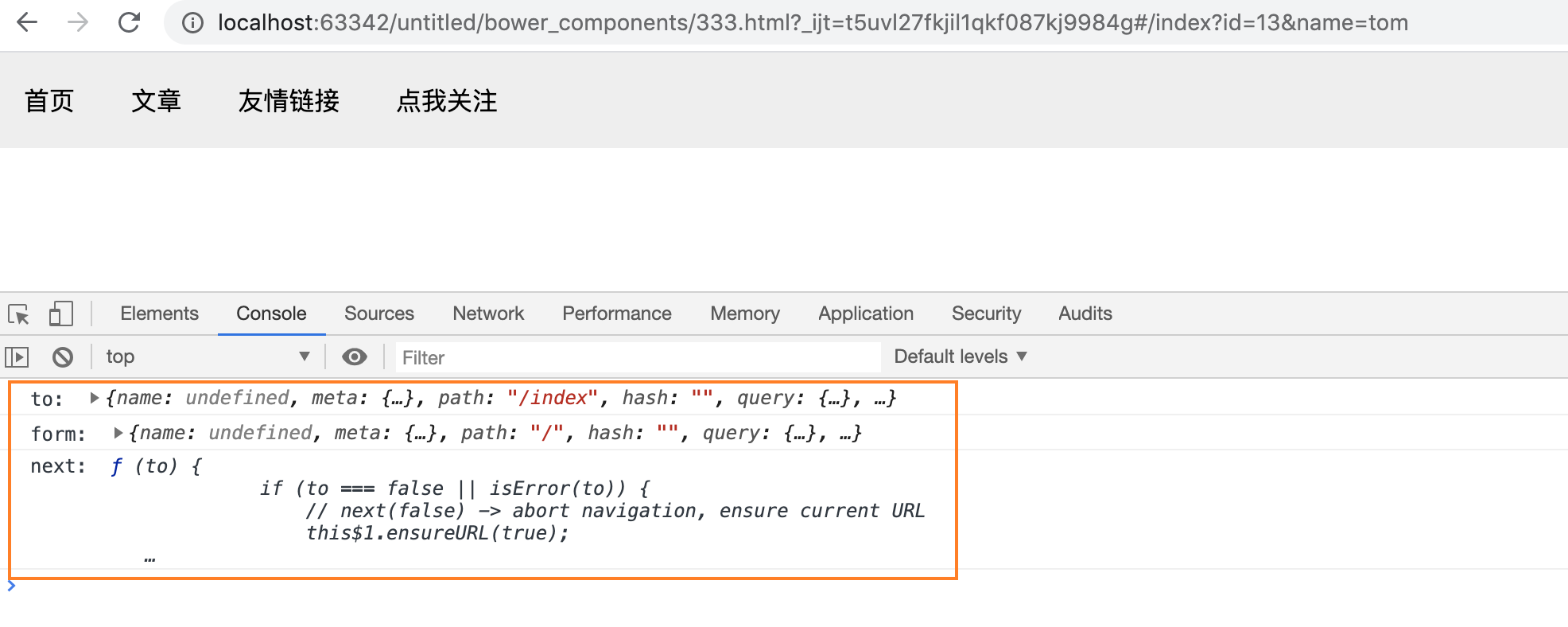
通过next函数发起路由的跳转,通常会使用这个特性干什么事呢? 比如我们可以在路由的跳转之前判断一下用户是否已经登陆了,是否有权限。
我们可以将其定义在模版中:
const indexComponent = {
template: `<div> id:{{id}} name:{{name}}</div>`,
props:["id","name"],
beforeRouteEnter:function (to,from,next) {
console.log("to: ",to)
console.log("form: ",from)
// next是一个函数
console.log("next: ",next)
// next(true) 表示进行路由的跳转
// next(false) 表示不进行路由的跳转
},
beforeRouteLeave:function (to,form,next) {
console.log("to: ",to)
console.log("form: ",from)
// next是一个函数
console.log("next: ",next)
// next(true) 表示进行路由的跳转
// next(false) 表示不进行路由的跳转
}
}
十六. 路由元信息
路由的元信息指是路由的 meta属性。注意我们说的是路由而不是路由器。
路由:this.$route
路由器:this.$router
常见的我们可以基于路由的元信息做安全验证相关的操作:点击看相关文章
下面再补充下,官网提供的demo :点击进入参考链接
首先贴出VueRouter部分的代码:
const router = new VueRouter({
// todo 如果说路由没有加载出来,也不报错,八成是VueRouter的这个属性名被写错了
routes: [
{
path: "/",
