05_消息机制的原理
跟消息机制相关的API一共有这么几个:①Looper轮询器②MessageQueue消息队列③Handler④Message 消息
这个消息实际上是放在消息队列里。写Handler的时候并没有写跟MessageQueue相关的代码。
消息是放在消息队列里面的,消息队列什么时候把这个消息取出来?实际上就用到了这么一个东西叫做Looper.Looper也叫做消息泵,能把这个消息不断地从消息队列里给它取出来。Looper消息泵和MessageQueue消息队列是消息机制里面不需要咱们手动去写的这个代码。在主线程不需要手动去写。在子线程你也想用消息队列,那你就要去写相应的代码。
主线程为什么不需要手动去写?因为框架已经帮咱们写好了。
/** * Initialize the current thread as a looper, marking it as an * application's main looper. The main looper for your application * is created by the Android environment, so you should never need * to call this function yourself. See also: {@link #prepare()} */ public static void prepareMainLooper() { prepare(false); synchronized (Looper.class) { if (sMainLooper != null) { throw new IllegalStateException("The main Looper has already been prepared."); } sMainLooper = myLooper(); } }
实际上应用一跑起来的时候它首先就会给当前的线程调一下这个prepareMainLooper,准备一个主要的消息轮询器。sThreadLocal是线程级的单例。就是我这一个线程用这个sThreadLocal.只要是这个线程里保存的这个对象只有一个,sThreadLocal实现一个线程对应着唯一一个对象。
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) { if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {//我当前这个线程里已经有了一个对象了 throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");//如果之前的线程已经有了一个Looper这个代码就走不下去了.马上就抛异常
//所以这里就保证了我的一个线程对应着唯一的一个Looper. } sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));//把创建好的Looper通过线程级的单例进行保存,这就实现了一个线程对应着唯一的一个Looper. }
Looper的构造是一个私有的,不允许你去调,所以说如果你直接去new出来这个东西是不行的。
private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) { mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);//创建这个Looper先创建了一个MessageQueue.new了一个MessageQueue,通过mQueue保存起来 mRun = true; mThread = Thread.currentThread(); }
想创建新的Looper就得调prepare这个方法。prepareMainLooper和prepare方法它们俩是public static void。
public static void prepare() { prepare(true); }
/** * Initialize the current thread as a looper, marking it as an * application's main looper. The main looper for your application * is created by the Android environment, so you should never need * to call this function yourself. See also: {@link #prepare()} */ public static void prepareMainLooper() { prepare(false); synchronized (Looper.class) { if (sMainLooper != null) { throw new IllegalStateException("The main Looper has already been prepared."); } sMainLooper = myLooper(); } }
final MessageQueue mQueue;
mQueue是一个final类型.final类型只要赋值了之后无法修改了.由于一个线程通过线程级的单例对应起了一个唯一的Looper.在创建这个Looper的时候又搞了一个MessageQueue,而且MessageQueue还是final的.所以一个Looper又对应起了唯一的MessageQueue.这就保证了一个线程对应一个消息队列.一个消息队列用一个消息泵取消息.所以说只要你这个消息队列创建好了之后,它就跟当前的线程对应起来了.只要是你在这一个线程里进行操作,不管是通过谁去丢消息,肯定丢不错。你丢到的都是同一个消息队列里。因为一个线程只有这么一个消息队列。
通过构造创建好了Looper还不够,下一步得让Looper转起来。真正的得不断地从消息队列里面去取消息,为什么子线程一sendMessage()这边主线程就取出来了?实际上有一段代码在不断地取消息。怎么实现不断地取消息?
