grad_cam下的自定义模型获取热力图
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/zxdd2018/article/details/125505352
另附:imagenet图对应https://www.cnblogs.com/cpxlll/p/13493247.html
1.(多张图片)
备注:gram_cam_1
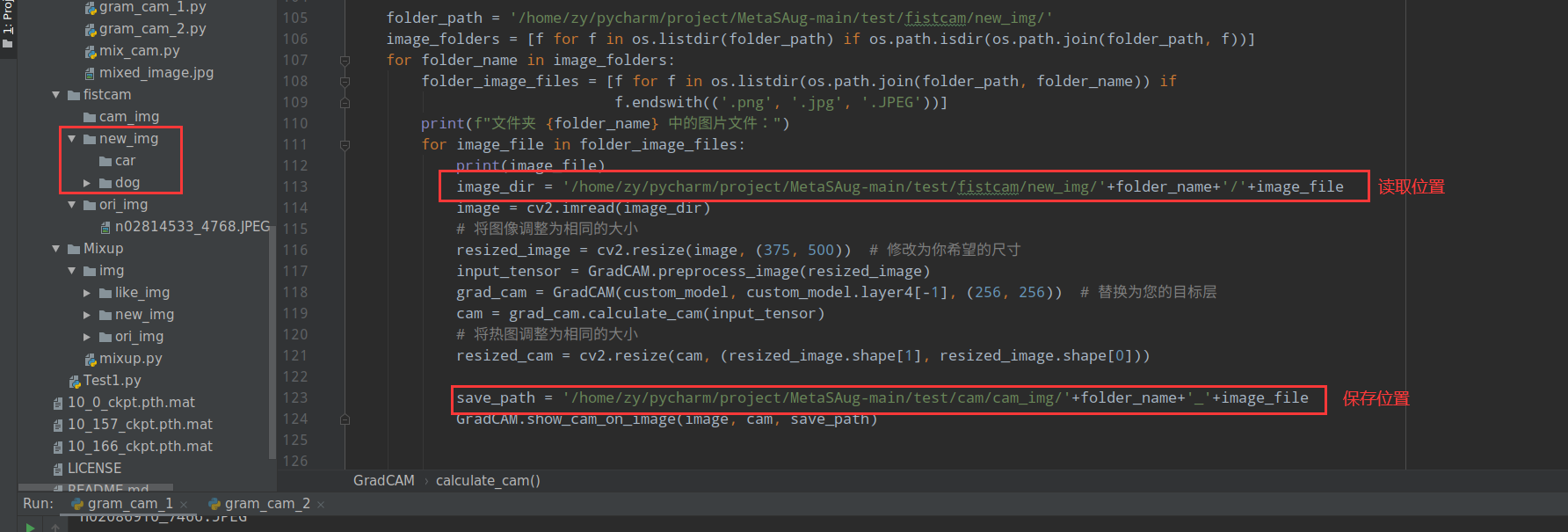
import os import numpy as np import torch import cv2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import torchvision.models as models from torchvision.transforms import Compose, Normalize, ToTensor from cifar.resnet import ResNet32 class GradCAM(): ''' Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization Selvaraju R R, Cogswell M, Das A, et al. https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_iccv_2017/html/Selvaraju_Grad-CAM_Visual_Explanations_ICCV_2017_paper.html ''' def __init__(self, model, target_layers, input_size, use_cuda=True): super(GradCAM).__init__() self.use_cuda = use_cuda self.model = model self.target_layers = target_layers self.target_layers.register_forward_hook(self.forward_hook) self.target_layers.register_full_backward_hook(self.backward_hook) self.activations = [] self.grads = [] self.input_size = input_size def forward_hook(self, module, input, output): self.activations.append(output[0]) def backward_hook(self, module, grad_input, grad_output): self.grads.append(grad_output[0].detach()) def calculate_cam(self, model_input): if self.use_cuda: device = torch.device('cuda') self.model.to(device) model_input = model_input.to(device) self.model.eval() # forward output, _ = self.model(model_input, 0) # 修改这里以匹配您模型的输出 y_hat = output max_class = np.argmax(y_hat.cpu().data.numpy(), axis=1) # backward self.model.zero_grad() y_c = y_hat[0, max_class] y_c.backward() # get activations and gradients activations = self.activations[0].cpu().data.numpy().squeeze() grads = self.grads[0].cpu().data.numpy().squeeze() # calculate weights weights = np.mean(grads.reshape(grads.shape[0], -1), axis=1) weights = weights.reshape(-1, 1, 1) cam = (weights * activations).sum(axis=0) cam = np.maximum(cam, 0) cam = cam / cam.max() return cam @staticmethod def show_cam_on_image(image, cam, save_path=None): h, w = image.shape[:2] cam = cv2.resize(cam, (w, h)) # 调整热图的尺寸与图像相同 cam = cam / cam.max() heatmap = cv2.applyColorMap((255 * cam).astype(np.uint8), cv2.COLORMAP_JET) heatmap = cv2.cvtColor(heatmap, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) image = image / image.max() heatmap = heatmap / heatmap.max() result = 0.4 * heatmap + 0.6 * image result = result / result.max() plt.figure() plt.imshow((result * 255).astype(np.uint8)) plt.colorbar(shrink=0.8) plt.tight_layout() if save_path: plt.savefig(save_path) # plt.show() @staticmethod def preprocess_image(img, mean=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5], std=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5]): preprocessing = Compose([ ToTensor(), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std) ]) return preprocessing(img.copy()).unsqueeze(0) if __name__ == '__main__': # 加载您的模型 # 假设您的模型保存在名为custom_model.pth.tar的文件中 checkpoint_path = '/home/zy/pycharm/project/MetaSAug-main/cifar/checkpoint1/151_31.21.pth.tar' # 模型的路径,你需要替换成你保存的模型的路径 custom_model = ResNet32(num_classes=100) # 假设你使用的是CIFAR-100数据集 checkpoint = torch.load(checkpoint_path) custom_model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict']) folder_path = '/home/zy/pycharm/project/MetaSAug-main/test/fistcam/new_img/' image_folders = [f for f in os.listdir(folder_path) if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(folder_path, f))] for folder_name in image_folders: folder_image_files = [f for f in os.listdir(os.path.join(folder_path, folder_name)) if f.endswith(('.png', '.jpg', '.JPEG'))] print(f"文件夹 {folder_name} 中的图片文件:") for image_file in folder_image_files: print(image_file) image_dir = '/home/zy/pycharm/project/MetaSAug-main/test/fistcam/new_img/'+folder_name+'/'+image_file image = cv2.imread(image_dir) # 将图像调整为相同的大小 resized_image = cv2.resize(image, (375, 500)) # 修改为你希望的尺寸 input_tensor = GradCAM.preprocess_image(resized_image) grad_cam = GradCAM(custom_model, custom_model.layer4[-1], (256, 256)) # 替换为您的目标层 cam = grad_cam.calculate_cam(input_tensor) # 将热图调整为相同的大小 resized_cam = cv2.resize(cam, (resized_image.shape[1], resized_image.shape[0])) save_path = '/home/zy/pycharm/project/MetaSAug-main/test/cam/cam_img/'+folder_name+'_'+image_file GradCAM.show_cam_on_image(image, cam, save_path)
2.(单个图片)
备注:gram_cam_2
import os import numpy as np import torch import cv2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import torchvision.models as models from torchvision.transforms import Compose, Normalize, ToTensor from cifar.resnet import ResNet32 class GradCAM(): ''' Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization Selvaraju R R, Cogswell M, Das A, et al. https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_iccv_2017/html/Selvaraju_Grad-CAM_Visual_Explanations_ICCV_2017_paper.html ''' def __init__(self, model, target_layers, input_size, use_cuda=True): super(GradCAM).__init__() self.use_cuda = use_cuda self.model = model self.target_layers = target_layers self.target_layers.register_forward_hook(self.forward_hook) self.target_layers.register_full_backward_hook(self.backward_hook) self.activations = [] self.grads = [] self.input_size = input_size def forward_hook(self, module, input, output): self.activations.append(output[0]) def backward_hook(self, module, grad_input, grad_output): self.grads.append(grad_output[0].detach()) def calculate_cam(self, model_input): if self.use_cuda: device = torch.device('cuda') self.model.to(device) model_input = model_input.to(device) self.model.eval() # forward output, _ = self.model(model_input, 0) # 修改这里以匹配您模型的输出 y_hat = output max_class = np.argmax(y_hat.cpu().data.numpy(), axis=1) # backward self.model.zero_grad() y_c = y_hat[0, max_class] y_c.backward() # get activations and gradients activations = self.activations[0].cpu().data.numpy().squeeze() grads = self.grads[0].cpu().data.numpy().squeeze() # calculate weights weights = np.mean(grads.reshape(grads.shape[0], -1), axis=1) weights = weights.reshape(-1, 1, 1) cam = (weights * activations).sum(axis=0) cam = np.maximum(cam, 0) cam = cam / cam.max() # Resize CAM to match the input size cam = cv2.resize(cam, (model_input.size(3), model_input.size(2))) return cam @staticmethod def show_cam_on_image(image, cam, save_path=None): h, w = image.shape[:2] cam = cv2.resize(cam, (w, h)) # 调整热图的大小与原图像相同 cam = cam / cam.max() heatmap = cv2.applyColorMap((255 * cam).astype(np.uint8), cv2.COLORMAP_JET) heatmap = cv2.cvtColor(heatmap, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) image = cv2.resize(image, (w, h)) # 调整原始图像的大小与热图相同 image = image / image.max() heatmap = heatmap / heatmap.max() result = 0.4 * heatmap + 0.6 * image result = result / result.max() plt.figure() plt.imshow((result * 255).astype(np.uint8)) plt.colorbar(shrink=0.8) plt.tight_layout() if save_path: plt.savefig(save_path) plt.show() @staticmethod def preprocess_image(img, mean=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5], std=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5]): preprocessing = Compose([ ToTensor(), Normalize(mean=mean, std=std) ]) return preprocessing(img.copy()).unsqueeze(0) if __name__ == '__main__': # 加载您的模型 # 假设您的模型保存在名为custom_model.pth.tar的文件中 # checkpoint_path = '/home/zy/pycharm/project/MetaSAug-main/cifar/checkpoint2/1_1.21.pth.tar' # 模型的路径,你需要替换成你保存的模型的路径 checkpoint_path = '/home/zy/pycharm/project/MetaSAug-main/cifar/checkpoint2/3_2.46.pth.tar' # 模型的路径,你需要替换成你保存的模型的路径 # checkpoint_path = '/home/zy/pycharm/project/MetaSAug-main/cifar/checkpoint2/40_20.66.pth.tar' # 模型的路径,你需要替换成你保存的模型的路径 # checkpoint_path = '/home/zy/pycharm/project/MetaSAug-main/cifar/checkpoint2/80_26.27.pth.tar' # 模型的路径,你需要替换成你保存的模型的路径 # checkpoint_path = '/home/zy/pycharm/project/MetaSAug-main/cifar/checkpoint2/120_26.86.pth.tar' # 模型的路径,你需要替换成你保存的模型的路径 # checkpoint_path = '/home/zy/pycharm/project/MetaSAug-main/cifar/checkpoint2/160_32.66.pth.tar' # 模型的路径,你需要替换成你保存的模型的路径 # checkpoint_path = '/home/zy/pycharm/project/MetaSAug-main/cifar/checkpoint1/151_31.21.pth.tar' # 模型的路径,你需要替换成你保存的模型的路径 # checkpoint_path = '/home/zy/pycharm/project/MetaSAug-main/cifar/checkpoint3/3_5.27.pth.tar' # 模型的路径,你需要替换成你保存的模型的路径 # checkpoint_path = '/home/zy/pycharm/project/MetaSAug-main/cifar/checkpoint3/40_20.96.pth.tar' # 模型的路径,你需要替换成你保存的模型的路径 # checkpoint_path = '/home/zy/pycharm/project/MetaSAug-main/cifar/checkpoint3/80_25.3.pth.tar' # 模型的路径,你需要替换成你保存的模型的路径 # checkpoint_path = '/home/zy/pycharm/project/MetaSAug-main/cifar/checkpoint3/120_25.62.pth.tar' # 模型的路径,你需要替换成你保存的模型的路径 # checkpoint_path = '/home/zy/pycharm/project/MetaSAug-main/cifar/checkpoint3/160_30.43.pth.tar' # 模型的路径,你需要替换成你保存的模型的路径 custom_model = ResNet32(num_classes=100) # 假设你使用的是CIFAR-100数据集 checkpoint = torch.load(checkpoint_path) custom_model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict']) image_dir = '/home/zy/Desktop/img2/n03792782_22692.JPEG' image = cv2.imread(image_dir) resized_image = cv2.resize(image, (256, 256)) # 修改为模型的输入尺寸 input_tensor = GradCAM.preprocess_image(resized_image) grad_cam = GradCAM(custom_model, custom_model.layer4[-1], (256, 256)) # 替换为您的目标层 cam = grad_cam.calculate_cam(input_tensor) save_path = '/home/zy/Desktop/img2/n03792782_22692_eda_1.jpg' GradCAM.show_cam_on_image(image, cam, save_path)
3.附件(ResNet32)
import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import math from torch.autograd import Variable import torch.nn.init as init import warnings import matplotlib.pyplot as plt warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # 定义了一个基类MetaModule,它是所有其他模块的父类。 # MetaModule提供了一些用于处理参数和更新参数的方法。 