bzoj 1095 捉迷藏
Description
捉迷藏 Jiajia和Wind是一对恩爱的夫妻,并且他们有很多孩子。某天,Jiajia、Wind和孩子们决定在家里玩
捉迷藏游戏。他们的家很大且构造很奇特,由N个屋子和N-1条双向走廊组成,这N-1条走廊的分布使得任意两个屋
子都互相可达。游戏是这样进行的,孩子们负责躲藏,Jiajia负责找,而Wind负责操纵这N个屋子的灯。在起初的
时候,所有的灯都没有被打开。每一次,孩子们只会躲藏在没有开灯的房间中,但是为了增加刺激性,孩子们会要
求打开某个房间的电灯或者关闭某个房间的电灯。为了评估某一次游戏的复杂性,Jiajia希望知道可能的最远的两
个孩子的距离(即最远的两个关灯房间的距离)。 我
将以如下形式定义每一种操作: C(hange) i 改变第i个房
间的照明状态,若原来打开,则关闭;若原来关闭,则打开。 G(ame) 开始一次游戏,查询最远的两个关灯房间的
距离。
Input
第一行包含一个整数N,表示房间的个数,房间将被编号为1,2,3…N的整数。接下来N-1行每行两个整数a, b,
表示房间a与房间b之间有一条走廊相连。接下来一行包含一个整数Q,表示操作次数。接着Q行,每行一个操作,如
上文所示。
Output
对于每一个操作Game,输出一个非负整数到hide.out,表示最远的两个关灯房间的距离。若只有一个房间是关
着灯的,输出0;若所有房间的灯都开着,输出-1。
Sample Input
1 2
2 3
3 4
3 5
3 6
6 7
6 8
7
G
C 1
G
C 2
G
C 1
G
Sample Output
3
3
4
HINT
对于100%的数据, N ≤100000, M ≤500000。
写个括号序列的做法。
首先dfs整棵树一遍,进入一个节点的时候加上一个左括号,然后是节点编号,当这个节点的所有子树遍历完后再添上一个右括号,这就是括号序列。(其实就是dfs序加上了括号而已)
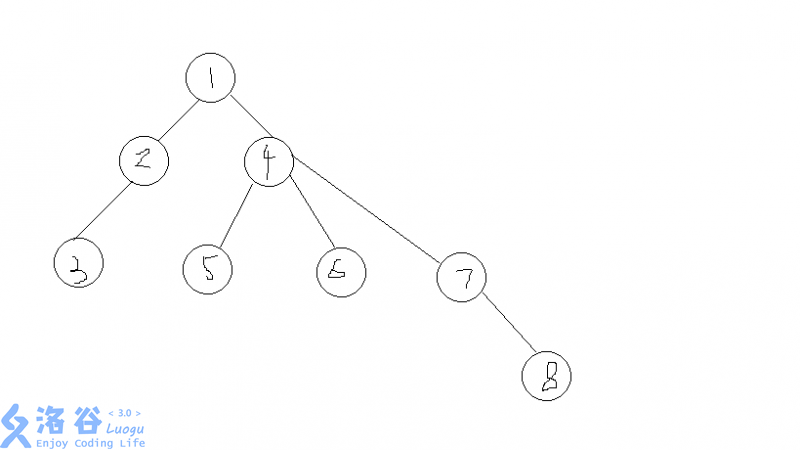
举个栗子,这棵树的括号序列是(1(2(3))(4(5)(6)(7(8))))
我们要求3到8的距离,截取两点间的括号序列为
3))(4(5)(6)(7(8
把编号和匹配的括号删掉
))(((
剩下了5个左右括号,而这就是3到8的距离。
这就是括号序列的性质。
怎么证明?脑补一下,到达i点时
1)添完了左右括号
那个点是i的祖先们的孩子。(不在i到根的路径上)
2)添了左括号没填右括号
那个点是i的祖先。(在i到根的路径上)
3)没添左括号
那个点是i的祖先们的孩子或者i的孩子(不在i到根的路径上)
因此,从s到t,删去的匹配括号们对于s来说是情况3,对于t来说是情况1,很显然这个点不在s到t的路径上。剩下的右括号,对于s来说是情况2,对于t来说是情况1,因此表示从s到达【t到根的这条链】经过的节点数。剩下的左括号,对于s来说是情况3,对于t来说是情况2,因此表示从t到达【s和t的lca(不包括lca)】的经过点数。
综上我们证明了删掉两点间所有匹配括号剩下的左右括号数为距离。
现在我们已经把整棵树压成了一个括号序列了,而我们要求的是两个黑点间的最大距离,我们考虑用线段树求解。
毫无疑问要记录每段区间删掉匹配括号后剩下的左右括号数,我们记右括号数为a,左括号数为b。
【注意我接下来说的所有左右区间都不限于线段树中的左右区间,任意连续的左右区间均可】
左右区间的a、b的合并:
显然左区间的左括号和右区间的右括号合并消去,谁多剩谁

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define R register int 4 #define rep(i,a,b) for(R i=a;i<=b;i++) 5 #define Rep(i,a,b) for(R i=a;i>=b;i--) 6 #define rp(i,x) for(int i=H[x];i!=-1;i=E[i].nt) 7 #define ms(i,a) memset(a,i,sizeof(a)) 8 #define gc() getchar() 9 #define lc (x<<1) 10 #define rc (x<<1|1) 11 #define mid (l+r)/2 12 template<class T>void read(T &x){ 13 x=0; char c=0; 14 while (!isdigit(c)) c=gc(); 15 while (isdigit(c)) x=x*10+(c^48),c=gc(); 16 } 17 int const N=100001; 