Appium自动化(6):原生app元素定位方法
元素定位方法介绍及应用:
Appium方法定位原生app元素:
通过appium inspector工具,可以获取元素的相关信息;在appium中提供了一系列的元素定位API,通过在这些API中输入指定的元素信息,就能完成元素定位,定位元素后就进行对元素进行自动操作。
appium中识别元素的方式有两种写法
方式一:driver.find_element_by_id(" ")
方式二:driver.find_element(By.ID," ") -----推荐使用
基本元素定位如下:
前置条件
代码示例:
from appium import webdriver # 导入appium 驱动包 from appium.webdriver.webdriver import By # 导入appium 定位的方法包 # 1、定义一个DesiredCapabilities配置的字典 des = { 'platformName':'Android', 'platformVersion':'6.0.1', # 填写android虚拟机/真机的系统版本号 'deviceName':'MuMu', # 填写安卓虚拟机/真机的设备名称 'appPackage':'com.sky.jisuanji', # 填写被测app包名 'appActivity':'.JisuanjizixieActivity', # 填写被测app的入口 'udid':'127.0.0.1:7555', # 填写通过命令行 adb devices 查看到的udid 'noReset':True, # 重置APP 'unicodeKeyboard':True, # 支持中文输入 'resetKeyboard':True, # 支持重置键盘 'newCommandTimeout':30 # 30秒没发送新命令就断开连接 } # 2、把配置的字典作为请求参数发送给appium服务器 driver = webdriver.Remote('http://127.0.0.1:4723/wd/hub',des)
1、ID定位(取resource-id、id、name)
driver.find_element(By.ID," ")
代码示例:
# ID 定位(取resource-id、id、name) driver.find_element(By.ID,'com.sky.jisuanji:id/btn6').click()
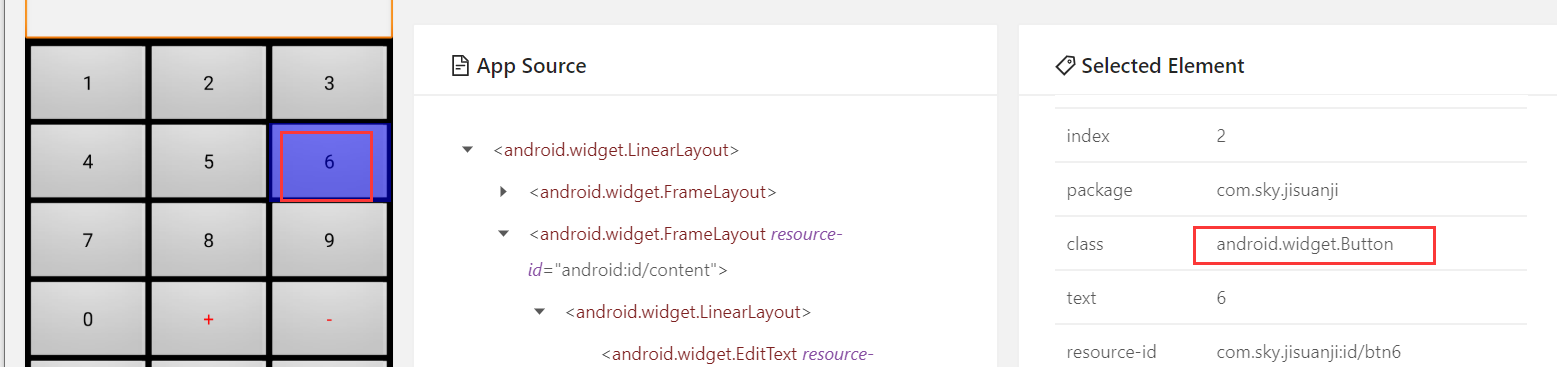
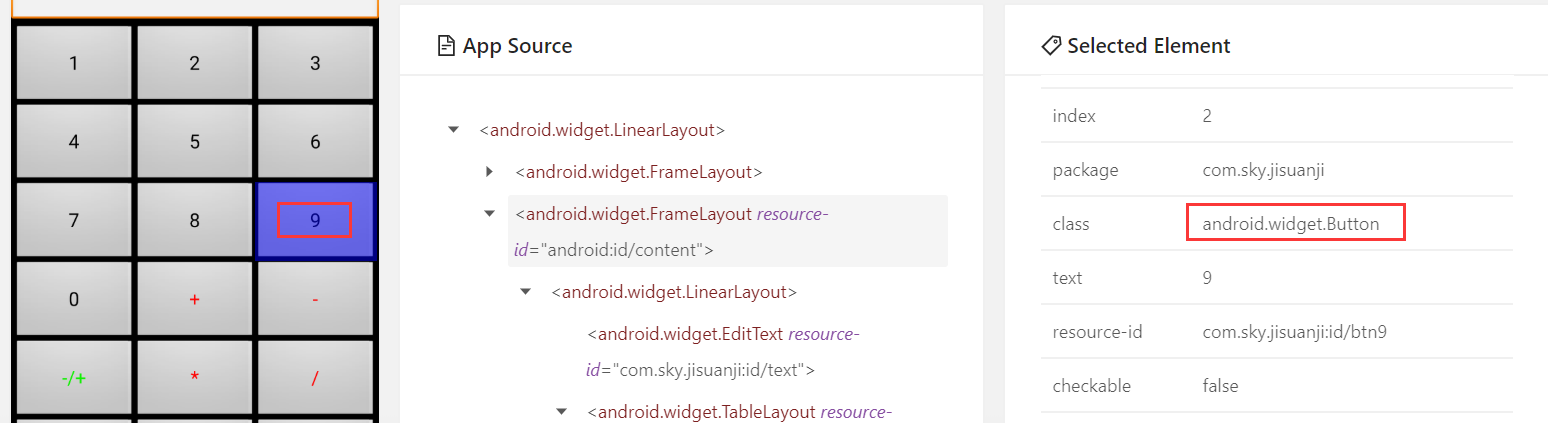
2、class定位(取class)
driver.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME," ")
代码示例:
# class定位(取class) driver.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME,'android.widget.Button').click()
注:class有时不是唯一的值,如计算器的数字按键6和9,它们的class都是相同的值,故class定位一般不推荐使用!
3、AccessibilityId定位(取content-desc)注:有些元素是没有content-desc的属性的
driver.find_element_by_accessibility_id('') 注:driver.find_element(By. ) 新定位方法By已经没有accessibility_id的方法了
代码示例:
# AccessibilityId定位(取content-desc) driver.find_element_by_accessibility_id('').click()
备注:其中name方式(取text)已不支持
Xpath定位方法:
xpath ==> XPATH 是一门标记语言 作用是在XML、XHTML 文档中查找元素
selenium xpath是1.0版本语法 appium xpath是2.0版本语法
1、绝对路径:
绝对路径 xpath 绝对路径 /开头 从根节点直接一层一层定位找到元素;元素的全路径,包含了全部节点。这种方法写起来很长,效率不高;另一方面由于涉及到太多层,一旦中间任何一层有变动,那元素就定位不到了

代码示例:通过绝对路径知道计算机的数字按键 5 并点击
# xpath 绝对路径定位/开头 从根节点直接一层一层定位找到元素 遇到同层级相同的元素,用下标区分,下标从1开始 driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'/hierarchy/android.widget.FrameLayout/android.widget.LinearLayout/android.widget.FrameLayout[2]/android.widget.LinearLayout/android.widget.TableLayout/android.widget.LinearLayout[2]/android.widget.Button[2]').click
2、使用属性定位
注:
appium中xpath属性定位格式:driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//类名[@text="text值"]')
网页中xpath属性定位格式:driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//标签[@id="id值"]')