/** * Run the message queue in this thread. Be sure to call * {@link #quit()} to end the loop. */ public static void loop() { final Looper me = myLooper();//实际上就是获取一下这个Looper. if (me == null) {//如果没有Looper,就抛出异常.所以这个方法不能先调,得先准备好一个Looper,然后才能去调它的Looper.loop(). throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread."); } final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;//拿出Looper之后把消息队列拿出来了. // Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process, // and keep track of what that identity token actually is. Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); for (;;) {//死循环,相当于while(true) Message msg = queue.next(); // 拿下一条消息,一条一条拿消息.might block 有可能会阻塞.当前消息队列是空的没消息那它就一直在那儿等.一旦有消息进来就马上把消息取出来. if (msg == null) {//取出一条消息就是Message. // No message indicates that the message queue is quitting. return; } // This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger Printer logging = me.mLogging; if (logging != null) { logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback + ": " + msg.what); } msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);//Message还有一个属性是target. if (logging != null) { logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback); } // Make sure that during the course of dispatching the // identity of the thread wasn't corrupted. final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); if (ident != newIdent) { Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x" + Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x" + Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to " + msg.target.getClass().getName() + " " + msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what); } msg.recycle(); } }
运行当前线程的消息队列。
/** * Return the Looper object associated with the current thread. Returns * null if the calling thread is not associated with a Looper. */ public static Looper myLooper() { return sThreadLocal.get();//通过线程级的单例保存这个Looper.直接从这个对象里面就可以把它获取到. }
实际上消息一取出来它就调了Handler的dispatchMessage.来看看Handler的dispatchMessage.
/** * Handle system messages here. */ public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) { if (msg.callback != null) { handleCallback(msg); } else { if (mCallback != null) { if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) { return; } } handleMessage(msg);//重写了handleMessage方法 } }
我的主线程一运行起来就准备了这么一个Looper,并且准备了一个消息队列.然后调了Looper的loop方法.loop方法不断地调从消息队列里不断地去取消息.一旦有消息取出来马上去调dispatchMessage.一调dispatchMessage实际上就走到了这个handleMessage这个方法.所以说咱们就实现了这个地儿你重写handleMessage往这儿一丢马上就能取出来.
发消息是怎么搞的?
/** * Pushes a message onto the end of the message queue after all pending messages * before the current time. It will be received in {@link #handleMessage}, * in the thread attached to this handler. * * @return Returns true if the message was successfully placed in to the * message queue. Returns false on failure, usually because the * looper processing the message queue is exiting. */ public final boolean sendMessage(Message msg) { return sendMessageDelayed(msg, 0);//发消息调的是sendMessageDelayed.sendMessageDelayed(msg,0)表示是马上执行的. }
/** * Enqueue a message into the message queue after all pending messages * before (current time + delayMillis). You will receive it in * {@link #handleMessage}, in the thread attached to this handler. * * @return Returns true if the message was successfully placed in to the * message queue. Returns false on failure, usually because the * looper processing the message queue is exiting. Note that a * result of true does not mean the message will be processed -- if * the looper is quit before the delivery time of the message * occurs then the message will be dropped. */ public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(Message msg, long delayMillis) { if (delayMillis < 0) { delayMillis = 0; } return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis);//SystemClock.uptimeMillis()获取系统当前的时间.拿着开机开多长时间+延迟多长的时间. }
Open Declaration long android.os.SystemClock.uptimeMillis() Returns milliseconds since boot, not counting time spent in deep sleep. Returns: milliseconds of non-sleep uptime since boot.
since boot从开机之后.机器开了多久那就获取一下这个时间.
/** * Enqueue a message into the message queue after all pending messages * before the absolute time (in milliseconds) <var>uptimeMillis</var>. * <b>The time-base is {@link android.os.SystemClock#uptimeMillis}.</b> * You will receive it in {@link #handleMessage}, in the thread attached * to this handler. * * @param uptimeMillis The absolute time at which the message should be * delivered, using the * {@link android.os.SystemClock#uptimeMillis} time-base. * * @return Returns true if the message was successfully placed in to the * message queue. Returns false on failure, usually because the * looper processing the message queue is exiting. Note that a * result of true does not mean the message will be processed -- if * the looper is quit before the delivery time of the message * occurs then the message will be dropped. */ public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) { MessageQueue queue = mQueue; if (queue == null) { RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException( this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue"); Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e); return false; } return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis); }
/** * Use the {@link Looper} for the current thread with the specified callback interface * and set whether the handler should be asynchronous. * * Handlers are synchronous by default unless this constructor is used to make * one that is strictly asynchronous. * * Asynchronous messages represent interrupts or events that do not require global ordering * with represent to synchronous messages. Asynchronous messages are not subject to * the synchronization barriers introduced by {@link MessageQueue#enqueueSyncBarrier(long)}. * * @param callback The callback interface in which to handle messages, or null. * @param async If true, the handler calls {@link Message#setAsynchronous(boolean)} for * each {@link Message} that is sent to it or {@link Runnable} that is posted to it. * * @hide */ public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) { if (FIND_POTENTIAL_LEAKS) { final Class<? extends Handler> klass = getClass(); if ((klass.isAnonymousClass() || klass.isMemberClass() || klass.isLocalClass()) && (klass.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) == 0) { Log.w(TAG, "The following Handler class should be static or leaks might occur: " + klass.getCanonicalName()); } } mLooper = Looper.myLooper();// 把当前线程的Looper给它获取到. if (mLooper == null) { throw new RuntimeException( "Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()"); } mQueue = mLooper.mQueue; mCallback = callback; mAsynchronous = async; }
当Handler一构造起来之后,为什么说Handler发消息发不错?我在主线程创建了Handler,一定是丢给了主线程。首先在构造Handler的时候调的是无参的构造,
/** * Default constructor associates this handler with the {@link Looper} for the * current thread. * * If this thread does not have a looper, this handler won't be able to receive messages * so an exception is thrown. */ public Handler() { this(null, false); }
无参构造调的是两个参数的构造。两个参数的有参构造首先是从 Looper.myLooper()开始.刚才已经看了myLooper()的源码.
