2分类1隐层nn, 作业默认设置:
- 1个输出单元, sigmoid激活函数. (因为二分类);
- 4个隐层单元, tanh激活函数. (除作为输出单元且为二分类任务外, 几乎不选用 sigmoid 做激活函数);
- n_x个输入单元, n_x为训练数据维度;
总的来说共三层: 输入层(n_x = X.shape[0]), 隐层(n_h = 4), 输出层(n_y = 1).
import 和预设置
# Package imports
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from testCases import *
import sklearn
import sklearn.datasets
import sklearn.linear_model
from planar_utils import plot_decision_boundary, sigmoid, load_planar_dataset, load_extra_datasets
%matplotlib inline
np.random.seed(1) # set a seed so that the results are consistent
4 - Neural Network model
Here is our model:
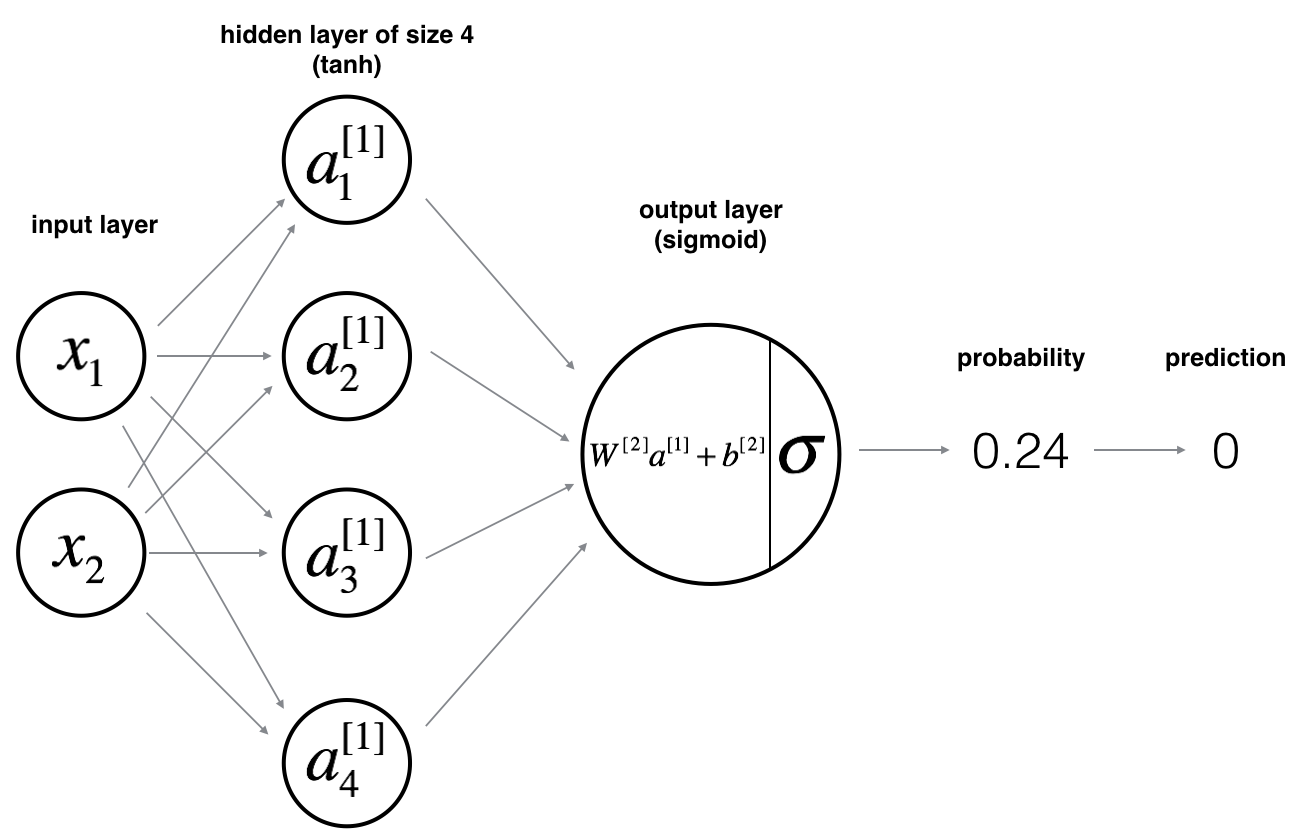
Mathematically:
For one example \(x^{(i)}\):
Given the predictions on all the examples, you can also compute the cost \(J\) as follows:
Reminder: The general methodology to build a Neural Network is to:
1. Define the neural network structure ( # of input units, # of hidden units, etc).
2. Initialize the model's parameters
3. Loop:
- Implement forward propagation
- Compute loss
- Implement backward propagation to get the gradients
- Update parameters (gradient descent)
You often build helper functions to compute steps 1-3 and then merge them into one function we call nn_model(). Once you've built nn_model() and learnt the right parameters, you can make predictions on new data.