text属性:
driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//类名[@text="text值"]')
resource-id属性:
driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//类名[@resource-id="属性值"]')
content-desc属性:
driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//类名[@content-desc="属性值"]')
class属性:
driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//类名')
多属性:
and表示并且 or表示或者
driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//类名[@属性名="属性值" and @属性名="属性值"]')
driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//类名[@属性名="属性值" or @属性名="属性值"]')
代码示例:
# 使用属性 定位 //类名[@属性名="属性值"] driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//android.widget.Button[@resource-id="com.sky.jisuanji:id/btn8"]').click() driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//android.widget.Button[@text="8"]').click() # 扩展:and/or # //类名[@属性名1=“属性值1” and @属性名2=“属性值2”] # //类名[@属性名1=“属性值1” or @属性名2=“属性值2”] driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//android.widget.Button[@text="8" and @resource-id="com.sky.jisuanji:id/btn8"]').click() driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//android.widget.Button[@text="8" or @bounds="sss"]').click() # find_elements() 把满足条件的所有元素按匹配顺序放入列表 所以是先匹配到8 然后到9 els = driver.find_elements(By.XPATH,'//android.widget.Button[@text="9" or @text="8"]') els[0].click() els[1].click()
备注:
1、所有元素的属性都可以进行定位,但必须该属性的值是界面上唯一的
2、xpath支持*代表任意个字符,比如find_element(By.XPATH,'//*[@text=text值]'),这种用法容易同时识别多个元素
3、使用部分属性值定位
当元素的属性值过长或者元素属性值内容中存在动态变化的情况下,可以使用该方法。
starts-with() contains() ends-with()--ends-with
起始位置匹配:starts-with()
driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//类名[starts-with(@属性名,"部分属性值")]')
包含匹配:contains()
driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//类名[contains(@属性名,"部分属性值")]')
末尾位置匹配:ends-with()
driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//类名[ends-with(@属性名,"部分属性值")]')
注:在selenium中没有该方法,ends-with()字符串结尾比对 ,是xpath2.0的函数库和语法,而xpath1.0不存在该函数,selenium中的xpath语法使用的是1.0语法,但是appium是使用xpath2.0及以上的语法
代码示例:
# 部分属性值定位 # 1、元素属性过长 使用ends-with()方法 driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//android.widget.Button[ends-with(@resource-id,"btn8")]').click() # 2、动态元素 第一次打开 text="id_9" 第二次打开text="id_10" 第三次打开text="id_11" # starts-with(@text,"id_") driver.find_element(By.XPATH,'//android.widget.Button[starts-with(@text,"id_")]').click()
uiautomator方法定位原生app元素:
appium在android端是调用其底层的UIAutomator2自动化测试框架去驱动自动化,在定位元素的时候,可以借助UIAutomator2的语法来实现定位。在代码实现上提供的API是find_element_by_android_uiautomator;利用android_uiautomator进行定位,语法必须属性值是双引号
1、根据text定位:
find_element_by_android_uiautomator('text("值")')
find_element_by_android_uiautomator('newUiSelector().text("值")') # 'newUiSelector()'推荐使用
代码示例:
# 通过text定位 driver.find_element_by_android_uiautomator('text("5")').click() # 推荐使用正规方法 driver.find_element_by_android_uiautomator('new UiSelector().text("5")').click()
text定位相关函数:
textContains:模糊匹配文本
textStartsWith:以某个文本开头来匹配
textMatches:正则匹配
代码示例:
# text定位相关函数: # textContains:模糊匹配文本 driver.find_element_by_android_uiautomator('new UiSelector().textContains("...")') # textStartsWith:以某个文本开头来匹配 driver.find_element_by_android_uiautomator('new UiSelector().textStartsWith("...")') # textMatches:正则匹配 driver.find_element_by_android_uiautomator('new UiSelector().textMatches("...")')
2、根据resourceId定位:
find_element_by_android_uiautomator('resourceId("值")')
find_element_by_android_uiautomator('newUiSelector().resourceId("值")')
代码示例:
# 根据resourceId定位: driver.find_element_by_android_uiautomator('new UiSelector().resourceId("...")').click()
3、根据className定位:关键字className
代码示例:
# 根据className定位:关键字className driver.find_element_by_android_uiautomator('new UiSelector().className("...")').click()
4、根据contenet-des定位:关键字description
代码示例:
# 根据contenet-des定位:关键字description driver.find_element_by_android_uiautomator('new UiSelector().description("...")').click()
5、组合定位(类名和文本)
newUiSelector().className("类名").text("值")其它组合定位方式类推
代码示例:
# 组合定位(类名和文本): driver.find_element_by_android_uiautomator('new UiSelector().className("android.widget.Button").text("7")').click() driver.find_element_by_android_uiautomator('new UiSelector().text("8").className("android.widget.Button")').click()
6、根据元素关系定位
1)后代元素定位:
使用条件:子元素属性不定,不唯一,只能通过父元素来定位
newUiSelector().resourceId("值").childSelector(className("值").instance(数字))
其中childSelector可以传入resourceId、description等方法
instance表示匹配的结果所有元素里面的第几个元素,从0开始计数
代码示例:
# 后代元素定位 driver.find_element_by_android_uiautomator('new UiSelector().resourceId("com.sky.jisuanji:id/tablelayout").childSelector(className("android.widget.Button").instance(3))').click()
2)兄弟元素定位
通过子元素找到父元素,然后通过父元素再去找兄弟元素
newUiSelector().resourceId("值").fromParent(text("值"))
fromParent()表示从元素的父元素下查找
代码示例:
# 兄弟元素定位 driver.find_element_by_android_uiautomator('new UiSelector().text("7").fromParent(text("9"))').click()
ends_with()字符串结尾比对 == 是xpath2.0的函数库、语法 而xpath1.0不存在该函数



