Educational Codeforces Round 104 (Rated for Div. 2) A~E题解
写在前边
A. Arena
链接:A题链接
题目大意:
给定一个长度为n的数组,表示n个英雄的初始积分,任意选两英雄作战,积分高的获胜,同时积分高的那个积分还会增加1,问有多少个英雄可以获胜。
思路:
明显,最低分的那个英雄永无出头之日,所以只需要排个序,让其他英雄与最低分的英雄作战即可。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#define Inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define PII pair<int, int>
#define P2LL pair<long long, long long>
#define endl '\n'
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef vector<long long> VLL;
typedef vector<int> VI;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b) {
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
const int N = 110;
int a[N];
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> a[i];
sort(a, a + n);
int res = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--) {
if (a[i] > a[0]) res++;
}
cout << res << endl;
}
int main()
{
//ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
B. Cat Cycle
链接:B题链接
题目大意:
一只大猫一只小猫不停的换位置睡觉,大猫的睡觉位置变化为n,n−1,n−2,...,1,小猫的睡觉位置变化为1,2,3,...,n−1,n−2,小猫不能和大猫睡到一起,一旦遇见小猫必须跳过当前位置到下一个位置,即如果在1遇到大猫,那么应该立即跳到2,求在两者各自移动k个位置后小猫在哪个位置。
思路:
可以看成两只猫背靠背朝反方向移动,如果是偶数,那么两者永远不会相遇,如果是奇数,那么很神奇的是每⌊n2⌋步两者就会相遇,那么小猫需要跳一步,更神奇的是这时两者又背靠背挨着了,向反方向移动,即小猫恰好在大猫后一个数,换句话说,就是说小猫每⌊n2⌋就会多跳一步那么令t=n2为一个周期,那么小猫就多跳了⌊kt⌋步,所以它处于的位置就是(k+⌊kt⌋)modn
那么把两种情况融合就是:
还有一个细节就是,上面公式只适合从0开始索引,如果像本题这样从1开始索引,那么可以先让k减1,然后modn后再加1,看下面代码。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#define Inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define PII pair<int, int>
#define P2LL pair<long long, long long>
#define endl '\n'
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef vector<long long> VLL;
typedef vector<int> VI;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b) {
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
void solve() {
int n, k;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &k);
k--;
if (n % 2 == 0) {
printf("%d\n", k % n + 1);
return;
}
int t = n / 2; //一个周期
printf("%d\n", (k + k / t) % n + 1);
}
int main()
{
//ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
C. Minimum Ties
链接:C题链接
题目大意:
有n支队伍,要进行n∗(n−1)2场比赛,即比如有3支队伍,有1-2,1-3,2-3三场比赛,胜者得3分,平局各得1分,败者不得分,现在要求我们通过让他们之间进行最少的平局使得所有队伍获得相同的分数。
思路:
首先明白,如果没有平局得情况下,那么所有队伍得分和为sum=3∗n∗(n−1)2,那么对于有奇数支队伍的时候,sum可以被n整除,所以对于奇数支来说,就让他们输赢对半分即可,把它们看成一个图上的几个点,当前队伍赢得它前边⌊n2⌋支队伍,输给其他队伍,那么这样就构成了一个欧拉图(明天补),假如有五支队伍,一个点的出边所连的点表示他干掉的队伍,指向它的点表示干掉它的队伍,那么构造答案即可。
