kuangbin专题五 并查集【从入门到熟练】【9+1题】
POJ 1611 The Suspects
基础并查集,由于需要知道数量维护一个total就可以了

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<cmath> #include<queue> #include<string> #include<stack> #include<fstream> #include<map> #include<iomanip> #include<algorithm> #include<vector> #define inf 2e9 #define maxnode 200000 #define ll long long #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) const int mod = 10007; const int maxn = 3e4 + 10; int dx[4]={0,0,1,-1}; int dy[4]={1,-1,0,0}; using namespace std; int par[maxn],total[maxn];//total[i]只对root有效,代表这个关系群的人数总数量 int get_root(int a){ if( par[a]==a ) return a; return par[a]=get_root( par[a] ); } void merge(int a,int b){ int root_a=get_root(a); int root_b=get_root(b); if( root_a==root_b ) return; par[ root_a ] = root_b; total[root_b]+=total[root_a]; } bool query(int a,int b){ return get_root(a)==get_root(b); } int main(){ while(1){ int n,m; scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); if(n==0 && m==0) break; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) par[i]=i; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) total[i]=1; for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ int k; scanf("%d",&k); int start; scanf("%d",&start); start++; for(int i=1;i<k;i++){ int x; scanf("%d",&x); x++; merge(start,x); } } printf("%d\n",total[get_root(1)] ); } return 0; }
HDU 3038 How Many Answers Are Wrong
网上blog普遍都用向量的角度去理解,但我一直不懂并查集是怎么跟向量扯上关系的?
其实其本质是逻辑,可以从偏移量的角度出发去理解。(套路是维护一个数组a[i]代表i与其祖先的某种关系(其实是与父节点的关系,经过路径压缩变成与祖先的关系))
对于这题还有一个难点,那就是对于给的a和b中,a要减一。
如果说 [1,5] = 3,[6,10] = 3
那应当推出来[1,10]是6(1到5偏移3,5到10再偏移3),所以需要a减一。【因为[a,b]的和,可以看成是a-1偏移到a,a偏移到a+1, ... , b-1偏移到b】

#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define inf 2e9 #define maxnode 200000 #define ll long long #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) const int mod = 10007; const int maxn = 2e5 + 10; int dx[4]={0,0,1,-1}; int dy[4]={1,-1,0,0}; using namespace std; int sum[maxn],par[maxn]; int find_root(int a){ if( par[a]==a ) return par[a]; int root = find_root(par[a]); sum[a]+=sum[ par[a] ];//得先改sum par[a]=root; return root; } int main(){ //freopen("1.in","r",stdin); int n,m; while( scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF ){ int cnt=0; for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){ par[i]=i; sum[i]=0; } for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ int a,b,v; scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&v); a--; int roota=find_root(a); int rootb=find_root(b); if( roota==rootb ){ if( v!=sum[a]-sum[b] ) cnt++; } else{ par[roota]=rootb; sum[roota]=sum[b]-sum[a]+v; } } printf("%d\n",cnt); } return 0; }
POJ 1182 食物链
赤裸裸的逻辑,比上一题简单。
其实理解关系并查集,能理解两幅图就行了,第一种是当x和y不在一个集合的时候。(x所在的集合里互相关系都知道,y所在集合里互相关系也都知道,那怎么建立rootx与rooty之间的关系?)
