【智能车】摄像头算法理论(3) Sobel算子的应用与实现
Sobel算子理论部分
智能车在场地光照环境复杂情况下赛道存在反光情况,二值化时出现将原本的非赛道区域误认为赛道,故借助CV中常用的一阶边缘检测算子Sobel算子,计算较为方便且准确。Sobel算子边缘检测的大致原理就是观察这一点处在周围各点亮度变化明显程度,明显的变化往往反映着现实中的突变、不连续,具体运算上是用Sobel卷积核去乘以这一点,这一过程类似于求梯度,或者说一阶导数,一旦这一变化(梯度/导数值)大于设定的某一阈值,我们认定这一点存在突变,以下即Sobel卷积核
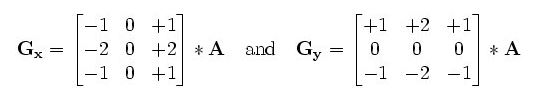
最终Gx和Gy加和为G,G即该点的特征,也是与阈值对比的判据,一旦G大于阈值,认定该点产生了突变
Gx = (-1)*f(x-1, y-1) + 0*f(x,y-1) + 1*f(x+1,y-1)
+ (-2)*f(x-1,y) + 0*f(x,y) + 2*f(x+1,y)
+ (-1)*f(x-1,y+1) + 0*f(x,y+1) + 1*f(x+1,y+1)
Gy = 1* f(x-1, y-1) + 2*f(x,y-1) + 1*f(x+1,y-1)
+ 0*f(x-1,y) + 0*f(x,y) + 0*f(x+1,y)
+(-1)*f(x-1,y+1) + (-2)*f(x,y+1) + (-1)*f(x+1, y+1)
Sobel算子算法实现
算法实现上相当简单,不赘述
//#define cam_h 60 //高度(行) //#define cam_w 120 //宽度(列) void sobel(uint8_t imag[cam_h][cam_w],uint8_t imag1[cam_h][cam_w]) { int tempx=0,tempy=0,temp=0,i=0,j=0; for(i=1;i <cam_h-1; i++) { for(j=1;j<cam_w-1;j++) { tempx=(- imag[i-1][j-1]) +(-2*imag[i ][j-1]) +(- imag[i+1][j-1]) +( imag[i-1][j+1]) +( 2*imag[i ][j+1]) +( imag[i+1][j+1]); if(tempx<0) tempx=-tempx; tempy=( imag[i+1][j-1]) +( 2*imag[i+1][j ]) +( imag[i+1][j+1]) +(- imag[i-1][j-1]) +(-2*imag[i-1][j ]) +(- imag[i-1][j+1]); if(tempy<0) tempy=-tempy; temp=tempx+tempy; if(temp>255) temp=255; imag1[i][j]=temp; } } } temp=sqrt(tempx*tempx+tempy*tempy);
参引: https://www.cnblogs.com/wj-1314/p/9800272.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/sdu20112013/p/11608469.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/lancidie/archive/2011/07/17/2108885.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/sophia-hxw/p/6088035.html
近期乱七八糟的事挺多,间断了挺久,后段闲了多更
2021/4/14 0:12
In HRB