Open Declaration Looper android.os.Looper.myLooper() Return the Looper object associated with the current thread. Returns null if the calling thread is not associated with a Looper.
把当前线程的Looper给它获取到.所以Handler一创建起来首先通过成员变量mLooper拿到了当前线程的Looper.拿到之后通过mLooper又拿到了mQueue.所以说Handler拿到了,你在哪个线程创建的Handler,最终你的消息就发到哪个线程对应的消息队列。最终对这个线程搞的Looper进行轮询。
/** * Enqueue a message into the message queue after all pending messages * before the absolute time (in milliseconds) <var>uptimeMillis</var>. * <b>The time-base is {@link android.os.SystemClock#uptimeMillis}.</b> * You will receive it in {@link #handleMessage}, in the thread attached * to this handler. * * @param uptimeMillis The absolute time at which the message should be * delivered, using the * {@link android.os.SystemClock#uptimeMillis} time-base. * * @return Returns true if the message was successfully placed in to the * message queue. Returns false on failure, usually because the * looper processing the message queue is exiting. Note that a * result of true does not mean the message will be processed -- if * the looper is quit before the delivery time of the message * occurs then the message will be dropped. */ public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis) { MessageQueue queue = mQueue;//拿到消息队列 if (queue == null) { RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException( this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue"); Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e); return false; } return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);//把消息队列传给enqueueMessage }
private boolean enqueueMessage(MessageQueue queue, Message msg, long uptimeMillis) { msg.target = this; if (mAsynchronous) { msg.setAsynchronous(true); } return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);//queue就是当前线程的消息队列,Handler是在主线程创建的,那么它就是主线程的消息队列. }
boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) {//when=当前系统开机的时间+延迟的时间 if (msg.isInUse()) { throw new AndroidRuntimeException(msg + " This message is already in use."); } if (msg.target == null) { throw new AndroidRuntimeException("Message must have a target."); } boolean needWake; synchronized (this) { if (mQuiting) { RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException( msg.target + " sending message to a Handler on a dead thread"); Log.w("MessageQueue", e.getMessage(), e); return false; } msg.when = when;//when是消息要执行的时间.通过消息要执行的时间进行排序. Message p = mMessages;//只记住了mMessages,只有一条消息 if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) {//p=null说明当前的消息队列是空的,when=0说明我这条消息需要立即执行.when<p.when都说明我这条新加进来的消息应该优先执行. 它应该排在消息队列的第一条.// New head, wake up the event queue if blocked. msg.next = p;//每一条消息都有一个成员变量next mMessages = msg;//mMessages等于传进来的msg needWake = mBlocked; } else {//当前传进去的消息不是优先执行的.比当前消息队列记住的第一条消息这个when要大. // Inserted within the middle of the queue. Usually we don't have to wake // up the event queue unless there is a barrier at the head of the queue // and the message is the earliest asynchronous message in the queue. needWake = mBlocked && p.target == null && msg.isAsynchronous(); Message prev; for (;;) {//for循环是给这个消息找到一个合适的位置 prev = p; p = p.next; if (p == null || when < p.when) { break; } if (needWake && p.isAsynchronous()) { needWake = false; } } msg.next = p; // invariant: p == prev.next prev.next = msg; } } if (needWake) { nativeWake(mPtr); } return true; }
虽然MessageQueue是消息队列,但是并没有什么队列的东西在里面。没有什么集合HashMap之类的。
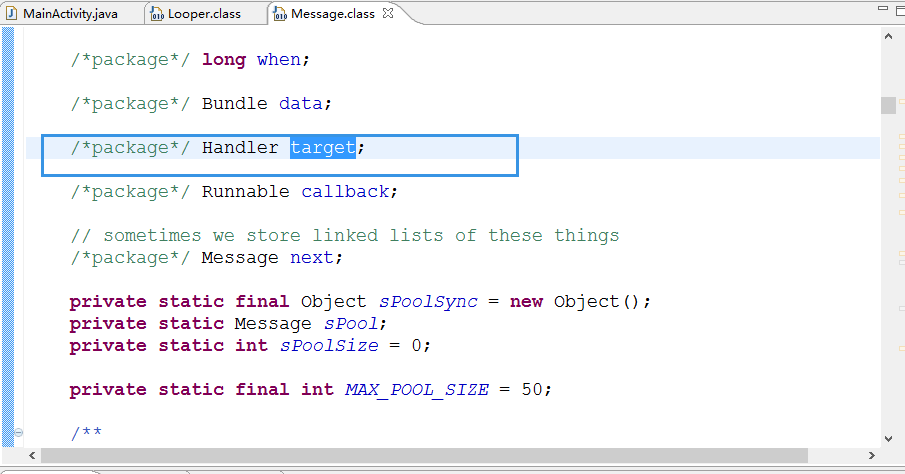
Message mMessages;//只记住了一条消息.通过Message类型的成员变量mMessages把消息队列里的第一条消息给它记住了
// sometimes we store linked lists of these things /*package*/ Message next;//每一条消息都有一个成员变量next
这个消息队列怎么去排的?就是这么去排的。
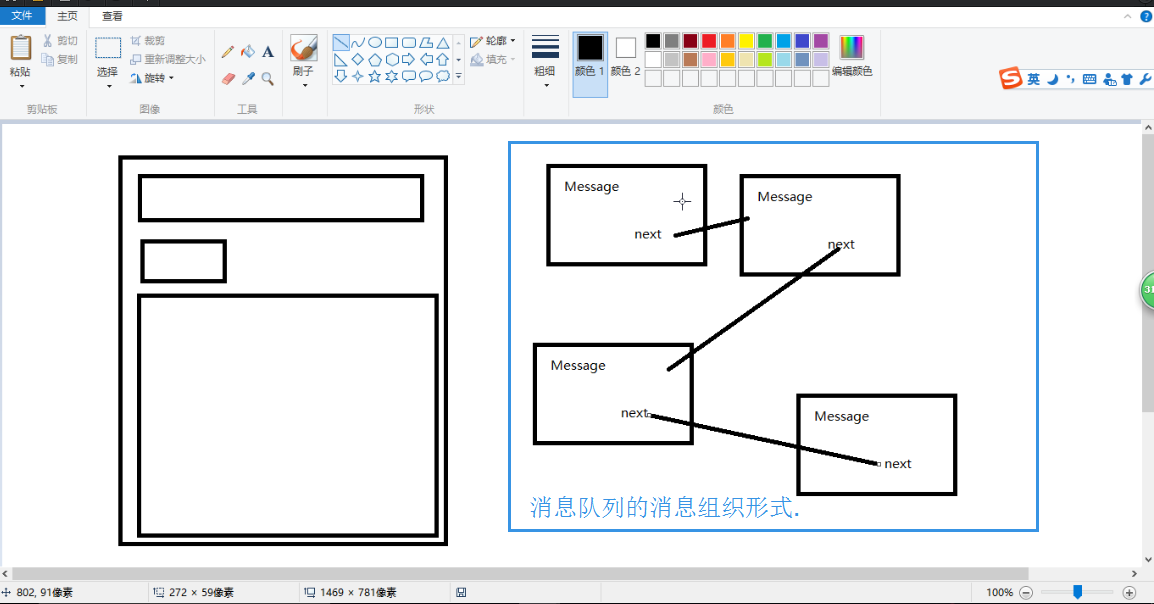
sendMessageAtTime最终调的是enqueueMessage(把消息进行入队)。把消息进行一下排序,怎么去排序呢?就是通过要执行的时间when进行排序。谁先执行谁就排在消息队列的前面,谁后执行谁就排在后面。怎么去排?实际上就是按照这个时间来。
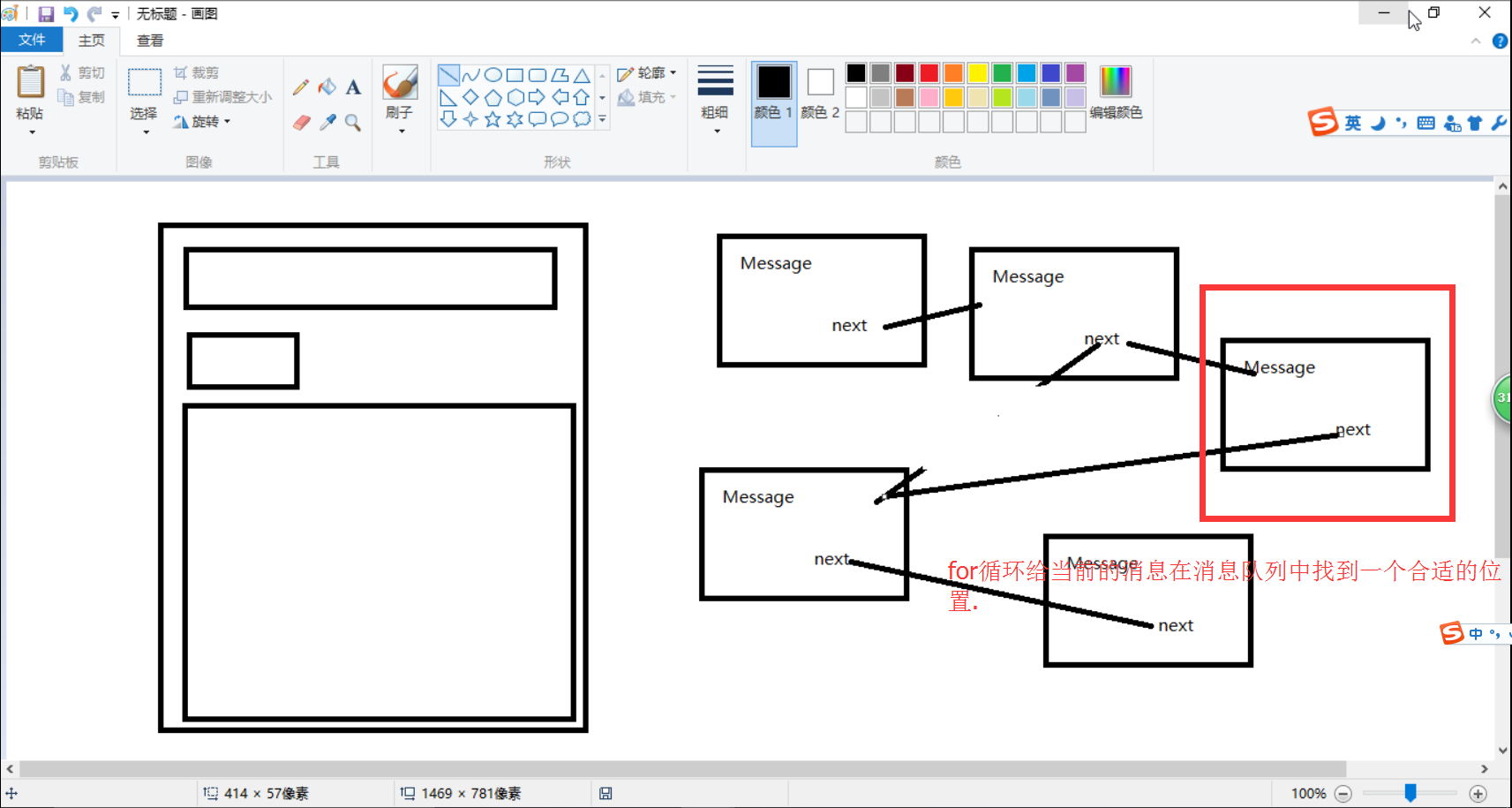
最终就按照消息要执行的先后时间把这个消息就入队了。
丢到这里这个Looper就不断地在转,