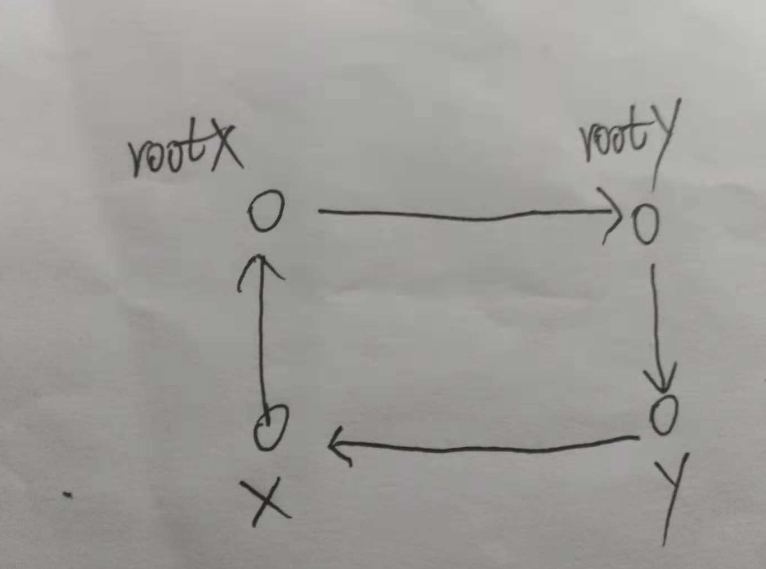
从偏移量的角度去想,x经过一些可量化的操作偏移到rootx,rootx偏移到rooty,rooty偏移到y,y再偏移到x,所有的偏移量加起来应该是0,因为又回到了原点。(这是逻辑,只不过画出来像向量的形式)
那就是 x->rootx + rootx->rootx->rooty + rooty->y + y->x = 0
化简得到 x->rootx + rootx->rooty - y->rooty - x->y = 0
再化简 rootx->rooty = y->rooty + x->y - x->rootx
即 relation[ rootx ] = relation[ y ] + d - relation[ x ]
另一种情况是x和y已经在一个集合里了,验证目前信息与之前的冲不冲突
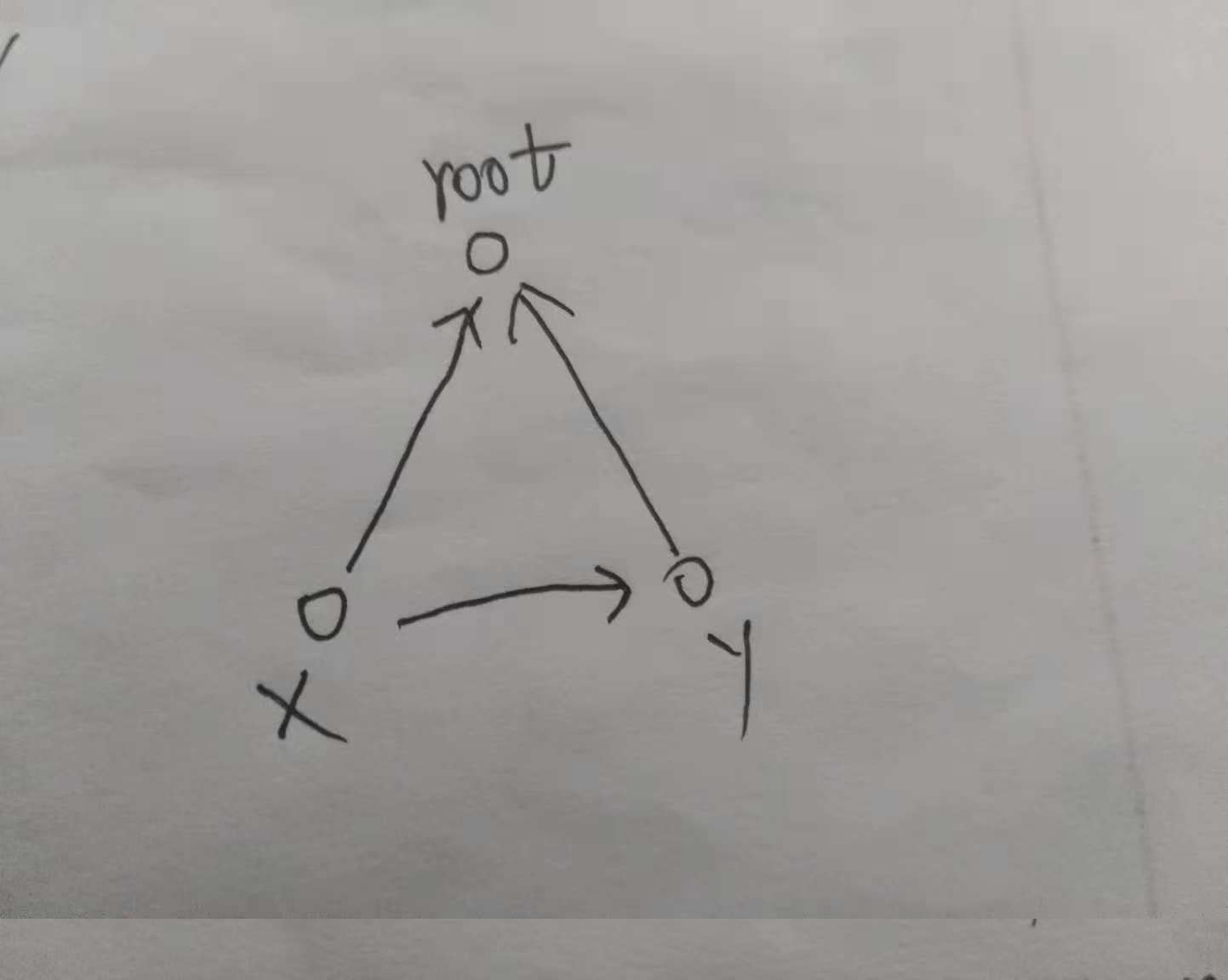
x->root + root->y +y->x = 0
x->root - y->root - x->y = 0
即验证 ( d == relation[x]-relation[y] )
那最后就在想这个【可量化的操作】该怎么量化就可以了,一般来说比较好想

#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<cmath> #include<queue> #include<string> #include<stack> #include<fstream> #include<map> #include<iomanip> #include<algorithm> #include<vector> #define inf 2e9 #define maxnode 200000 #define ll long long #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) const int mod = 10007; const int maxn = 5e4 + 10; int dx[4]={0,0,1,-1}; int dy[4]={1,-1,0,0}; using namespace std; int par[maxn],relation[maxn]; //relation[i]==0 代表 i跟par[i]是同类 //relation[i]==1 代表 i吃par[i] //relation[i]==2 代表 i被par[i]吃 int find_root(int a){//会顺手把par改掉,所以也要顺手把relation改掉 if( par[a]==a ) return par[a]; int root=find_root(par[a]); relation[a] = (relation[ par[a] ]+relation[a])%3; //a与root的关系,是par与root的关系加上a与par的关系 return par[a]=root; } void merge(int a,int b,int relat){//relat是 a->b是relat,b->a就不是了 int roota=find_root(a); int rootb=find_root(b); if( roota==rootb ) return; par[rootb]=roota; relation[rootb]=3-( (relat+relation[b]-relation[a]+3)%3); } int find_relation(int a){ if( par[a]==a ) return 0; return (relation[a]+find_relation(par[a]))%3; } int main(){ int n,k; scanf("%d%d",&n,&k); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) par[i]=i; int cnt=0; for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){ int d,x,y; scanf("%d%d%d",&d,&x,&y); if( d==2 && x==y ) cnt++; else if( x>n || y>n ) cnt++; else{ if( d==1 ){ int rx=find_root(x); int ry=find_root(y); if( rx!=ry ) merge(x,y,0); else{ if( find_relation(x)==find_relation(y) ) continue; else cnt++; } } else{ int rx=find_root(x); int ry=find_root(y); if( rx!=ry ) merge(x,y,1); else{ if( (1+find_relation(y)-find_relation(x)+3)%3==0 ) continue; else cnt++; } } } } printf("%d\n",cnt); return 0; }
