C++第十五章_友元类_友元成员函数_异常机制_将对象作为异常类型_栈解退_C风格字符串和C++字符串输入问题
目录
1、友元类
01)什么时候使用友元类?
假如要编写一个电视机Tv类和一个遥控器Remote类,很显然,Tv类不是Remote类,Remote类也不是Tv类,即不存在is-a关系;
遥控器Remote类也不是电视Tv类的一部分,反之亦然,因此包含、私有继承、保护继承的has-a关系也不存在;
事实上,遥控器可以改变电视机的状态,这表明Remote类作为Tv类的一个友元。
02)下面的语句使Remote成为友元类:
friend class Remote;
友元声明可以位于Tv类的公有、私有或保护部分,其位置无关紧要;由于Remote类中使用了Tv类的一些方法,所以要先声明
Tv类,然后声明Remote类;也可以使用前向声明,以后将介绍;
03)友元类的所有方法都可以访问原始类的私有成员和保护成员,例如:

1 class A 2 { 3 friend class B; 4 5 private: int aa; 6 }; 7 8 class B 9 { 10 public: 11 void output() 12 { 13 cout << a.aa << endl; //直接访问A类中的私有数据aa 14 } 15 private: A a; //创建A类对象 16 17 } 18 19 20 ———————————————— 21 版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「风雪残存」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 by-sa版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。 22 原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/u012230798/article/details/86576169
参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/u012230798/article/details/86576169

1 #ifndef TV_H_ 2 #define TV_H_ 3 4 class Tv 5 { 6 private: 7 int state; //on or off 8 int volume; //音量 9 int maxchannel; //频道的最大数 10 int channel; //选择的频道 11 int mode; //Antenna or able 12 int input; //TV or DVD 13 public: 14 friend class Remote; //声明Remote为Tv的一个友元类 15 enum {Off, On}; //电视机的开关 16 enum {MinVal,MaxVal}; //声音的最小和最大值 17 enum {Antenna, Cable}; //天线or电缆 18 enum {TV,DVD}; //TV模式orDVD模式 19 20 Tv(int s=Off,int mc=125) : state(s),volume(5),maxchannel(mc),channel(2),mode(Cable),input(TV) {}; 21 22 void onoff() {state = (state == On) ? Off:On;} //若state == On成立,则state=Off,否则state=On 23 bool ison() const {return state == On;} 24 bool volup(); //增大音量 25 bool voldown(); //减小音量 26 void chanup(); //频道数增大 27 void chandown(); //频道数减小 28 void set_mode() {mode = (mode == Antenna) ? Cable : Antenna;} 29 void set_input() {input = (input == DVD) ? TV:DVD;} 30 void settings() const; //diaplay all the settings 31 }; 32 33 /*Remote中的方法除了构造函数外,都调用了原始类Tv中的方法*/ 34 class Remote 35 { 36 private: 37 int mode; 38 public: 39 Remote(int m = Tv::TV) : mode(m) {} 40 bool volup(Tv & t) {return t.volup();} //直接调用Tv中的volup() 41 bool voldown(Tv & t) {return t.voldown();} 42 void onoff(Tv & t) {t.onoff();} 43 void chanup(Tv & t) {t.chanup();} 44 void chandown(Tv & t) {t.chandown();} 45 void set_chan(Tv & t,int c) {t.channel = c;} //友元类的所有方法(Tv & t也是)都可以访问原始类的私有成员和保护成员 46 void set_mode(Tv & t) {t.set_mode();} 47 void set_input(Tv & t) {t.set_input();} 48 }; 49 50 #endif

