题目集4、5及期中考试总结
-
前言:
-
设计与分析:
-
第四次作业
- 用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与四边形有关的计算。
以下四边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是四边形、平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。
2:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是菱形、矩形、正方形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
3:输入四个点坐标,判断是凹四边形(false)还是凸四边形(true),输出四边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
4:输入六个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后四个点构成一个四边形或三角形,输出直线与四边形(也可能是三角形)相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出四边形(或三角形)被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与四边形或三角形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形的输入,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
后四个点构成三角形的情况:假设三角形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z 不与xy都相邻,如z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
5:输入五个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后四个点所构成的四边形(限定为凸四边形,不考虑凹四边形)或三角形(判定方法见选项4)的内部(若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle或者on the quadrilateral"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。 -
输入格式:
基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。点的x、y坐标之间以英文","分隔,点与点之间以一个英文空格分隔。
-
输出格式:
基本输出格式见每种选项的描述。
异常情况输出:
如果不符合基本格式,输出"Wrong Format"。
如果符合基本格式,但输入点的数量不符合要求,输出"wrong number of points"。
注意:输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0选项1、2、3中,若四边形四个点中有重合点,输出"points coincide"。
选项4中,若前两个输入线的点重合,输出"points coincide"。
- 用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与四边形有关的计算。
-
个人认为本题的难点在于判断输入是否为四边形以及4和5选项对输入坐标进行是三角形还是四边形的区分;
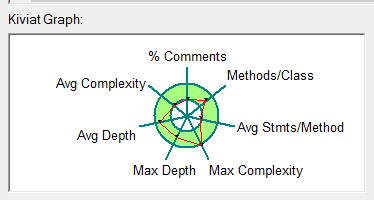
经过对函数的拆分使得平均复制度和最大复杂度都处在相对合理的范围之内
其中最主要的拆分是针对主函数的拆分使得最大复杂度较之上次有明显下降,并且为代码的加上了注释,大大提高了代码的可读性,主类代码如下:
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Processing input = new Processing(); 4 try { 5 input.isLegal(); 6 Point[] p = input.createPointArray(input.whichCase()); 7 switch(input.whichCase()) { 8 case 1: 9 condition1(p); 10 break; 11 case 2: 12 condition2(p); 13 break; 14 case 3: 15 condition3(p); 16 break; 17 case 4: 18 condition4(p); 19 break; 20 case 5: 21 condition5(p); 22 break; 23 } 24 } 25 catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { 26 27 System.out.println(ex.getMessage()); 28 } 29 } 30 31 private static void condition5(Point[] p) { 32 Point[] vertex = new Point[4]; 33 System.arraycopy(p, 1, vertex, 0, vertex.length); 34 Polygon polygon = Polygon.distinguish(vertex); 35 String string1 = null; 36 if (polygon instanceof Triangle) 37 string1 = "triangle"; 38 else 39 string1 = "quadrilateral"; 40 String string2 = null; 41 if(polygon.isPointOnPolygon(p[0])) 42 string2 = "on the "; 43 else if(polygon.isPointInPolygon(p[0])) 44 string2 = "in the "; 45 else 46 string2 = "outof the "; 47 48 System.out.println(string2 + string1); 49 } 50 51 private static void condition4(Point[] p) { 52 Line l = new Line(p[0],p[1]); 53 Point[] points = new Point[4]; 54 System.arraycopy(p, 2, points, 0, points.length); 55 Polygon polygon = Polygon.distinguish(points); 56 polygon.isLineCoincideWithEdge(l); 57 58 Point[] intersection = polygon.intersectionOfLineAndPolygon(l); 59 String s = polygon.intersectionOfLineAndPolygon(l).length + ""; 60 if(intersection.length == 2) { 61 s = condition4GetArea(s,polygon,l,intersection); 62 } 63 System.out.println(s); 64 } 65 /* 处理选项四需要求面积的情况 */ 66 private static String condition4GetArea(String s, Polygon polygon,Line l,Point[] intersection) { 67 Point[] m = polygon.whichSideOfLine(l); 68 Polygon t = null; 69 70 switch (m.length) { 71 case 1: { 72 Point[] vertex = {intersection[0],intersection[1],m[0]}; 73 t = new Triangle(vertex); 74 break; 75 } 76 case 2: { 77 Point[] vertex = {intersection[1],intersection[0],m[0],m[1]}; 78 t = new Quadrilateral(vertex); 79 break; 80 } 81 default:{ 82 83 } 84 } 85 double[] area = new double[2]; 86 area[0] = t.getArea(); 87 area[1] = polygon.getArea() - area[0]; 88 area[0] = Processing.rounding(area[0]); 89 area[1] = Processing.rounding(area[1]); 90 String s1 = s + " " + Math.min(area[0], area[1]) + " " + Math.max(area[0], area[1]); 91 return s1; 92 } 93 94 private static void condition3(Point[] p) { 95 Quadrilateral q = new Quadrilateral(p); 96 double perimeter = Processing.rounding(q.getPerimeter()); 97 double area = Processing.rounding(q.getArea()); 98 System.out.println(q.isConvexPolygon() + " " + perimeter + " " + area); 99 } 100 101 private static void condition2(Point[] p) { 102 Quadrilateral q = new Quadrilateral(p); 103 System.out.println(q.isDiamond() + " " + q.isRectangle() + " " + q.isSquare()); 104 } 105 106 private static void condition1(Point[] p) { 107 Quadrilateral q = null; 108 boolean isQuadrilateral = false; 109 boolean isParallelogram = false; 110 try { 111 q = new Quadrilateral(p); 112 isQuadrilateral = Quadrilateral.isQuadrilateral(p,q.edge); 113 isParallelogram = q.isParallelogram(); 114 } 115 catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { 116 } 117 finally { 118 if(Polygon.isPolygon2(p)) 119 throw new IllegalArgumentException("points coincide"); 120 System.out.println(isQuadrilateral + " " + isParallelogram); 121 } 122 } 123 }
代码的编写加入了Java抛出错误的特性,使得题目中各式各样的错误输入能够更加简洁地输出提示信息。在各个类中分别判断自己需要辨别的错误输入类型,最后再在主类中统一catch,显示错误信息,大大缩减了if-else分支条件判断。
题中一选项判断是否构成四边形是一个重要的判断,所以在相应类中也是抛出错误,所以为了使得一选项能够正确地显示不构成四边形的情况(false),而不是显示错误提示(not a quadrilateral),在condition1函数中增加了一个catch补捉错误但不做任何处理,达到能够输出false的目的。