POJ 1417 True Liars
背包+进阶并查集
按关系并查集做那么最后会得到多个集合,其中每个集合中每两个人的互相关系已知(比如一共sum个人,那与root关系为0的有sum1个,与root关系为1的有sum2个,满足sum=sum1+sum2)那可能有sum1个圣人,也可能有sum2个,我们不知道。但这个集合要么为圣人做出sum1个人头的贡献,要么做出sum2个人头的贡献。那就变成了x个集合,每个集合有s1,s2,看能不能从每个集合里都取一个数最终凑成p1。那这不就是变成了个背包问题吗?能不能从前x种商品里恰好凑出p1(每种商品二选一买一个)

//#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<cstring> #include<algorithm> #define inf 2e9 #define maxnode 200000 #define ll long long #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) const int mod = 10007; const int maxn = 1e3 + 10; int dx[4]={0,0,1,-1}; int dy[4]={1,-1,0,0}; using namespace std; int par[maxn],relation[maxn];//relation[i]是i与祖先的关系 //0代表一样,1代表不一样 int find_root(int a){ if( par[a]==a ) return par[a]; int root = find_root(par[a]); relation[a] += relation[ par[a] ];//得先改sum relation[a]%=2; par[a]=root; return root; } int a[maxn][2];//a[i][0]代表第i个大集合中有多少个在一个集合,a[i][1]代表第i个大集合中有多少个在另一个集合 int used[maxn]; vector<int> b[maxn][2];//代表i大集合里的0所代表小集合里有谁 int dp[maxn][maxn],pre[maxn][maxn];//dp[i][j]代表前i个大集合凑出j个数的方案,答案是dp[cnt][p1] //pre[i][j]记录第i个大集合选了0还是1 int main(){ //freopen("1.in","r",stdin); int n,p1,p2,relate; while(1){ scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&p1,&p2); if( n==0 && p1==0 && p2==0 ) break; for(int i=1;i<=p1+p2;i++){ par[i]=i; relation[i]=0; } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ int x,y; scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); char s[10]; scanf("%s",s); if( s[0]=='n' ) relate=1; else relate=0; int roota=find_root(x); int rootb=find_root(y); par[roota]=rootb; relation[roota]=(relation[y]-relation[x]+relate+2)%2; //cout<<"!!! "<<x<<" "<<y<<" "<<s<<" "<<relate<<endl; //cout<<x<<" "<<roota<<endl<<y<<" "<<rootb<<endl; } //现在分成了很多集合,每个集合又分成两个子集合,代表好人和坏人 memset(used,0,sizeof(used)); memset(a,0,sizeof(a)); for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++) b[i][0].clear(),b[i][1].clear(); int cnt=0; for(int i=1;i<=p1+p2;i++) if( !used[i] ){ cnt++; int tmp=find_root(i); for(int j=1;j<=p1+p2;j++)//遍历与i在一个大集合里的元素 if( tmp==find_root(j) ){ used[j]=1;//标记j为用过,这样大集合不会重复 a[cnt][ relation[j] ]++; b[cnt][ relation[j] ].push_back(j); } } /* for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++){ cout<<"1"<<endl; for(int j=0;j<b[i][1].size();j++) cout<<b[i][1][j]<<" "; cout<<endl; cout<<"0"<<endl; for(int j=0;j<b[i][0].size();j++) cout<<b[i][0][j]<<" "; cout<<endl; cout<<i<<" "<<a[i][0]<<" "<<a[i][1]<<endl; }*/ //开始dp memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp)); memset(pre,0,sizeof(pre)); dp[0][0]=1; for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++){ for(int j=0;j<=p1;j++){ if( j>=a[i][0] ) dp[i][j]+=dp[i-1][ j-a[i][0] ]; if( j>=a[i][1] ) dp[i][j]+=dp[i-1][ j-a[i][1] ]; if( dp[i][j]==1 ){ if( j>=a[i][0] && dp[i-1][j-a[i][0] ]==1 ) pre[i][j]=0; else pre[i][j]=1; } // cout<<"!!! "<<i<<" "<<j<<" "<<dp[i][j]<<" "<<pre[i][j]<<endl; } } if( dp[cnt][p1]==1 ){ vector<int> ans; ans.clear(); int id=cnt,p=p1; while( id ){ int choice=pre[id][p]; //cout<<id<<" "<<p<<endl; //cout<<"??? "<<choice<<endl; if( choice==1 ) for(int i=0;i<b[id][1].size();i++) ans.push_back( b[id][1][i] ); else for(int i=0;i<b[id][0].size();i++) ans.push_back( b[id][0][i] ); p-=a[id][choice]; id--; } sort(ans.begin(),ans.end()); for(int i=0;i<ans.size();i++) printf("%d\n",ans[i]); printf("end\n"); } else{ printf("no\n"); } } return 0; }
POJ 1733 Parity Game
离散化搞一下,还要注意x-1的问题。一般跟区间 [l,r] 和有关的东西都要考虑 l 减一
考验一点码力

//#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<map> #include<vector> #define inf 2e9 #define maxnode 200000 #define ll long long #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) const int mod = 10007; const int maxn = 1e4 + 10; int dx[4]={0,0,1,-1}; int dy[4]={1,-1,0,0}; using namespace std; int par[maxn],relation[maxn]; int find_root(int a){ if( a==par[a] ) return par[a]; int root = find_root(par[a]); relation[a] += relation[ par[a] ]; relation[a]%=2; return par[a] = root; } //even浠h〃0锛宱dd浠h〃1 int x[5010],y[5010]; char a[5050][10]; vector<int> p; map<int,int> mp; int main(){ //绂绘暎鍖? //ios::sync_with_stdio(false); int n; while( scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF ){ int m; scanf("%d",&m); p.clear(); mp.clear(); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) scanf("%d%d%s",x+i,y+i,a[i]); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) p.push_back(x[i]-1),p.push_back(y[i]); sort(p.begin(),p.end()); p.erase( unique(p.begin(),p.end()),p.end() ); //for(int