1 //tv.cpp 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include "tv.h" 4 5 /*Tv类中增大音量函数*/ 6 bool Tv::volup() 7 { 8 if(volum < MaxVal) 9 { 10 volume++; 11 return true; 12 } 13 else 14 return false; 15 } 16 17 /*Tv类中减小音量函数*/ 18 bool Tv::voldown() 19 { 20 if(volume > MinVal) 21 { 22 volume--; 23 return true; 24 } 25 else 26 return false; 27 } 28 29 /*Tv类中增大频道数函数*/ 30 void Tv::chanup() 31 { 32 if(channel < maxchannel) 33 channel++; 34 else 35 channel = 1; //增大到maxchannel后回到频道1 36 } 37 38 /*Tv类中减小频道数函数*/ 39 void Tv::chandown() 40 { 41 if(channel > 1) 42 channel--; 43 else 44 channel = maxchannel; //减小到频道1后换到频道最大值 45 } 46 47 /*diaplay all the settings*/ 48 void Tv::settings() const 49 { 50 using std::cout; 51 using std::endl; 52 53 cout << "Tv is " << (state = Off ? "Off" : "On") << endl; //此处则可以省略下面if的else语句 54 if(state == On) //On是在Tv中定义的一个枚举量 55 { 56 cout << "Volume setting = " << volume << endl; 57 cout << "Channel setting = " << channel <<endl; 58 cout << "Mode = " << (mode == Antenna ? "antenna":"cable") << endl; //在Tv类和Remote类中都定义了mode 59 cout << "Input = " << (input == DVD ? "DVD":"TV") << endl; 60 } 61 }

1 //use_tv.cpp 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include "tv.h" 4 5 int main() 6 { 7 using std::cout; 8 Tv s42; //此处将调用Tv类中的构造函数,由于Tv类中的构造函数都有默认参数,所以此处相当于省略了参数而使用默认参数,来初始化s42 9 cout<<"Tv对象初始化设置:"<<endl; 10 s42.settings(); //显示设置 11 12 s42.onoff(); //切换开关状态 13 s42.chanup(); //频道加 14 cout<<"使用电视机本身设置后的参数:"<<endl; 15 s42.sttings(); 16 17 Remote grey; //使用Remote类构造函数中的默认参数初始化并创建Remote对象 18 grey.volup(s42); //增大音量 19 grey.volup(s42); //再次增大音量 20 grey.chanup(s42); //频道加 21 grey.set_chan(s42.5); //设置频道5; 22 cout<<"使用遥控器设置后的参数:"<<endl; 23 s42.settings(); 24 25 Tv s58(Tv::On); //使用参数On创建Tv对象s58 26 s58.set_mode(); 27 s58.settings() 28 29 }
2、友元成员函数
01)从上一个例子中我们可以看出,在Remote类中只有Remote::set_chan()方法直接影响了Tv类中的私有数据(channel);
而友元函数的特点之一就是可以访问类的私有数据(P391),所以我们可以只让Remote::set_chan()方法成为Tv类的友元,
而不是让Remote类中的所有方法都成为Tv类中的友元函数。
02)让Remote::set_chan()成为Tv类的友元方法是在Tv类中做如下声明:
1 class Tv 2 { 3 friend void Remote::set_chan(Tv & t, int c); 4 ... 5 };
这里存在矛盾的地方:
一、因为在Tv类中使用了Remote类,所以要让编译器能够处理这条语句,它必须知道Remote类的存在,否则编译器无法知道
Remote类的存在,也就无法知道Remote类中的set_chan()方法,解决方法是让Remote定义在Tv定义之前;
二、由friend void Remote::set_chan(Tv & t, int c)可知,在set_chan()方法中使用了Tv类对象,这意味着Tv定义应该放在Rmeote
定义之前。
解决以上矛盾的方法是使用前向声明:class Tv;
这样声明的排序次序应如下:
1 class Tv; //前向声明 2 class Remote {...}; 3 class Tv {...};
能否像下面这样排序呢?
1 class Remote; 2 class Tv {...}; 3 class Remote {...};
答案是不能。因为Remote类中的set_chan()方法在Tv中用到,所以必须先声明Remote类,再声明Tv类,即要将Tv类做前向声明。
03)还有一个问题,例如在Remote类中一个函数的定义如下:
void onoff(Tv & t) {t.onoff();}
在Remote类中将调用Tv类中的方法,然而Tv类证明在Remote类声明之后,解决方法是在Remote类中只包含类的声明,不包含
类方法的定义即可.
注:tvfm.h包含了函数声明和方法定义:

