spring-boot 2.5.4,nacos 作为配置、服务发现中心,Cloud Native Buildpacks 打包镜像,GitLab CI/CD
spring-boot 2.5.4,nacos 作为配置、服务发现中心,Cloud Native Buildpacks 打包镜像,GitLab CI/CD
本文主要介绍 Java 通过 Cloud Native Buildpacks 打包镜像,通过 Gitlab 配置 CI/CD。以及使用 nacos 作为配置中心,使用 grpc 作为 RPC 框架。
前置条件:
spring-boot gradle 插件
spring-boot gradle 插件在 gradle 中提供 spring-boot 支持。该插件可以打 jar 或者 war 包。
plugins {
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '2.5.4'
}
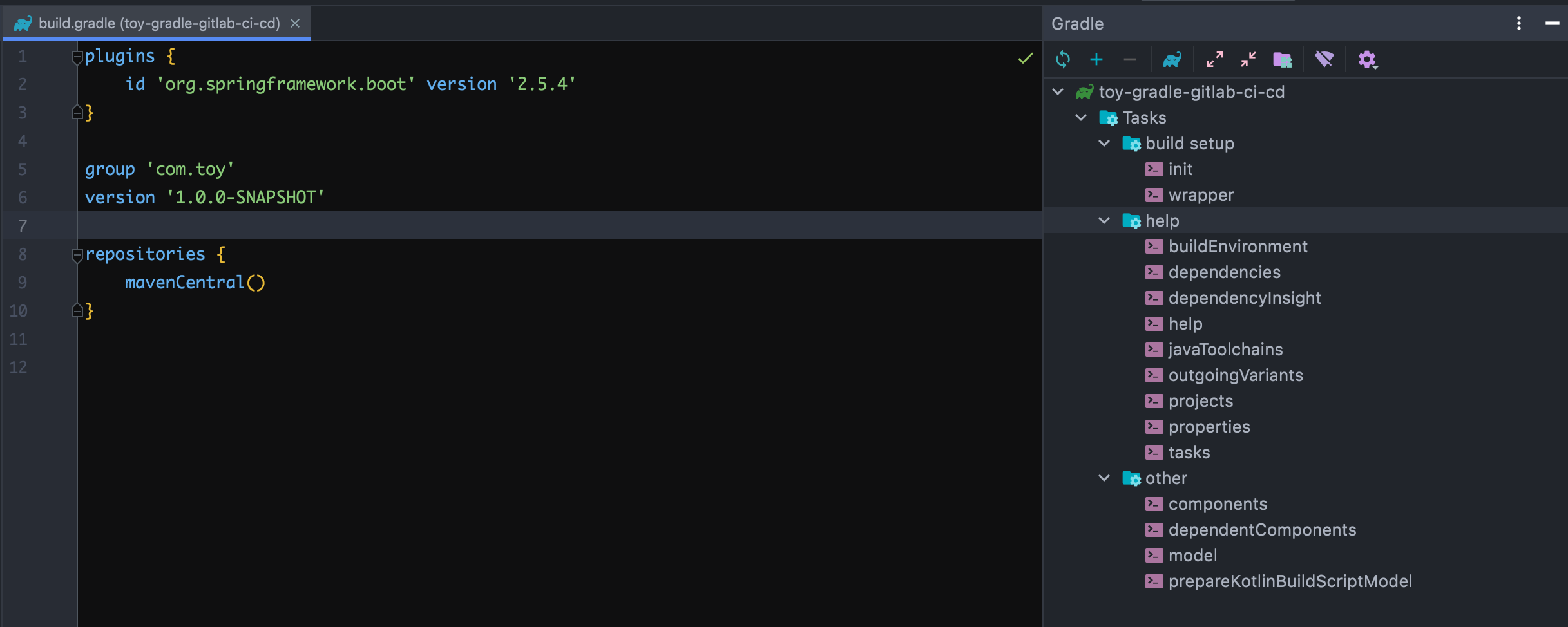
新建一个 gradle 项目,该项目在只引用 id 'org.springframework.boot' version '2.5.4' 插件的情况下,gralde 任务分布完全没有变化,如下图所示。
引入 java 插件
plugins {
id 'java'
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '2.5.4'
}
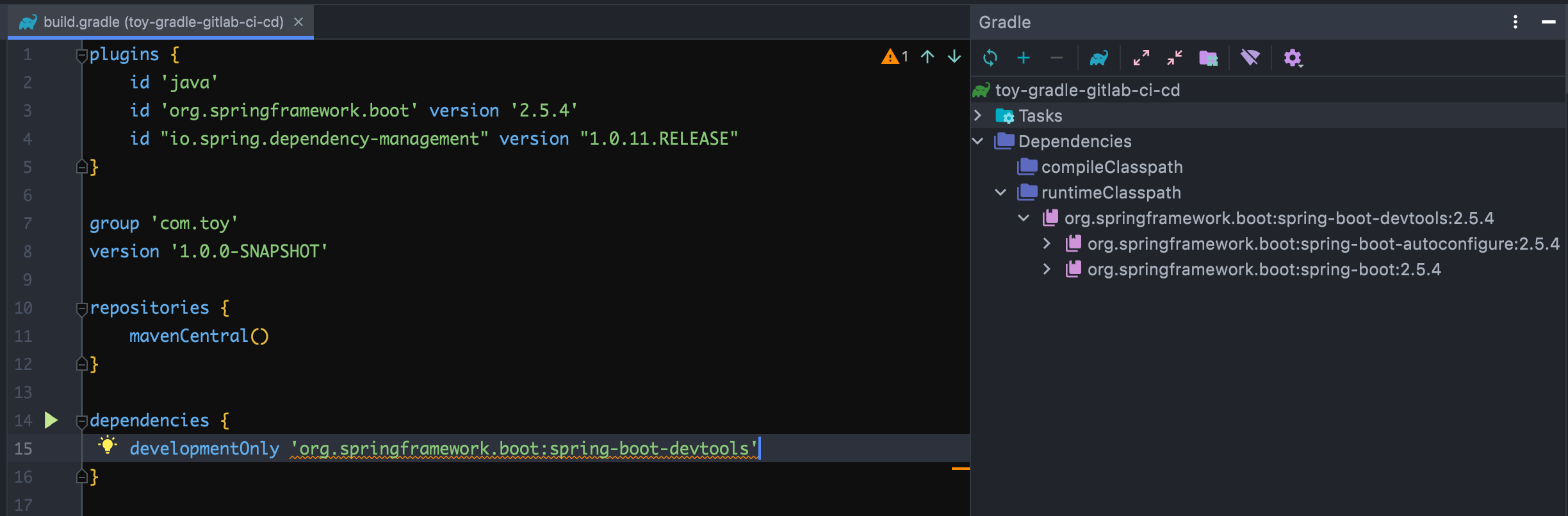
但当引入 java 插件后,情况就大大不同了,可见,spring-boot 插件和 java 插件一起应用后,将产生如下反应:
-
创建
bootJar任务,执行该任务会生成一个 fat jar。该 jar 包把所有的类文件打包进BOOT-INF/classes中,把项目依赖的所有 jar 包打包进BOOT-INF/lib中。 -
配置
assemble任务,该任务依赖于bootJar任务,所以执行assemble任务的时候也会执行bootJar。 -
配置
jar任务,该任务可以配置 jar 包的classifier。配置方式如下,默认情况下 classifier 为空字符串:bootJar { classifier = 'boot' } jar { classifier = '' } -
创建
bootRun任务用于运行应用程序。 -
创建
bootArchives配置,注意这里是配置,不是任务。当应用maven插件时会为bootArchives配置创建uploadBootArchives任务。bootArchives默认情况下包含bootJar或bootWar任务生成的文件。uploadBootArchives { repositories { mavenDeployer { repository url: 'https://repo.example.com' } } } -
创建
developmentOnly配置。该配置用于管理开发时的依赖,比如org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-devtools,该依赖仅在开发时使用,无需打进 jar 包中。dependencies { developmentOnly 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-devtools' } -
创建
productionRuntimeClasspath配置。它等价于runtimeClasspath中的依赖减去developmentOnly配置中的依赖。 -
配置
JavaCompile任务默认使用UTF-8。 -
配置
JavaCompile任务使用-parameters配置编译器参数。
引入 io.spring.dependency-management 插件
引入该插件后,将自动管理依赖版本。
plugins {
id 'java'
id 'org.springframework.boot' version '2.5.4'
id "io.spring.dependency-management" version "1.0.11.RELEASE"
}
group 'com.toy'
version '1.0.0-SNAPSHOT'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
developmentOnly 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-devtools'