component: navComponent,
children: [
{
path: "/index",
component: indexComponent,
props: function (router) {
console.log(router)
return router.query
},
meta: {requiresAuth: true}
}
]
},
]
})
router.beforeEach((to, form, next) => {
console.log("to: ", to)
console.log("form: ", form)
next()
})
最终可以实现的效果如图:
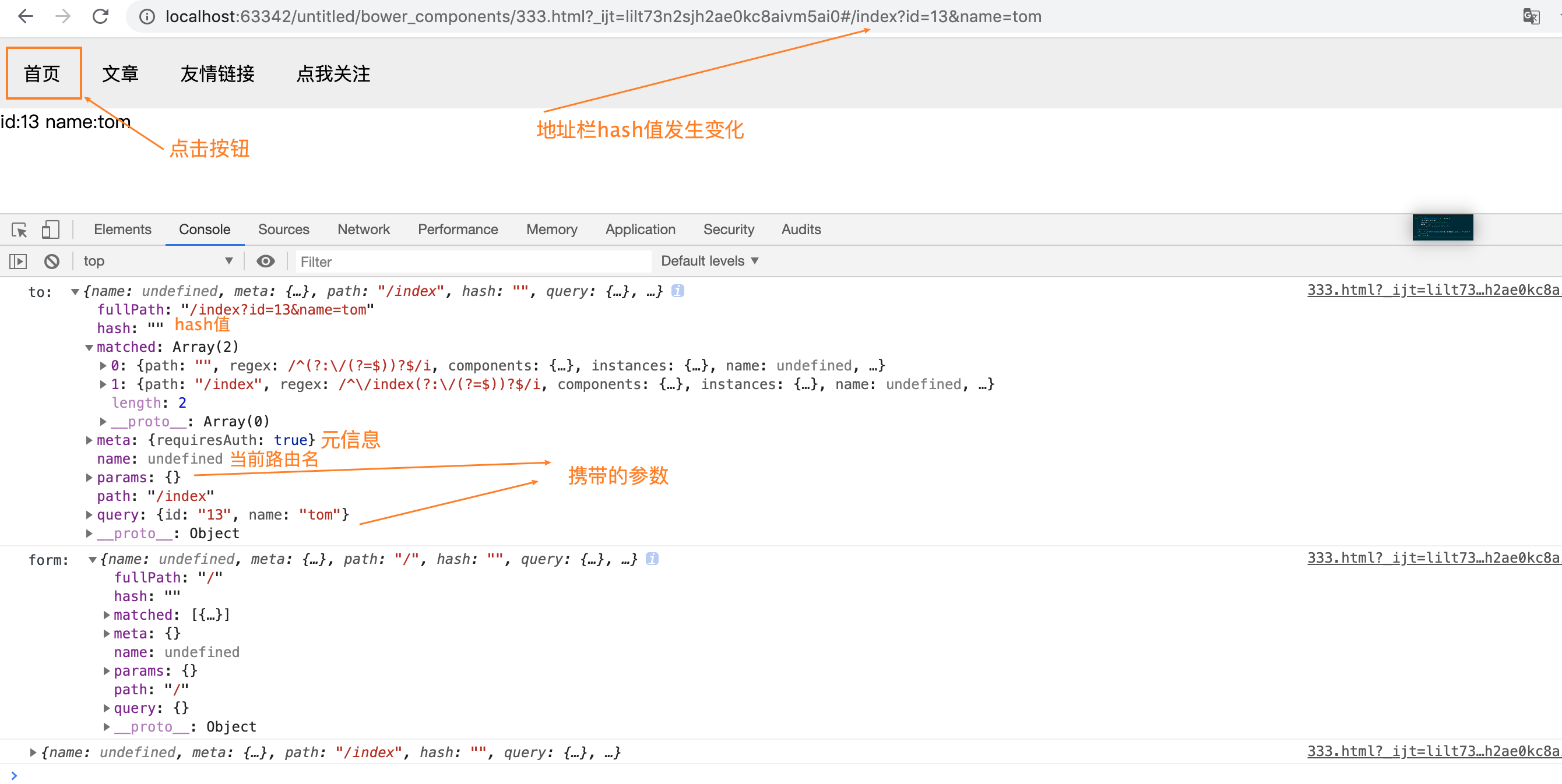
贴着张图是啥意思呢?其一是可以比较完成的看到route的各个属性,其二是我们可以看到他有个属性叫做match 它是个数组。里面记录着匹配到的route的信息。 看上图的目的很大一部分原因是去看看这个matched属性是个数组。因为在官方的demo中编码如下:
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/foo',
component: Foo,
children: [
{
path: 'bar',
component: Bar,
// a meta field
meta: { requiresAuth: true }
}
]
}
]
})
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
if (to.matched.some(record => record.meta.requiresAuth)) {
// this route requires auth, check if logged in
// if not, redirect to login page.
