JDBC的学习笔记
1、JDBC是什么?
1.1 JDBC:Java DataBase Connectivity(Java语言连接数据库),是SUN公司制定的一套接口(interface)
思考:为什么sun制定一套JDBC的接口呢?
因为每一个数据库的底层实现原理都不一样
1.2 JDBC的接口的实现者与调用者之间的关系
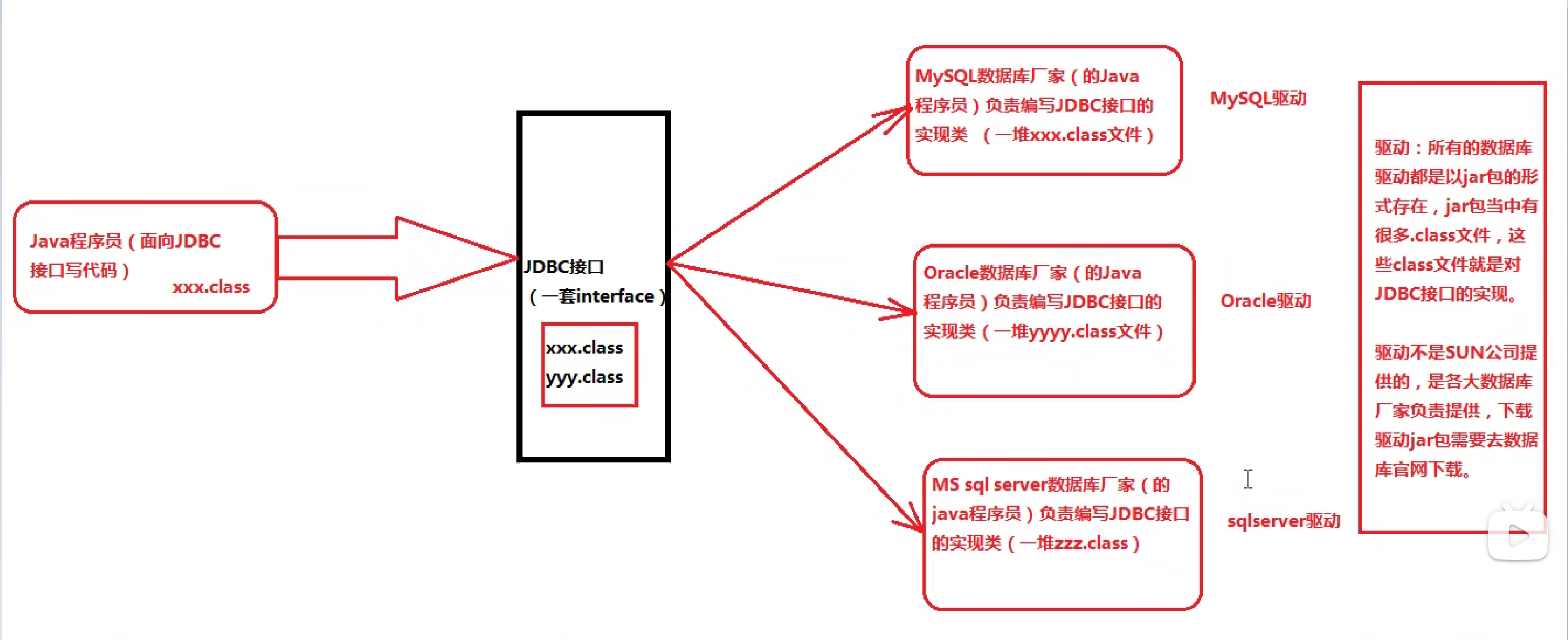
1.3 JDBC的本质:一套接口
2、JDBC编程六步(需要背会)
2.1 注册驱动#
有两种方式:
第一种:
//先导包
import java.sql.*;
Driver driver = new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
第二种(常用):
//通过类加载去注册驱动,因为在MySQL的驱动中的Driver方法里的静态代码块已经实现了注册驱动
Class.forname("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
2.2 获取连接#
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(String url, String user, String password);
System.out.println("数据库连接对象", + conn);
2.3 获取数据库操作对象(用来执行sql语句)#
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
2.4 执行sql语句#
String sql = "DML语句";
//executeUpdate();这个方法专门执行DML语句,返回值是”影响数据库中的记录条数“
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(String sql);
例:System.out.println(count == 1 ? "保存成功" : "保存失败");
2.5 处理查询结果集#
String sql = "DQL语句";
//executeQuery(); 这个方法专门执行DQL语句,其返回值是一个ResultSet集合
ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(String sql);
这个ResultSet集合的图示:
while(rs.next()){
String empno = rs.getString("deptno");
String ename = rs.getString("dname");
String sal = rs.getString("loc");
System.out.println(empno + "," + ename + "," + sal);
}
getString("deptno"); 这个方法里的列表名是以查询结果里的列表名为准,而不是实际的表格里的列表名。
2.6 释放资源#
写在finally的子句中,释放资源应该遵循从小到大的顺序释放,并且分别对其捕捉异常
finally {
//6、释放资源(遵循从小到大原则,并且分别对其进行捕捉异常)
try{
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
try{
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
}catch (SQLException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
编程六步代码:#
package jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
public class JdbcTest05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("jdbc");
String driver = bundle.getString("driver");
String url = bundle.getString("url");
String user = bundle.getString("user");
String password = bundle.getString("password");
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try{
//1、注册驱动
Class.forName(driver);
//2、获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
//3、获取数据库操作对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//4、执行sql语句
String sql = "select * from dept";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//5、处理查询结果集
while(rs.next()){
String empno = rs.getString("deptno");
String ename = rs.getString("dname");
String sal = rs.getString("loc");
System.out.println(empno + "," + ename + "," + sal);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
3、SQL注入现象
3.1 用户登录业务代码#
package jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class JdbcTest06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//用户登录,输入用户名和密码
Map<String,String> userLoginInfo = userLogin();
//接收到用户名和密码之后,验证用户名和密码是否正确
boolean LoginFlag = login(userLoginInfo);
System.out.println(LoginFlag ? "登录成功" : "登录失败");
}
/**
*
* @param userLoginInfo 用户的登录信息
* @return true表示登录成功
* false表示登录失败
*/
private static boolean login(Map<String, String> userLoginInfo) {
boolean LoginFlag = false;
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("jdbc");
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try{
//注册驱动
Class.forName(bundle.getString("driver"));
//获取连接
String url = bundle.getString("url");
String user = bundle.getString("user");
String password = bundle.getString("password");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
//获取数据库操作对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//执行sql语句
String userName = userLoginInfo.get("userName");
String userPassword = userLoginInfo.get("userPassword");
String sql = "select * from t_user where userName = '"+userName+"' and userPassword = '"+userPassword+"'";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
LoginFlag = rs.next();
}catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return LoginFlag;
}
/**
*
* @return 返回用户输入的用户名和密码,返回值是一个Map集合
*/
private static Map<String, String> userLogin() {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