4.1 - Defining the neural network structure
# GRADED FUNCTION: layer_sizes
def layer_sizes(X, Y):
"""
Arguments:
X -- input dataset of shape (input size, number of examples)
Y -- labels of shape (output size, number of examples)
Returns:
n_x -- the size of the input layer
n_h -- the size of the hidden layer
n_y -- the size of the output layer
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 3 lines of code)
n_x = X.shape[0] # size of input layer
n_h = 4
n_y = Y.shape[0] # size of output layer
### END CODE HERE ###
return (n_x, n_h, n_y)
4.2 - Initialize the model's parameters
# GRADED FUNCTION: initialize_parameters
def initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y):
"""
Argument:
n_x -- size of the input layer
n_h -- size of the hidden layer
n_y -- size of the output layer
Returns:
params -- python dictionary containing your parameters:
W1 -- weight matrix of shape (n_h, n_x)
b1 -- bias vector of shape (n_h, 1)
W2 -- weight matrix of shape (n_y, n_h)
b2 -- bias vector of shape (n_y, 1)
"""
np.random.seed(2) # we set up a seed so that your output matches ours although the initialization is random.
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)
W1 = np.random.randn(n_h, n_x) * 0.01
b1 = np.zeros((n_h, 1))
W2 = np.random.randn(n_y, n_h) * 0.01
b2 = np.zeros((n_y, 1))
### END CODE HERE ###
assert (W1.shape == (n_h, n_x))
assert (b1.shape == (n_h, 1))
assert (W2.shape == (n_y, n_h))
assert (b2.shape == (n_y, 1))
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2}
return parameters
4.3 - The Loop
注意, 若换激活函数,有两个地方需要改:
- forward_propagation()中 A1 = np.tanh(Z1)处;
- backward_propagation()中 dZ1中 1 - np.power(A1, 2) 处.
# GRADED FUNCTION: forward_propagation
def forward_propagation(X, parameters):
"""
Argument:
X -- input data of size (n_x, m)
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters (output of initialization function)
Returns:
A2 -- The sigmoid output of the second activation
cache -- a dictionary containing "Z1", "A1", "Z2" and "A2"
"""
# Retrieve each parameter from the dictionary "parameters"
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
### END CODE HERE ###
# Implement Forward Propagation to calculate A2 (probabilities)
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)
Z1 = np.dot(W1, X) + b1
A1 = np.tanh(Z1)
Z2 = np.dot(W2, A1) + b2
A2 = sigmoid(Z2)
### END CODE HERE ###
assert(A2.shape == (1, X.shape[1]))
cache = {"Z1": Z1,
"A1": A1,
"Z2": Z2,
"A2": A2}
return A2, cache
# GRADED FUNCTION: compute_cost
def compute_cost(A2, Y, parameters):
"""
Computes the cross-entropy cost given in equation (13)
Arguments:
A2 -- The sigmoid output of the second activation, of shape (1, number of examples)
Y -- "true" labels vector of shape (1, number of examples)
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters W1, b1, W2 and b2
Returns:
cost -- cross-entropy cost given equation (13)
"""
m = Y.shape[1] # number of example
# Compute the cross-entropy cost
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
logprobs = np.multiply(np.log(A2), Y) + np.multiply(np.log(1 - A2), 1 - Y)
cost = -np.sum(logprobs)/m
### END CODE HERE ###
cost = np.squeeze(cost) # makes sure cost is the dimension we expect.