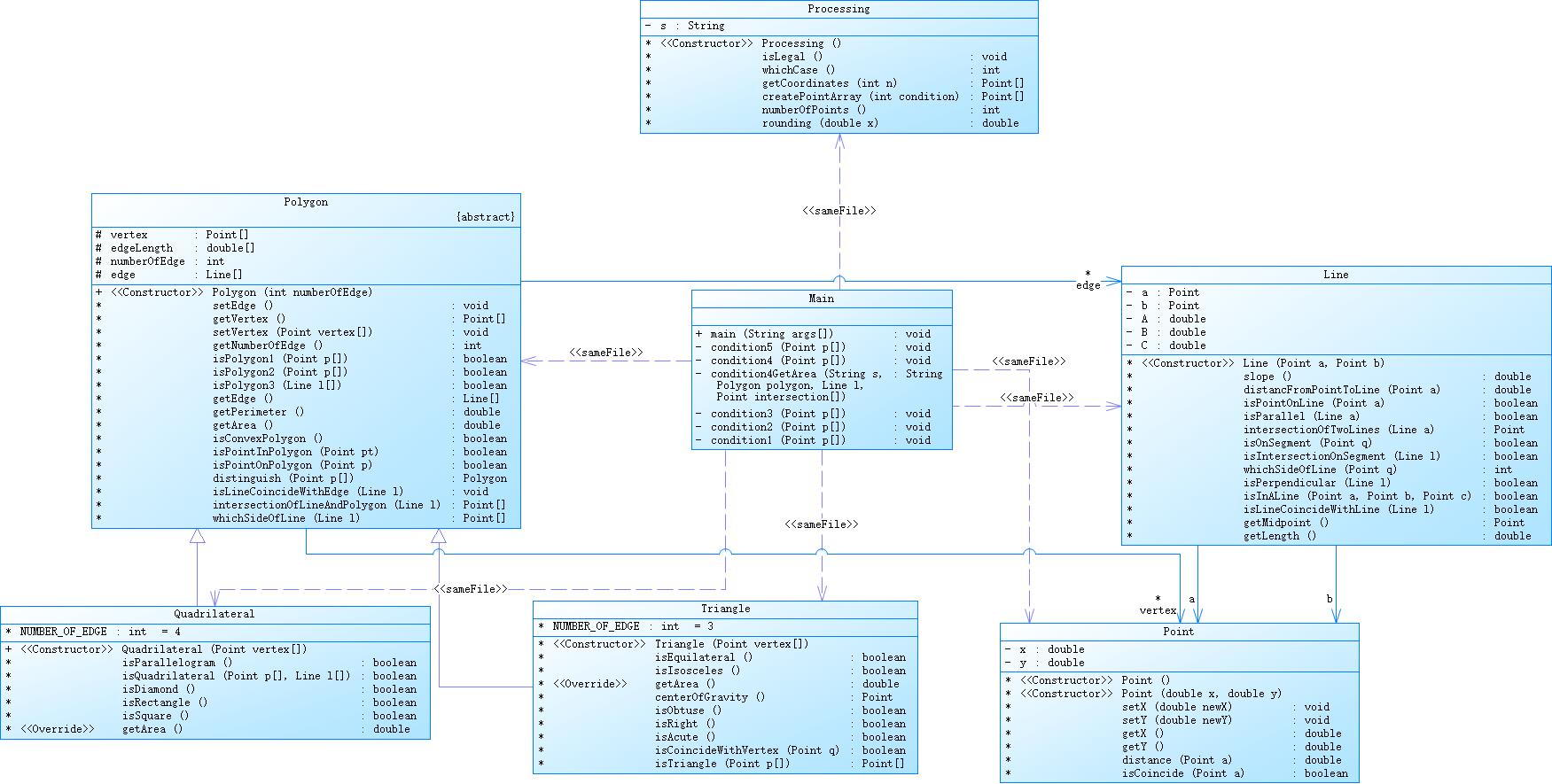
抽象类多边形类Polygon为四边形类Quadrilateral和三角形类Triangle父类,四边形和三角形所共有的方法,例如:求一个点是否在多边形内、求周长、求面积(抽象方法)都定义在多边形类内部。在4、5选项中即可运用Java的多态特性简化代码。
能否构成四边形要做以下三个判断:1.是否有三点在同一直线上;2.是否有任意两点重合;3.连续输入的点在多边形中是否相邻;进行这三个判断后即可判断输入的四个点能否构成四边形,代码如下:
1 /*判断是否有任意三点在同一直线上:输入:Point数组;输出:有:true;无:false */ 2 static boolean isPolygon1(Point[] p) { 3 boolean index = false; 4 for (int i = 0; i < p.length; i++) 5 for (int j = i + 1; j < p.length; j++) 6 for (int k = j + 1; k < p.length; k++) 7 if(Line.isInALine(p[i],p[j],p[k])) 8 index = true; 9 return index; 10 } 11 /*判断是否有任意两点重合:输入:Point数组;输出:有:true;无:false */ 12 static boolean isPolygon2(Point[] p) { 13 boolean index = false; 14 for (int i = 0; i < p.length; i++) 15 for (int j = i + 1; j < p.length; j++) 16 if (p[i].isCoincide(p[j])) 17 index = true; 18 return index; 19 } 20 /*判断所以连续输入的点在多边形中是否存相邻:输入:Line数组;输出:相邻:true;不相邻:false */ 21 static boolean isPolygon3(Line[] l) { 22 boolean index = true; 23 for (int i = 0; i < l.length; i++) { 24 if(l[i].isIntersectionOnSegment(l[(i + 2) % l.length])) 25 index = false; 26 } 27 return index; 28 29 }
比较难的一点就是如何判断所输入的四个点是否能按照要求构成三角形或四边形。我所采取的方法为先判断能否构成四边形。然后,如果不能构成四边形再判断能否构成三角形。
去除重复点后,若存在连续三点不在同一直线上,则不能构成三角形。判断代码如下:
/* 判断四点能否按要求构成三角形:若不能,则抛出错误;若能,则返回所构成三角形的顶点 */ static Point[] isTriangle(Point[] p) throws IllegalArgumentException{ Point[] newPoints = new Point[NUMBER_OF_EDGE]; ArrayList<Point> pointsList = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(p)); //去除重复点 for (int i = 0; i < pointsList.size(); i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < pointsList.size(); j++) { if(pointsList.get(i).isCoincide(pointsList.get(j))) { pointsList.remove(j); continue; } } } //去除在线段上的点 for (int i = 0; i < pointsList.size(); i++) { int j = (i + 1) % pointsList.size(); int k = (i - 1 + pointsList.size()) % pointsList.size(); Line l = new Line(pointsList.get(j), pointsList.get(k)); if (l.isPointOnLine(pointsList.get(i)) && l.isOnSegment(pointsList.get(i))) { pointsList.remove(i); } } if(pointsList.size() == NUMBER_OF_EDGE) pointsList.toArray(newPoints); else throw new IllegalArgumentException("not a triangle"); return newPoints; } }
求分割后两部分面积的方法为:先求出顶点在直线两侧每一侧的数量,在用较少的一侧的点和交点来构成多边形。这样做就把多种情况划分为两种:1.一个点;2.两个点。这两种情况和交点分别构成三角形和四边形,求出这一部分面积后再用原面积减去这部分即可得到另一部分的面积。代码如下:
/* 处理选项四需要求面积的情况 */ private static String condition4GetArea(String s, Polygon polygon,Line l,Point[] intersection) { Point[] m = polygon.whichSideOfLine(l); Polygon t = null; switch (m.length) { case 1: { Point[] vertex = {intersection[0],intersection[1],m[0]}; t = new Triangle(vertex); break; } case 2: { Point[] vertex = {intersection[1],intersection[0],m[0],m[1]}; t = new Quadrilateral(vertex); break; } default:{ } } double[] area = new double[2]; area[0] = t.getArea(); area[1] = polygon.getArea() - area[0]; area[0] = Processing.rounding(area[0]); area[1] = Processing.rounding(area[1]); String s1 = s + " " + Math.min(area[0], area[1]) + " " + Math.max(area[0], area[1]); return s1; }
剩下部分相对简单,不做过多介绍,完整代码如下:
1 package four72; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 import java.util.ArrayList; 5 import java.util.Arrays; 6 7 public class Main { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 Processing input = new Processing(); 10 try { 11 input.isLegal(); 12 Point[] p = input.createPointArray(input.whichCase()); 13 switch(input.whichCase()) { 14 case 1: 15 condition1(p); 16 break; 17 case 2: 18 condition2(p); 19 break; 20 case 3: 21 condition3(p); 22 break; 23 case 4: 24 condition4(p); 25 break; 26 case 5: 27 condition5(p); 28 break; 29 } 30 } 31 catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { 32 33 System.out.println(ex.getMessage()); 34 } 35 } 36 37 private static void condition5(Point[] p) { 38 Point[] vertex = new Point[4]; 39 System.arraycopy(p, 1, vertex, 0, vertex.length); 40 Polygon polygon = Polygon.distinguish(vertex); 41 String string1 = null; 42 if (polygon instanceof Triangle) 43 string1 = "triangle"; 44 else 45 string1 = "quadrilateral"; 46 String string2 = null; 47 if(polygon.isPointOnPolygon(p[0])) 48 string2 = "on the "; 49 else if(polygon.isPointInPolygon(p[0])) 50 string2 = "in the "; 51 else 52 string2 = "outof the "; 53 54 System.out.println(string2 + string1); 55 } 56 57 private static void condition4(Point[] p) { 58 Line l = new Line(p[0],p[1]); 59 Point[] points = new Point[4]; 60 System.arraycopy(p, 2, points, 0, points.length); 61 Polygon polygon = Polygon.distinguish(points); 62 polygon.isLineCoincideWithEdge(l); 63 64 Point[] intersection = polygon.intersectionOfLineAndPolygon(l); 65 String s = polygon.intersectionOfLineAndPolygon(l).length + ""; 66 if(intersection.length == 2) { 67 s = condition4GetArea(s,polygon,l,intersection); 68 } 69 System.out.println(s); 70 } 71 /* 处理选项四需要求面积的情况 */ 72 private static String condition4GetArea(String s, Polygon polygon,Line l,Point[] intersection) { 73 Point[] m = polygon.whichSideOfLine(l); 74 Polygon t = null; 75 76 switch (m.length) { 77 case 1: { 78 Point[] vertex = {intersection[0],intersection[1],m[0]}; 79 t = new Triangle(vertex); 80 break; 81 } 82 case 2: { 83 Point[] vertex = {intersection[1],intersection[0],m[0],m[1]}; 84 t = new Quadrilateral(vertex); 85 break; 86 } 87 default:{ 88 89 } 90 } 91 double[] area = new double[2]; 92 area[0] = t.getArea(); 93 area[1] = polygon.getArea() - area[0]; 94 area[0] = Processing.rounding(area[0]); 95 area[1] = Processing.rounding(area[1]); 96 String s1 = s + " " + Math.min(area[0], area[1]) + " " + Math.max(area[0], area[1]); 97 return s1; 98 } 99 100 private static void condition3(Point[] p) { 101 Quadrilateral q = new Quadrilateral(p); 102 double perimeter = Processing.rounding(q.getPerimeter()); 103 double area = Processing.rounding(q.getArea()); 104 System.out.println(q.isConvexPolygon() + " " + perimeter + " " + area); 105 } 106 107 private static void condition2(Point[] p) { 108 Quadrilateral q = new Quadrilateral(p); 109 System.out.println(q.isDiamond() + " " + q.isRectangle() + " " + q.isSquare()); 110 } 111 112 private static void condition1(Point[] p) { 113 Quadrilateral q = null; 114 boolean isQuadrilateral = false; 115 boolean isParallelogram = false; 116 try { 117 q = new Quadrilateral(p); 118 isQuadrilateral = Quadrilateral.isQuadrilateral(p,q.edge); 119 isParallelogram = q.isParallelogram(); 120 } 121 catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { 122 } 123 finally { 124 if(Polygon.isPolygon2(p)) 125 throw new IllegalArgumentException("points coincide"); 126 System.out.println(isQuadrilateral + " " + isParallelogram); 127 } 128 } 129 } 130 131 class Processing { 132 private String s; 133 Processing() { 134 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 135 s = input.nextLine(); 136 input.close(); 137 } 138 /* 判断输入是否符合格式,不符合则抛出错误 */ 139 void isLegal() throws IllegalArgumentException{ 140 String S = "[+-]?((0|[1-9][\\d]*)([\\.][\\d]+)?)"; 141 String REGEX = "[1-5]:" + S + "," + S + "(\\s" + S +","+ S + ")*[\\s]*"; 142 if(!s.matches(REGEX)) 143 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Wrong Format"); 144 } 145 int whichCase() { 146 return s.charAt(0) - '0'; 147 } 148 149 /* 从字符串中提取坐标 */ 150 Point[] getCoordinates(int n) { 151 Point[] a = new Point[n]; 152 String[] tokens = s.split(":"); 153 String[] coordinate = tokens[1].split("\\s"); 154 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) { 155 String[] number = coordinate[i].split(","); 156 a[i] = new Point(Double.parseDouble(number[0]),Double.parseDouble(number[1])); 157 } 158 return a; 159 } 160 /* 用提取的坐标创建Point数组并返回,若点的数量不对则抛出错误 */ 161 Point[] createPointArray(int condition) throws IllegalArgumentException { 162 Point[] p = null; 163 int[] numberOfPoint = {4,4,4,6,5}; 164 if(numberOfPoints() == numberOfPoint[condition - 1]) { 165 p = getCoordinates(numberOfPoint[condition - 1]); 166 return p; 167 } 168 else { 169 throw new IllegalArgumentException("wrong number of points"); 170 } 171 172 } 173 /* 返回字符串中点的数量 */ 174 int numberOfPoints() { 175 String[] tokens = this.s.split("\\s"); 176 return tokens.length; 177 } 178 /* 进行四舍五入 */ 179 static double rounding(double x) { 180 return (int)(x * 1e3 + 0.5) / 1e3 / 1.0; 181 } 182 } 183 184 class Point { 185 private double x,y; 186 Point() { 187 this(0, 0); 188 } 189 Point(double x,double y) { 190 this.x = x; 191 this.y = y; 192 } 193 void setX(double newX) { 194 x = newX; 195 } 196 void setY(double newY) { 197 y = newY; 198 } 199 double getX() { 200 return x; 201 } 202 double getY() { 203 return y; 204 } 205 double distance(Point a) { 206 double distance = Math.sqrt(Math.pow(this.x - a.x,2) + Math.pow(this.y - a.y,2)); 207 return distance; 208 } 209 boolean isCoincide(Point a) { 210 return (Math.abs(this.x - a.x) < 1e-6 && Math.abs(this.y - a.y) < 1e-6); 211 } 212 } 213 214 class Line { 215 private Point a,b; 216 private double A,B,C; //ֱ直线一般方程的参数 217 Line(Point a,Point b) { 218 this.a = a; 219 this.b = b; 220 A = b.getY() - a.getY(); 221 B = a.getX() - b.getX(); 222 C = b.getX() * a.getY() - a.getX() * b.getY() ; 223 } 224 double slope() { 225 double k = -A / B; 226 return k; 227 } 228 double distancFromPointToLine(Point a) { 229 double distance = Math.abs(A * a.getX() + B * a.getY() + C) / Math.sqrt(Math.pow(A,2) + Math.pow(B,2)); 230 return distance; 231 } 232 /* 判断点是否在直线上:是:true;否:false */ 233 boolean isPointOnLine(Point a) { 234 return (Math.abs(A * a.getX() + B * a.getY() + C) < 1e-5); 235 } 236 /* 判断两直线是否平行 */ 237 boolean isParallel(Line a) { 238 return (Math.abs(this.A * a.B - a.A * this.B) < 1e-5); 239 } 240 /* 求两条直线的交点 */ 241 Point intersectionOfTwoLines(Line a) { 242 Point intersection; 243 double denominator = this.A * a.B - a.A * this.B; 244 if(Math.abs(denominator) < 1e-6) 245 intersection = null; 246 else { 247 double x = -(a.B * this.C - this.B * a.C) / denominator; 248 double y = -(this.A * a.C - a.A * this.C) / denominator; 249 intersection = new Point(x,y); 250 } 251 return intersection; 252 } 253 /* 判断点是否在线段上:是:true;否:false */ 254 boolean isOnSegment(Point q) { 255 return (Math.min(a.getX() , b.getX()) <= q.getX() && q.getX() <= Math.max(a.getX() , b.getX()) 256 && Math.min(a.getY() , b.getY()) <= q.getY() && q.getY() <= Math.max(a.getY() , b.getY())); 257 } 258 /* 判断两直线交点是否在线段上:是:true;否:false */ 259 boolean isIntersectionOnSegment(Line l) { 260 boolean index = false; 261 Point intersection = intersectionOfTwoLines(l); 262 if(intersection != null) 263 index = (isOnSegment(intersection) && l.isOnSegment(intersection)); 264 return index; 265 266 } 267 /* 判断在直线的哪一侧 */ 268 int whichSideOfLine(Point q) { 269 if(A * q.getX() + B * q.getY() + C > 0) 270 