MySQL基础(一)
写在前面:
虽说可以用DOS窗口直接操作,但还是有一个可视化的工具编辑比较直观,这里推荐SQLyog和MySQLWorkbench;
数据库每句命令后必须加分号。
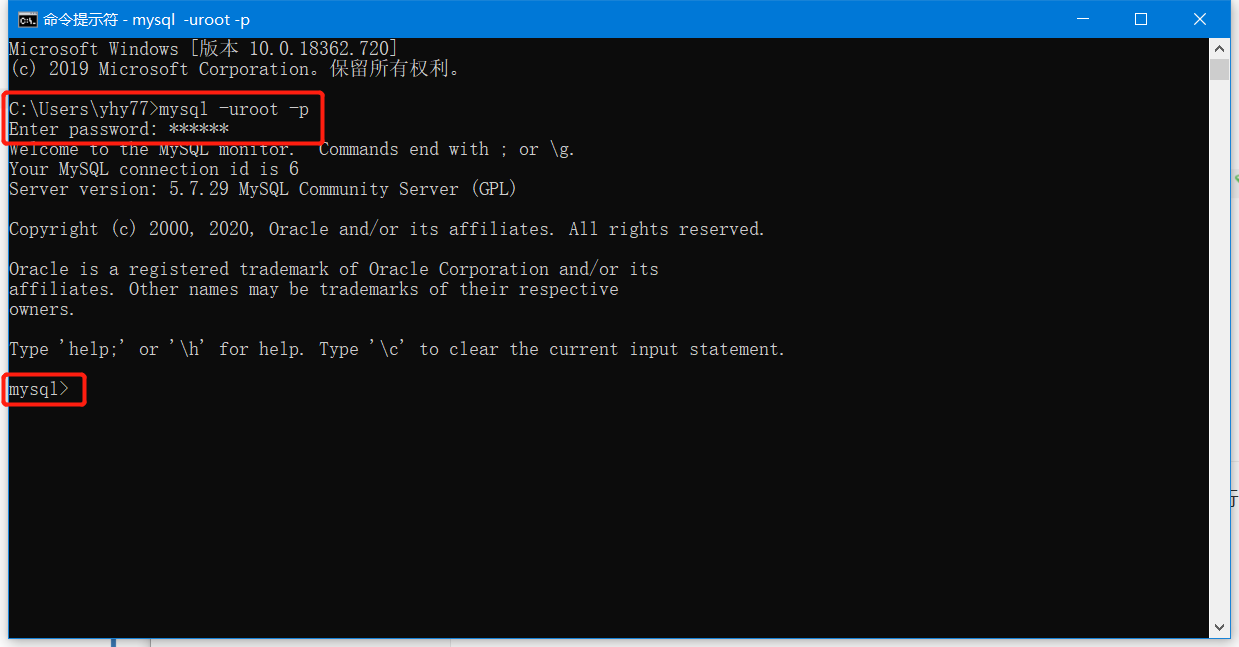
1. 连接数据库
mysql -uroot -p123456 -- 连接数据库//这个是windows操作命令 -- 连接数据库,sql语句注释为--+空格,多行注释为/**/ -- 分号结尾 -- sql命令可通过SQLyog中的历史记录来查看学习 update mysql.user set authentication_string=password('YourPassword') where user='root' and Host = 'localhost'; -- 修改密码 flush privileges; -- 刷新权限 show databases; -- 查看数据库 use schoolLearn; -- 使用/切换schoolLearn数据库 show tables; -- 查看数据库中所有表 describe student; -- 查看名字为student的表 ctrl+c -- 强行终止操作,误操作(比如输入错误信息)时使用 create database;-- 创建一个新数据库 exit -- 退出连接 /* MySQL数据库四种语言 DML database