18 int const M=500001; 19 int const inf=1e9; 20 int num,s[N*3],pos[N*10],H[N],n,m,cnt,tot,c[N]; 21 struct Edge{ 22 int to,nt; 23 }E[N<<1]; 24 void add(int a,int b){ 25 E[num]=(Edge){b,H[a]};H[a]=num++; 26 } 27 struct node{ 28 int a,b,l1,r1,l2,r2,dist; 29 }t[N*3<<2]; 30 void dfs(int x,int fa){ 31 s[++tot]=-1;s[++tot]=x; pos[x]=tot; 32 rp(i,x){ 33 int v=E[i].to; 34 if(v==fa) continue; 35 dfs(v,x); 36 } 37 s[++tot]=-2; 38 } 39 void push(int x,int p){ 40 t[x]=(node){0,0,-inf,-inf,-inf,-inf}; 41 if(s[p]==-1) t[x].b=1; 42 else if(s[p]==-2) t[x].a=1; 43 else if(!c[s[p]]) t[x].l1=t[x].l2=t[x].r1=t[x].r2=0; 44 } 45 void merge(int x){ 46 if(t[lc].b>t[rc].a) t[x].a=t[lc].a,t[x].b=t[lc].b-t[rc].a+t[rc].b; 47 else t[x].b=t[rc].b,t[x].a=t[lc].a+t[rc].a-t[lc].b; 48 t[x].l1=max(t[lc].l1,max(t[rc].l1+t[lc].a-t[lc].b,t[rc].l2+t[lc].a+t[lc].b)); 49 t[x].l2=max(t[lc].l2,t[rc].l2-t[lc].a+t[lc].b); 50 t[x].r1=max(t[rc].r1,max(t[lc].r1-t[rc].a+t[rc].b,t[lc].r2+t[rc].a+t[rc].b)); 51 t[x].r2=max(t[rc].r2,t[lc].r2+t[rc].a-t[rc].b); 52 t[x].dist=max(max(t[lc].r1+t[rc].l2,t[lc].r2+t[rc].l1),max(t[lc].dist,t[rc].dist)); 53 } 54 void build(int x,int l,int r){ 55 if(l==r) { 56 push(x,l); return ; 57 } 58 build(lc,l,mid); build(rc,mid+1,r); 59 merge(x); 60 } 61 void modify(int x,int l,int r,int p){ 62 if(l==r) { 63 push(x,l); return ; 64 } 65 if(p<=mid) modify(lc,l,mid,p); 66 else modify(rc,mid+1,r,p); 67 merge(x); 68 } 69 70 int main(){ 71 read(n);ms(-1,H); 72 rep(i,1,n-1){ 73 int x,y; read(x);read(y); 74 add(x,y); add(y,x); 75 } 76 dfs(1,0); cnt=n ; 77 build(1,1,tot); 78 read(m); 79 while (m--){ 80 char s[2]; scanf("%s",s); 81 if(s[0]=='C'){ 82 int x; read(x); 83 cnt+=c[x]? 1: -1; 84 c[x]^=1; 85 modify(1,1,tot,pos[x]); 86 }else if(cnt==0) printf("-1\n"); 87 else if(cnt==1) printf("0\n"); 88 else printf("%d\n",t[1].dist); 89 } 90 return 0; 91 }
思路2: 动态点分治。
点分治的过程是对树块找重心之后分成多个小树块,降低规模分别处理的过程,把链的信息收到其中“最高重心”上,从所有的重心处像分治中的不同子树索取到重心的链,就可以覆盖所有链的信息。动态点分治就像把序列分治变成线段树一样,在分治的架子上加了信息维护,实现树链信息维护与查询。
需要什么?