//输入用户名
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String userName = s.nextLine();
//输入密码
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String userPas = s.nextLine();
Map<String,String> userLogInfo = new HashMap<>();
userLogInfo.put("userName",userName);
userLogInfo.put("userPassword",userPas);
return userLogInfo;
}
}
以上代码存在SQL注入问题:用户输入的中带有sql关键字,编译的时候将sql关键字执行了,曲解了密码的原意
请输入用户名:
fdsa
请输入密码:
fdsa' or '1'='1
登录成功
这种情况导致不法分子可以随便登录某一个账户,不安全,需要解决
3.2 解决SQL注入#
代码演示
package jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class JdbcTest07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//用户登录,输入用户名和密码
Map<String,String> userLoginInfo = userLogin();
//接收到用户名和密码之后,验证用户名和密码是否正确
boolean LoginFlag = login(userLoginInfo);
System.out.println(LoginFlag ? "登录成功" : "登录失败");
}
/**
*
* @param userLoginInfo 用户的登录信息
* @return true表示登录成功
* false表示登录失败
*/
private static boolean login(Map<String, String> userLoginInfo) {
boolean LoginFlag = false;
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("jdbc");
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try{
//注册驱动
Class.forName(bundle.getString("driver"));
//获取连接
String url = bundle.getString("url");
String user = bundle.getString("user");
String password = bundle.getString("password");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
//获取数据库操作对象
String userName = userLoginInfo.get("userName");
String userPassword = userLoginInfo.get("userPassword");
String sql = "select * from t_user where userName = ? and userPassword = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//给占位符?传值
ps.setString(1,userName);
ps.setString(2,userPassword);
//执行sql语句
rs = ps.executeQuery();
LoginFlag = rs.next();
}catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return LoginFlag;
}
/**
*
* @return 返回用户输入的用户名和密码,返回值是一个Map集合
*/
private static Map<String, String> userLogin() {
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
//输入用户名
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String userName = s.nextLine();
//输入密码
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String userPas = s.nextLine();
Map<String,String> userLogInfo = new HashMap<>();
userLogInfo.put("userName",userName);
userLogInfo.put("userPassword",userPas);
return userLogInfo;
}
}
测试结果:
请输入用户名:
fdas
请输入密码:
fdas' or '1'='1
登录失败
以上代码利用PreparedStatement接口解决了SQL注入的问题
3.3 用PreparedStatement进行crud#
package jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
/**
* 用PreparedStatement进行crud
*/
public class JdbcTest08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Update();
}
private static void Update() {
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("jdbc");
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
//注册驱动
Class.forName(bundle.getString("driver"));
//获取连接
String url = bundle.getString("url");
String user = bundle.getString("user");
String password = bundle.getString("password");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//获取预编译数据库操作对象
//String sql = "insert into dept values(?,?,?)"; 插入一条数据
//String sql = "Update dept set deptno = ?,dname = ?,loc = ? where deptno = 50"; 修改一条数据
String sql = "delete from dept where deptno = ?"; //删除一条数据
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//给占位符?传值
ps.setInt(1,60);
/*ps.setString(2,"销售部");
ps.setString(3,"永州");*/
//执行sql语句
int count = ps.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(count);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
3.4 演示JDBC的自动提交事务#
package jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
public class JdbcTest09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("jdbc");
String driver = bundle.getString("driver");
String url = bundle.getString("url");
String user = bundle.getString("user");
String password = bundle.getString("password");
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try{
//1、注册驱动
Class.forName(driver);
//2、获取连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
//3、获取数据库操作对象