define language DDL database manage language DQL database query language DCL database control language */
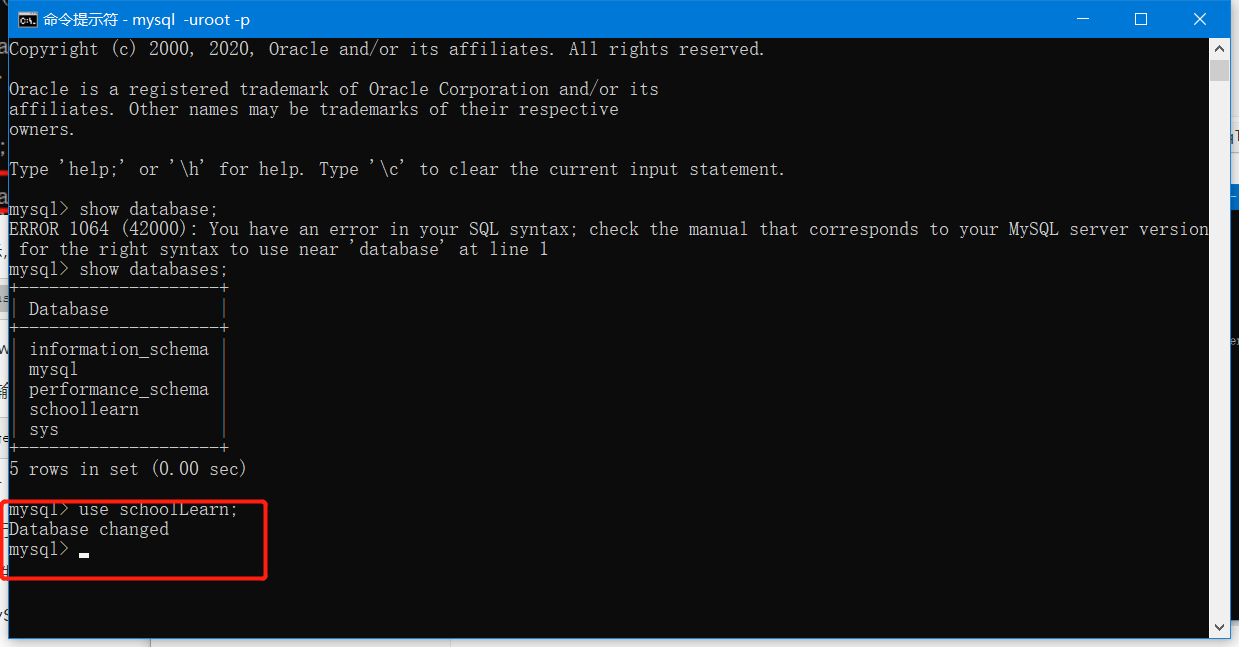
2. 数据库的创建和查看
-- 创建数据库 CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS schoolLearn03; -- 删除数据库 DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS hello; --使用数据库 USE schoolLearn; --如果表名或字段名是一个特殊字符,就需要使用`` --查看数据库 SHOW DATABASES; --选中并显示某字段 SELECT `ID` FROM `student`; --选中student中的ID单元 select * from `student`; -- 选中所有被选中表数据并显示
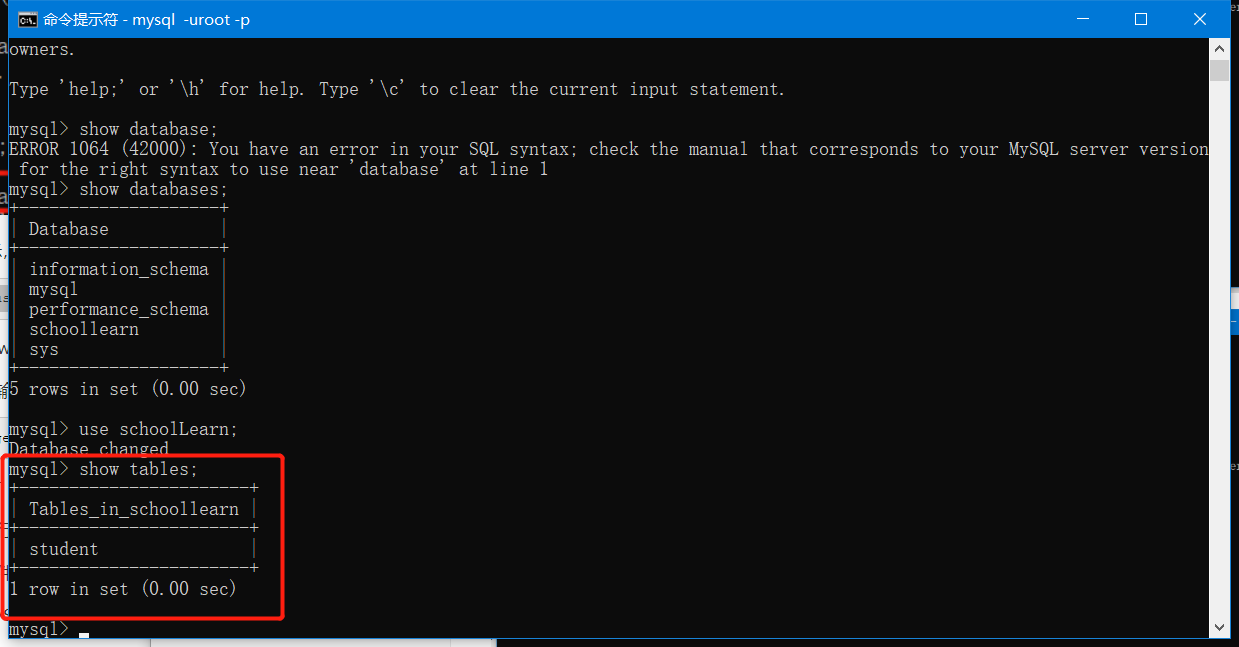
3. 数据库基本属性
数据库database-->schema-->表table-->字段(依次向下包含)
3.1 表(table)字段类别
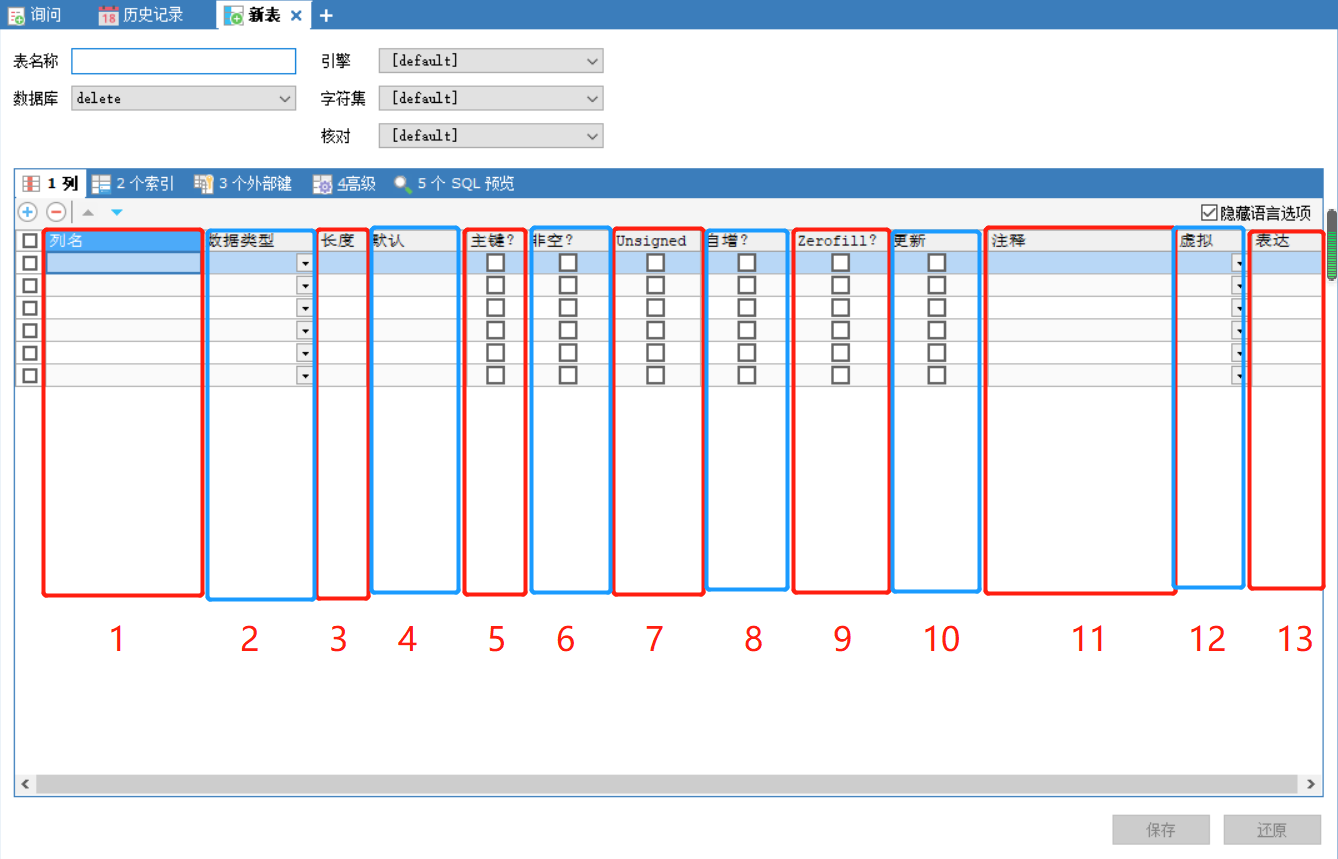