return 1; 271 else if(A * q.getX() + B * q.getY() + C < 0) 272 return 2; 273 else 274 return 3; 275 } 276 /* 判断两直线是否垂直 */ 277 boolean isPerpendicular(Line l) { 278 return (Math.abs(A * l.A + B * l.B) < 1e-5); 279 } 280 static boolean isInALine(Point a,Point b,Point c) { 281 if(a.isCoincide(b) || a.isCoincide(c) || b.isCoincide(c)) 282 return true; 283 else { 284 Line l = new Line(a,b); 285 if(l.isPointOnLine(c)) 286 return true; 287 else 288 return false; 289 } 290 } 291 /* 判断两直线是否重合 */ 292 boolean isLineCoincideWithLine(Line l) { 293 return (isParallel(l) && isPointOnLine(l.a)); 294 } 295 /* 求线段中点 */ 296 Point getMidpoint() { 297 Point midPoint = new Point((a.getX() + b.getX()) / 2,(a.getY() + b.getY()) / 2); 298 return midPoint; 299 } 300 /* 求线段长度 */ 301 double getLength() { 302 double length = a.distance(b); 303 return length; 304 305 } 306 } 307 308 class Triangle extends Polygon{ 309 static final int NUMBER_OF_EDGE = 3; 310 Triangle(Point[] vertex) { 311 super(NUMBER_OF_EDGE); 312 super.setVertex(vertex); 313 super.setEdge(); 314 } 315 boolean isEquilateral() { 316 return (Math.abs(edgeLength[0] - edgeLength[1]) < 1e-6 && Math.abs(edgeLength[0] - edgeLength[2]) < 1e-6 && Math.abs(edgeLength[1] - edgeLength[2]) < 1e-6); 317 } 318 boolean isIsosceles() { 319 return (Math.abs(edgeLength[0] - edgeLength[1]) < 1e-6 || Math.abs(edgeLength[0] - edgeLength[2]) < 1e-6 || Math.abs(edgeLength[1] - edgeLength[2]) < 1e-6); 320 } 321 double getArea() { 322 double p = getPerimeter() / 2; 323 double s = Math.sqrt(p * (p - edgeLength[0]) * (p - edgeLength[1]) * (p - edgeLength[2])) ; 324 return s; 325 } 326 Point centerOfGravity() { 327 double x = (vertex[0].getX() + vertex[1].getX() + vertex[2].getX()) / 3; 328 double y = (vertex[0].getY() + vertex[1].getY() + vertex[2].getY()) / 3; 329 Point g = new Point(x,y); 330 return g; 331 } 332 boolean isObtuse() { 333 return (Math.pow(edgeLength[0],2) + Math.pow(edgeLength[1],2) - Math.pow(edgeLength[2],2) < 0); 334 } 335 boolean isRight() { 336 return (!this.isObtuse() && !this.isAcute()); 337 //return (Math.pow(x,2) + Math.pow(y,2) == Math.pow(z,2)); 338 } 339 boolean isAcute() { 340 return (Math.pow(edgeLength[0],2) + Math.pow(edgeLength[1],2) - Math.pow(edgeLength[2],2) > 0); 341 } 342 /* 判断点是否和顶点重合 */ 343 boolean isCoincideWithVertex(Point q) { 344 boolean index = false; 345 for(int i = 0;i < NUMBER_OF_EDGE;i++) 346 if(q.isCoincide(this.getVertex()[i])) 347 index = true; 348 return index; 349 } 350 /* 判断四点能否按要求构成三角形:若不能,则抛出错误;若能,则返回所构成三角形的顶点 */ 351 static Point[] isTriangle(Point[] p) throws IllegalArgumentException{ 352 Point[] newPoints = new Point[NUMBER_OF_EDGE]; 353 ArrayList<Point> pointsList = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(p)); 354 //去除重复点 355 for (int i = 0; i < pointsList.size(); i++) { 356 for (int j = i + 1; j < pointsList.size(); j++) { 357 if(pointsList.get(i).isCoincide(pointsList.get(j))) { 358 pointsList.remove(j); 359 continue; 360 } 361 } 362 } 363 //去除在线段上的点 364 for (int i = 0; i < pointsList.size(); i++) { 365 int j = (i + 1) % pointsList.size(); 366 int k = (i - 1 + pointsList.size()) % pointsList.size(); 367 Line l = new Line(pointsList.get(j), pointsList.get(k)); 368 if (l.isPointOnLine(pointsList.get(i)) && l.isOnSegment(pointsList.get(i))) { 369 pointsList.remove(i); 370 } 371 } 372 373 if(pointsList.size() == NUMBER_OF_EDGE) 374 pointsList.toArray(newPoints); 375 else 376 throw new IllegalArgumentException("not a triangle"); 377 return newPoints; 378 } 379 } 380 381 382 class Quadrilateral extends Polygon{ 383 static final int NUMBER_OF_EDGE = 4; 384 public Quadrilateral(Point[] vertex) throws IllegalArgumentException{ 385 super(NUMBER_OF_EDGE); 386 super.setVertex(vertex); 387 super.setEdge(); 388 if(!Quadrilateral.isQuadrilateral(vertex,edge)) 389 throw new IllegalArgumentException("not a quadrilateral"); 390 } 391 /* 判断是否为平行四边形:输入:无;输出:是:true;否:false */ 392 boolean isParallelogram() { 393 return (edge[0].isParallel(edge[2]) && edge[1].isParallel(edge[3])); 394 } 395 /*判断是否为四边形:输入:一组点和一组直线;输出:是:true;否:false */ 396 static boolean isQuadrilateral(Point[] p,Line[] l) { 397 return !Quadrilateral.isPolygon1(p) && !Quadrilateral.isPolygon2(p) && Quadrilateral.isPolygon3(l); 398 } 399 /* 判断是否为菱形:输入:无;输出:是:true;否:false */ 400 boolean isDiamond() { 401 boolean index = true; 402 for (int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_EDGE; i++) { 403 int j = (i + 1) % NUMBER_OF_EDGE; 404 if(edgeLength[i] != edgeLength[j]) 405 index = false; 406 } 407 return index; 408 } 409 /* 判断是否为矩形:输入:无;输出:是:true;否:false */ 410 boolean isRectangle() { 411 boolean index = false; 412 boolean isRight = false; 413 for (int i = 0; i < NUMBER_OF_EDGE; i++) { 414 int j = (i + 1) % NUMBER_OF_EDGE; 415 if(edge[i].isPerpendicular(edge[j])) 416 isRight = true; 417 } 418 index = (isRight && isParallelogram()); 419 return index; 420 } 421 /* 判断是否为正方形:输入:无;输出:是:true;否:false */ 422 boolean isSquare() { 423 boolean index = false; 424 if(isDiamond() && isRectangle()) 425 index = true; 426 return index; 427 } 428 double getArea() { 429 /* 不相邻两边中点的连线长乘以另两边的任一中点到该连线距离的2倍 */ 430 Line l = new Line(edge[0].getMidpoint(),edge[2].getMidpoint()); 431 double distance = l.distancFromPointToLine(edge[1].getMidpoint()); 432 double area = 2 * distance * l.getLength(); 433 return area; 434 } 435 } 436 