C++第十四章_引入_包含(公有继承)和私有继承_is-a关系和has-a关系_私有继承_使用using重新定义获得访问权限_多重继承的问题与改进_虚基类_类模板类模板类模板_栈指针
目录
1、引入(使用公有继承)
/*关闭隐式转换的原因*/
Student doh("xiaoming",10); //使用构造函数Student(const std::string s,int n)创建Stident对象doh
doh = 5;
//如果没有关键字explict,doh=5 将调用Student(int n) : name("NUll name"),scores(n) {},并使用NUll name来设置name的值
//如果加上explicit则不会进行隐式转换
/*valarray类的介绍*/
01)需包含头文件#include <valarray>
02)使用时,需要在valarray后面加上一对尖括号并在里面写上要使用的数据类型
valarray<int> q_values; //an array of int
valarray<double> weights; //an array of double
03)使用valarray类构造函数创建对象的例子:
double gpa = {3.1,4.2,5.4,3.2,5.6,7.8}; //创建一个double数组
valarray<double> v1; //an array of double,size 0
valarray<int> v2(8); //an array of int,size 8
valarray<int> v3(10,8); //an array of int,size 8,each set to 10
valarray<double> v4(gpa,4); //an array of double,size 4,each set to first 4 elements of gpa
valarray<int> v5 = {10,9,8,7}; //c++11
04)valarray类方法
operator[]() //访问各个元素
size(); //返回包含元素数
sum(); //返回包含元素和
max(); //返回包含元素最大值
min(); //返回包含元素最小值
05)在第四章中介绍的vector和array也可以存储数据,但是这些泪提供的算术支持没有valarray多

1 /*Student类公有继承*/ 2 #ifndef STUDENT_H 3 #define STUDENT_H 4 5 #include <iostream> 6 #include <string> 7 #include <valarray> 8 9 class Student 10 { 11 private: 12 typedef std::valarray<double> ArrayDb; //给std::valarray<double>起别名为ArrayDb 13 14 std::string name; //name为一个包含对象 15 ArrayDb scores; //scores为一个包含对象 16 std::ostream & arr_out(std::ostream & os) const; //私有方法 17 public: 18 Student() : name("Null Student"),scores() {} //定义构造函数,并使用成员初始化列表对name和scores进行初始化 19 explicit Student(const std::string s) : name(s),scores() {} //explicit表示关闭隐式转换 20 explicit Student(int n) : name("NUll name"),scores(n) {} //set name to Null name and creat array of n elements 21 Student(const std::string s,int n) : name(s),scores(n) {} 22 Student(const std::string s, const ArrayDb & a) : name(s),scores(a) {} 23 Student(const char* str,const double* pd,int n) : name(s),scores(pd,n) {} 24 ~Student() {} //析构函数 25 26 double Average() const; 27 const std::string & Name() const; 28 double & operator[](int i); //对[]的重载 29 double operator[](int i) const; //对[]的重载 30 31 //friends 32 friend std::istream & operator>>(std::istream & is, Student & stu); //输入一个单词 33 friend std::istream & getline(std::istream & is, Student & stu); //输入一行 34 friend std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os,Student & stu); //输出 35 36 }; 37 38 #endif 39 40 /*关闭隐式转换的原因*/ 41 /* 42 Student doh("xiaoming",10); //使用构造函数Student(const std::string s,int n)创建Stident对象doh 43 doh = 5; 44 //如果没有关键字explict,doh=5 将调用Student(int n) : name("NUll name"),scores(n) {},并使用NUll name来设置name的值 45 //如果加上explicit则不会进行隐式转换 46 */ 47 48 /*valarray类的介绍*/ 49 /* 50 01)需包含头文件#include <valarray> 51 02)使用时,需要在valarray后面加上一对尖括号并在里面写上要使用的数据类型 52 valarray<int> q_values; //an array of int 53 valarray<double> weights; //an array of double 54 03)使用valarray类构造函数创建对象的例子: 55 double gpa = {3.1,4.2,5.4,3.2,5.6,7.8}; //创建一个double数组 56 valarray<double> v1; //an array of double,size 0 57 valarray<int> v2(8); //an array of int,size 8 58 valarray<int> v3(10,8); //an array of int,size 8,each set to 10 59 valarray<double> v4(gpa,4); //an array of double,size 4,each set to first 4 elements of gpa 60 valarray<int> v5 = {10,9,8,7}; //c++11 61 04)valarray类方法 62 operator[]() //访问各个元素 63 size(); //返回包含元素数 64 sum(); //返回包含元素和 65 max(); //返回包含元素最大值 66 min(); //返回包含元素最小值 67 05)在第四章中介绍的vector和array也可以存储数据,但是这些泪提供的算术支持没有valarray多 68 */