i=0;i<p.size();i++) cout<<p[i]<<" "; cout<<endl; for(int i=0;i<p.size();i++) mp[ p[i] ] = i+1;//绂绘暎鍖? for(int i=1;i<=p.size();i++) par[i]=i,relation[i]=0; int ans=m; for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ int rt1 = find_root( mp[x[i]-1] ); int rt2 = find_root( mp[y[i]] ); int odd=0; if( a[i][0]=='o' ) odd=1; //cout<<"!!!"<<endl; //cout<<x[i]-1<<" "<<mp[x[i]-1]<<endl<<y[i]<<" "<<mp[y[i]]<<endl<<rt1<<" "<<rt2<<" "<<odd<<endl; if( rt1!=rt2 ){ par[rt1] = rt2; relation[rt1]=(odd+relation[ mp[y[i]] ]-relation[ mp[x[i]-1] ]+2)%2; } else{ int rel = (relation[ mp[x[i]-1] ]-relation[ mp[y[i]] ]+2)%2; if( rel!=odd ){ ans=i-1; break; } } } printf("%d\n",ans); } return 0; }
POJ 1984 Navigation Nightmare
乍一看好像没啥思路,其实很简单。
将偏移量分成两个(南北 和 东西),再定义个正方向,记录就好了

//#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<map> #include<vector> #define inf 2e9 #define maxnode 200000 #define ll long long #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) const int mod = 10007; const int maxn = 4e4 + 10; int dx[4]={0,0,1,-1}; int dy[4]={1,-1,0,0}; using namespace std; int par[maxn],relation1[maxn],relation2[maxn];//偏移量有两个维度 int from[maxn],to[maxn],len[maxn]; char dir[maxn]; vector< pair<int,int> > query[maxn]; int find_root(int a){ if( a==par[a] ) return a; int root = find_root(par[a]); relation1[a] += relation1[ par[a] ]; relation2[a] += relation2[ par[a] ]; return par[a] = root; } int main(){ //ios::sync_with_stdio(false); int n,m; while( scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF){ for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) par[i]=i; memset(relation1,0,sizeof(relation1)); memset(relation2,0,sizeof(relation2)); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) query[i].clear(); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) scanf("%d%d%d %c",from+i,to+i,len+i,dir+i); int k; scanf("%d",&k); for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){ int x,y,index; scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&index); query[index].push_back( make_pair(x,y) ); } for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ //先把路加进去 //N S W E int rt1 = find_root(from[i]); int rt2 = find_root(to[i]); par[ rt1 ] = rt2; int len1,len2; if( dir[i]=='S' ) len1=-len[i],len2=0; if( dir[i]=='N' ) len1=len[i],len2=0; if( dir[i]=='W' ) len1=0,len2=-len[i]; if( dir[i]=='E' ) len1=0,len2=len[i]; /*cout<<"!!!"