app自动化测试----多设备并行运行
1. 总结
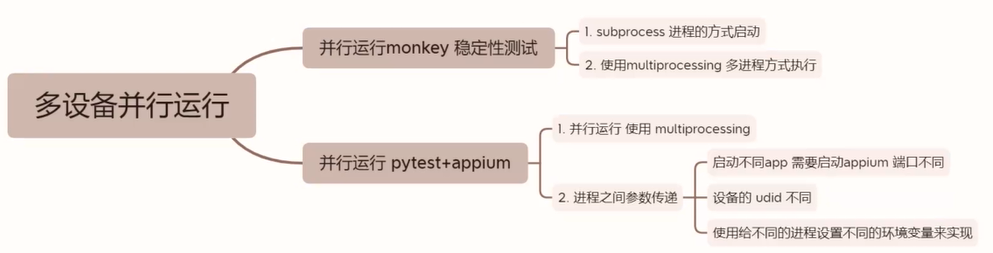
app自动化测试---多台设备并行运行monkey(subprocss 子进程方式 && multiprocessing 多进程方式)
app自动化测试----使用Python代码启动和关闭 一个/多个设备Appium
app自动化测试---- pytest 多设备连接,并行执行测试用例(pytest 通过设置变量的方式传参)
2.样例代码展示
main.py (项目运行文件)
""" 项目运行文件,并添加测试报告 """ import pytest import os,time import multiprocessing from utils.adb_handler import get_connect_devices def run(device): # 进程启动之后设置变量 os.environ['udid'] = str(device[0]) os.environ['port'] = str(device[1]) report_dir = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)), 'reports') if not os.path.exists(report_dir): os.mkdir(report_dir) report = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S') + '_' + str(device[1]) reportfile = os.path.join(report_dir, report + '.html') pytest.main(['testcases', '-s', '-v', f'--html={reportfile}']) if __name__ == '__main__': # 获取所有的连接设备 devices = get_connect_devices() process = [] for device in devices: #创建进程 p = multiprocessing.Process(target=run,args=(device,)) p.start() process.append(p) for proc in process: proc.join()
conftest.py (pytest配置文件)
from appium import webdriver import os, time,pytest from utils.adb_handler import start_appium, stop_appium from utils.file_handler import FileHandler chromedriver= os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)),'drivers/chrome/75.0.3770.140/chromedriver.exe') # scope='session' 标记的方法执行域为---->所有测试用例运行之前/之后 运行的方法 @pytest.fixture(scope='session',autouse=True) def driver(): # 启动appium服务 port = os.environ['port'] start_appium(port) desired_caps = { 'platformName': 'Android', # 测试Android系统 'udid': os.environ['udid'], # adb devices 命令查看 设置为自己的设备 'automationName': 'UiAutomator2', # 自动化引擎 'noReset': False, # 不要重置app的状态 'fullReset': False, # 不要清理app的缓存数据 'chromedriverExecutable': chromedriver, # chromedriver 对应的绝对路径 'appPackage': "org.cnodejs.android.md", # 应用的包名 'appActivity': ".ui.activity.LaunchActivity" # 应用的活动页名称(appium会启动app的加载页) } driver = webdriver.Remote('http://127.0.0.1:4723/wd/hub', desired_capabilities=desired_caps) driver.implicitly_wait(5) # 全局的隐式等待时间 yield driver # 将driver 传递出来 # 所有的用例执行之后 driver.quit() stop_appium(port) # 该方法是用来获取测试用例执行的结果(passed / FAILED) @pytest.hookimpl(tryfirst=True,hookwrapper=True) def pytest_runtest_makereport(item, call): outcome = yield rep = outcome.get_result() # 获取用例的执行结果 # print('用例的执行结果rep---->',rep) setattr(item, "rep_" + rep.when, rep) # 将执行结果保存到 item 属性中 , req.when 执行时 # scope='function' 标记的方法执行域为---->每个测试用例运行之前/之后 运行的方法 @pytest.fixture(scope='function',autouse=True) def case_run(driver:webdriver,request): # request 为 pytest_runtest_makereport 方法获取到的执行结果(固定参数和用法) yield if request.node.rep_call.failed: file_handler = FileHandler() screenshots = file_handler.save_file_dir('img') casename: str = request.node.nodeid # print("执行测试用例的名字:", casename) # 测试用例的名字很长 testcases/test_ddt/test_ddt_login.py::TestDdtLogin::test_login[....] # 对字符串进行截取,截取之后显示为 test_ddt_login-TestDdtLogin casename = casename[casename.rfind('/')+1:casename.rfind('::')].replace('.py', '').replace('::', '-') filename = time.strftime('%H_%M_%S') + '-' + casename +".png" screenshot_file = os.path.join(screenshots, filename) # 保存截图 driver.save_screenshot(screenshot_file)
utils/adb_handler.py (adb命令处理文件类)
""" adb命令处理文件类 """ import subprocess import os,sys,time from utils.file_handler import FileHandler from config import appoum_port file_handler = FileHandler() logs_dir = file_handler.save_file_dir('log') # 获取所有的连接设备 def get_connect_devices(): devices = [] port = appoum_port proc = subprocess.Popen('adb devices',stdout=subprocess.PIPE,shell=True) for line in proc.stdout.readlines(): # 将字节类型转换为字符串 line_str = line.decode(encoding='utf8') if '\tdevice' in line_str: # 字符串分割 提取 deviceid值 device_id = line_str.strip().split('\tdevice')[0] devices.append((device_id,port)) port += 2 print('devices连接设备----》', devices) return devices # 使用命令行的方式启动appium def start_appium(port): """ 启动appium 服务 :param port: 服务的端口号 :return: """ stop_appium(port) cmd = f"appium -p {port}" logsdir = file_handler.save_file_dir('log') log_name = time.strftime('%Y_%m_%d') + '-appium_log-' + str(port) +".log" appium_logs_dirName = os.path.join(logsdir,log_name) with open(appium_logs_dirName, mode='a', encoding="utf8") as file: subprocess.Popen(cmd, shell=True, stdout=file,stderr=subprocess.PIPE) # 使用命令行的方式关闭appium def stop_appium(port): mac_cmd = f"lsof -i tcp:{port}" win_cmd = f"netstat -ano | findstr {port}" # 判断操作系统 os_platform = sys.platform print('操作系统:',os_platform) # #windows 系统 if os_platform == "win32": win_p = subprocess.Popen(win_cmd,shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE,stderr=subprocess.PIPE) for line in win_p.stdout.readlines(): if line: line = line.decode('utf8') if "LISTENING" in line: win_pid = line.split("LISTENING")[1].strip() os.system(f"taskkill -f -pid {win_pid}") else: # unix系统 p = subprocess.Popen(mac_cmd,shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE,stderr=subprocess.PIPE) for line in p.stdout.readlines(): line = line.decode('utf8') if "node" in line: stdoutline = line.split(" ") # print(stdoutline) pid = stdoutline[4] os.system(f"kill {pid}")


