HDU1506(单调栈或者DP) 分类: 数据结构 2015-07-07 23:23 2人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
Largest Rectangle in a Histogram
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 13997 Accepted Submission(s): 3982
Problem Description
A
histogram is a polygon composed of a sequence of rectangles aligned at a
common base line. The rectangles have equal widths but may have
different heights. For example, the figure on the left shows the
histogram that consists of rectangles with the heights 2, 1, 4, 5, 1, 3,
3, measured in units where 1 is the width of the rectangles:
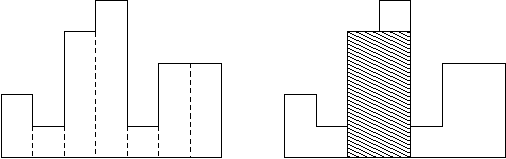
Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.

Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.
Input
The
input contains several test cases. Each test case describes a histogram
and starts with an integer n, denoting the number of rectangles it is
composed of. You may assume that 1 <= n <= 100000. Then follow n
integers h1, ..., hn, where 0 <= hi <= 1000000000. These numbers
denote the heights of the rectangles of the histogram in left-to-right
order. The width of each rectangle is 1. A zero follows the input for
the last test case.
Output
For
each test case output on a single line the area of the largest
rectangle in the specified histogram. Remember that this rectangle must
be aligned at the common base line.
Sample Input
7 2 1 4 5 1 3 3
4 1000 1000 1000 1000
0
Sample Output
8
4000
Source
Difficulty:单调栈:栈内的元素,按照某种方式排序下(单调递增或者单调递减) 如果新入栈的元素破坏了单调性,就弹出栈内元素,直到满足单调性
单调栈模板:
1 int top=0,s[maxn]; 2 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 3 { 4 while(top&&h[s[top]]>=h[i])//根据改变大于号小于号来改变单调性。 5 { 6 --top;//出栈,一般在while这重循环里添加东西去满足题意。 7 } 8 s[++top]=i; //入栈 9 }
单调栈解法:
1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<cstdlib> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 long long h[100006]; 8 int s[100006]; 9 long long area[100006]; 10 int L[100006]; 11 int R[100006]; 12 int n; 13 long long ans; 14 bool cmp( int a, int c) 15 { 16 return a>c; 17 18 } 19 int main() 20 { 21 while(~scanf("%d",&n)&&n) 22 { 23 int top=0; 24 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 25 { 26 scanf("%lld",&h[i]); 27 while(top&&h[s[top]]>=h[i]) 28 --top; 29 L[i]=(top==0?1:s[top]+1); 30 s[++top]=i; 31 } 32 top=0; 33 for(int i=n;i>=1;i--) 34 { 35 while(top&&h[s[top]]>=h[i]) 36 --top; 37 R[i]=(top==0?n:s[top]-1); 38 s[++top]=i; 39 } 40 ans=-1; 41 42 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 43 { 44 area[i]=h[i]*(R[i]-L[i]+1); 45 if(ans<area[i]) 46 ans=area[i]; 47 48 } 49 printf("%lld\n",ans); 50 } 51 return 0; 52 }
DP解法:
1 #include<cstdio> 2 #include<cstring> 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<algorithm> 5 using namespace std; 6 #define maxn 251000+5 7 long long h[maxn]; 8 int L[maxn]; 9 int R[maxn]; 10 int n,m; 11 int main() 12 { 13 while(~scanf("%d",&n)) 14 { 15 if(n==0) 16 break; 17 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 18 { 19 scanf("%lld",&h[i]); 20 R[i]=L[i]=i; 21 } 22 h[0]=-1; 23 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 24 { 25 while(h[i]<=h[L[i]-1]) 26 L[i]=L[L[i]-1]; 27 } 28 h[n+1]=-1; 29 for(int i=n;i>=1;i--) 30 { 31 while(h[i]<=h[R[i]+1]) 32 R[i]=R[R[i]+1]; 33 } 34 long long max1=0; 35 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) 36 { 37 max1=max(max1,(R[i]-L[i]+1)*h[i]); 38 } 39 printf("%lld\n",max1); 40 } 41 42 return 0; 43 }
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号