1 #ifndef TVFM_H_ 2 #define TVFM_H_ 3 4 class Tv; //前向声明 5 6 class Remote 7 { 8 public: 9 enum State{Off, On}; //电视机的开关 10 enum {MinVal,MaxVal}; //声音的最小和最大值 11 enum {Antenna, Cable}; //天线or电缆 12 enum {TV,DVD}; //TV模式orDVD模式 13 private: 14 int mode; 15 public: 16 Remote(int m = Tv::TV) : mode(m) {} 17 bool volup(Tv & t); //除了构造函数外,均只声明方法,因为Tv定义在Rmeote声明在Tv声明之后 18 bool voldown(Tv & t); 19 void onoff(Tv & t); 20 void chanup(Tv & t); 21 void chandown(Tv & t); 22 void set_chan(Tv & t,int c); 23 void set_mode(Tv & t); 24 void set_input(Tv & t); 25 } 26 27 class Tv 28 { 29 private: 30 int state; //on or off 31 int volume; //音量 32 int maxchannel; //频道的最大数 33 int channel; //选择的频道 34 int mode; //Antenna or able 35 int input; //TV or DVD 36 public: 37 friend void Remote::set_chan(Tv & t, int c); //声明Remote中的set_chan()方法为Tv的一个友元函数 38 39 enum {Off, On}; //电视机的开关 40 enum {MinVal,MaxVal}; //声音的最小和最大值 41 enum {Antenna, Cable}; //天线or电缆 42 enum {TV,DVD}; //TV模式orDVD模式 43 44 Tv(int s=Off,int mc=125) : state(s),volume(5),maxchannel(mc),channel(2),mode(Cable),input(TV) {}; 45 46 void onoff() {state = (state == On) ? Off:On;} //若state == On成立,则state=Off,否则state=On 47 bool ison() const {return state == On;} 48 bool volup(); //增大音量 49 bool voldown(); //减小音量 50 void chanup(); //频道数增大 51 void chandown(); //频道数减小 52 void set_mode() {mode = (mode == Antenna) ? Cable : Antenna;} 53 void set_input() {input = (input == DVD) ? TV:DVD;} 54 void settings() const; //diaplay all the settings 55 }; 56 57 /* 58 01)Remote类中的方法定义,加上关键字inline使所有方法均成为内联函数 59 02)必须将定义放在后面,因为在Remote中的方法中要使用Tv对象 60 */ 61 inline bool Remote::volup(Tv & t) {return t.volup();} //直接调用Tv中的volup() 62 inline bool Remote::voldown(Tv & t) {return t.voldown();} 63 inline void Remote::onoff(Tv & t) {t.onoff();} 64 inline void Remote::chanup(Tv & t) {t.chanup();} 65 inline void Remote::chandown(Tv & t) {t.chandown();} 66 inline void Remote::set_chan(Tv & t,int c) {t.channel = c;} //友元函数的所有方法(Tv & t也是)都可以访问原始类的私有成员和保护成员 67 inline void Remote::set_mode(Tv & t) {t.set_mode();} 68 inline void Remote::set_input(Tv & t) {t.set_input();} 69 #endif
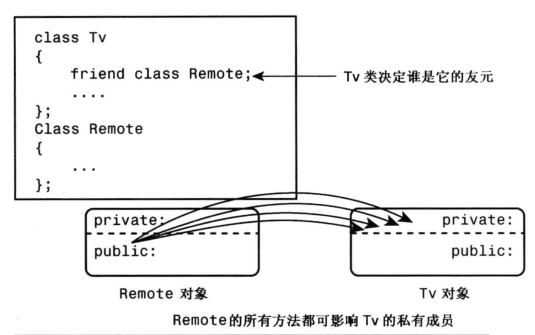
Remote类成为Tv类的友元类:Remote中的所有方法均可以影响Tv类中的私有成员;如下图所示:
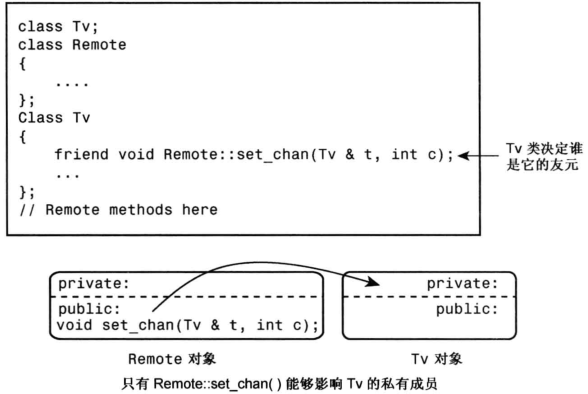
只让Remote中的set_chan()方法成为Tv类的友元函数,则只有Remote::set_chan()可以影响Tv类中的私有变量;如下图所示:
3、异常机制
01)调用abort()函数,需包含头文件#include <cstdlib>;在程序中调用abort()会打印一个随系统而异的文字
02)异常机制:使用try、throw、catch关键字