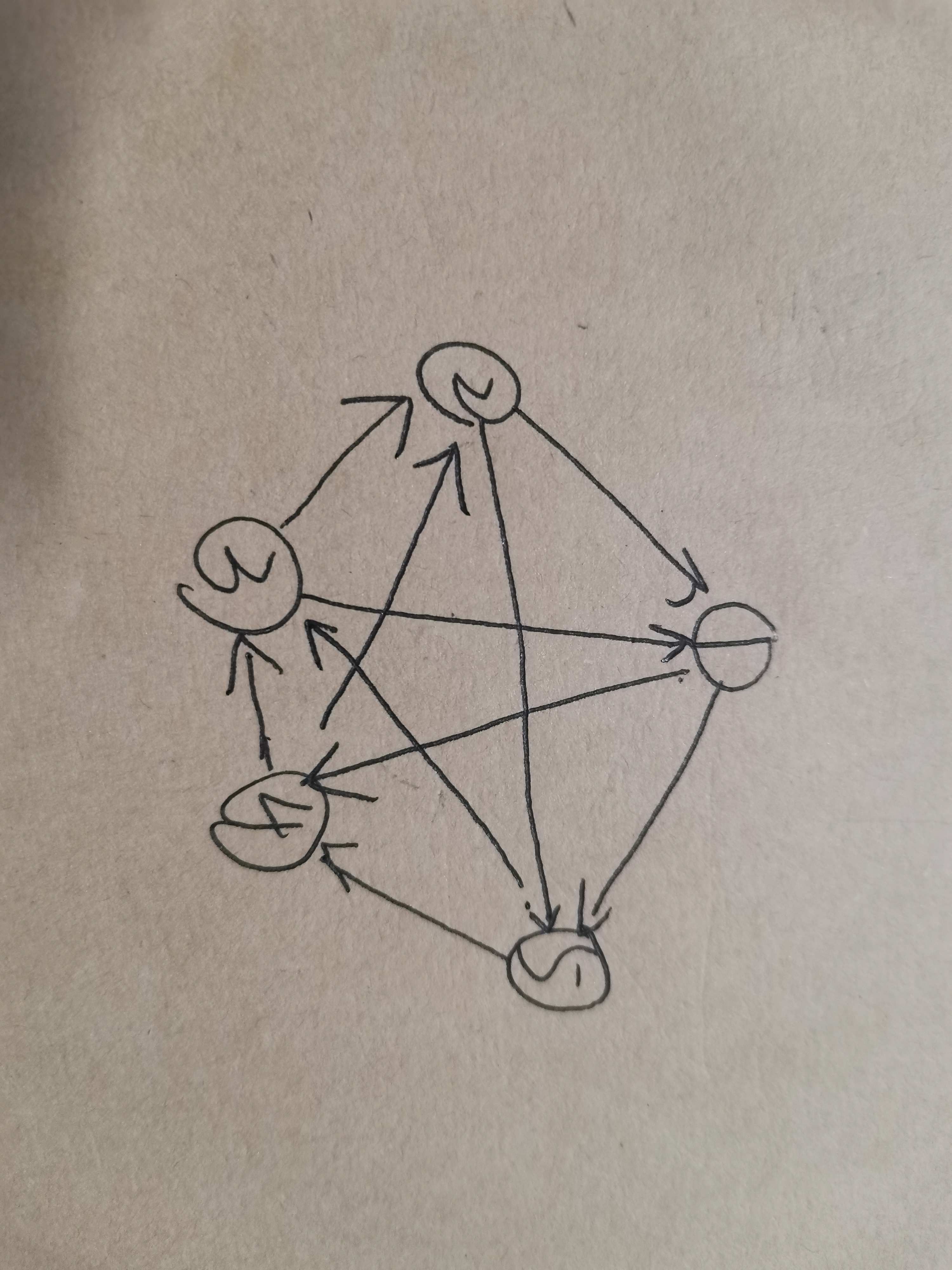
对于n为偶数情况下,是不能这样搞的,因为会发现sum无法被n整除,所以我们可以通过让它们之间产生平局来使sum被n整除,假设产生t个平局,一个平局则让总分减少1,那么要使得3n(n−1)2−t被n整除,可得t=n/2,因为(3n(n−1)2+2n)modn=n2,注意这里加2n再取模是为了让余数得到正数(刚学到的技巧),同时只有n为偶数时这种情况下的公式才可以成立,不然得到−n2就意味着我们需要给总分加分,显然不合理。这样之后我们就知道,需要进行n2场平局,那么还是可以看成一个图,让每个队伍战胜它前边第n2支队伍前的队伍,输掉它后边第n2支队伍后的队伍,对于恰好它前边恰好第n2支队伍打成平局,那么这样平局恰好是n2场。
构造答案即可。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#define Inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define PII pair<int, int>
#define P2LL pair<long long, long long>
#define endl '\n'
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef vector<long long> VLL;
typedef vector<int> VI;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b) {
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
if (n % 2 == 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (j - i <= n / 2) {
cout << 1 << " ";
} else {
cout << -1 << " ";
}
}
}
puts("");
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (j - i < n / 2) {
cout << 1 << " ";
} else if (j - i == n / 2) {
cout << 0 << " ";
} else {
cout << -1 << " ";
}
}
}
puts("");
}
}
int main()
{
//ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
D. Pythagorean Triples
链接:D题链接
题目大意:
找出一个三元组1≤a≤b≤c≤n,使得满足c2=a2+b2与c=a2−b。
思路:
推公式,两方程联立得:c(c−1)=b(b+1),那么可得c=b+1,那么带入c=a2−b得到a2=2b+1。那么可以看出,有唯一b对应唯一的奇数a2(≥3),那么我们就枚举所有的a即可,同时要求c<n,即要求b<n−1,那么,a2最多就到2∗n−1即可。复杂度约为O(√n)
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
#define Inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define PII pair<int, int>
#define P2LL pair<long long, long long>
#define endl '\n'
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef vector<long long> VLL;
typedef vector<int> VI;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b) {
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
void solve() {
int res = 0, n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 3; i * i <= 2 * n - 1; i += 2) res++;
printf("%d\n", res);
}
int main()
{
//ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--) {
solve();
}
return 0;
}
E. Cheap Dinner
链接:E题链接
题目大意:
有四类菜,每类菜又有多种,给定它们的价格,同时在第一类与第二类,第二类与第三类,第三类与第四类之间还存在冲突,我们从四类菜种各选一类菜,要求它们之间不能有冲突,并且我们花费的价格最小。
思路:
本质就是数字三角形DP吧,不过不一样的是这题加了一下限制。