# E.g., turns [[17]] into 17
assert(isinstance(cost, float))
return cost
反向传播时用到的公式:
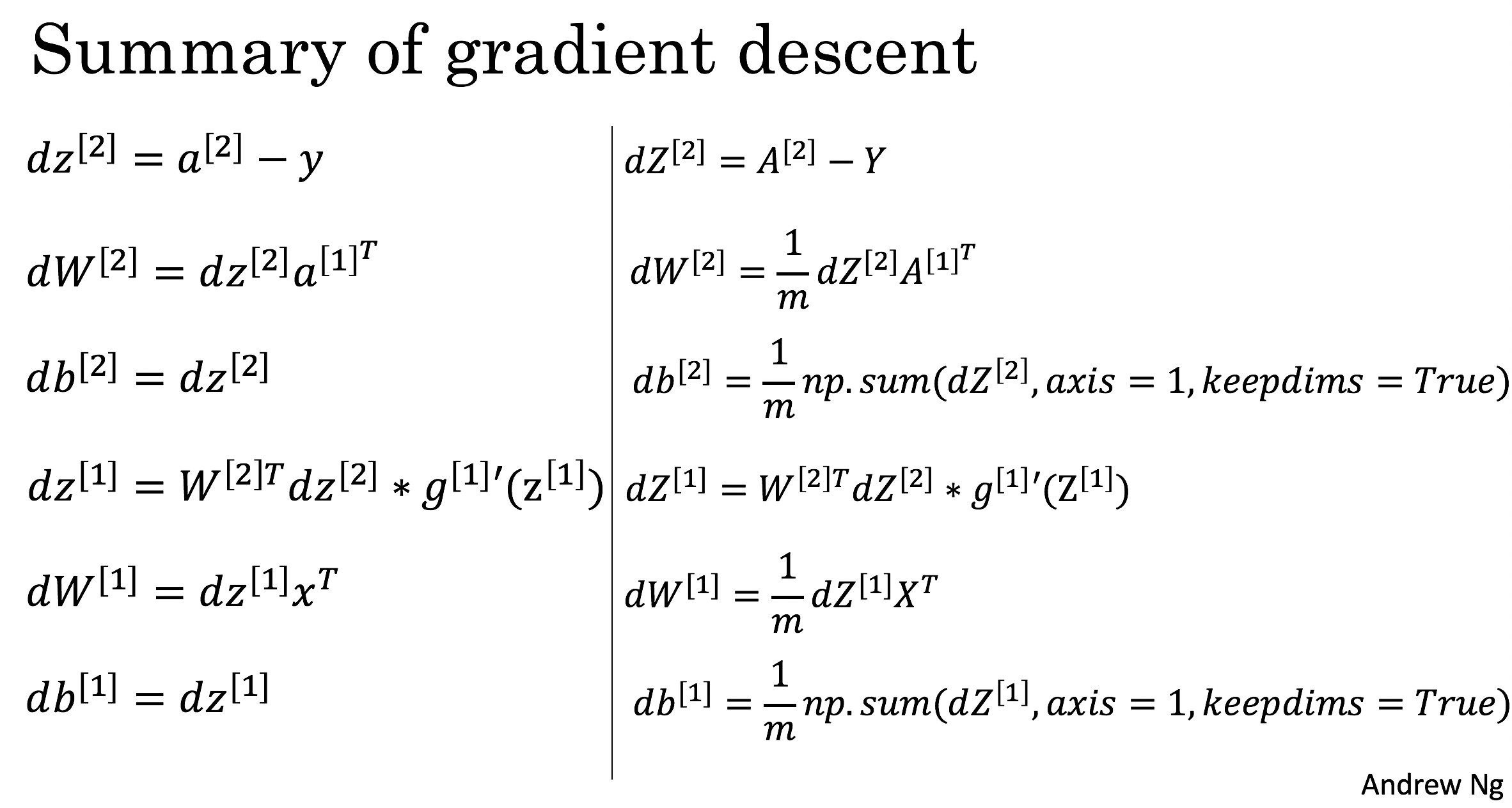
# GRADED FUNCTION: backward_propagation
def backward_propagation(parameters, cache, X, Y):
"""
Implement the backward propagation using the instructions above.
Arguments:
parameters -- python dictionary containing our parameters
cache -- a dictionary containing "Z1", "A1", "Z2" and "A2".
