Vuex的基本概念、项目搭建、入坑点

前言:Vuex是一个专门为Vue.js应用程序开发的状态管理模式, 它采用集中式存储管理所有组件的公共状态, 并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化.
Vuex的四大核心
1.state 驱动应用的数据源
2.mutations 基因突变 类如C# 属性get set
3.actions 行为
4.getters 读取器
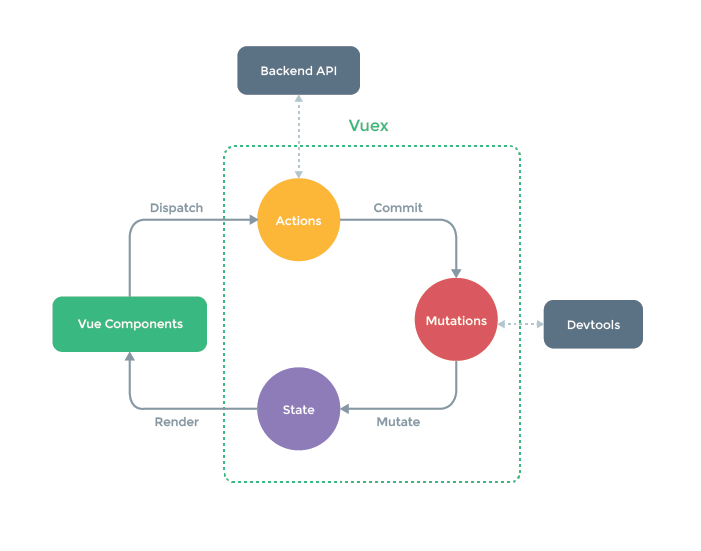
上图中绿色虚线包裹起来的部分就是Vuex的核心, state中保存的就是公共状态, 改变state的唯一方式就是通过mutations进行更改. 可能你现在看这张图有点不明白, 等经过本文的解释和案例演示, 再回来看这张图, 相信你会有更好的理解.
如何引入Vuex?
1.npm install vuex
2.装好了之后,在全局上去使用你的Vuex
3.创建Store对象,最好在src创建一个store这样的文件夹然后创建index.js
4.在main.js中注册使用
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use( Vuex );
const store = new Vuex.Store({
//待添加
})
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
render: h => h(App)
})
为了讲解Vuex,我们做了一个项目,这个项目需要连接apicloud,异步操作使用了axios以及样式bootstrap,其中包括了登录注册以及其中的父组件向子节点传值等,我们给项目安装相关的modules
npm install bootstrap
npm install axios
router.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
Vue.use(Router)
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: 'index',
component:()=>import('../views/index.vue')
},
{
path:'/detail/:id',
name:'detail',
component:()=>import ('../views/detail.vue')
},
{
path:'/login',
name:'login',
component:()=>import ('../views/login.vue')
},
{
path:'/register',
name:'register',
component:()=>import ('../views/register.vue')
}
]
})
store.js
我们来上述代码中来讲解其中vuex的奥秘,State就是所有组件提出来的data,用于所有组件公共数据,而其中mutations就像C#中get\set,属性赋值器,其中方法的两个参数除了state只能带一个参数。
actions是操作数据的方法,说过说你的actions中需要改变state中的数据,那么必须要通过commit关键字去提交给mutations,还有一点就是actions中很多操作都是关于异步处理的,最关键就是它是操作state数据的,那getters是什么呢?它是组件访问vuex的入口,里面写好了方法去操作,它也是过滤器,就像程序中的三层架构BLL.
main.js
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command
// (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias.
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
import boostrap from 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.css'
import store from './store/index.js'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store,//在全局对象上加载仓库
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})
两个组件
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import API from '../utils/api.js'
var api = new API('goods')
var userApi = new API('userinfo');
Vue.use(Vuex);
const state = {
user: null,
products: []
}
const mutations = {
//加载产品数据
INIT_PRODUCTS(state, data) {
state.products = data;
},
SET_LOGIN_USER(state, u) {
state.user = u;
}
}
const actions = {
LOAD_PRODUCTS({ commit }) {
api.Select().then(res => {
commit('INIT_PRODUCTS', res.data);
})
},
LOGIN({ commit }, user) {
return userApi.Select().then(res => {
let users = res.data;//所有的用户
for (let u of users) {
if (u.name == user.name && u.password == user.password) {
commit('SET_LOGIN_USER', u);
return u;
}
}
})
},
REGISTER({ commit }, user) {
return userApi.Insert(user).then(res => {
console.log(res.data);
return 'OK';
}).catch(err => {
return err;
})
}
}
const getters = {
ALL_PRODUCTS(state) {
return state.products;
},
GET_PRODUCT_BYID: (state) => function (id) {
//遍历 is == id
for (let p of state.products) {
if (p.id == id) {
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
}
//仓库
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: state,
mutations: mutations,
actions: actions,
getters: getters
})
export default store;
navbar.vue
<template>
<nav class="navbar navbar-expand-lg navbar-dark bg-dark">
<div class="container">
<a class="navbar-brand" href="#">购物车</a>
<ul class="navbar-nav ml-auto">
<li class="nav-item active dropdown" v-if="user!==null">
<a class="nav-link dropdown-toggle" data-toggle="dropdown" @click="showDropdown=!showDropdown">欢迎你:{{user.name}} </a>
<div class="dropdown-menu show">
<a class="dropdown-item" href="#">我的订单</a>
<div class="dropdown-divider"></div>
<a class="dropdown-item" >注销</a>
</div>
</li>
<li class="nav-item active" style="margin-right:5px" v-if="user===null">
<router-link class="nav-link btn btn-warning btn-sm" style="color:#fff" to="/login">登录</router-link>
</li>
<li class="nav-item active" v-if="user===null">
<router-link class="nav-link btn btn-danger btn-sm" style="color:#fff" to="/register">注册</router-link>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</nav>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
showDropdown:false
}
},
computed:{
user(){
return this.$store.state.user;
}
}
}
</script>
product.vue 该组件用于显示商品的详细信息
<template>
<div class="card">
<img class="card-img-top" src="../../assets/logo.png" alt="Card image cap">
<div class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">{{product.name}}</h5>
<p class="card-text">{{product.description===null?"暂无描述":product.description}}</p>
<p>价格: {{product.price}}</p>
<a href="#" class="btn btn-warning float-left" @click="goDetail">查看详情</a>
