day38 05-Spring的BeanFactory与ApplicationContext区别
ApplicationContext怎么知道它是一个工厂呢?
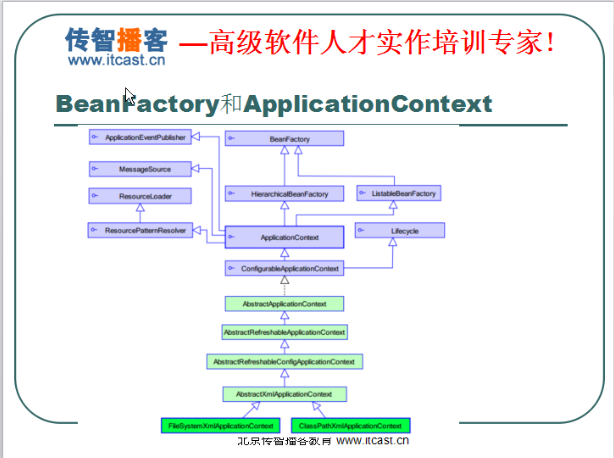

BeanFactory也可以做刚才那些事情,只不过ApplicationContext对它有扩展。ApplicationContext间接继承BeanFactory。

ApplicationContext继承了很多接口,

其中接口HierarchicalBeanFactory继承了BeanFactory。所以说ApplicationContext继承了BeanFactory。

BeanFactory是延迟加载,使用到这个类才创建,不使用到这个类就不创建。ApplicationContext是只要一加载这个配置文件,就会创建这个类了。




package cn.itcast.spring3.demo1; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource; import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource; public class SpringTest1 { @Test //传统方式 public void demo1(){ //造成程序紧密耦合. //应该采用工厂+配置文件+反射的机制 HelloService helloService = new HelloServiceImpl(); helloService.sayHello(); } @Test //Spring开发 public void demo2(){ //创建一个Spring的工厂类. ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); //ApplicationContext就是Spring的工厂类 //不写applicationContextx.xml的全路径,默认会去WEB-INF下面找applicationContextx.xml //但是现在applicationContextx.xml写好之后已经发布到WEB-INF的classes里面 HelloService helloService = (HelloService) applicationContext.getBean("helloService"); helloService.sayHello(); } @Test //加载磁盘路径下的配置文件: public void demo3(){ ApplicationContext applicationContext = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); HelloService helloService = (HelloService) applicationContext.getBean("helloService"); helloService.sayHello(); } @Test public void demo4(){ // ClassPathResource FileSystemResource //BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("applicationContext.xml")); @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(new FileSystemResource("applicationContext.xml")); HelloService helloService= (HelloService) beanFactory.getBean("helloService"); helloService.sayHello(); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- 别去schema,schema是文件,本地的文件,你得引那个头 --> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 把接口和实现类在这个配置文件中配置,有了实现类的全路径之后到时候才能用工厂反射 --> <!-- 通过一个<bean>标签来设置类的信息,通过id属性为类起个标识. --> <!-- 接口,实现类,配置文件也都有了 --> <!-- 现在有一个工厂Spring为我们提供好了,其实就是解析这个XML文件 --> <!-- 这个工厂你自己写会不会写?你用dom4j找里面的bean标签,找到class的属性值,然后就可以Class.forName()反射生成类的实例.其实Spring 也是这么做的,只不过工厂由Spring提供好了 --> <bean id="helloService" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo1.HelloServiceImpl"> <!-- 使用<property>标签注入属性 value指的是普通值 ref指的是对象 --> <property name="info" value="传智播客(磁盘路径)"></property> </bean> </beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- 别去schema,schema是文件,本地的文件,你得引那个头 --> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 把接口和实现类在这个配置文件中配置,有了实现类的全路径之后到时候才能用工厂反射 --> <!-- 通过一个<bean>标签来设置类的信息,通过id属性为类起个标识. --> <!-- 接口,实现类,配置文件也都有了 --> <!-- 现在有一个工厂Spring为我们提供好了,其实就是解析这个XML文件 --> <!-- 这个工厂你自己写会不会写?你用dom4j找里面的bean标签,找到class的属性值,然后就可以Class.forName()反射生成类的实例.其实Spring 也是这么做的,只不过工厂由Spring提供好了 --> <bean id="helloService" class="cn.itcast.spring3.demo1.HelloServiceImpl"> <!-- 使用<property>标签注入属性 value指的是普通值 ref指的是对象 --> <property name="info" value="传智播客"></property> </bean> </beans>