}
引入 grpc 框架
基于本示例使用 nacos 作为服务发现中心,本示例将使用 net.devh:grpc-spring-boot-starter 依赖作为框架。
工程结构
目前为止,我们介绍了 java 项目中引入 spring gradle 所需的插件,以及各个组件的作用。接下来我们介绍如何引入 grpc,以及引入 grpc 后,我们的工程结构。
改造后工程结构总体如下:
protobuf
用于保存 proto 文件,以及发布 proto 文件,当客户端引用时,保证 jar 包最小。build.gradle 文件内容如下:
plugins {
id 'java'
id 'idea'
id 'com.google.protobuf' version '0.8.17' //google proto 插件
id 'maven-publish'
}
group 'com.toy'
version '1.0.0-SNAPSHOT'
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
//用于生成 java 类
compileOnly 'io.grpc:grpc-protobuf:1.39.0'
compileOnly 'io.grpc:grpc-stub:1.39.0'
}
protobuf {
protoc {
artifact = "com.google.protobuf:protoc:3.17.3"
}
plugins {
grpc {
artifact = 'io.grpc:protoc-gen-grpc-java:1.39.0'
}
}
generateProtoTasks {
all()*.plugins {
grpc {
}
}
}
}
publishing {
publications {
proto_package(MavenPublication) {
}
}
repositories {
maven {
allowInsecureProtocol = true
url '你的 Maven 仓库地址'
credentials {
username = 'Maven 账号'
password = 'Maven 密码'
}
}
}
}
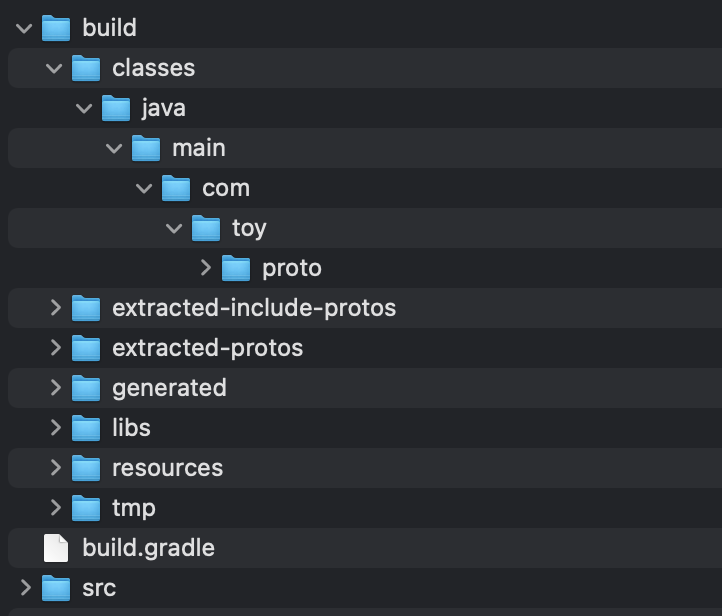
生成的 Java 类路径为 $projectName/build/.. 如下所示,生成的所有 class 文件位于 proto 文件夹下:
rpc
-
在 rpc 项目中添加启动类
ToyApplication,内容如下:package com.toy.rpc; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; /** * @author Zhang_Xiang * @since 2021/8/20 15:34:58 */ @SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = {"com.toy.*"}) public class ToyApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ToyApplication.class, args); } } -
在包
com.toy.rpc.impl中添加HelloImpl文件,内容如下:package com.toy.rpc.impl; import com.toy.proto.GreeterGrpc; import com.toy.proto.HelloReply; import com.toy.proto.HelloRequest; import io.grpc.stub.StreamObserver; import net.devh.boot.grpc.server.service.GrpcService; /** * @author Zhang_Xiang * @since 2021/8/20 15:35:56 */ @GrpcService public class HelloImpl extends GreeterGrpc.GreeterImplBase { @Override public void sayHello(HelloRequest request, StreamObserver<HelloReply> responseObserver) { HelloReply reply = HelloReply.newBuilder().setMessage("Hello " + request.getName()).build(); responseObserver.onNext(reply); responseObserver.onCompleted(); } } -