1 #include <iostream> 2 3 double hmean(double a, double b); //声明一个函数 4 5 int main() 6 { 7 double x,y,z; 8 9 std::cout<<"Enter two numbers: "; 10 while(cin>>x>>y) 11 { 12 try 13 { 14 z = hmean(x,y); 15 } 16 catch(const char *s) //catch是关键字,并不是函数; throw后的string会赋给s;如果没有执行throw(即没有异常)会忽略catch中的语句 17 { 18 std::cout << s << std::endl; 19 std::cout << "Enter a new pair of numbes: "; 20 continue; //返回到while继续执行 21 } 22 std::cout<<"Harmonic mean of " << x << " and " << y << " is " << z <<std::endl; 23 std::cout << "Enter next set of numbers <q to qiut>" << std::endl; //继续执行while循环 24 } 25 26 std::cout << "Bye!" << std::endl; 27 return 0; 28 } 29 30 double hmean(double a, double b) 31 { 32 if(a == -b) 33 throw "Bad hmean() arguments: a=-b not allowed"; //由于throw后的字符串和main()中catch中的char *s匹配,所以执行throw后会执行catch 34 return 2.0*a*b/(a+b); 35 } 36 /* 37 01)若输入的两个数字为6,10,则直接执行try中的语句,执行完毕后,跳过catch中的语句; 38 02)若输入的两个数字为6,-6,则执行try中的hmean(),后执行throw,然后跳转到main()中的catch,执行catch中的语句 39 03)程序执行到throw后,程序会沿函数调用的顺序后退,直到遇到try块的函数 40 */
对于以上程序,注:
01)若输入的两个数字为6,10,则直接执行try中的语句,执行完毕后,跳过catch中的语句;
02)若输入的两个数字为6,-6,则执行try中的hmean(),后执行throw,然后跳转到main()中的catch,执行catch中的语句
03)程序执行到throw后,程序会沿函数调用的顺序后退,直到遇到try块的函数

4、将对象作为异常类型

1 /*将对象作为异常类型*/ 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 class bad_hmean 5 { 6 private: 7 double v1; 8 double v2; 9 public: 10 bad_hmean(double a=0, double b=0) : v1(a),v2(b) {} //使用默认值初始化私有变量,创建对象时,可以使用新值覆盖默认值 11 void mesg(); //用于报告错误信息 12 }; 13 inline void bad_hmean::mesg() 14 { 15 std::cout << "hmean(" << v1 << ", " << v2 << "):" << "invalid arguments: a=-b not allowed!" << std::endl; 16 } 17 18 class bad_gmean 19 { 20 private: 21 double v1; 22 double v2; 23 public: 24 bad_gmean(double a=0, double b=0) : v1(a),v2(b) {} //使用默认值初始化私有变量,创建对象时,可以使用新值覆盖默认值 25 const char* mesg(); //用于报告错误信息 26 }; 27 inline const char* bad_gmean::mesg() 28 { 29 return "gmean() arguments should be >=0" << std::endl;