/** * Run the message queue in this thread. Be sure to call * {@link #quit()} to end the loop. */ public static void loop() { final Looper me = myLooper(); if (me == null) { throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread."); } final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue; // Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process, // and keep track of what that identity token actually is. Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); for (;;) { Message msg = queue.next(); // might block Looper不断地在转 if (msg == null) { // No message indicates that the message queue is quitting. return; } // This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the logger Printer logging = me.mLogging; if (logging != null) { logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback + ": " + msg.what); } msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg); if (logging != null) { logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback); } // Make sure that during the course of dispatching the // identity of the thread wasn't corrupted. final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity(); if (ident != newIdent) { Log.wtf(TAG, "Thread identity changed from 0x" + Long.toHexString(ident) + " to 0x" + Long.toHexString(newIdent) + " while dispatching to " + msg.target.getClass().getName() + " " + msg.callback + " what=" + msg.what); } msg.recycle(); } }
一旦有消息丢进来了,检查一下这个时间,如果这个时间需要立即执行,这就涉及到一个next()方法。next()就是从消息队列里去取消息。
Message next() { int pendingIdleHandlerCount = -1; // -1 only during first iteration int nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0; for (;;) { if (nextPollTimeoutMillis != 0) { Binder.flushPendingCommands(); } nativePollOnce(mPtr, nextPollTimeoutMillis);//nativePollOnce后面还会介绍,是通过C来实现的. synchronized (this) { // Try to retrieve the next message. Return if found. final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis(); Message prevMsg = null; Message msg = mMessages; if (msg != null && msg.target == null) { // Stalled by a barrier. Find the next asynchronous message in the queue. do { prevMsg = msg; msg = msg.next; } while (msg != null && !msg.isAsynchronous()); } if (msg != null) { if (now < msg.when) {//拿到消息之后比一下时间,与第一条消息比一下时间,是不是当前的时间.如果不是当前时间的话说明我这个消息不需要立即执行.now>msg.when是需要立即执行的.