添加集成测试
(1)添加集成测试配置
package com.toy.config; import net.devh.boot.grpc.client.autoconfigure.GrpcClientAutoConfiguration; import net.devh.boot.grpc.server.autoconfigure.GrpcServerAutoConfiguration; import net.devh.boot.grpc.server.autoconfigure.GrpcServerFactoryAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.ImportAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.TestConfiguration; /** * @author Zhang_Xiang * @since 2021/8/12 16:26:25 */ @TestConfiguration @ImportAutoConfiguration({ GrpcServerAutoConfiguration.class, // Create required server beans GrpcServerFactoryAutoConfiguration.class, // Select server implementation GrpcClientAutoConfiguration.class}) // Support @GrpcClient annotation public class IntegrationTestConfigurations { }(2)添加测试类
package com.toy; import com.toy.config.IntegrationTestConfigurations; import com.toy.proto.GreeterGrpc; import com.toy.proto.HelloReply; import com.toy.proto.HelloRequest; import net.devh.boot.grpc.client.inject.GrpcClient; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test; import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest; import org.springframework.test.annotation.DirtiesContext; import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringJUnitConfig; import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals; /** * @author Zhang_Xiang * @since 2021/8/20 16:02:41 */ @SpringBootTest(properties = { "grpc.server.inProcessName=test", // Enable inProcess server "grpc.server.port=-1", // Disable external server "grpc.client.inProcess.address=in-process:test" // Configure the client to connect to the inProcess server }) @SpringJUnitConfig(classes = {IntegrationTestConfigurations.class}) @DirtiesContext public class HelloServerTest { @GrpcClient("inProcess") private GreeterGrpc.GreeterBlockingStub blockingStub; @Test @DirtiesContext public void sayHello_replyMessage() { HelloReply reply = blockingStub.sayHello(HelloRequest.newBuilder().setName("Zhang").build()); assertEquals("Hello Zhang", reply.getMessage()); } } -