437 abstract class Polygon{ 438 protected Point[] vertex; //顶点 439 protected double[] edgeLength; //边长 440 protected int numberOfEdge; //边数 441 protected Line[] edge; //边 442 public Polygon(int numberOfEdge) { 443 this.numberOfEdge = numberOfEdge; 444 vertex = new Point[numberOfEdge]; 445 edgeLength = new double[numberOfEdge]; 446 edge = new Line[numberOfEdge]; 447 448 } 449 void setEdge() { 450 for(int i = 0;i < numberOfEdge;i++) { 451 edgeLength[i] = vertex[i].distance(vertex[(i + 1) % numberOfEdge]); 452 edge[i] = new Line(vertex[i],vertex[(i + 1) % numberOfEdge]); 453 } 454 Arrays.sort(edgeLength); 455 } 456 Point[] getVertex() { 457 return vertex; 458 } 459 void setVertex(Point[] vertex){ 460 this.vertex = vertex; 461 } 462 int getNumberOfEdge() { 463 return numberOfEdge; 464 } 465 /*判断是否有任意三点在同一直线上:输入:Point数组;输出:有:true;无:false */ 466 static boolean isPolygon1(Point[] p) { 467 boolean index = false; 468 for (int i = 0; i < p.length; i++) 469 for (int j = i + 1; j < p.length; j++) 470 for (int k = j + 1; k < p.length; k++) 471 if(Line.isInALine(p[i],p[j],p[k])) 472 index = true; 473 return index; 474 } 475 /*判断是否有任意两点重合:输入:Point数组;输出:有:true;无:false */ 476 static boolean isPolygon2(Point[] p) { 477 boolean index = false; 478 for (int i = 0; i < p.length; i++) 479 for (int j = i + 1; j < p.length; j++) 480 if (p[i].isCoincide(p[j])) 481 index = true; 482 return index; 483 } 484 /*判断所以连续输入的点在多边形中是否存相邻:输入:Line数组;输出:相邻:true;不相邻:false */ 485 static boolean isPolygon3(Line[] l) { 486 boolean index = true; 487 for (int i = 0; i < l.length; i++) { 488 if(l[i].isIntersectionOnSegment(l[(i + 2) % l.length])) 489 index = false; 490 } 491 return index; 492 493 } 494 Line[] getEdge() { 495 return edge; 496 } 497 double getPerimeter() { 498 double c = 0; 499 for (double length : edgeLength) 500 c += length; 501 return c; 502 } 503 abstract double getArea(); 504 /*判断是否为凸多边形:输入:无;输出:是:true;否:false */ 505 boolean isConvexPolygon() { 506 boolean index = true; 507 ArrayList<Point> vertexArrayList = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(vertex)); 508 /* 若任意一顶点在剩余顶点所构成多边形内部则为凹多边形,否则为凸多边形 */ 509 for (int i = 0; i < vertexArrayList.size(); i++) { 510 Point tpoint = vertexArrayList.get(i); 511 vertexArrayList.remove(i); 512 Point[] tVertex = new Point[vertexArrayList.size()]; 513 vertexArrayList.toArray(tVertex); 514 Polygon t = null; 515 switch (vertexArrayList.size()) { 516 case 3: 517 t = new Triangle(tVertex); 518 break; 519 case 4: 520 t = new Quadrilateral(tVertex); 521 break; 522 } 523 if (t.isPointInPolygon(tpoint)) { 524 index = false; 525 } 526 vertexArrayList.add(i, tpoint); 527 } 528 return index; 529 } 530 /* 判断点是否在多边形内:输入:无;输出:是:true;否:false */ 531 boolean isPointInPolygon(Point pt) { 532 Point[] pts = this.getVertex(); 533 int counter = 0; 534 double xinters; 535 Point p1,p2; 536 for(int i = 0;i < pts.length;i++) { 537 p1 = pts[i]; 538 p2 = pts[(i + 1) % pts.length]; 539 if (Math.min(p1.getY(),p2.getY()) < pt.getY() && pt.getY() <= Math.max(p1.getY(),p2.getY())) { 540 xinters = (pt.getY() - p1.getY()) * (p2.getX() - p1.getX()) / (p2.getY() - p1.getY()) + p1.getX(); 541 if (p1.getY() == p2.getY() || pt.getX() <= xinters) { 542 counter++; 543 } 544 } 545 } 546 return (counter % 2 != 0); 547 } 548 /* 判断点是否在多边形上:输入:无;输出:是:true;否:false */ 549 boolean isPointOnPolygon(Point p) { 550 boolean index = false; 551 for(int i = 0;i < numberOfEdge;i++) 552 if(edge[i].isPointOnLine(p) && edge[i].isOnSegment(p)) 553 index = true; 554 return index; 555 } 556 557 /* 区分输入的点构成三角形还是四边形:若能构成则返回三角形或四边形对象;若不能则抛出错误 */ 558 static Polygon distinguish(Point[] p) throws IllegalArgumentException{ 559 560 Polygon polygon = null; 561 try { 562 polygon = new Quadrilateral(p); 563 //若不能构成四边形则抛出错误,判断是否能构成三角形 564 } 565 catch (IllegalArgumentException ex1) { 566 try { 567 p = Triangle.isTriangle(p); 568 polygon = new Triangle(p); 569 } 570 catch (IllegalArgumentException ex2) { 571 throw new IllegalArgumentException("not a quadrilateral or triangle"); 572 } 573 } 574 return polygon; 575 } 576 /* 判断直线是否与多边形某条边重合:是则抛出错误 */ 577 void isLineCoincideWithEdge(Line l) throws IllegalArgumentException{ 578 boolean index = false; 579 for (int i = 0; i < edge.length; i++) { 580 if (edge[i].isLineCoincideWithLine(l)) 581 index = true; 582 } 583 if(index) 584 throw new IllegalArgumentException("The line is coincide with one of the lines"); 585 } 586 /* 求直线与多边形交点 */ 587 Point[] intersectionOfLineAndPolygon(Line l) { 588 Point[] intersection = null; 589 ArrayList<Point> potential = new ArrayList<>(); 590 /*求出直线与每一条边的交点*/ 591 for(int i = 0;i < numberOfEdge;i++) { 592 Point a = l.intersectionOfTwoLines(edge[i]); 593 if(a != null && edge[i].isOnSegment(a)) 594 potential.add(l.intersectionOfTwoLines(edge[i])); 595 } 596 /* 排除重复的点,即直线与多边形顶点的交点 */ 597 for(int i = 0;i < potential.size();i++) 598 for(int j = i + 1;j < potential.size();j++) 599 if(potential.get(i).isCoincide(potential.get(j))) 600 potential.remove(j); 601 602 intersection = new Point[potential.size()]; 603 potential.toArray(intersection); 604 return intersection; 605 } 606 Point[] whichSideOfLine(Line l) { 607 Point[] p = null; 608 ArrayList<Point> p1 = new ArrayList<>(); 609 ArrayList<Point> p2 = new ArrayList<>(); 610 for(int i = 0;i < numberOfEdge;i++) { 611 if(l.whichSideOfLine(vertex[i]) == 1) 612 p1.add(vertex[i]); 613 else if(l.whichSideOfLine(vertex[i]) == 2) 614 p2.add(vertex[i]); 615 } 616 if (p1.size() <= p2.size()) { 617 p = new Point[p1.size()]; 618 p1.toArray(p); 619 } 620 else { 621 p = new Point[p2.size()]; 622 p2.toArray(p); 623 } 624 return p; 625 } 626 }