class MetaModule(nn.Module): # adopted from: Adrien Ecoffet https://github.com/AdrienLE def params(self): for name, param in self.named_params(self): yield param def named_leaves(self): return [] def named_submodules(self): return [] def named_params(self, curr_module=None, memo=None, prefix=''): if memo is None: memo = set() if hasattr(curr_module, 'named_leaves'): for name, p in curr_module.named_leaves(): if p is not None and p not in memo: memo.add(p) yield prefix + ('.' if prefix else '') + name, p else: for name, p in curr_module._parameters.items(): if p is not None and p not in memo: memo.add(p) yield prefix + ('.' if prefix else '') + name, p for mname, module in curr_module.named_children(): submodule_prefix = prefix + ('.' if prefix else '') + mname for name, p in self.named_params(module, memo, submodule_prefix): yield name, p def update_params(self, lr_inner, first_order=False, source_params=None, detach=False): if source_params is not None: for tgt, src in zip(self.named_params(self), source_params): name_t, param_t = tgt grad = src if first_order: grad = to_var(grad.detach().data) tmp = param_t - lr_inner * grad self.set_param(self, name_t, tmp) else: for name, param in self.named_params(self): if not detach: grad = param.grad if first_order: grad = to_var(grad.detach().data) tmp = param - lr_inner * grad self.set_param(self, name, tmp) else: param = param.detach_() self.set_param(self, name, param) def set_param(self, curr_mod, name, param): if '.' in name: n = name.split('.') module_name = n[0] rest = '.'.join(n[1:]) for name, mod in curr_mod.named_children(): if module_name == name: self.set_param(mod, rest, param) break else: setattr(curr_mod, name, param) def detach_params(self): for name, param in self.named_params(self): self.set_param(self, name, param.detach()) def copy(self, other, same_var=False): for name, param in other.named_params(): if not same_var: param = to_var(param.data.clone(), requires_grad=True) self.set_param(name, param) # 线性层:继承自MetaModule类,并重写了前向传播方法。 class MetaLinear(MetaModule): def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): super().__init__() ignore = nn.Linear(*args, **kwargs) self.register_buffer('weight', to_var(ignore.weight.data, requires_grad=True)) self.register_buffer('bias', to_var(ignore.bias.data, requires_grad=True)) def forward(self, x): return F.linear(x, self.weight, self.bias) def named_leaves(self): return [('weight', self.weight), ('bias', self.bias)] # 归一化线性层:继承自MetaModule类,并重写了前向传播方法。 class MetaLinear_Norm(MetaModule): def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): super().__init__() temp = nn.Linear(*args, **kwargs) temp.weight.data.uniform_(-1, 1).renorm_(2, 1, 1e-5).mul_(1e5) self.register_buffer('weight', to_var(temp.weight.data.t(), requires_grad=True)) self.weight.data.uniform_(-1, 1).renorm_(2, 1, 1e-5).mul_(1e5) def forward(self, x): out = F.normalize(x, dim=1).mm(F.normalize(self.weight, dim=0)) return out def named_leaves(self): return [('weight', self.weight)] # 卷积层:继承自MetaModule类,并重写了前向传播方法。 class MetaConv2d(MetaModule): def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): super().__init__() ignore = nn.Conv2d(*args, **kwargs) self.in_channels = ignore.in_channels self.out_channels = ignore.out_channels self.stride = ignore.stride self.padding = ignore.padding self.dilation = ignore.dilation self.groups = ignore.groups self.kernel_size = ignore.kernel_size self.register_buffer('weight', to_var(ignore.weight.data, requires_grad=True)) if ignore.bias is not None: self.register_buffer('bias', to_var(ignore.bias.data, requires_grad=True)) else: self.register_buffer('bias', None) def forward(self, x): return F.conv2d(x, self.weight, self.bias, self.stride, self.padding, self.dilation, self.groups) def named_leaves(self): return [('weight', self.weight), ('bias', self.bias)] # 转置卷积层:继承自MetaModule类,并重写了前向传播方法。 