String sql = "Update t_act set balance = ? where account = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setInt(1,10000);
ps.setDouble(2,10);
//4、执行sql语句
int count = ps.executeUpdate();
String str = null;
str.length();
sql = "Update t_act set balance = ? where account = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setInt(1,10000);
ps.setDouble(2,20);
count += ps.executeUpdate();
conn.commit();
System.out.println(count);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
if(conn != null) {
try {
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if (ps != null) {
try {
ps.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
JDBC中是默认自动提交事务的,但是这并不符合编程的业务。比如上面的银行转账事务演示代码中账号10在向账号20转账10000元的时候遇到了异常,程序终止。这个时候这10000应该是没有转出去才对,可是因为JDBC的事务是自动提交的,在遇到异常之前账号10的10000元就已经转出去了,可是却没有落到账号20的账上。少了10000元钱!!!
写JDBC程序的时候,需要将自动提交事务关闭
Connection接口中有关事务的三个方法:
conn.setAutoCommit(false); 默认为自动提交事务,false即为关闭自动提交
conn.commit(); 提交事务,在执行完一个事务之后,手动进行提交,一般放在事务语句的最后
conn.rollback(); 回滚事务,事务执行失败之后,手动进行回滚,一般放在catch子句当中(事务执行失败,跳转到catch子句捕捉异常,此时回滚事务)
4、JDBC工具类的封装
4.1 代码演示#
package jdbc.tool;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
/**
* JDBC工具类的封装,简化JDBC编程
*/
public class DBTool {
static{
//注册驱动
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private DBTool() {}
/**
* 获取连接对象
* @return 返回连接对象
* @throws SQLException 异常上抛
*/
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("jdbc");
String url = bundle.getString("url");
String user = bundle.getString("user");
String password = bundle.getString("password");
//获取连接
return DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
}
/**
* 释放资源
* @param conn 连接对象
* @param stmt 数据库操作对象
* @param rs 查询结果集
*/
public static void close(Connection conn, Statement stmt, ResultSet rs){
if (rs != null) {
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stmt != null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
4.2 测试工具类#
package jdbc;
import jdbc.tool.DBTool;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* 1、测试封装的JDBC工具类好不好用
* 2、实现模糊查询
*/
public class JdbcTest10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
//获取连接
conn = DBTool.getConnection();
//获取预编译数据库操作对象
String sql = "select ename from emp where ename like ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//给占位符?传值
ps.setString(1,"_A%");
//执行sql语句
rs = ps.executeQuery();
//处理查询结果集
while(rs.next()){
System.out.println(rs.getString(1));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
DBTool.close(conn,ps,rs);
}
}
}
5、悲观锁(行级锁)和乐观锁机制
5.1 演示行级锁机制#
以下代码进行行级锁,称为“事务一”
package jdbc;
import jdbc.tool.DBTool;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* 演示悲观锁(行级锁)
* 这里进行行级锁
*/
public class JdbcTest11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
conn = DBTool.getConnection();
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql = "select ename,job,sal from emp where job = ? for update";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1,"MANAGER");
rs = ps.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()){
System.out.println(rs.getString(1) + "," + rs.getString(2) + "," + rs.getString(3));
}
conn.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
DBTool.close(conn,ps,rs);
}
}
}
以下代码对锁定的行进行修改,称为“事务二”
package jdbc;
import jdbc.tool.DBTool;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* 这里对锁定的行进行修改
*/
public class JdbcTest12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try {
conn = DBTool.getConnection();
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
String sql = "update emp set sal = sal * 1.1 where job = ?";
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1,"MANAGER");
int count = ps.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(count);
conn.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
if (conn != null) {
try {
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
DBTool.close(conn,ps,null);
}
}
}
测试结果:
在事务一没有提交事务之前,事务二的程序只能卡着无法往下执行;直到事务一提交事务之后,事务二立马输出3





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!