build.gradle
plugins { id 'java' id 'idea' id 'org.springframework.boot' version '2.5.4' id "io.spring.dependency-management" version "1.0.11.RELEASE" } group 'com.toy' version '1.0.0-SNAPSHOT' repositories { mavenCentral() } dependencies { implementation platform('io.grpc:grpc-bom:1.39.0') //使所有 protobuf 插件的版本保持一致 implementation 'net.devh:grpc-spring-boot-starter:2.12.0.RELEASE' developmentOnly 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-devtools' implementation project(':protobuf') //引入 protobuf 项目 testImplementation 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-api:5.7.2' testRuntimeOnly 'org.junit.jupiter:junit-jupiter-engine:5.7.2' testImplementation 'io.grpc:grpc-testing' testImplementation('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test') } bootBuildImage { imageName = "harbor.xxx.com/rpc/${project.name}:${project.version}" publish = true docker { publishRegistry { username = "admin" password = "admin" url = "harbor.xxx.com" } } } test { useJUnitPlatform() }
至此,整个 grpc 项目基础结构完成。
添加 nacos 配置中心、服务发现
-
在 rpc 项目 build.gradle 文件中引入读取 nacos 配置的 jar 包和注册服务到 nacos 中的 jar 包。
dependencies{ implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web' //用于注册服务 //添加此引用的原因是为了解决 spring boot 2.5.4 无法读取 nacos 配置的问题 implementation 'org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap:3.0.3' implementation 'com.alibaba.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery:2021.1' implementation 'com.alibaba.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config:2021.1' } -
添加读取服务配置,在 rpc 项目中添加
bootstrap.propertise,内容如下:spring.profiles.active=dev spring.application.name=toy添加
bootstrap-dev.properties,内容如下:spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr=127.0.0.1:8848 spring.cloud.nacos.config.namespace=52f2f610-46f6-4c57-a089-44072099adde spring.cloud.nacos.config.file-extension=yaml spring.cloud.nacos.config.group=DEFAULT_GROUP spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.namespace=52f2f610-46f6-4c57-a089-44072099adde spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.server-addr=127.0.0.1:8848