每个重心需要其每个分离子树到它的信息(很重要,否则形成链的重复部分,并且还需要一个自己到自己的空信息维护单链上来的信息)
每个重心需要它到父分治块的信息
全局需要维护每个重心的信息
因此,考虑问题的静态版本,需要维护每个节点每个子树内的最长链,那么为了修改,最大化应换成堆维护。
每个重心维护一个堆,表示其分离子树中每个到它的最长链,c堆。
每个重心维护一个堆,表示其块内到父重心的每条链的长度,f堆。
全局维护一个堆,表示每个重心处的最长链,ans堆。
修改时只要从一个节点作为重心的块开始向上修改,就可以遍历到所有包含它的块,修改到父重心的信息,修改父重心的信息
注意开始时的节点的分离子树那个堆要插一个0表示单链,而改掉节点值的时候0的存在性也要相应地变化。
堆也比较有技巧:封装双堆分别为值和删了的值,取的时候两堆顶相同则pop,相当于变种删除标记

1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define R register int 4 #define rep(i, a, b) for (R i = a; i <= b; i++) 5 #define Rep(i, a, b) for (R i = a; i >= b; i--) 6 #define rp(i, x) for (R i = H[x]; i != -1; i = E[i].nt) 7 #define ms(i, a) memset(a, i, sizeof(a)) 8 #define gc() getchar() 9 #define LL long long 10 template <class T> 11 void read(T &x) 12 { 13 x = 0; 14 char c = 0; 15 while (!isdigit(c)) 16 c = gc(); 17 while (isdigit(c)) 18 x = x * 10 + (c ^ 48), c = gc(); 19 } 20 int const N = 100003; 21 int cnt, H[N], n, m, vis[N], mx, tg, s[N], sz, prt[N], d[N], fa[N][21], co[N], tin[N], tout[N], sum; 22 struct Priority_queue 23 { 24 priority_queue<int> q, del; 25 void push(int x) { q.push(x); } 26 void erase(int x) { del.push(x); } 27 int top() 28 { 29 while (del.size() && del.top() == q.top()) 30 del.pop(), q.pop(); 31 return q.top(); 32 } 33 void pop() 34 { 35 while (del.size() && del.top() == q.top()) 36 del.pop(), q.pop(); 37 q.pop(); 38 } 39 int sec_top() 40 { 41 int tmp = top(); 42 pop(); 43 int se = top(); 44 push(tmp); 45 return se; 46 } 47 int size() { return q.size() - del.size(); } 48 } c[N], f[N], ans; 49 struct Edge 50 { 51 int to, nt; 52 } E[N << 1]; 53 void add(int a, int b) 54 { 55 E[cnt] = (Edge){b, H[a]}; 56 H[a] = cnt++; 57 } 58 void dfs(int x, int p) 59 { 60 fa[x][0] = p; 61 tin[x] = ++sum; 62 rp(i, x) 63 { 64 int v = E[i].to; 65 if (v == p) 66 continue; 67 d[v] = d[x] + 1; 68 dfs(v, x); 69 } 70 tout[x] = ++sum; 71 } 72 73 void insert(Priority_queue &s) 74 { 75 if (s.size() > 1) 76 ans.push(s.top() + s.sec_top()); 77 } 78 void erase(Priority_queue &s) 79 { 80 if (s.size() > 1) 81 ans.erase(s.top() + s.sec_top()); 82 } 83 84 void init() 85 { 86 read(n); 87 ms(-1, H); 88 rep(i, 1, n - 1) 89 { 90 int x, y; 91 read(x); 92 read(y); 93 add(x, y); 94 add(y, x); 95 } 96 d[1] = 1; 97 dfs(1, 1); 98 rep(j, 1, 17) rep(i, 1, n) fa[i][j] = fa[fa[i][j - 1]][j - 1]; 99 } 100 101 void dp(int x, int p) 102 { 103 s[x] = 1; 104 rp(i, x) 105 { 106 int v = E[i].to; 107 if (v == p || vis[v]) 108 