<<endl; cout<<from[i]<<" "<<to[i]<<" "<<endl; cout<<relation1[to[i]]<<" "<<len1<<" "<<relation1[from[i]]<<endl; cout<<relation2[to[i]]<<" "<<len2<<" "<<relation2[from[i]]<<endl;*/ relation1[ rt1 ] = relation1[ to[i] ] + len1 - relation1[ from[i] ]; relation2[ rt1 ] = relation2[ to[i] ] + len2 - relation2[ from[i] ]; //cout<<relation1[rt1]<<" "<<relation2[rt1]<<endl; //处理询问 for(int j=0;j<query[i].size();j++){ int x = query[i][j].first, y = query[i][j].second; int rootx = find_root(x), rooty = find_root(y); if( rootx!=rooty ) printf("-1\n"); else{ int ans= abs(relation1[x]-relation1[y])+abs(relation2[x]-relation2[y]); printf("%d\n",ans); } } } } return 0; }
POJ 2492 A Bug's Life
这么水的题应该放到前面去啊

//#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<map> #include<vector> #define inf 2e9 #define maxnode 200000 #define ll long long #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) const int mod = 10007; const int maxn = 2e3 + 10; int dx[4]={0,0,1,-1}; int dy[4]={1,-1,0,0}; using namespace std; int par[maxn],relation[maxn]; int find_root(int a){ if( a==par[a] ) return a; int root = find_root(par[a]); relation[a] += relation[ par[a] ]; relation[a]%=2; return par[a] = root; } int main(){ //ios::sync_with_stdio(false); int t,tc=0; scanf("%d",&t); while(t--){ int n,m; scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) par[i]=i; memset(relation,0,sizeof(relation)); bool flag=true; for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ int x,y; scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); if( !flag ) continue; int rt1 = find_root(x),rt2 = find_root(y); if( rt1==rt2 ){ if( (relation[x]-relation[y]+2)%2!=1 ) flag=false; } else{ par[rt1]=rt2; relation[rt1] = ( relation[y]+1-relation[x] )%2; } } printf("Scenario #%d:\n",++tc); if( flag ) printf("No suspicious bugs found!\n"); else printf("Suspicious bugs found!\n"); printf("\n"); } return 0; }
POJ 2912 Rochambeau
我原本以为并查集就不能暴力了,哈哈哈,结果这道题要暴力一下,我服了哈哈哈
脑回路比较清奇
与其在发生冲突的时候想哪个人可能是coach(实际上是想不到的,因为集合里的人都可能是),他这个是枚举每个人是coach的情况。
那么如果你是个合法的coach的话,那就把有你参加的round全部扔掉,然后看其他的是不是自洽。(就是食物链有木有!)