-
- 第五次作业
-
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与五边形有关的计算。
以下五边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入五个点坐标,判断是否是五边形,判断结果输出true/false。
2:输入五个点坐标,判断是凹五边形(false)还是凸五边形(true),如果是凸五边形,则再输出五边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。若五个点坐标无法构成五边形,输出"not a pentagon"
3:输入七个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后五个点构成一个凸五边形、凸四边形或凸三角形,输出直线与五边形、四边形或三角形相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与多边形形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后五个点不符合五边形输入,若前两点重合,输出"points coincide"。以上3选项中,若输入的点无法构成多边形,则输出"not a polygon"。输入的五个点坐标可能存在冗余,假设多边形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如:x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z不与xy都相邻,如:z x y s、x z s y、x s z y4:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),判断它们两个之间是否存在包含关系(一个多边形有一条或多条边与另一个多边形重合,其他部分都包含在另一个多边形内部,也算包含)。
两者存在六种关系:1、分离(完全无重合点) 2、连接(只有一个点或一条边重合) 3、完全重合 4、被包含(前一个多边形在后一个多边形的内部)5、交错 6、包含(后一个多边形在前一个多边形的内部)。
各种关系的输出格式如下:
1、no overlapping area between the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon and the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
2、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is connected to the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
3、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon coincides with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
4、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is inside the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
5、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is interlaced with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
6、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon contains the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon5:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),输出两个多边形公共区域的面积。注:只考虑每个多边形被另一个多边形分割成最多两个部分的情况,不考虑一个多边形将另一个分割成超过两个区域的情况。
6:输入六个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后五个点所构成的多边形(限定为凸多边形,不考虑凹多边形),的内部(若是五边形输出in the pentagon/outof the pentagon,若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。输入入错存在冗余点要排除,冗余点的判定方法见选项5。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle/on the quadrilateral/on the pentagon"。
以上4、5、6选项输入的五个点坐标可能存在冗余,假设多边形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如:x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z不与xy都相邻,如:z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
-
- 第五次作业
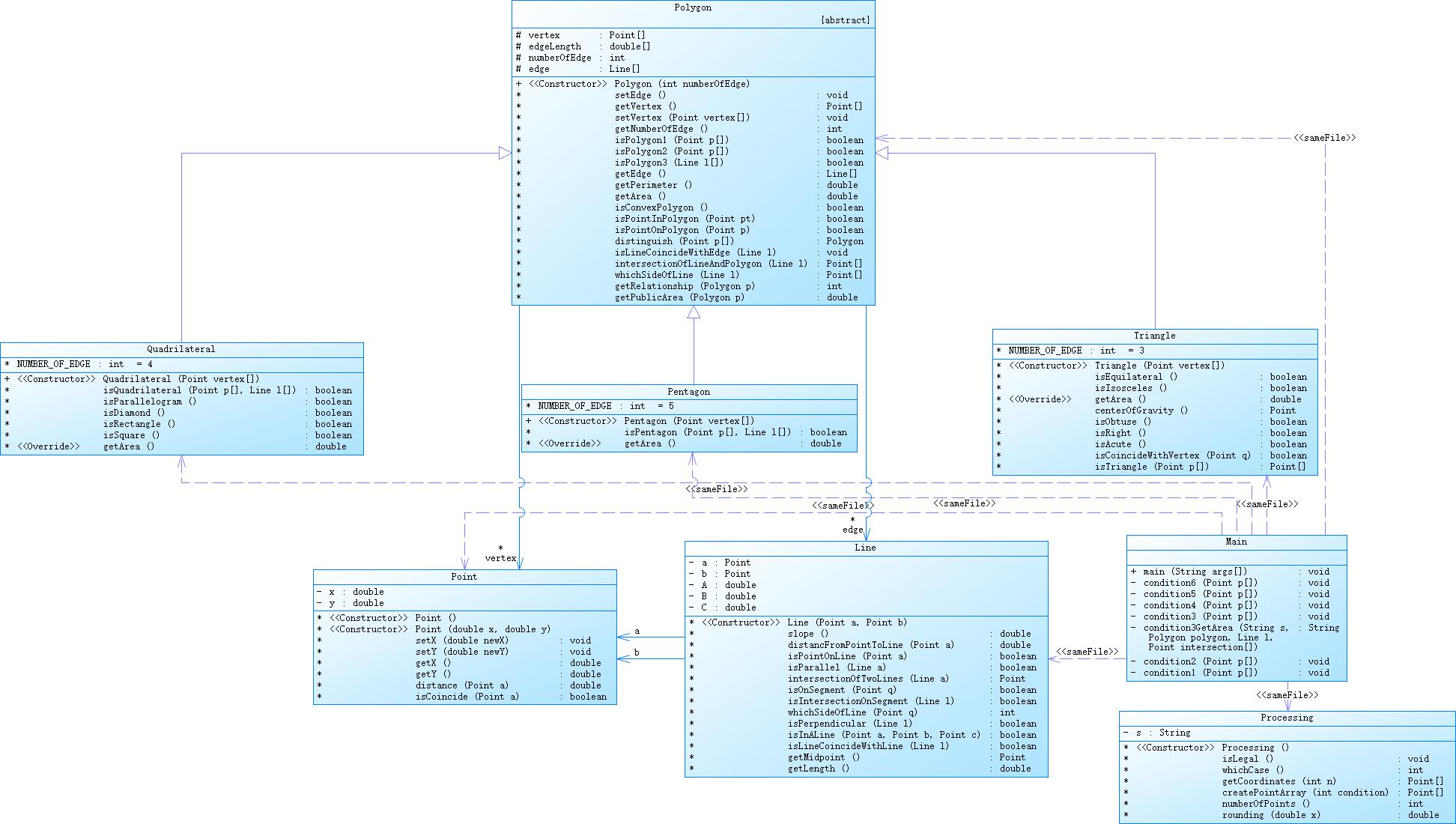
三角形、四边形、五边形类均继承自多边形类,处理选项4和5的多边形类方法getRelationship()和getPublicArea()方法参数均为抽象类Polygon,利用多态特性简化代码
3、4、5、6选项均为三角形、四边形、五边形都可能出现,所以创建对象时均采用多边形类创建,以便利用多态特征简化代码。
以选项六为例,在distinguish方法中创建多边形对象,然后使用instanceof关键字判断是哪一类对象从而确定输出,而求点是否在多边形内部的方法定义在抽象父类Polygon中,简化各种判断,代码如下:
1 private static void condition6(Point[] p) { 2 Point[] vertex = new Point[5]; 3 System.arraycopy(p, 1, vertex, 0, vertex.length); 4 Polygon polygon = Polygon.distinguish(vertex); 5 String string1 = null; 6 if (polygon instanceof Triangle) 7 string1 = "triangle"; 8 else if(polygon instanceof Quadrilateral) 9 string1 = "quadrilateral"; 10 else 11 string1 = "pentagon"; 12 String string2 = null; 13 if(polygon.isPointOnPolygon(p[0])) 14 string2 = "on the "; 15 else if(polygon.isPointInPolygon(p[0])) 16 string2 = "in the "; 17 else 18 string2 = "outof the "; 19 20 System.out.println(string2 + string1); 21 }
-
-
期中考试
- 1.设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的点Point,私有属性分别为横坐标x与纵坐标y,数据类型均为实型数,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出该坐标点的坐标信息,格式如下:
(x,y),数值保留两位小数。为简化题目,其中,坐标点的取值范围设定为(0,200]。若输入有误,系统则直接输出Wrong Format。设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的线Line,私有属性除了标识线段两端的点point1、point2外,还有一个字符串类型的color,用于表示该线段的颜色,同样,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于计算该线段长度的方法getDistance(),还有一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出线段的相关信息,输出格式如下:
- 1.设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的点Point,私有属性分别为横坐标x与纵坐标y,数据类型均为实型数,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出该坐标点的坐标信息,格式如下:
-
题目较为简单,按要求写出即可,代码如下:
1 package mid; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 import static java.lang.Math.*; 5 6 public class Main { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 9 double beginX = input.nextDouble(); 10 double beginY = input.nextDouble(); 11 double endX = input.nextDouble(); 12 double endY = input.nextDouble(); 13 String color = input.next(); 14 try { 15 Point begin = new Point(beginX,beginY); 16 Point end = new Point(endX,endY); 17 Line line = new Line(begin,end,color); 18 line.display(); 19 } 20 catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { 21 System.out.println(ex.getMessage()); 22 } 23 input.close(); 24 } 25 } 26 27 class Point { 28 private double x; 29 private double y; 30 31 public Point() { 32 this(0, 0); 33 } 34 35 public Point(double x,double y) { 36 if(x <=0 || x > 200 || y <=0 || y > 200) 37 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Wrong Format"); 38 this.x = x; 39 this.y = y; 40 } 41 42 public double getX() { 43 return x; 44 } 45 46 public double getY() { 47 return y; 48 } 49 50 public