poj 1743
Musical Theme
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 30000K | |
| Total Submissions: 36995 | Accepted: 12210 |
Description
A musical melody is represented as a sequence of N (1<=N<=20000)notes that are integers in the range 1..88, each representing a key on the piano. It is unfortunate but true that this representation of melodies ignores the notion of musical timing; but, this programming task is about notes and not timings.
Many composers structure their music around a repeating &qout;theme&qout;, which, being a subsequence of an entire melody, is a sequence of integers in our representation. A subsequence of a melody is a theme if it:
Transposed means that a constant positive or negative value is added to every note value in the theme subsequence.
Given a melody, compute the length (number of notes) of the longest theme.
One second time limit for this problem's solutions!
Many composers structure their music around a repeating &qout;theme&qout;, which, being a subsequence of an entire melody, is a sequence of integers in our representation. A subsequence of a melody is a theme if it:
- is at least five notes long
- appears (potentially transposed -- see below) again somewhere else in the piece of music
- is disjoint from (i.e., non-overlapping with) at least one of its other appearance(s)
Transposed means that a constant positive or negative value is added to every note value in the theme subsequence.
Given a melody, compute the length (number of notes) of the longest theme.
One second time limit for this problem's solutions!
Input
The input contains several test cases. The first line of each test case contains the integer N. The following n integers represent the sequence of notes.
The last test case is followed by one zero.
The last test case is followed by one zero.
Output
For each test case, the output file should contain a single line with a single integer that represents the length of the longest theme. If there are no themes, output 0.
Sample Input
30 25 27 30 34 39 45 52 60 69 79 69 60 52 45 39 34 30 26 22 18 82 78 74 70 66 67 64 60 65 80 0
Sample Output
5
Hint
Use scanf instead of cin to reduce the read time.
Source
本题是男人八题其中一题,题意要看懂,我们先对相邻两个数做差,然后每个数+100。
题目意思是求不重叠的最长相同变化的子串,输出该长度