用dp[i][j]表示走到第i类菜的第j道菜获得的最小代价,所以得到方程就是:
而我们要快速得到最优的dp[i−1][k],肯定不能用枚举的方式,可以用map来存所用到的每一类菜价格,同时记录关联,有关联的菜品会先从map中删除,由于map会自动排序,那么map中剩余的第一个元素就是我们所需要的。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
#include <cstring>
//#pragma GCC optimize(2)
//#pragma GCC optimize(3,"Ofast","inline")
using namespace std;
#define Inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define PII pair<int, int>
#define P2LL pair<long long, long long>
#define endl '\n'
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
typedef vector<long long> VLL;
typedef vector<int> VI;
const int Mod = 10000007;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b) {
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
const int N = 150010;
const int INF = 1e9;
int n[5];
int dish[5][N];
vector<int> relation[5][N];
void solve() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) scanf("%d", &n[i]);
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n[i]; j++) {
scanf("%d", &dish[i][j]);
}
}
int m;
for (int i = 2; i <= 4; i++) {
scanf("%d", &m);
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
int v1, v2;
scanf("%d%d", &v1, &v2);
relation[i][v2].push_back(v1); //后一类的第v2道菜与前一类的第v1道有关联
}
}
for (int i = 2; i <= 4; i++) { //从第二类菜开始处理
map<int, int> st; //map有自动排序功能
for (int j = 1; j <= n[i - 1]; j++) st[dish[i - 1][j]]++; //预处理前一类菜的价格
for (int j = 1; j <= n[i]; j++) {
for (auto &k : relation[i][j]) {
st[dish[i - 1][k]]--; //删去有关联的
if (!st[dish[i - 1][k]]) st.erase(dish[i - 1][k]);
}
if (st.size()) dish[i][j] += st.begin()->first;
else dish[i][j] = INF;
for (auto &k : relation[i][j]) st[dish[i - 1][k]]++; //恢复
}
}
int res = INF;
for (int i = 1; i <= n[4]; i++) {
res = min(res, dish[4][i]);
}
if (res == INF) puts("-1");
else printf("%d\n", res);
}
int main()
{
//ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(nullptr), cout.tie(nullptr);
solve();
return 0;
}



【推荐】还在用 ECharts 开发大屏?试试这款永久免费的开源 BI 工具!
【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(下)
· 从二进制到误差:逐行拆解C语言浮点运算中的4008175468544之谜
· .NET制作智能桌面机器人:结合BotSharp智能体框架开发语音交互
· 软件产品开发中常见的10个问题及处理方法
· .NET 原生驾驭 AI 新基建实战系列:向量数据库的应用与畅想
· C# 13 中的新增功能实操
· Ollama本地部署大模型总结
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(4)
· 2025成都.NET开发者Connect圆满结束
· langchain0.3教程:从0到1打造一个智能聊天机器人