立即执行就给它拽出来.如果now<msg.when的话说明还得接着等,接着等的话记一下时间然后就当前的这个Looper就接着顺下去了. // Next message is not ready. Set a timeout to wake up when it is ready. nextPollTimeoutMillis = (int) Math.min(msg.when - now, Integer.MAX_VALUE); } else { // Got a message. mBlocked = false; if (prevMsg != null) { prevMsg.next = msg.next; } else { mMessages = msg.next; } msg.next = null; if (false) Log.v("MessageQueue", "Returning message: " + msg); msg.markInUse(); return msg; } } else { // No more messages. nextPollTimeoutMillis = -1; } // Process the quit message now that all pending messages have been handled. if (mQuiting) { dispose(); return null; } // If first time idle, then get the number of idlers to run. // Idle handles only run if the queue is empty or if the first message // in the queue (possibly a barrier) is due to be handled in the future. if (pendingIdleHandlerCount < 0 && (mMessages == null || now < mMessages.when)) { pendingIdleHandlerCount = mIdleHandlers.size(); } if (pendingIdleHandlerCount <= 0) { // No idle handlers to run. Loop and wait some more. mBlocked = true; continue; } if (mPendingIdleHandlers == null) { mPendingIdleHandlers = new IdleHandler[Math.max(pendingIdleHandlerCount, 4)]; } mPendingIdleHandlers = mIdleHandlers.toArray(mPendingIdleHandlers); } // Run the idle handlers. // We only ever reach this code block during the first iteration. for (int i = 0; i < pendingIdleHandlerCount; i++) { final IdleHandler idler = mPendingIdleHandlers[i]; mPendingIdleHandlers[i] = null; // release the reference to the handler boolean keep = false; try { keep = idler.queueIdle(); } catch (Throwable t) { Log.wtf("MessageQueue", "IdleHandler threw exception", t); } if (!keep) { synchronized (this) { mIdleHandlers.remove(idler); } } } // Reset the idle handler count to 0 so we do not run them again. pendingIdleHandlerCount = 0; // While calling an idle handler, a new message could have been delivered // so go back and look again for a pending message without waiting. nextPollTimeoutMillis = 0; } }
究竟这个消息什么时候执行,是取决于时间的.



