20162329 2017-2018-1 《程序设计与数据结构》第七周学习总结
20162329 2017-2018-1 《程序设计与数据结构》第七周学习总结
教材学习内容总结
一.学习目标
-
理解树抽象数据类型
-
会用树解决问题
-
掌握树的遍历方法
-
掌握二叉树的实现(数组,链表)
-
会用二叉树表示决策树
-
分析Java Collections API中树相关的类
二.学习内容
1.树
由一组节点及一组边构成,节点用来保存元素,边表示节点之间的连接。每一个节点都处在树的某一层中。树的根是树的最顶层中唯一的结点。树中只有唯一的根节点。通常分为一般树和二叉树,二叉树更为常用。
2.树的遍历
树的遍历有五种方法:
- 先序遍历 —— 访问根,自左至右遍历子树。
- 中序遍历 —— 先遍历左子树,然后访问根,然后自左至右遍历余下的各个子树。
- 后序遍历 —— 自左至右遍历各子树,然后访问根。
- 层序遍历 —— 从树的顶层即根开始,每一层从左至右,访问树中每层的每个节点。
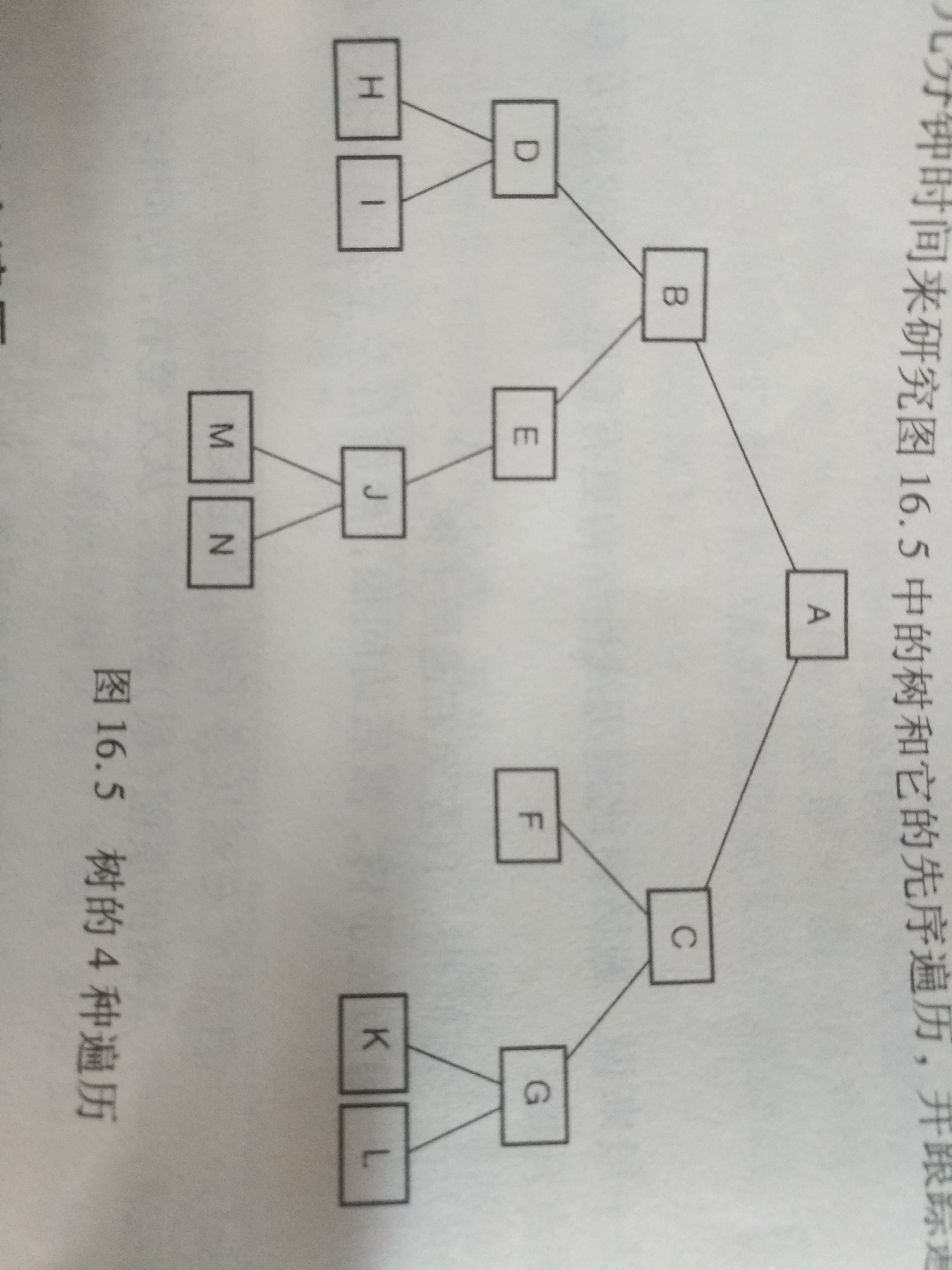
如图遍历结果如下:
先序:ABDHIEJMNCFGKL
中序:HDIBEMJNAFCKGL
后序:HIDMNJEBFKLGCA
层序:ABCDEFGHIJKLMN
3.树的实现策略
因为树是非线性结构,用数组实现树的话是非常繁琐的,所以多用链式结构来实现树,但是数组实现树也不是不可能的。
-
数组实现树策略
1.数组计算链:
将位于位置n的元素的左孩子放置在数组(2n+1)的位置,其右孩子放在(2 X (n + 1))的位置。
2.在数组中保存链:
以数组队列的方式将树中每个元素的引用存在数组中,元素储存的顺序以他们入树的顺序来决定。
4.二叉树的实现
-
书上已经给出了一个二叉树的接口,然后根据接口又给出了部分代码,我们只需要根据书上给的实例在未实现的方法中加入相应的逻辑就可以了。
具体接口代码如下:public interface BinaryTree<T> extends Iterable<T> { // Returns the element stored in the root of the tree. public T getRootElement() throws Exception; // Returns the left