比如1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10,最长长度为5,因为子串1 2 3 4 5 和 6 7 8 9 10变化都一样的
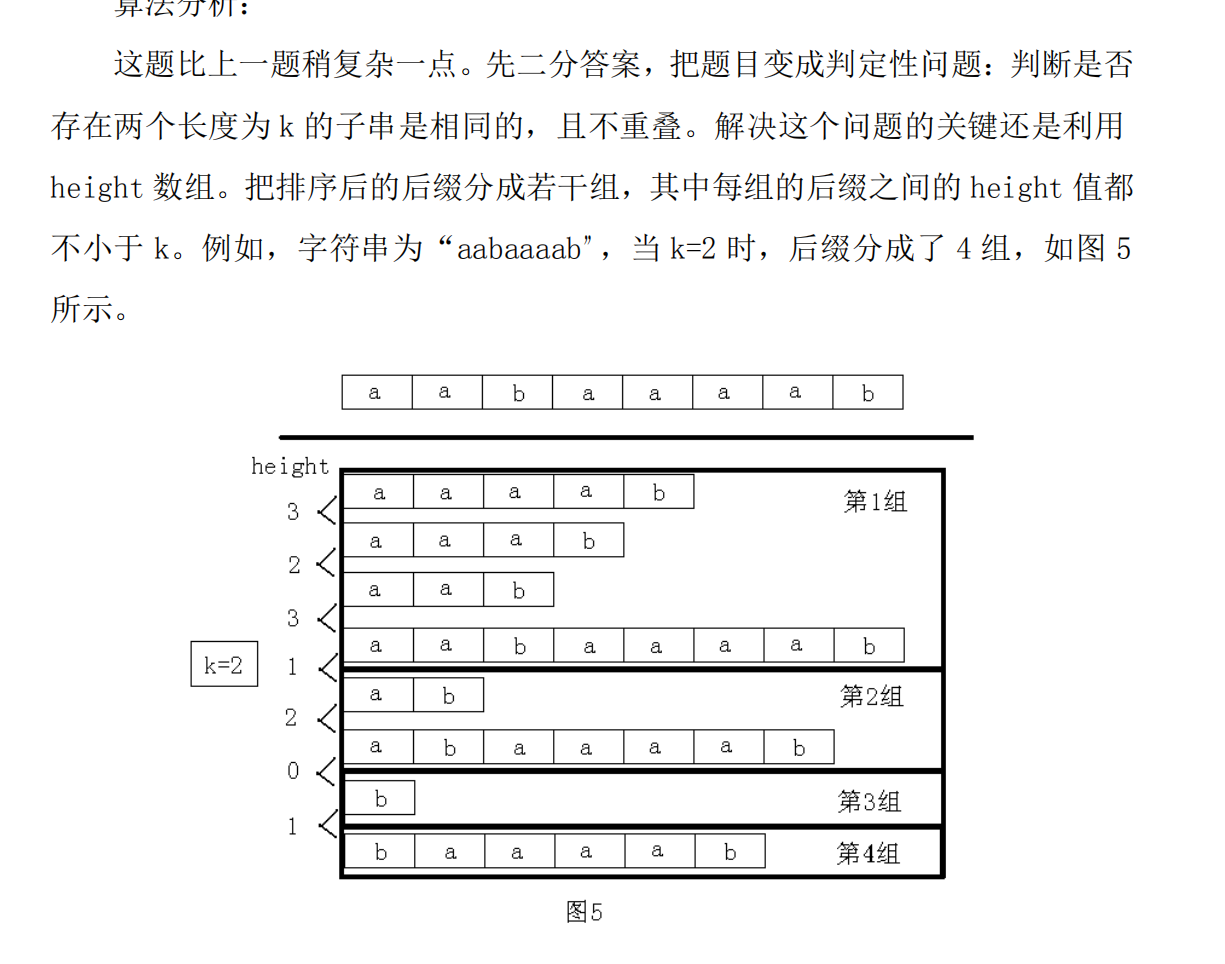
容易看出,有希望成为最长公共前缀不小于 k 的两个后缀一定在同一组。然
后对于每组后缀,只须判断每个后缀的 sa 值的最大值和最小值之差是否不小于
k。如果有一组满足,则说明存在,否则不存在。整个做法的时间复杂度为
O(nlogn)。本题中利用 height 值对后缀进行分组的方法很常用,请读者认真体
会。
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<cstdio> 3 #include<cstring> 4 #include<cmath> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 int const N=20003; 8 int const inf=1e8; 9 int sa[N],num[N],n,wa[N<<1],wb[N<<1],wv[N],r[N],rk[N],h[N],a[N]; 10 int cmp(int *r,int x,int y,int z){ 11 return r[x]==r[y] && r[x+z]==r[y+z]; 12 } 13 void build_sa(int *r,int *sa,int n,int m){ 14 int i,j,p,*x=wa,*y=wb; 15 for(i=0;i<m;i++) num[i]=0; 16 for(i=0;i<n;i++) num[x[i]=r[i]]++; 17 for(i=1;i<m;i++) num[i]+=num[i-1]; 18 for(i=n-1;i>=0;i--) sa[--num[x[i]]]=i; 19 for(j=1,p=1;p<n;j<<=1,m=p){ 20 for(p=0,i=n-j;i<n;i++) y[p++]=i; 21 for(i=0;i<n;i++) if(sa[i]>=j) y[p++]=sa[i]-j; 22 for(i=0;i<m;i++) num[i]=0; 23 for(i=0;i<n;i++) wv[i]=x[y[i]]; 24 for(i=0;i<n;i++) num[wv[i]]++; 25 for(i=1;i<m;i++) num[i]+=num[i-1]; 26 for(i=n-1;i>=0;i--) sa[--num[wv[i]]]=y[i]; 27 swap(x,y); 28 for(p=1,x[sa[0]]=0,i=1;i<n;i++) 29 x[sa[i]]=cmp(y,sa[i-1],sa[i],j)? p-1:p++; 30 } 31 for(i=0;i<n;i++) rk[i]=x[i]; 32 } 33 void build_h(int *r,int *sa,int n){ 34 int k=0; 35 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 36 if(k) k--; 37 int j=sa[rk[i]-1]; 38 while (r[i+k]==r[j+k]) k++; 39 h[rk[i]]=k; 40 } 41 } 42 int check(int mid,int n ){ 43 int x=inf,y=-inf; 44 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 45 if(h[i]>=mid) { 46 x=min(x,sa[i-1]); 47 x=min(x,sa[i]); 48 y=max(y,sa[i-1]); 49 y=max(y,sa[i]); 50 if(y-x>=mid) return 1; 51 }else { 52 x=inf,y=-inf; 53 } 54 } 55 return 0; 56 } 57 int main(){ 58 while (scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF && n){ 59 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 60 scanf("%d",&a[i]); 61 } 62 for(int i=1;i<n;i++){ 63 r[i-1]=a[i]-a[i+1]+100; 64 } 65 n--; 66 build_sa(r,sa,n+1,200); 67 build_h(r,sa,n); 68 int l=4,r=n/2,ans=0; 69 while (l<=r){ 70 int mid=(l+r)/2; 71 if(check(mid,n)){ 72 ans=mid+1; 73 l=mid+1; 74 }else r=mid-1; 75 } 76 printf("%d\n",ans); 77 } 78 return 0; 79 }