1 /*error4.cpp for exc_mean.h*/ 2 #inlude <iostream> 3 #include "exc_mean.h" 4 5 using std::cin; 6 using std::cout: 7 using std::endl; 8 9 double hmean(double a, double b); 10 double gmean(double a, double b); 11 12 int main() 13 { 14 double x,y,z; 15 16 while(cin>>x>>y) 17 { 18 try 19 { 20 z = hmean(x,y); 21 z = gmean(x,y); 22 } 23 catch(bad_hmean & b) //与hmean()中的throw匹配 24 { 25 b.mesg(); 26 cout << "继续输入数字或者是按下任意字母退出程序!"<< endl; 27 continue; //会到while循环 28 } 29 catch(bad_gmean & h) //与gmean()中的throw匹配 30 { 31 h.mesg(); 32 cout << "Try again!" << endl; 33 cout << "继续输入数字或者是按下任意字母退出程序!"<< endl;//如果输入的是字母,则while中的条件会判断不成立从而退出循环 34 continue; //会到while循环 35 } 36 } 37 cout << "Bye!\n"; 38 return 0; 39 } 40 41 double hmean(double a, double b) 42 { 43 bad_hmean bh(a,b); //使用a、b创建并初始化类对象bh 44 if(a == -b) 45 throw bh; //如果执行该语句,则返回到main()中的catch(bad_hmean & b)处继续执行 46 return 2.0*a*b/(a+b); 47 } 48 double gmean(double a, double b) 49 { 50 bad_gmean bg(a,b); //使用a、b创建并初始化类对象bg 51 if(a<0 || b<0) 52 throw bg; //如果执行该语句,则返回到main()中的catch(bad_gmean & h)处继续执行 53 return std::sqrt(a*b); 54 }
5、栈解退
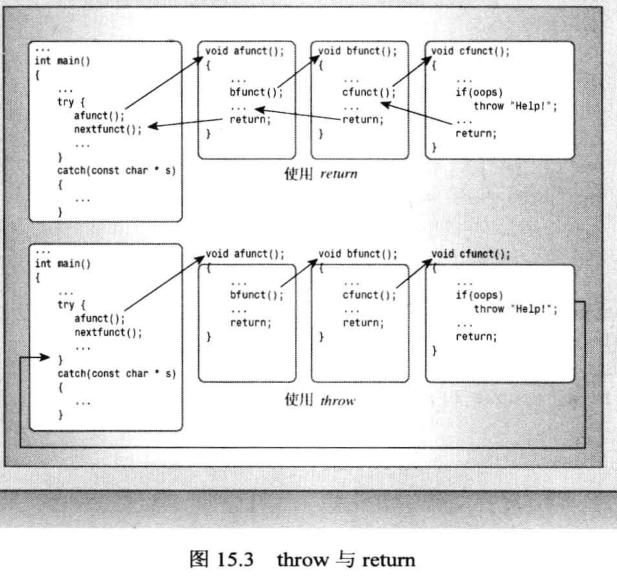
栈解退定义:


1 /*将对象作为异常类型*/ 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 class bad_hmean 5 { 6 private: 7 double v1; 8 double v2; 9 public: 10 bad_hmean(double a=0, double b=0) : v1(a),v2(b) {} //使用默认值初始化私有变量,创建对象时,可以使用新值覆盖默认值 11 void mesg(); //用于报告错误信息 12 }; 13 inline void bad_hmean::mesg() 14 { 15 std::cout << "hmean(" << v1 << ", " << v2 << "):" << "invalid arguments: a=-b not allowed!" << std::endl; 16 } 17 18 class bad_gmean 19 { 20 private: 21 double v1; 22 double v2; 23 public: 24 bad_gmean(double a=0, double b=0) : v1(a),v2(b) {} //使用默认值初始化私有变量,创建对象时,可以使用新值覆盖默认值 25 const char* mesg(); //用于报告错误信息 26 }; 27 inline const char* bad_gmean::mesg() 28 { 29 return "gmean() arguments should be >=0" << std::endl;