1 /*公有继承Student.cpp实现*/ 2 #include "Student.h" 3 4 using std::ostream; 5 using std::istream; 6 using std::endl; 7 using std::string; 8 9 /*私有方法定义*/ 10 std::ostream & arr_out(std::ostream & os) const 11 { 12 int i; 13 int lim = scores.size(); 14 if(lim>0) 15 { 16 for(i=0; i<lim; i++) 17 { 18 os<<scores[i]<<" " 19 if(i%5 == 4) //scores中的四个数据为一行 20 os<<endl; 21 } 22 if(i%5!=0) 23 os<<endl; 24 } 25 else 26 os<<"Empty array"; 27 return os; 28 } 29 30 /*计算分数平均值*/ 31 double Student::Average() const 32 { 33 if(scores.size()>0) 34 return scores.sum()/scores.size(); //直接调用valarray类中的方法 35 else 36 return 0; 37 } 38 39 /*利用类方法访问私有数据*/ 40 const std::string & Student::Name() const 41 { 42 return name; 43 } 44 45 /*对[]的重载*/ 46 double & Student::operator[](int i) 47 { 48 return scores[i]; //同样直接使用valarray类中的方法operator[]() 49 } 50 /*对[]的重载*/ 51 double Student::operator[](int i) const 52 { 53 return scores[i]; //同样直接使用valarray类中的方法operator[]() 54 } 55 /*友元函数定义--输入一个单词*/ 56 std::istream & operator>>(std::istream & is, Student & stu) 57 { 58 is>>stu.name; 59 return is; 60 } 61 62 /*友元函数定义--输入一行*/ 63 std::istream & getline(std::istream & is, Student & stu) 64 { 65 getline(is,stu.name); 66 return is; 67 } 68 69 /*友元函数定义--输出*/ 70 std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os,Student & stu) 71 { 72 os<<"Scores for "<<stu.name<<":\n"; 73 stu.arr_out(os); //使用私有方法 74 return os; 75 }

1 /*user_stu.cpp*/ 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include "Student.h" 4 5 using std::cout; 6 using std::cin; 7 using std::endl; 8 9 void set(Student &sa,int n); //在主函数内声明方法 10 const int pupils = 3; //定义常数 11 const int quizzes = 5; 12 13 int main() 14 { 15 Student ada[pupils] = {Student(quizzes),Student(quizzes),Student(quizzes)}; //定义Student类矩阵,内包含了三个Student类对象 16 int i; 17 for(i = 0;i<pupils; i++) 18 set(ada[i],quizzes); 19 cout<<"\nStudent List:\n"; 20 for(i=0;i<pupils;i++) 21 cout<<ada[i].Name()<<endl; 22 cout<<"Results:\n"; 23 for(i=0;i<quizzes;i++) 24 { 25 cout<<endl<<ada[i]; //这里的<<ada[i]将会首先调用std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os,Student & stu)这个函数,在该函数内继续调用arr_out()函数 26 cout<<"average: "<<ada[i].Average()<<endl; 27 } 28 29 cout<<"Done.\n" 30 return 0; 31 } 32 33 /*子函数定义*/ 34 void set(Student &sa,int n); 35 { 36 cout<<"Please input the student's name: "; 37 getline(cin,sa); 38 cout<<"Please input "<<n<<"quiz scires:\n"; 39 for(i=0;i<n;i++) 40 cin>>sa[i]; //这里将会调用double & Student::operator[](int i)函数,返回的是scores[i] 41 while(cin.get() !='\n') 42 continue; //如果没有接收到换行符,那么继续去接收换行符;接收到了换行符则推出此while循环 43 }
注意:在主函数中,使用了sa[i],这个是使用了对[]的重载函数,返回的是scores[i],详见user_main.cpp,刚开始的没看明白
2、包含(公有继承)和私有继承