如果出现多个合法coach那就can't determine;如果没有合法coach那就impossible;如果一个coach,那就说明其他人是coach的时候都会不合法,看其他人最晚是在哪个line都被淘汰的。帅的么

//#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<cstring> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<map> #include<vector> #define inf 2e9 #define maxnode 200000 #define ll long long #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) const int mod = 10007; const int maxn = 5e2 + 10; int dx[4]={0,0,1,-1}; int dy[4]={1,-1,0,0}; using namespace std; int par[maxn],relation[maxn]; int find_root(int a){ if( a==par[a] ) return a; int root = find_root( par[a] ); relation[a]+=relation[par[a]]; relation[a]%=3; return par[a]=root; } int x[2010],y[2010],d[2010]; //小于是1 //相等是0 //大于是2 int main(){ //离散化 //ios::sync_with_stdio(false); int n,m; while( scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF ){ if(m==0){ if(n==1) printf("Player 0 can be determined to be the judge after 0 lines\n"); else printf("Can not determine\n"); continue; } for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ char op; scanf("%d%c%d",x+i,&op,y+i); if( op=='<' ) d[i]=1; else if(op=='=') d[i]=0; else d[i]=2; } int cnt=0,coach;//多少个合法coach int last=0;//最后的冲突line for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ memset(relation,0,sizeof(relation)); for(int j=0;j<n;j++) par[j]=j; for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){ if( x[j]==i || y[j]==i ){ if(j==m) { cnt++; coach=i; } continue; } int rootx = find_root(x[j]); int rooty = find_root(y[j]); if( rootx!=rooty ){ par[rootx]=rooty; relation[rootx] = (d[j]+relation[y[j]]-relation[x[j]]+3)%3; } else{ int rel = (relation[x[j]]-relation[y[j]]+3)%3; if( rel!=d[j] ) { last=max(last,j); break; } } if(j==m) { cnt++; coach=i; }//有了合法coach } } if( cnt==0 ) printf("Impossible\n"); else if(cnt==1) printf("Player %d can be determined to be the judge after %d lines\n",coach,last); else printf("Can not determine\n"); } return 0; }
ZOJ 3261 Connections in Galaxy War
这道题也好骚啊,我一开始看要做逆操作直接懵了。
实际上思路也确实很妙啊,离线一下反向回答询问就行了

#include<stdio.h> #include<cstring> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<map> #include<vector> #define inf 2e9 #define maxnode 200000 #define ll long long #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) const int mod = 10007; const int maxn = 1e4 + 10; int dx[4]={0,0,1,-1}; int dy[4]={1,-1,0,0}; using namespace std; int par[maxn],p[maxn]; int find_root(int a){ if( a==par[a] ) return a; return par[a]=find_root( par[a] ); } int x[2*maxn],y[2*maxn]; int op[5*maxn],i1[5*maxn],i2[5*maxn];//1是询问,0是摧毁 map<int,int> mp[maxn]; vector<int> ans; int main(){ //离散化 //ios::sync_with_stdio(false); int n; bool first=true; while( scanf("%d",&n)==1 ){ if(first) first=false; else printf("\n"); ans.clear(); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",p+i); int m; scanf("%d",&m); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) scanf("%d%d",x+i,y+i); for(int i=0;i<=n;i++) mp[i].clear(); for(int i=0;i<=n;i++) par[i]=i; int q; scanf("%d",&q); for(int i=1;i<=q;i++){ char a[10]; scanf("%s",a); if( a[0]=='q' ) op[i]=1; else op[i]=0; if(op[i]) scanf("%d",i1+i); else { scanf("%d%d",i1+i,i2+i); mp[ i1[i] ][ i2[i] ] = 1; mp[ i2[i] ][ i1[i] ]=1; } // cout<<"!!!"<<a<<" "<<op[i]<<" "<<i1[i]<<" "<<i2[i]<<endl; } //把所有未摧毁的tunnel连起来 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ if( mp[x[i]][y[i]] ) continue; int rootx = find_root(x[i]);//x[i]所能联系到的最大星系 int rooty = find_root(y[i]); if( p[rootx]==p[rooty] ){//用编号小的 if(rootx<=rooty) par[rooty]=rootx; else par[rootx]=rooty; } else if( p[rootx]<p[rooty] ) par[rootx] = rooty; else if( p[rootx]>p[rooty] ) par[rooty] = rootx; } for(int i=q;i>=1;i--){//逆向处理所有操作 if( op[i] ){//询问 int root = find_root(i1[i]); if( p[root]>p[i1[i]] ) ans.push_back(root); else ans.push_back(-1); } else{ int rootx = find_root(i1[i]);//x[i]所能联系到的最大星系 int rooty = find_root(i2[i]); if( p[rootx]==p[rooty] ){//用编号小的 if(rootx<=rooty) par[rooty]=rootx; else par[rootx]=rooty; } else if( p[rootx]<p[rooty] ) par[rootx] = rooty; else if( p[rootx]>p[rooty] ) par[rooty] = rootx; } } for(int i=ans.size()-1;i>=0;i--) printf("%d\n",ans[i]); } return 0; }
POJ 1308 Is It A Tree?