void setX(double x) { 51 this.x = x; 52 } 53 54 public void setY(double y) { 55 this.y = y; 56 } 57 58 void display() { 59 System.out.println("(" + String.format("%.2f", x) +"," + String.format("%.2f", y) + ")"); 60 } 61 } 62 63 class Line { 64 private Point point1; 65 private Point point2; 66 private String color; 67 68 public Line() { 69 } 70 71 public Line(Point point1,Point point2,String color) { 72 this.point1 = point1; 73 this.point2 = point2; 74 this.color = color; 75 } 76 77 public void setPoint1(Point point1) { 78 this.point1 = point1; 79 } 80 81 public void setPoint2(Point point2) { 82 this.point2 = point2; 83 } 84 85 public void setColor(String color) { 86 this.color = color; 87 } 88 89 public Point getPoint1() { 90 return point1; 91 } 92 93 public Point getPoint2() { 94 return point2; 95 } 96 97 public String getColor() { 98 return color; 99 } 100 101 double getDistance() { 102 double distance = sqrt(pow(point1.getX() - point2.getX(), 2) + pow(point1.getY() - point2.getY(), 2)); 103 return distance; 104 } 105 106 void display() { 107 System.out.println("The line's color is:" + color); 108 System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); 109 point1.display(); 110 System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); 111 point2.display(); 112 System.out.println("The line's length is:" + String.format("%.2f", getDistance())); 113 } 114 }
-
-
- 2.对题目中的点Point类和线Line类进行进一步抽象,定义一个两个类的共同父类Element(抽象类),将display()方法在该方法中进行声明(抽象方法),将Point类和Line类作为该类的子类。再定义一个Element类的子类面Plane,该类只有一个私有属性颜色color,除了构造方法和属性的getter、setter方法外,display()方法用于输出面的颜色,输出格式如下:
The Plane's color is:颜色在主方法内,定义两个Point(线段的起点和终点)对象、一个Line对象和一个Plane对象,依次从键盘输入两个Point对象的起点、终点坐标和颜色值(Line对象和Plane对象颜色相同),然后定义一个Element类的引用,分别使用该引用调用以上四个对象的display()方法,从而实现多态特性。
- 2.对题目中的点Point类和线Line类进行进一步抽象,定义一个两个类的共同父类Element(抽象类),将display()方法在该方法中进行声明(抽象方法),将Point类和Line类作为该类的子类。再定义一个Element类的子类面Plane,该类只有一个私有属性颜色color,除了构造方法和属性的getter、setter方法外,display()方法用于输出面的颜色,输出格式如下:
-
代码如下:
1 package mid2; 2 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 import static java.lang.Math.*; 5 6 public class Main { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 9 double beginX = input.nextDouble(); 10 double beginY = input.nextDouble(); 11 double endX = input.nextDouble(); 12 double endY = input.nextDouble(); 13 String color = input.next(); 14 try { 15 Point p1 = new Point(beginX,beginY); 16 Point p2 = new Point(endX,endY); 17 Line line = new Line(p1,p2,color); 18 Plane plane = new Plane(color); 19 20 Element element = null; 21 element = p1;//起点Point 22 element.display(); 23 24 element = p2;//终点Point 25 element.display(); 26 27 element = line;//线段 28 element.display(); 29 30 element = plane;//面 31 element.display(); 32 33 } 34 catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { 35 System.out.println(ex.getMessage()); 36 } 37 input.close(); 38 } 39 } 40 41 abstract class Element { 42 abstract void display(); 43 } 44 45 class Point extends Element{ 46 private double x; 47 private double y; 48 49 public Point() { 50 this(0, 0); 51 } 52 53 public Point(double x,double y) { 54 if(x <=0 || x > 200 || y <=0 || y > 200) 55 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Wrong Format"); 56 this.x = x; 57 this.y = y; 58 } 59 60 public double getX() { 61 return x; 62 } 63 64 public double getY() { 65 return y; 66 } 67 68 public void setX(double x) { 69 this.x = x; 70 } 71 72 public void setY(double y) { 73 this.y = y; 74 } 75 76 @Override 77 void display() { 78 System.out.println("(" + String.format("%.2f", x) +"," + String.format("%.2f", y) + ")"); 79 } 80 } 81 82 class Line extends Element{ 83 private Point point1; 84 private Point point2; 85 private String color; 86 87 public Line() { 88 } 89 90 public Line(Point point1,Point point2,String color) { 91 this.point1 = point1; 92 this.point2 = point2; 93 this.color = color; 94 } 95 96 public void setPoint1(Point point1) { 97 this.point1 = point1; 98 } 99 100 public void setPoint2(Point point2) { 101 this.point2 = point2; 102 } 103 104 public void setColor(String color) { 105 this.color = color; 106 } 107 108 public Point getPoint1() { 109 return point1; 110 } 111 112 public Point getPoint2() { 113 return point2; 114 } 115 116 public String getColor() { 117 return color; 118 } 119 120 double getDistance() { 121 double distance = sqrt(pow(point1.getX() - point2.getX(), 2) + pow(point1.getY() - point2.getY(), 2)); 122 return distance; 123 } 124 125 @Override 126 void display() { 127 System.out.println("The line's color is:" + color); 128 System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); 129 point1.display(); 130 System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); 131 point2.display(); 132 System.out.println("The line's length is:" + String.format("%.2f", getDistance())); 133 } 134 } 135 136 class Plane extends Element { 137 private String color; 138 139 public Plane(String color) { 140 this.color = color; 141 } 142 public Plane() { 143 } 144 145 public void setColor(String color) { 146 this.color = color; 147 } 148 149 public String getColor() { 150 return color; 151 } 152 153 @Override 154 void display() { 155 System.out.println("The Plane's color is:" + color); 156 157 } 158 159 }
-
-
- 3.在“点与线(继承与多态)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,增加容器类保存点、线、面对象,并对该容器进行相应增、删、遍历操作。在原有类设计的基础上,增加一个GeometryObject容器类,其属性为