class MetaConvTranspose2d(MetaModule): def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): super().__init__() ignore = nn.ConvTranspose2d(*args, **kwargs) self.stride = ignore.stride self.padding = ignore.padding self.dilation = ignore.dilation self.groups = ignore.groups self.register_buffer('weight', to_var(ignore.weight.data, requires_grad=True)) if ignore.bias is not None: self.register_buffer('bias', to_var(ignore.bias.data, requires_grad=True)) else: self.register_buffer('bias', None) def forward(self, x, output_size=None): output_padding = self._output_padding(x, output_size) return F.conv_transpose2d(x, self.weight, self.bias, self.stride, self.padding, output_padding, self.groups, self.dilation) def named_leaves(self): return [('weight', self.weight), ('bias', self.bias)] # 批归一化层:继承自MetaModule类,并重写了前向传播方法。 class MetaBatchNorm2d(MetaModule): def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs): super().__init__() ignore = nn.BatchNorm2d(*args, **kwargs) self.num_features = ignore.num_features self.eps = ignore.eps self.momentum = ignore.momentum self.affine = ignore.affine self.track_running_stats = ignore.track_running_stats if self.affine: self.register_buffer('weight', to_var(ignore.weight.data, requires_grad=True)) self.register_buffer('bias', to_var(ignore.bias.data, requires_grad=True)) if self.track_running_stats: self.register_buffer('running_mean', torch.zeros(self.num_features)) self.register_buffer('running_var', torch.ones(self.num_features)) else: self.register_parameter('running_mean', None) self.register_parameter('running_var', None) def forward(self, x): return F.batch_norm(x, self.running_mean, self.running_var, self.weight, self.bias, self.training or not self.track_running_stats, self.momentum, self.eps) def named_leaves(self): return [('weight', self.weight), ('bias', self.bias)] class LambdaLayer(MetaModule): def __init__(self, lambd): super(LambdaLayer, self).__init__() self.lambd = lambd def forward(self, x): return self.lambd(x) # BasicBlock类,它是ResNet中的基本块。它继承自MetaModule类,并重写了前向传播方法。 class BasicBlock(MetaModule): expansion = 1 def __init__(self, in_planes, planes, stride=1, option='A'): super(BasicBlock, self).__init__() self.conv1 = MetaConv2d(in_planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False) self.bn1 = MetaBatchNorm2d(planes) self.conv2 = MetaConv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False) self.bn2 = MetaBatchNorm2d(planes) self.shortcut = nn.Sequential() if stride != 1 or in_planes != planes: if option == 'A': self.shortcut = LambdaLayer(lambda x: F.pad(x[:, :, ::2, ::2], (0, 0, 0, 0, planes // 4, planes // 4), "constant", 0)) elif option == 'B': self.shortcut = nn.Sequential( MetaConv2d(in_planes, self.expansion * planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False), MetaBatchNorm2d(self.expansion * planes) ) def forward(self, x): out = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x))) out = self.bn2(self.conv2(out)) out += self.shortcut(x) out = F.relu(out) return out # for metamodel # 定义了ResNet32类,它是一个完整的ResNet模型。 # 它继承自MetaModule类,并定义了ResNet的整体结构和前向传播方法。 class ResNet32_meta(MetaModule): # _first_init_done = False def __init__(self, num_classes, block=BasicBlock, num_blocks=[5, 5, 5]): super(ResNet32_meta, self).__init__() self.in_planes = 16 self.conv1 = MetaConv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False) self.bn1 = MetaBatchNorm2d(16) self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 16, num_blocks[0], stride=1) self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 32, num_blocks[1], stride=2) self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 64, num_blocks[2], stride=2) self.linear = MetaLinear(64, num_classes) self.apply(_weights_init) def _make_layer(self, block, planes, num_blocks, stride): strides = [stride] + [1] * (num_blocks - 1) layers = [] for stride in strides: layers.append(block(self.in_planes, planes, stride)) self.in_planes = planes * block.expansion return nn.Sequential(*layers) def forward(self, x, epoch): out = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x))) out = self.layer1(out) out = self.layer2(out) out = self.layer3(out) out = F.avg_pool2d(out, out.size()[3]) out = out.view(out.size(0), -1) y = self.linear(out) return out, y # for main class ResNet32(MetaModule): def __init__(self, num_classes, block=BasicBlock, num_blocks=[5, 5, 5, 5]): super(ResNet32, self).__init__() self.in_planes = 16 self.conv1 = MetaConv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False) self.bn1 = MetaBatchNorm2d(16) self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 16, num_blocks[0], stride=1) self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 32, num_blocks[1], stride=2) self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 64, num_blocks[2], stride=2) self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 128, num_blocks[3], stride=2) # Add # print("Using self attention") # self.modulatedatt = ModulatedAttLayer(in_channels=64 * block.expansion) # # # self.cbam = CBAM(64 * block.expansion, 64) # self.scse1 = SCse(16*block.expansion) # self.scse2 = SCse(32*block.expansion) # self.scse3 = SCse(64*block.expansion) self.linear = MetaLinear(128, num_classes) self.apply(_weights_init) def _make_layer(self, block, planes, num_blocks, stride): strides = [stride] + [1] * (num_blocks - 1) layers = [] for stride in strides: layers.append(block(self.in_planes, planes, stride)) self.in_planes = planes * block.expansion return nn.Sequential(*layers) def forward(self, x, epoch): out = F.relu(self.bn1(self.conv1(x))) out = self.layer1(out) out = self.layer2(out) out = self.layer3(out) out = self.layer4(out) out = F.avg_pool2d(out, out.size()[3]) # out = F.avg_pool2d(out, kernel_size=(13, 18)) out = out.view(out.size(0), -1) y = self.linear(out) return out, y def to_var(x, requires_grad=True): if torch.cuda.is_available(): x = x.cuda() return Variable(x, requires_grad=requires_grad) def _weights_init(m): classname = m.__class__.__name__ if isinstance(m, MetaLinear) or isinstance(m, MetaConv2d): init.kaiming_normal(m.weight)
本文作者:太好了还有脑子可以用
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/ZarkY/p/18111458
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步