求两条线段的交点
两条线段的两个端点坐标(x1,y1) (x2,y2) (x3,y3) (x4,y4)
b1=(y2-y1)*x1+(x1-x2)*y1
b2=(y4-y3)*x3+(x3-x4)*y3
D=(x2-x1)(y4-y3)-(x4-x3)(y2-y1)
D1=b2*(x2-x1)-b1*(x4-x3)
D2=b2*(y2-y1)-b1*(y4-y3)
交点(x0,y0)
x0=D1/D y0=D2/D
推导:http://www.cnblogs.com/dwdxdy/p/3230485.html
You are given nn segments on a Cartesian plane. Each segment's endpoints have integer coordinates. Segments can intersect with each other. No two segments lie on the same line.
Count the number of distinct points with integer coordinates, which are covered by at least one segment.
The first line contains a single integer nn (1≤n≤10001≤n≤1000) — the number of segments.
Each of the next nn lines contains four integers Axi,Ayi,Bxi,ByiAxi,Ayi,Bxi,Byi (−106≤Axi,Ayi,Bxi,Byi≤106−106≤Axi,Ayi,Bxi,Byi≤106) — the coordinates of the endpoints AA, BB (A≠BA≠B) of the ii-th segment.
It is guaranteed that no two segments lie on the same line.
Print a single integer — the number of distinct points with integer coordinates, which are covered by at least one segment.
9
0 0 4 4
-1 5 4 0
4 0 4 4
5 2 11 2
6 1 6 7
5 6 11 6
10 1 10 7
7 0 9 8
10 -1 11 -1
42
4
-1 2 1 2
-1 0 1 0
-1 0 0 3
0 3 1 0
7
The image for the first example:
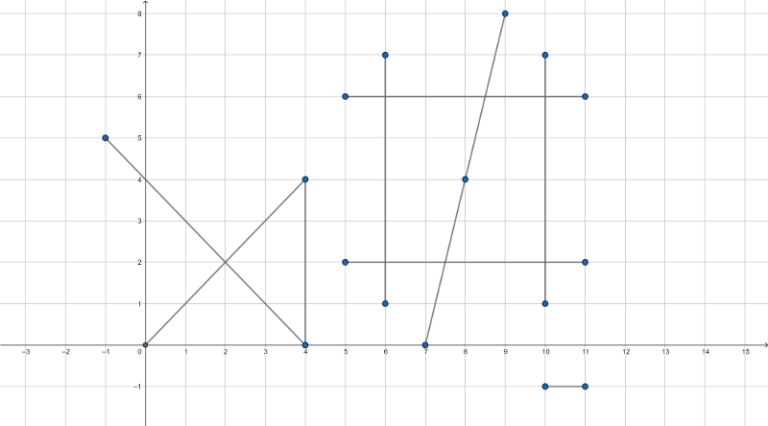
Several key points are marked blue, the answer contains some non-marked points as well.
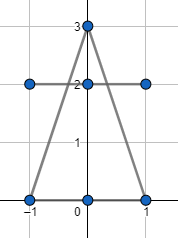
The image for the second example:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
struct Point{
ll x,y;
Point(ll x=0,ll y=0):x(x),y(y){};
};
ll gcd(ll a,ll b)
{
return a==0?b:gcd(b%a,a);
}
bool cheak(ll op1,ll a,ll b){
if(a>b)
swap(a,b);
return op1>=a&&op1<=b;
}
Point point_of_intersection(Point f1,Point f2,Point f3,Point f4,bool &mark)
{
ll a1,a2,b1,b2,c1,c2,c3,c4,D,D1,D2;
a1=f2.y-f1.y;
a2=f1.x-f2.x;
b1=a1*f1.x+a2*f1.y;
///b1=(y2-y1)*x1+(x1-x2)*y1
c1=f4.y-f3.y;
c2=f3.x-f4.x;
b2=c1*f3.x+c2*f3.y;
///b2=(y4-y3)*x3+(x3-x4)*y3
c3=f2.x-f1.x;
c4=f4.x-f3.x;
D=c3*c1-c4*a1;
Point res;
if(D==0){
mark=false;
return res;
}
D1=b2*c3-b1*c4;
if(D1%D){
mark=false;
return res;
}
res.x=int(D1/D);
D2=b2*a1-b1*c1;
if(D2%D){
mark=false;
return res;
}
res.y=int(D2/D);
if(!cheak(res.x,f1.x,f2.x)||!cheak(res.x,f3.x,f4.x)){
mark=false; return res;
}
if(!cheak(res.y,f1.y,f2.y)||!cheak(res.y,f3.y,f4.y)){
mark=false; return res;
}
return res;
}
Point edge[1006][2];
int main()
{
int n;
while( ~scanf("%d",&n)){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld",&edge[i][0].x,&edge[i][0].y,&edge[i][1].x,&edge[i][1].y);
}
set<pair<ll,ll> > re;
long long ans=0,tmp;
bool mark;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
tmp=gcd(abs(edge[i][0].x-edge[i][1].x),abs(edge[i][0].y-edge[i][1].y))+1;
re.clear();
for(int j=1;j<i;j++){
mark=true;
Point res=point_of_intersection(edge[i][0],edge[i][1],edge[j][0],edge[j][1],mark);
if(mark)
re.insert(make_pair(res.x,res.y));
}
ans+=tmp-re.size();
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}