subtree of the root. public BinaryTree<T> getLeft() throws Exception; // Returns the right subtree of the root. public BinaryTree<T> getRight() throws Exception; // Returns true if the binary tree contains an element that // matches the specified element and false otherwise. public boolean contains (T target) throws Exception; // Returns a reference to the element in the tree matching // the specified target. public T find (T target) throws Exception; // Returns true if the binary tree contains no elements, and // false otherwise. public boolean isEmpty(); // Returns the number of elements in this binary tree. public int size(); // Returns the string representation of the binary tree. public String toString(); // Returns a preorder traversal on the binary tree. public ArrayList<T> preorder(); // Returns an inorder traversal on the binary tree. public ArrayList<T> inorder(); // Returns a postorder traversal on the binary tree. public ArrayList<T> postorder(); // Performs a level-order traversal on the binary tree. public ArrayList<T> levelorder() throws Exception; }
三.学习中遇到的问题
问题1:
在本章的学习中,最重要的部分莫过于二叉树的实现,在实现的过程中,根据书上伪代码所给出的逻辑,其他的方法都很好实现,就是在一个地方我很疑惑。
如下图: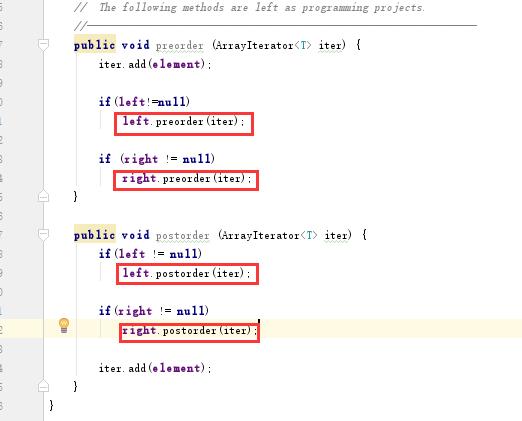
该方法是树的一个递归的遍历方法,在方法体中书上是这样写的,而我经过思考认为,红线标注的地方应该返回出left或者right的下一个指针,而书上却递归的传入了一个迭代器的方法这是让我不能理解的。
解决办法:
我四处问了一下同学,看到刘伟康同学的方法是将所有的ArrayIterator类都替换成了ArrayList类,代码是完成了但是并没有经过测试,目前不清楚是否可以运行。
结对及互评
本周并没有在结对方面有什么合作项目
点评模板:
- 博客中值得学习的或问题:
- 界面很好看
- 问题分析可以更详细
- 其他
希望我们结对在这学期能相互促进,技术更上一层楼。
本周结对学习情况
- [20162302](博客链接)
- 结对学习内容
- 一起讨论学习。
四.代码托管
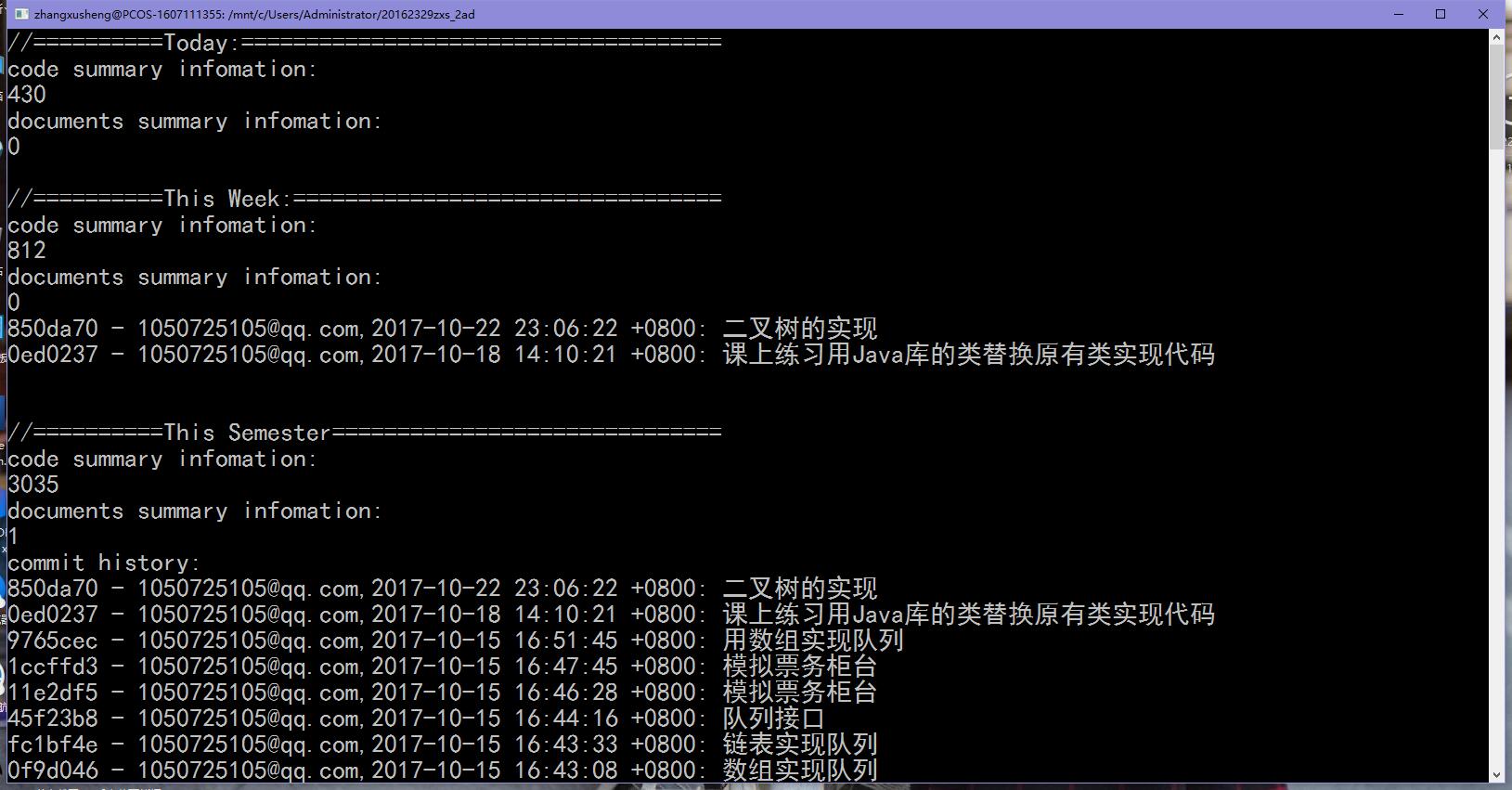
其他
本学期的课程已经进半,大项目即将开始,但是我对于Android方面还不是很熟悉,还需要进一步学习,希望接下来的自己能有更大的进步!
学习进度条
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积) | 学习时间(新增/累积) | 重要成长 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标 | 5000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 | |
| 第一周 | 0/0 | 1/2 | 10/20 | 了解数据结构及算法 |
| 第二周 | 664/664 | 2/3 | 10/20 | 系统的学习了查找和排序 |
| 第五周 | 1333/1997 | 2/5 | 15/60 | 栈数据结构的学习 |
| 第七周 | 812/3035 | 15/80 | 树的学习和实现 |