数据库的列类型(2)
数值
-
tinyint 十分小的数据,1byte(s)
-
smallint 较小的数据,2byte(s)
-
-
int 标准整形数据,4byte(s),常用
-
bigint 较大的数据,8byte(s)
-
float 单精度 4byte(s)
-
double 双精度 8byte(s)
-
decimal 字符串形式的浮点数
字符串
-
char 字符串|固定大小的,0~255(2^8-1)
-
varchar 字符串|可变,0~65535(2^16-1)常用的String
-
tinytext 微型文本 2^8-1
-
text 文本串 2^16-1 保存大文本
时间日期
-
date YYYY-MM-DD 日期格式
-
time HH: mm : ss 时间格式
-
datatime YYYY-MM-DD HH: mm : ss,常用
-
timestamp 时间戳 1970.1.1到现在的毫秒数
-
year 年份表示
null
-
没有值,未知
-
不要使用null计算(结果为null)
数据库的字段属性(4, 6, 7, 8, 9)
default 默认 (4)
-
设置默认值,如果不指定指就会设定为被设定的默认值
主键 primary key (5)
-
数据库中的每一张表都要有唯一主键,但是构成主键的字段可以多于一个(primary key (1,2,3))
非空? null not null(6)
-
假设设置为not null,如果不给它赋值,就会报错
-
null,如果不填写值,默认为null
unsigned(7)
-
-
声明该列不能为负数
自增?anto-increment?(8)
-
通常理解为自增,自动在上一条记录的基础上+1(默认)
-
通常用来设计唯一的主键-->index(e.g.),必须是整数类型
-
可以自定义设计主键自增的起始值和步长
zerofill?(9)
-
0填充
-
不足的位数使用0来填充(e.g. int(3) 输入:5--->005)
3.2 创建数据库表
-- 格式 use database `数据库名`; create table if not exist `表名`( -- 必填:`字段名` 列类型 [属性] [索引] [注释], -- 必填:`字段名` 列类型 [属性] [索引] [注释], -- 必填:`字段名` 列类型 [属性] [索引] [注释], ...... -- 必填:`字段名` 列类型 [属性] [索引] [注释] )[表类型][字符集设置][注释]
例子
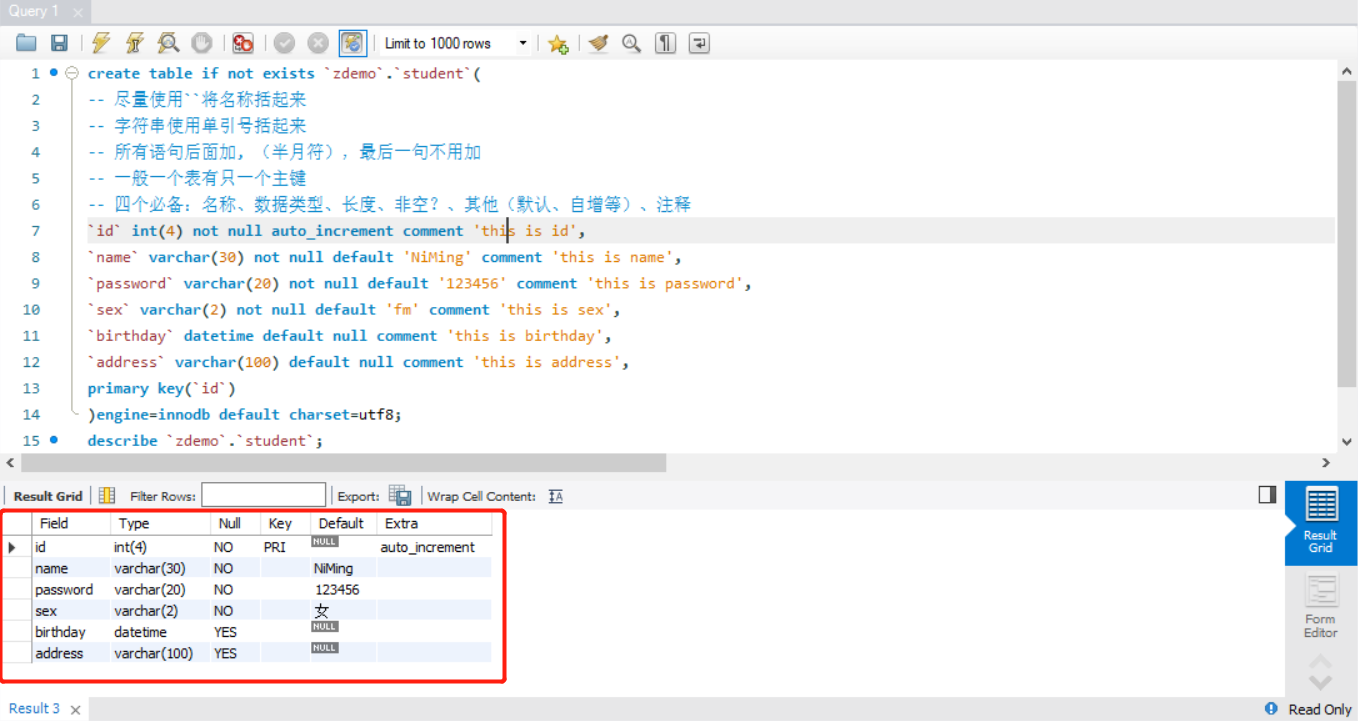
create table if not exists `zdemo`.`student`( -- 尽量使用``将名称括起来 -- 字符串使用单引号括起来 -- 所有语句后面加, (半月符),最后一句不用加 -- 一般一个表有只一个主键 -- 四个必备:名称、数据类型、长度、非空?、其他(默认、自增等)、注释 `id` int(4) not null auto_increment comment 'this is id', `name` varchar(30) not null default 'NiMing' comment 'this is name', `password` varchar(20) not null default '123456' comment 'this is password', `sex` varchar(2) not null default 'fm' comment 'this is sex', `birthday` datetime default null comment 'this is birthday', `address` varchar(100) default null comment 'this is address', primary key(`id`) )engine=innodb default charset=utf8; /* INODB 默认使用,安全性高,事务的处理,多表多用户操作 MYISAM 以前会使用,节约空间,速度较快 */ describe `zdemo`.`student`; -- 查看表内容


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号