X -- input data of shape (2, number of examples)
Y -- "true" labels vector of shape (1, number of examples)
Returns:
grads -- python dictionary containing your gradients with respect to different parameters
"""
m = X.shape[1]
# First, retrieve W1 and W2 from the dictionary "parameters".
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
W1 = parameters["W1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
### END CODE HERE ###
# Retrieve also A1 and A2 from dictionary "cache".
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
A1 = cache["A1"]
A2 = cache["A2"]
### END CODE HERE ###
# Backward propagation: calculate dW1, db1, dW2, db2.
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 6 lines of code, corresponding to 6 equations on slide above)
dZ2 = A2 - Y
dW2 = np.dot(dZ2, A1.T)/m
db2 = np.sum(dZ2, axis=1, keepdims=True)/m
# tanh的导数 1-A1^2
# 若换激活函数,有两个地方需要改
# 1. forward_propagation()中 A1 = np.tanh(Z1)处
# 2. 就是这里backward_propagation()中 dZ1中 1 - np.power(A1, 2) 处
dZ1 = np.multiply(np.dot(W2.T, dZ2), 1 - np.power(A1, 2)) # <--
dW1 = np.dot(dZ1, X.T)/m
db1 = np.sum(dZ1, axis=1, keepdims=True)/m
### END CODE HERE ###
grads = {"dW1": dW1,
"db1": db1,
"dW2": dW2,
"db2": db2}
return grads
# GRADED FUNCTION: update_parameters
def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate = 1.2):
"""
Updates parameters using the gradient descent update rule given above
Arguments:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters
grads -- python dictionary containing your gradients
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your updated parameters
"""
# Retrieve each parameter from the dictionary "parameters"
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
### END CODE HERE ###
# Retrieve each gradient from the dictionary "grads"
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)
dW1 = grads["dW1"]
db1 = grads["db1"]
dW2 = grads["dW2"]
db2 = grads["db2"]
## END CODE HERE ###
# Update rule for each parameter
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)
W1 -= learning_rate*dW1
b1 -= learning_rate*db1
W2 -= learning_rate*dW2
b2 -= learning_rate*db2
### END CODE HERE ###
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2}
return parameters
4.4 - Integrate parts 4.1, 4.2 and 4.3 in nn_model()
# GRADED FUNCTION: nn_model
def nn_model(X, Y, n_h, num_iterations = 10000, print_cost=False):
"""
Arguments:
X -- dataset of shape (2, number of examples)
Y -- labels of shape (1, number of examples)
n_h -- size of the hidden layer
num_iterations -- Number of iterations in gradient descent loop
print_cost -- if True, print the cost every 1000 iterations
Returns:
parameters -- parameters learnt by the model. They can then be used to predict.
"""
np.random.seed(3)
n_x = layer_sizes(X, Y)[0]
n_y = layer_sizes(X, Y)[2]
# Initialize parameters, then retrieve W1, b1, W2, b2. Inputs: "n_x, n_h, n_y". Outputs = "W1, b1, W2, b2, parameters".
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 5 lines of code)
parameters = initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y)
W1 = parameters["W1"]
b1 = parameters["b1"]
W2 = parameters["W2"]
b2 = parameters["b2"]
### END CODE HERE ###
# Loop (gradient descent)
for i in range(0, num_iterations):
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)
# Forward propagation. Inputs: "X, parameters". Outputs: "A2, cache".
A2, cache = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
# Cost function. Inputs: "A2, Y, parameters". Outputs: "cost".
cost = compute_cost(A2, Y, parameters)
# Backpropagation. Inputs: "parameters, cache, X, Y". Outputs: "grads".
grads = backward_propagation(parameters, cache, X, Y)
# Gradient descent parameter update. Inputs: "parameters, grads". Outputs: "parameters".
parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Print the cost every 1000 iterations
if print_cost and i % 1000 == 0:
print ("Cost after iteration %i: %f" %(i, cost))
return parameters
4.5 Predictions
Reminder: predictions = \(y_{prediction} = \mathbb 1 \text{{activation > 0.5}} = \begin{cases} 1 & \text{if}\ activation > 0.5 \\ 0 & \text{otherwise} \end{cases}\)
As an example, if you would like to set the entries of a matrix X to 0 and 1 based on a threshold you would do: X_new = (X > threshold)
# GRADED FUNCTION: predict
def predict(parameters, X):
"""
Using the learned parameters, predicts a class for each example in X
Arguments:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters
X -- input data of size (n_x, m)
Returns
predictions -- vector of predictions of our model (red: 0 / blue: 1)
"""
# Computes probabilities using forward propagation, and classifies to 0/1 using 0.5 as the threshold.
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 2 lines of code)
A2, cache = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
predictions = (A2[0] > 0.5) # [ True False True] 而不是 [1 0 1]
### END CODE HERE ###
return predictions
使用模型
# Build a model with a n_h-dimensional hidden layer
# 模型经训练后,最终得到 parameters = W2, b2, W1, b1
parameters = nn_model(X, Y, n_h = 4, num_iterations = 10000, print_cost=True)