就是并查集在找环时的应用,再考虑一下自环和空树就行了。
代码写的比较丑

#include<stdio.h> #include<cstring> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<map> #include<vector> #define inf 2e9 #define maxnode 200000 #define ll long long #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) const int mod = 10007; const int maxn = 1e5 + 10; int dx[4]={0,0,1,-1}; int dy[4]={1,-1,0,0}; using namespace std; int par[maxn],vis[maxn]; int find_root(int a){ if( a==par[a] ) return a; return par[a]=find_root( par[a] ); } int main(){ //离散化 //ios::sync_with_stdio(false); int tc=0; while(1){ memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); int num=0,len=0; for(int i=1;i<=maxn-10;i++) par[i]=i; int l,r; scanf("%d%d",&l,&r); if(l==-1 && r==-1) break; if(l==0 && r==0) { printf("Case %d is a tree.\n",++tc); continue; } if(l==r) { vis[l]=1; num=1; len=1; } else{ par[l]=r; vis[l]=vis[r]=1; num=2; len=1; } bool flag=true;//回答yes while(1){ int x,y; scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); if(x==0 && y==0) break; if(!flag) continue; int rootx = find_root(x); int rooty = find_root(y); if(rootx!=rooty){ par[rootx]=rooty; if(!vis[x]) { num++; vis[x]=1; } if(!vis[y]) { num++; vis[y]=1; } len++; } else flag=false; } if(flag){ if( len==num-1 ) printf("Case %d is a tree.\n",++tc); else printf("Case %d is not a tree.\n",++tc); } else printf("Case %d is not a tree.\n",++tc); } return 0; }
NOIP2010 关押罪犯
用并查集的情况下有两种做法,难的做法是对第i个囚犯再对应一个点为i+n,那么与i+n在一个集合里的人都不跟i在一个监狱(画画图就能理解了),这样就巧妙的解决了即便知道两个罪犯要分开,但不知道哪个罪犯进哪个监狱的问题;
另一种做法就超简单,用关系并查集,1代表不在一个监狱,0代表在一个监狱,然后一直做到冲突为止

//#include<bits/stdc++.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<map> #include<vector> #define inf 2e9 #define maxnode 200000 #define ll long long #define lowbit(x) (x&(-x)) const int mod = 10007; const int maxn = 2e4 + 10; int dx[4]={0,0,1,-1}; int dy[4]={1,-1,0,0}; using namespace std; int par[maxn],relation[maxn]; struct node{ int x,y,v; }nodes[100000+10]; bool cmp(node n1,node n2){ return n1.v>n2.v; } int find_root(int a){ if( a==par[a] ) return a; int root = find_root(par[a]); relation[a] += relation[ par[a] ]; relation[a]%=2; return par[a] = root; } int main(){ //ios::sync_with_stdio(false); int n,m; scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) par[i]=i; memset(relation,0,sizeof(relation)); for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) scanf("%d%d%d",&nodes[i].x,&nodes[i].y,&nodes[i].v); sort(nodes+1,nodes+1+m,cmp); //1不在一个监狱,0在一个监狱 for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ int x=nodes[i].x,y=nodes[i].y; int rt1 = find_root(x),rt2 = find_root(y); if( rt1==rt2 ){ if( (relation[x]-relation[y]+2)%2!=1 ) { printf("%d\n",nodes[i].v); return 0; } } else{ par[rt1]=rt2; relation[rt1] = ( relation[y]+1-relation[x] )%2; } } printf("0\n"); return 0; }




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步