<a href="#" class="btn btn-primary float-right">加入购物车</a>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props:['product'],
methods:{
goDetail(){
console.log(this.product.id);
this.$router.push(`/detail/${this.product.id}`);
}
}
}
</script>
程序入口APP.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<nav-bar></nav-bar>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import NavBar from './views/components/navbar'
export default {
name: 'App',
components:{NavBar}
}
</script>
注册:通过this.$store.dispatch去调用actions中的方法,其中有趣的是commit的参数竟然被方法名给..这个以后在思考。。
<template>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="card" style="margin:50px auto;width:400px">
<div class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">注册</h5>
<hr>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">用户名</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" v-model="user.name">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">真实姓名</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" v-model="user.realname">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">密码</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" v-model="user.password">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<button class="btn btn-primary btn-block" @click="register">注册</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return{
user:{
name:'',
realname:'',
password:''
}
}
},methods:{
register(){
this.$store.dispatch('REGISTER',this.user).then(res=>{
if(res=="OK")
this.$router.push('/index');
})
}
}
}
</script>
登录
<template>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="card" style="margin:50px auto;width:400px">
<div class="card-body">
<h5 class="card-title">登录</h5>
<hr>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">用户名</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" v-model="user.name">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">密码</label>
<input type="password" class="form-control" v-model="user.password">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<button class="btn btn-primary btn-block" @click="login">登录</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return {
user:{
name:'',
password:''
}
}
},
methods:{
login(){
this.$store.dispatch('LOGIN',this.user).then(res=>{
console.log(res);
if (res){
this.$router.push('/')
}
})
}
}
}
</script>
主页面
<template>
<div class="container">
<h1>商品列表</h1>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4" v-for="p in products" :key="p.id">
<!-- 传递商品信息到子组件 -->
<product-card :product="p"></product-card>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import ProductCard from './components/product.vue'
export default {
components:{ProductCard},
computed:{
products(){
return this.$store.getters.ALL_PRODUCTS;
}
},
created(){
this.$store.dispatch('LOAD_PRODUCTS');
}
}
</script>
本文结语知识总结:
获取url中的参数
let id = this.$route.params.id; this.details = this.$store.getters.GET_PRODUCT_BYID(id);
有的小伙伴在复制我的代码运行报错,说什么未初始化;一定要在index.vue添加这个代码,LOAD_PRODUCTS给数据初始化
created(){
this.$store.dispatch('LOAD_PRODUCTS');
}
跳转路由
this.$router.push('/')
ApiClound万能帮助类
import crypto from 'crypto' // 加密
import axios from 'axios'
class API {
constructor(classname){
this.api = `https://d.apicloud.com/mcm/api/${classname}`;
let ID = '';
let KEY = '';
let now = Date.now(); //当前时间
let sha1 = crypto.createHash('sha1');
sha1.update(ID + "UZ" + KEY + "UZ" + now);
axios.defaults.headers["X-APICloud-AppId"] = ID;
axios.defaults.headers["X-APICloud-AppKey"] = sha1.digest('hex') + "." + now;
}
Select(){
return axios.get(this.api);
}
Insert(obj){
return axios.post(this.api,obj);
}
Update(id,obj){
// RESTFUL API
return axios.put(this.api+`/${id}`,obj);
}
Delete(id){
return axios.delete(this.api + `/${id}`);
}
}
export default API;
还有同学问我父组件和子组件如何传值?
在父页面引用的地方以":"表示的值都可以在子页面的props获取到
<template>
<div>
<h3>图书管理</h3><hr>
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4 col-sm-4" v-for="b in books" :key="b.id">
<book-detail @abc="xyz" :Book="b" :MSG="abc"></book-detail>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import BookDetail from './components/BookDetails.vue'
export default{
components:{BookDetail},
data(){
return {
abc:'heheda',
books:[{
id:1,
name:'7天 JAVA 从入门到放弃',
text:'到底是人性的扭曲,还是道德的沦丧. 青年男子为何突然脱发,中年男人为何删库跑路。',
price:20,
img:'img2.jpg',
showHehe:true
},{
id:2,
name:'7天 C# 从入门到自杀',
text:'到底是人性的扭曲啊,还是道德的沦丧啊. 祖国的花朵为何自杀。',
price:20,
img:'../../static/img2.jpg',
showHehe:false
}]
}
},
methods:{
xyz(bid){
alert(bid);
}
}
}
</script>
在子页面中可以这么搞
<script>
export default{
props:["Book","MSG"],
created(){
console.log(this.Book.name);
},
methods:{
select(id){
this.$emit('abc',id);
},
detail(bid){
this.$router.push(`/admin/Details/${bid}`);
}
}
}
</script>
而其中的$emit是可以调用父页面的方法的。
谢谢大家收看!!!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号