1 /*栈解退*/ 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <cmath> //for sqrt() 4 #include <string> 5 #include "exc_mean.h" 6 7 /*定义一个类*/ 8 class demo 9 { 10 private: 11 std::string word; 12 public: 13 demo(const std::string & str) //构造函数的定义 14 { 15 word = str; 16 std::cout << "demo " << word << " created\n"; 17 } 18 ~demo() 19 { 20 std::cout << "demo " << word << " destroyed\n"; 21 } 22 void show() const 23 { 24 std::cout << "demo " << word << " lives\n"; 25 } 26 }; 27 28 /*声明函数*/ 29 double hmean(double a, double b); 30 double gmean(double a, double b); 31 double means(double a, double b); 32 33 int main() 34 { 35 using std::cout; 36 using std::cin; 37 using std::endl; 38 39 double x,y,z; //使用一个函数块 40 { 41 demo d1("found in block in main()"); //创建demo对象 42 cout << "Enter two numbers: "; 43 while(cin>>x>>y) 44 { 45 try //正常执行完try中的语句后会自动回到while处继续执行 46 { 47 z = means(x,y); 48 cout << "The mean mean of " << x << " and " <<y << " is " << z << endl; 49 cout << "继续输入数字或者是按下任意字母退出程序!"<< endl;//如果输入的是字母,则while中的条件会判断不成立从而退出循环 50 } 51 catch(bad_hmean & b) //与hmean()中的throw匹配 52 { 53 b.mesg(); 54 cout << "继续输入数字或者是按下任意字母退出程序!"<< endl; 55 continue; //会到while循环 56 } 57 catch(bad_gmean & h) //与gmean()中的throw匹配 58 { 59 h.mesg(); 60 cout << "Try again!" << endl; 61 cout << "继续输入数字或者是按下任意字母退出程序!"<< endl;//如果输入的是字母,则while中的条件会判断不成立从而退出循环 62 continue; //会到while循环 63 } 64 } 65 } 66 cout << "Bye!\n"; 67 cin.get(); //使dos界面停止 68 return 0; 69 } 70 71 /*函数定义*/ 72 double hmean(double a, double b) 73 { 74 bad_hmean bh(a,b); //使用a、b创建并初始化类对象bh 75 if(a == -b) 76 throw bh; //如果执行该语句,则返回到means()中的catch(bad_hmean & b)处继续执行 77 //因为程序是沿着函数调用的反方向去寻找try块,找到了try块之后,程序会到try块的最后处继续执行(即执行try块后面的语句) 78 return 2.0*a*b/(a+b); 79 } 80 double gmean(double a, double b) 81 { 82 bad_gmean bg(a,b); //使用a、b创建并初始化类对象bg 83 if(a<0 || b<0) 84 throw bg; //如果执行该语句,则去means()中找有没有catch(bad_gmean & h)处继续执行,若没有则到main()中去找与bg匹配的catch 85 //因为程序是沿着函数调用的反方向去寻找try块,找到了try块之后,程序会到try块的最后处继续执行(即执行try块后面的语句) 86 return std::sqrt(a*b); 87 } 88 double means(double a, double b) 89 { 90 double am,bm,gm; 91 demo d2("found in means()"); //创建另外一个demo对象 92 am = (a+b)/2.0; 93 try 94 { 95 hm = hmean(a,b); 96 gm = gmean(a,b); 97 } 98 catch(bad_hmean & b) 99 { 100 b.mesg(); //调用bad_hmean类中的mesg() 101 std::cout << "Caught in means()\n"; 102 throw; //该throw会导致means()终止执行,并将标识为bad_hmean & b(bad_hmean类对象)传递给main()中的catch(bad_hmean & b) 103 } 104 d2.show(); //假如上面的throw 被执行,则不会执行该句 105 return (am+bm+gm)/3.0; 106 }
程序执行过程如下:
情况1:

情况2:

6、C风格字符串和C++字符串输入问题
01)对于C风格字符串
1 char info[100]; 2 cin >> info; //读入一个单词 3 cin.getline(info,100); //读入一行,并直接从输入流中删除掉了键盘输入的换行符(可以接收空格).读入100个字符,并将info[100]设置为\0 4 cin.getline(info,100,':'); //读入一行,直到遇到:,并且丢弃: 5 cin.get(info,100); //读入一行,把键盘输入的换行符留着了输入缓冲区中(可以接收空格).读入100个字符,并将info[100]设置为\0
02)对于string对象(有两种方式输入)
1 string stuff; 2 cin >> stuff; //读入一个单词 3 getline(cin,stuff); //读入一行,并从输入流中删除掉了键盘输入的换行符(可以接收空格) 4 getline(stuff,':'); //读入一行,直到遇到:,并且丢弃:
string版本的getline()将自动调整string对象的大小,使之刚好能够存储输入的字符,且不需要指定读取多少个字符的数值参数
03)string结束读入的条件:
(1)到达文件尾。此时输入流的eofbit将被设置,意味着方法fial()和eof()都将返回true;
(2)遇到分界字符(默认为\n),这时将把分界字符从输入流中删除它,但不存储它;
(3)读取的字符数达到最大允许值,这时将设置输入流的fialbit,这意味着方法fail()将返回true。