# Plot the decision boundary
# 新数据 x 和训练好的参数 parameters 送入 predict() 后, 经过一个前向, 得到A2,
# 再经threshold得到预测结果.
# Print accuracy
predictions = predict(parameters, X)
print ('Accuracy: %d' % float((np.dot(Y,predictions.T) + np.dot(1-Y,1-predictions.T))/float(Y.size)*100) + '%')
4.6 - Tuning hidden layer size (optional/ungraded exercise)
plt.figure(figsize=(16, 32))
hidden_layer_sizes = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 20]
for i, n_h in enumerate(hidden_layer_sizes):
plt.subplot(5, 2, i+1)
plt.title('Hidden Layer of size %d' % n_h)
parameters = nn_model(X, Y, n_h, num_iterations = 5000)
plot_decision_boundary(lambda x: predict(parameters, x.T), X, Y)
predictions = predict(parameters, X)
accuracy = float((np.dot(Y,predictions.T) + np.dot(1-Y,1-predictions.T))/float(Y.size)*100)
print ("Accuracy for {} hidden units: {} %".format(n_h, accuracy))
最后顺便把作业里的两个动画(表现学习率设置不合适导致发散,反过来收敛)也弄上来:
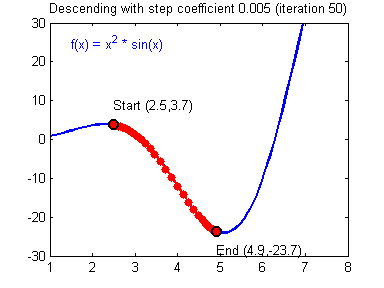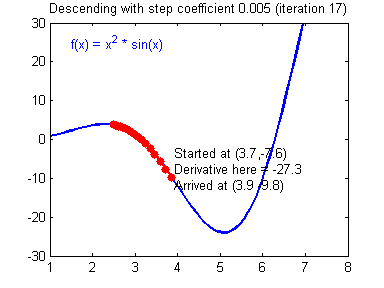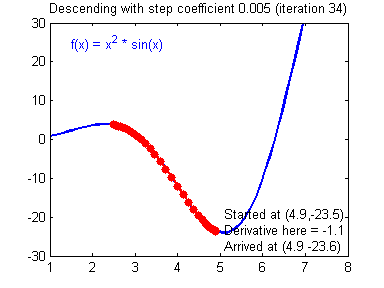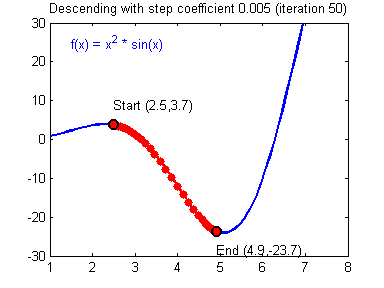
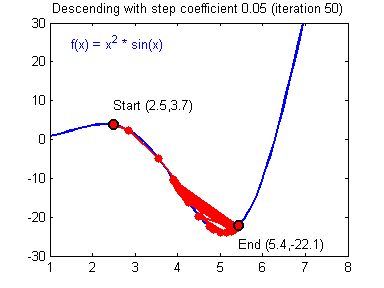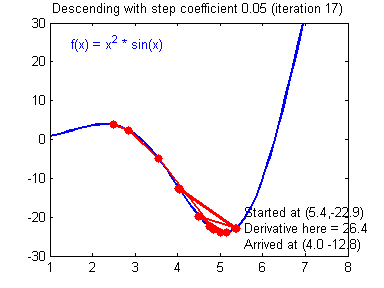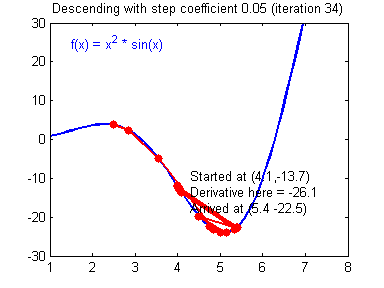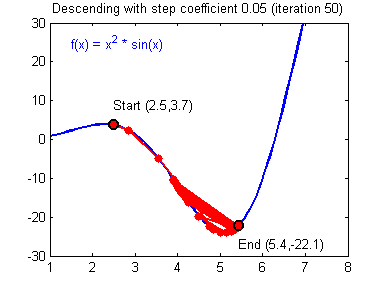




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步