if (!auth.loggedIn()) {
next({
path: '/login',
query: { redirect: to.fullPath }
})
} else {
next()
}
} else {
next() // 确保一定要调用 next()
}
})
在官方的demo中,路由的全局守卫使用到了这个matched属性以及Array的some方法,some方法的入参接受一个函数,官网demo中的实现采用了ES6的新特性去实现的。
致至为止,相信我们都能很好的理解这个demo了。
十七. VueRouter中的数据获取
VueRouter中的数据的指的是我们何时像后端发送请求,将组件中需要的数据获取到进而渲染组件。
通常来说有两个时机:
-
导航完成之后获取
导航完成之后说明我们已经找到对应的组件了。而组件中又需要渲染一些动态的数据,这时我们只能选择在组件相应的生命周期回调中(比如created,mounted)向后端发送请求完成拉去数据。
如果想让用户有个良好的体验,我们可以添加上进度条,或者是loding标记。
-
导航完成之前渲染
这种方式指的是在路由的守卫中完成数据的拉取,数据获取到之后,再进行导航。
十八. VueRouter的滚动行为
VueRouter支持我们自定义切换到一个新的路由时页面的滚动方式。
比如像下面的这个例子,当我们在同步的路由之间切换时,默认的浏览器的下拉框总会定位到上次我们所在的位置。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<script src="./vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="./vue-router/dist/vue-router.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</body>
<script>
const home = {
template: `
<div>
<h1>文章:</h1>
<p>学习 vuerouter 的滚动行为</p>
<p>学习 vuerouter 的滚动行为</p>
<p>学习 vuerouter 的滚动行为</p>
<p>学习 vuerouter 的滚动行为</p>
<p>学习 vuerouter 的滚动行为</p>
<p>学习 vuerouter 的滚动行为</p>
<p>学习 vuerouter 的滚动行为</p>
<p>学习 vuerouter 的滚动行为</p>
<p>学习 vuerouter 的滚动行为</p>
<p>学习 vuerouter 的滚动行为</p>
<p>学习 vuerouter 的滚动行为</p>
<p>学习 vuerouter 的滚动行为</p>
<p>学习 vuerouter 的滚动行为</p>
<p>学习 vuerouter 的滚动行为</p>
<p>学习 vuerouter 的滚动行为</p>
<router-link to="/detail">点击进入detail</router-link>
</div>
`
}
const detail = {
template: `
<div>
<h1>this is detail</h1>
<p>this is detail</p>
<p>this is detail</p>
<p>this is detail</p>
<p>this is detail</p>
<p>this is detail</p>
<p>this is detail</p>
<p>this is detail</p>
<p>this is detail</p>
<p>this is detail</p>
<p>this is detail</p>
<p>this is detail</p>
<p>this is detail</p>
<p>this is detail</p>
<p>this is detail</p>
<p>this is detail</p>
<p>this is detail</p>
<router-link to="/">点击进入首页</router-link>
</div>`
}
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: "/",
component: home
},
{
path: "/detail",
component: detail
}
]
})
var app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
router,
data: {}
})
</script>
</html>
Vue-Router支持我们定制这个滚动的集体位置。
定制这个滚动的具体位置需要借助一个VueRouter的函数:scrollBehavior
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [...],
scrollBehavior (to, from, savedPosition) {
// return 期望滚动到哪个的位置
return { x: number, y: number }
// (offset 只在 2.6.0+ 支持)
return { selector: string, offset? : { x: number, y: number }}
// 返回按下前进/后退按钮时,浏览器记录下的原生状态
return savedPosition
}
})
如果页面中有锚点,也能像下面这样模拟hash锚点定位
scrollBehavior (to, from, savedPosition) {
if (to.hash) {
return {
selector: to.hash
}
}
}
当然也支持异步滚动
scrollBehavior (to, from, savedPosition) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve({ x: 0, y: 0 })
}, 500)
})
}