continue; 109 dp(v, x); 110 s[x] += s[v]; 111 } 112 } 113 114 void Biggest(int x, int p) 115 { 116 int num = 0; 117 rp(i, x) 118 { 119 int v = E[i].to; 120 if (v == p || vis[v]) 121 continue; 122 Biggest(v, x); 123 num = max(num, s[v]); 124 } 125 if (mx > max(num, sz - s[x])) 126 mx = max(num, sz - s[x]), tg = x; 127 } 128 129 int findroot(int x) 130 { 131 mx = n + 1; 132 tg = 0; 133 dp(x, 0); 134 sz = s[x]; 135 Biggest(x, 0); 136 return tg; 137 } 138 139 int inline ancestor(int x, int y) 140 { 141 return tin[x] <= tin[y] && tout[y] <= tout[x]; 142 } 143 144 int lca(int x, int y) 145 { 146 if (ancestor(x, y)) 147 return x; 148 if (ancestor(y, x)) 149 return y; 150 Rep(i, 17, 0) if (!ancestor(fa[x][i], y)) x = fa[x][i]; 151 return fa[x][0]; 152 } 153 int dist(int x, int y) 154 { 155 return d[x] + d[y] - 2 * d[lca(x, y)]; 156 } 157 void work(int x, int p, int g) 158 { 159 f[g].push(dist(x, prt[g])); 160 rp(i, x) 161 { 162 int v = E[i].to; 163 if (v == p || vis[v]) 164 continue; 165 work(v, x, g); 166 } 167 } 168 int Div(int x, int p) 169 { 170 int g = findroot(x); 171 prt[g] = p; 172 work(g, 0, g); 173 vis[g] = 1; 174 c[g].push(0); 175 rp(i, g) 176 { 177 int v = E[i].to; 178 if (vis[v]) 179 continue; 180 int gg = Div(v, g); 181 c[g].push(f[gg].top()); 182 } 183 insert(c[g]); 184 return g; 185 } 186 void light(int x) 187 { 188 erase(c[x]); 189 c[x].erase(0); 190 insert(c[x]); 191 for (int k = x; prt[k]; k = prt[k]) 192 { 193 erase(c[prt[k]]); 194 if (f[k].size()) 195 c[prt[k]].erase(f[k].top()); 196 f[k].erase(dist(x, prt[k])); 197 if (f[k].size()) 198 c[prt[k]].push(f[k].top()); 199 insert(c[prt[k]]); 200 } 201 } 202 void weight(int x) 203 { 204 erase(c[x]); 205 c[x].push(0); 206 insert(c[x]); 207 for (int k = x; prt[k]; k = prt[k]) 208 { 209 erase(c[prt[k]]); 210 if (f[k].size()) 211 c[prt[k]].erase(f[k].top()); 212 f[k].push(dist(x, prt[k])); 213 if (f[k].size()) 214 c[prt[k]].push(f[k].top()); 215 insert(c[prt[k]]); 216 } 217 } 218 void solve() 219 { 220 cnt = n; 221 read(m); 222 while (m--) 223 { 224 char ch[5]; 225 scanf("%s", ch); 226 if (ch[0] == 'G') 227 { 228 if (cnt == 1) 229 printf("%d\n", cnt - 1); 230 else 231 printf("%d\n", ans.top()); 232 } 233 else 234 { 235 int x; 236 read(x); 237 if (!co[x]) 238 cnt--, light(x); 239 else 240 cnt++, weight(x); 241 co[x] ^= 1; 242 } 243 } 244 } 245 246 int main() 247 { 248 init(); 249 Div(1, 0); 250 solve(); 251 return 0; 252 }




