CF Round #427 (Div. 2) C. Star sky [dp]
The Cartesian coordinate system is set in the sky. There you can see n stars, the i-th has coordinates (xi, yi), a maximum brightness c, equal for all stars, and an initial brightness si (0 ≤ si ≤ c).
Over time the stars twinkle. At moment 0 the i-th star has brightness si. Let at moment t some star has brightness x. Then at moment (t + 1) this star will have brightness x + 1, if x + 1 ≤ c, and 0, otherwise.
You want to look at the sky q times. In the i-th time you will look at the moment ti and you will see a rectangle with sides parallel to the coordinate axes, the lower left corner has coordinates (x1i, y1i) and the upper right — (x2i, y2i). For each view, you want to know the total brightness of the stars lying in the viewed rectangle.
A star lies in a rectangle if it lies on its border or lies strictly inside it.
The first line contains three integers n, q, c (1 ≤ n, q ≤ 105, 1 ≤ c ≤ 10) — the number of the stars, the number of the views and the maximum brightness of the stars.
The next n lines contain the stars description. The i-th from these lines contains three integers xi, yi, si(1 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 100, 0 ≤ si ≤ c ≤ 10) — the coordinates of i-th star and its initial brightness.
The next q lines contain the views description. The i-th from these lines contains five integers ti, x1i, y1i, x2i, y2i (0 ≤ ti ≤ 109, 1 ≤ x1i < x2i ≤ 100, 1 ≤ y1i < y2i ≤ 100) — the moment of the i-th view and the coordinates of the viewed rectangle.
For each view print the total brightness of the viewed stars.
2 3 3
1 1 1
3 2 0
2 1 1 2 2
0 2 1 4 5
5 1 1 5 5
3
0
3
3 4 5
1 1 2
2 3 0
3 3 1
0 1 1 100 100
1 2 2 4 4
2 2 1 4 7
1 50 50 51 51
3
3
5
0
Let's consider the first example.
At the first view, you can see only the first star. At moment 2 its brightness is 3, so the answer is 3.
At the second view, you can see only the second star. At moment 0 its brightness is 0, so the answer is 0.
At the third view, you can see both stars. At moment 5 brightness of the first is 2, and brightness of the second is 1, so the answer is 3.
我们可以得到状态cnt[t][x][y]表示在t时刻区间[1,x],[1,y]构成的矩形内星星的总亮度。
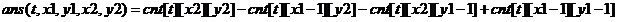
那么状态怎么转移呢?
我们还可以知道,第i颗星星在t时刻的亮度为。
由简单的二维dp就可以写出
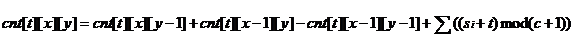
t很大???模c+1就好啦?
这样子就通过这道题啦。
1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<iostream> 4 using namespace std; 5 #define dbg(x) cout<<#x<<" = "<<x<<endl; 6 7 int read(){ 8 bool flag=0; 9 int re=0; 10 char ch; 11 while((ch=getchar())!='-'&&(ch<'0'||ch>'9')); 12 ch=='-'?flag=1:re=ch-'0'; 13 while((ch=getchar())>='0'&&ch<='9') re=re*10+ch-'0'; 14 return flag?-re:re; 15 } 16 17 const int maxn=100005,maxsize=105,maxc=13; 18 const int X=100,Y=100; 19 20 int n,m,head[maxsize][maxsize],nxt[maxn],s[maxn]; 21 int dp[maxc][maxsize][maxsize],c; 22 23 int main(){ 24 scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&c); c++; 25 for(int i=1,x,y;i<=n;i++){ 26 scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&s[i]); 27 nxt[i]=head[x][y]; 28 head[x][y]=i; 29 } 30 for(int i=0,pos;i<c;i++) 31 for(int x=1;x<=X;x++) 32 for(int y=1;y<=Y;y++){ 33 pos=0; 34 for(int j=head[x][y];j;j=nxt[j]) 35 pos+=(s[j]+i)%c; 36 dp[i][x][y]=dp[i][x-1][y]+dp[i][x][y-1]-dp[i][x-1][y-1]+pos; 37 // printf("dp[%d][%d][%d] = %d\n",i,x,y,dp[i][x][y]); 38 } 39 for(int i=0,t,x1,y1,x2,y2;i<m;i++){ 40 scanf("%d%d%d%d%d",&t,&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2); t%=c; 41 printf("%d\n",dp[t][x2][y2]-dp[t][x1-1][y2]-dp[t][x2][y1-1]+dp[t][x1-1][y1-1]); 42 // printf("%d %d %d %d\n",dp[t][x2][y2],dp[t][x1-1][y2],dp[t][x2][y1-1],dp[t][x1-1][y1-1]); 43 } 44 return 0; 45 }