ArrayList<Element>类型的对象(若不了解泛型,可以不使用<Element>)增加该类的add()方法及remove(int index)方法,其功能分别为向容器中增加对象及删除第index - 1(ArrayList中index>=0)个对象在主方法中,用户循环输入要进行的操作(choice∈[0,4]),其含义如下:1:向容器中增加Point对象;2:向容器中增加Line对象;3:向容器中增加Plane对象;4:删除容器中第index - 1个数据,若index数据非法,则无视此操作;0:输入结束
- 3.在“点与线(继承与多态)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,增加容器类保存点、线、面对象,并对该容器进行相应增、删、遍历操作。在原有类设计的基础上,增加一个GeometryObject容器类,其属性为
-
在index非法的情况下,ArrayList的remove方法本身就会抛出错误,要无视错误操作则直接catch后不做任何操作即可,代码如下:
1 case 4://delete index - 1 object from list 2 int index = input.nextInt(); 3 try { 4 geometryObject.remove(index); 5 } 6 catch (Exception e) { 7 } 8 }
完整代码如下:
1 package mid3; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 import java.util.Scanner; 5 import static java.lang.Math.*; 6 7 public class Main { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 10 try { 11 GeometryObject geometryObject = new GeometryObject(); 12 int choice = input.nextInt(); 13 while(choice != 0) { 14 switch(choice) { 15 case 1://insert Point object into list 16 double pX = input.nextDouble(); 17 double pY = input.nextDouble(); 18 geometryObject.add(new Point(pX,pY)); 19 break; 20 case 2://insert Line object into list 21 double beginX = input.nextDouble(); 22 double beginY = input.nextDouble(); 23 double endX = input.nextDouble(); 24 double endY = input.nextDouble(); 25 String color1 = input.next(); 26 geometryObject.add(new Line(new Point(beginX,beginY),new Point(endX,endY),color1)); 27 break; 28 case 3://insert Plane object into list 29 String color2 = input.next(); 30 geometryObject.add(new Plane(color2)); 31 break; 32 case 4://delete index - 1 object from list 33 int index = input.nextInt(); 34 try { 35 geometryObject.remove(index); 36 } 37 catch (Exception e) { 38 } 39 } 40 choice = input.nextInt(); 41 } 42 for (Element element : geometryObject.getList()) { 43 element.display(); 44 } 45 46 } 47 catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { 48 System.out.println(ex.getMessage()); 49 } 50 input.close(); 51 } 52 } 53 54 abstract class Element { 55 abstract void display(); 56 } 57 58 class Point extends Element{ 59 private double x; 60 private double y; 61 62 public Point() { 63 this(0, 0); 64 } 65 66 public Point(double x,double y) { 67 if(x <=0 || x > 200 || y <=0 || y > 200) 68 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Wrong Format"); 69 this.x = x; 70 this.y = y; 71 } 72 73 public double getX() { 74 return x; 75 } 76 77 public double getY() { 78 return y; 79 } 80 81 public void setX(double x) { 82 this.x = x; 83 } 84 85 public void setY(double y) { 86 this.y = y; 87 } 88 89 @Override 90 void display() { 91 System.out.println("(" + String.format("%.2f", x) +"," + String.format("%.2f", y) + ")"); 92 } 93 } 94 95 class Line extends Element{ 96 private Point point1; 97 private Point point2; 98 private String color; 99 100 public Line() { 101 } 102 103 public Line(Point point1,Point point2,String color) { 104 this.point1 = point1; 105 this.point2 = point2; 106 this.color = color; 107 } 108 109 public void setPoint1(Point point1) { 110 this.point1 = point1; 111 } 112 113 public void setPoint2(Point point2) { 114 this.point2 = point2; 115 } 116 117 public void setColor(String color) { 118 this.color = color; 119 } 120 121 public Point getPoint1() { 122 return point1; 123 } 124 125 public Point getPoint2() { 126 return point2; 127 } 128 129 public String getColor() { 130 return color; 131 } 132 133 double getDistance() { 134 double distance = sqrt(pow(point1.getX() - point2.getX(), 2) + pow(point1.getY() - point2.getY(), 2)); 135 return distance; 136 } 137 138 @Override 139 void display() { 140 System.out.println("The line's color is:" + color); 141 System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:"); 142 point1.display(); 143 System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:"); 144 point2.display(); 145 System.out.println("The line's length is:" + String.format("%.2f", getDistance())); 146 } 147 } 148 149 class Plane extends Element { 150 private String color; 151 152 public Plane(String color) { 153 this.color = color; 154 } 155 public Plane() { 156 } 157 158 public void setColor(String color) { 159 this.color = color; 160 } 161 162 public String getColor() { 163 return color; 164 } 165 166 @Override 167 void display() { 168 System.out.println("The Plane's color is:" + color); 169 170 } 171 172 } 173 174 class GeometryObject{ 175 private ArrayList<Element> list = new ArrayList<>(); 176 177 public GeometryObject() { 178 } 179 void add(Element element) { 180 list.add(element); 181 } 182 183 void remove(int index) { 184 list.remove(index - 1); 185 } 186 187 public ArrayList<Element> getList() { 188 return list; 189 } 190 }
-
踩坑心得:
- 如果抛出(throw)了异常一定要进行捕获(catch),否则程序会直接退出。如果希望程序只是忽略这个异常则可以在catch块中什么都不做。
-
可以使用语句import static java.lang.Math.*;来使使用数学函数时省略Math,增加代码可读性。
- 如果抛出(throw)了异常一定要进行捕获(catch),否则程序会直接退出。如果希望程序只是忽略这个异常则可以在catch块中什么都不做。
-
改进建议:
-
类class的访问器getter不应该返回类内部属性对象的引用,这样会使得外部仍然有可能更改类的private属性,这样就使封装失去了意义,解决方法为使用Object类中的clone方法(在属性对象中还有别的时需要重写)
- 类的属性不应该能从别的属性中推导而来,如果有则很可能在修改其中一个时没有更新另一个产生冲突
- 谨慎使用继承关系,父类和子类应该是一种严格的“是-一种”(is-a)关系,不要简单地为了复用一个方法而继承自一个父类
- 为了使类拥有某个方法时可以使用接口(interface)
-
-
总结:
- 经过这个月的学习对面向对戏程序设计的三大支柱有了初步的认识与应用,是一次令人印象深刻的练习与难能可贵的进步,让我初步窥探到了面向对象程序设计的精妙与便捷之处。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义