至此,完成了服务端通过 nacos 读取配置,并且把服务端注册到 nacos 中。
gitlab CI/CD
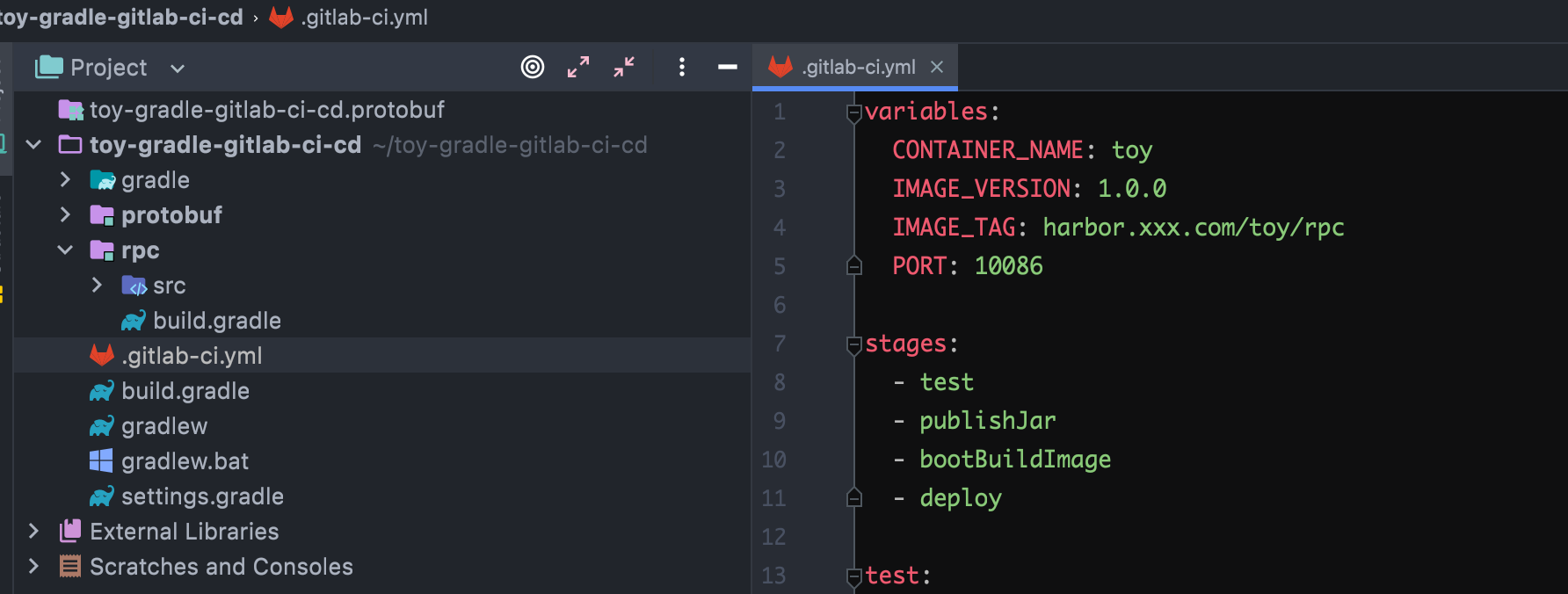
在根项目目录下添加 .gitlab-ci.yml 文件。当 gitlab 安装了 runner 后,将自动触发 CI/CD,内容如下:
variables:
CONTAINER_NAME: toy
IMAGE_VERSION: 1.0.0
IMAGE_TAG: harbor.xxx.com/toy/rpc
PORT: 10086
stages:
- test
- publishJar
- bootBuildImage //spring-boot 从 2.3.0 版本以后引入了 BootBuildImage 任务。
- deploy
test:
stage: test
script:
- gradle clean
- gradle rpc:test
publishProtoBuf:
stage: publishJar
script:
- gradle protobuf:publish
bootBuildImage:
stage: bootBuildImage
script:
- gradle rpc:bootBuildImage
deployDev:
stage: deploy
script:
- ssh $SERVER_USER@$SERVER_IP "docker login --username=$REGISTERY_NAME --password=$REGISTRY_PWD harbor.xxx.com; docker pull $IMAGE_TAG:$IMAGE_VERSION;"
- ssh $SERVER_USER@$SERVER_IP "docker container rm -f $CONTAINER_NAME || true"
- ssh $SERVER_USER@$SERVER_IP "docker run -d -p $PORT:$PORT -e JAVA_OPTS='-Xms512m -Xmx512m -Xss256K' --net=host --name $CONTAINER_NAME $IMAGE_TAG:$IMAGE_VERSION"
when: manual
这几个步骤什么意思呢?
- 定义项目级别的变量
- 定义了 4 个步骤,其中每个步骤中的任务又是可以并行的
- test:运行项目中的单元测试(项目中没有写单元测试)、集成测试
- publishJar:发布项目中 protobuf 项目到私有 maven 仓库中
- bootBuildImage:打包镜像,并根据配置发布到镜像仓库中,这里打包过程需要详细说明
- deploy:部署镜像到远程服务器中,在此步骤中配置了
when:manual,意思是手动触发此步骤
注意: 这里 SERVER_USER、SERVER_IP、$REGISTERY_NAME 和 $REGISTRY_PWD 在 Gitlab 中通过超级管理员做了全局配置,即在所有项目中都可以使用。
定义 gitlab CI/CD 变量
CI/CD 变量一共有 4 种定义方式,如下:
变量优先级(从高到低)
- 触发变量、流水线变量、手动流水线变量
- 项目变量
- 组变量
- 全局变量
- 继承变量
.gitlab-ci.yml文件中,job 中定义的变量.gitlab-ci.yml中定义的变量,job 外的变量- 部署变量
- 预定义变量
作者:Zhang-Xiang
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/Zhang-Xiang/p/15176081.html
版权:本作品采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际」许可协议进行许可。






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· DeepSeek如何颠覆传统软件测试?测试工程师会被淘汰吗?