【填算符】(log 值域的做法)
填算符
下发题解说的神马东西,赛时根本想不到
讲一个赛时想得到的
我们处理出二进制下每一位上的 1 的最后一次出现的位置,将第
同时我们设 bitor 的操作数
有以下结论:由于 bitor。
发现有以下情况:
-
若
bitor的总操作数多,也就是说在bitand操作,所以这种情况下这一位一定不对答案有贡献 -
若
bitor操作,那么这样第bitor操作,对于这种情况的 -
若
bitor操作,但bitand
所以我们特判从第 1 个位置到bitand能不能让到第
对于所有合法位的 bitor,此时有一下两种可能,而我们想尽量构成第二种可能:
-
bitor,这样我们一定能达到答案最大了,想使答案最优直接让从bitor就好了 -
bitand也是可以使答案最大的,所以我们判断能不能让bitand同样使答案最大;
发现可以的条件相当于从第bitor操作得到一个答案,使得这个答案第bitand。
满足条件的判断又和上述的第三个情况判断一致了,相当于以
形式化如下:
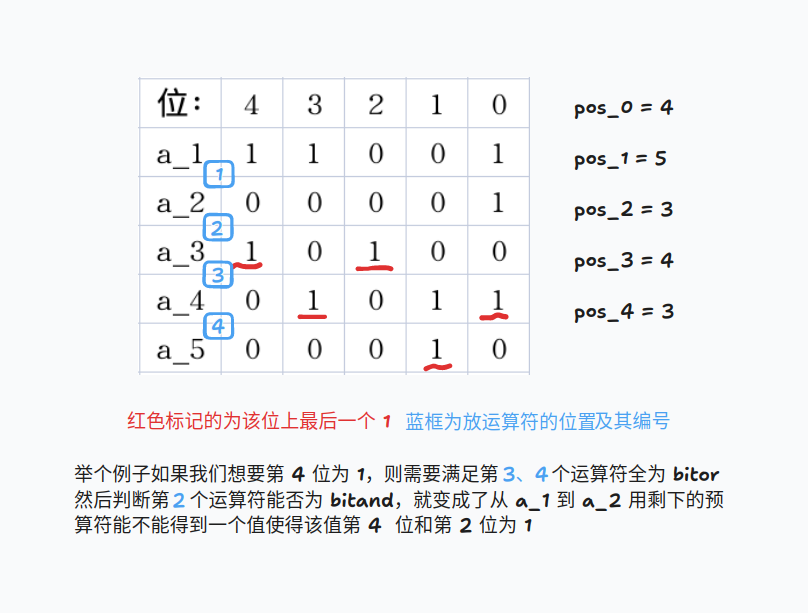
所以一个递归 bitor 操作,判断能不能得到我想要的答案:
若不能则直接从第 bitand 就是答案(bitand 的个数)
若能则第 bitand,并设 bitand。
code:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define Aqrfre(x, y) freopen(#x ".in", "r", stdin),freopen(#y ".out", "w", stdout)
#define mp make_pair
#define Type ll
#define qr(x) x=read()
typedef __int128 INT;
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
inline ll read(){
char c=getchar(); ll x=0, f=1;
while(!isdigit(c)) (c=='-'?f=-1:f=1), c=getchar();
while(isdigit(c)) x=(x<<1)+(x<<3)+(c^48), c=getchar();
return x*f;
}
const int N = 1e6 + 5;
const int maxn = 1e8;
int n, k, K; ll a[N], b[N];
int la[62], pre[62][N], zh[62], X;
vector<int>v[N], ans, tem, num;
inline bool check(int pos, int op){ // 判断从第一个运算符到第 pos 个全为 & 能不能使得到的值满足条件
int now = pos + 1; ll x = 0;
for(int i : v[now]) x += (1 << i);
if(~X) x += (1 << X);
int y = a[1];
for(int i=2; i<=now; i++)
y = y & a[i];
if(y & x == x) return true;
return false;
}
inline void dfs(int pos, int H){ // 递归函数
if(pos <= 0 and H <= 0) return;
int now = pos + 1, end = 2e9;
bool f = true; X = -1;
for(int x : tem) v[pre[x][now]].clear(); //为方便更新新的一层的 V ,先清空
for(int x : tem){
if(pos - pre[x][now] > H or !pre[x][now]){
f = false; break;
}
else if(pos - pre[x][now] < H) // 合法则更新 end 并加入 V
end = min(end, pre[x][now] - 1), v[pre[x][now]].emplace_back(x);
else{
X = x;
if(pre[x][now] == 1 or check(pre[x][now] - 1, 1))
end = min(end, pre[x][now] - 1), v[pre[x][now]].emplace_back(x);
else f = false;
}
}
if(f) ans.emplace_back(pos), k--; // pos 位可以为 &,加到答案中
if(!k) return;
if(f and end >= k){
tem.clear(); for(int x : v[end+1]) tem.emplace_back(x);
dfs(end, H-(pos-end-1)); //继续递归判断 end 位可否为 &
}
else{
int cnt = k; // pos 位不可以为 &,则最优方案为从 pos-1 到 pos-cnt 全为 &
for(int i=pos-cnt; i<pos; i++)
k--, cout<<i<<" ";
return;
}
}
signed main(){ // bitop
Aqrfre(bitop, bitop);
qr(n); qr(k); K = k;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
qr(a[i]);
for(int j=0; j<62; j++){
if(a[i] & (1ll << j)) pre[j][i] = la[j], la[j] = i;
else pre[j][i] = pre[j-ans.size()][i-1]; // 二进制下第 j 位为 1 在第 i 个数之前一次出现的位置
}
}
if(k == n - 1){
for(int i=1; i<=k; i++) cout<<i<<" ";
return 0;
}
for(int j=0; j<62; j++) // V 存当前这一层递归的下界包含的 最后一个 1 出现在这个下界的 二进制位
if(la[j]) zh[j] = la[j], v[zh[j]].emplace_back(j);
int H = n - 1 - k, endi = 1e9; bool go = false;
for(int i=0; i<62; i++){ // 把第一次递归剖出来单独做
if(!zh[i]) continue;
if(n - zh[i] > H) continue;
if(n - zh[i] < H){
endi = min(endi, zh[i] - 1);
continue;
}
if(go) continue;
if(n - zh[i] == H){
if(check(zh[i] - 1, 0)){ //特殊的:合法直接输出
for(int i=1; i<=k; i++)
cout<<i<<" ";
return 0;
}
go = true;
}
}
for(int x : v[endi+1]) tem.emplace_back(x); //tem 暂存下界这个数的 V
H -= (n - endi - 1);
dfs(endi, H);
sort(ans.begin(), ans.end());
for(int x : ans) cout<<x<<" ";
return 0;
}




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现
· 25岁的心里话