3、is-a关系和has-a关系(复习回顾)
01)is-a关系即派生类对象也是一个基类对象,可以对基类对象执行任何操作;例如有一个Fruit类,保存水果的重量和热量,
因为apple是一种水果,所以可以从Fruit类中派生出apple类,apple类将继承Fruit类所有的数据成员(重量和热量),也可以有属于自己的
数据成员,但是属于apple的数据成员不属于Fruit类;公有继承创建is-a关系,它是一种包含关系。
02)has-a关系:例如午餐可能包含水果(Fruit类),但是午餐并不是水果,所以不能从Fruit类中派生出Lunch类来在午餐中添加水果;在午餐中
添加水果的正确方法是创建has-a关系,即午餐中有水果,最容易的方式是,将Fruit对象做为Lunch类的数据成员,即私有继承。
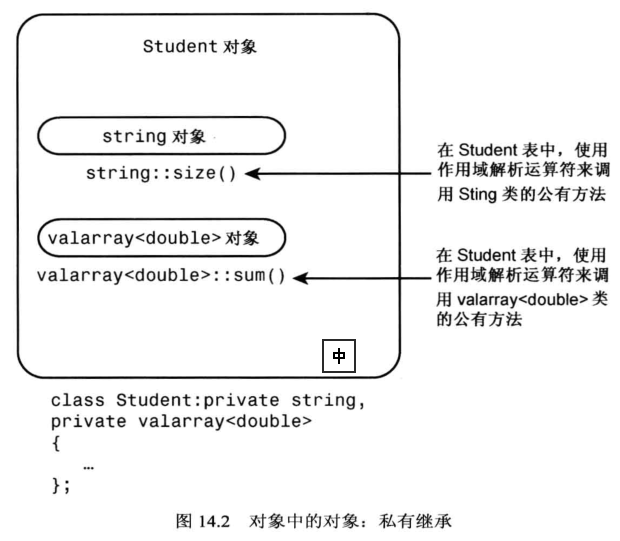
4、私有继承
01)使用私有继承,基类的公有成员和保护成员都将成为派生类的私有成员;这意味着基类方法不会成为派生类的
对象公有接口的一部分,但是可以在派生类的成员函数中使用它们;
02)包含(公有继承)将对象做为一个命名的成员对象添加到类中,而私有继承将对象做为一个未被命名的继承对象
添加到类中;
03)声明方法:
1 class Student : private std::string, private std::valarray 2 { 3 public: 4 ... 5 };
(1)其中private可以省略,默认值为private
(2)私有继承不需要私有数据,因为两个基类已经提供了所需的数据成员。
包含版本(公有继承)提供了两个被显式命名的对象成员,而私有继承提供了两个无名称的自对象成员。
04)公有继承构造函数初始化基类变量方法:
Student(const char *str, const double *pd,int n) : name(str),scores(pd,n) {} //公有继承构造函数定义方法
私有继承构造函数初始化基类变量方法:
Student(const char *str, const double *pd,int n) : std::string(str),std::valarray<double>(pd,n) {}//私有继承构造函数定义方法
05)公有继承访问基类中的方法(函数):
double Student::Average() const { if(scores.size()>0) return scores.sum()/scores.size(); else return 0; }
私有继承访问基类中的方法(函数):
double Student::Average() const { if(ArrayDb::size()>0) return ArrayDb::sum()/ArrayDb::size(); else return 0; }
注意:typedef std::valarray<double> ArrayDb
06)访问基类对象方法
由于string类对象在私有继承中没有名字,此时使用强制转换将Student类转换为string类
const string & Student::Name() const { return (const string &) *this; //转换结果是继承而来的string对象 }
上述方法返回一个引用,改引用指向用于调用该方法的Student对象中继承而来的string对象
07)以下是Student.h等代码使用私有继承方法实现

1 #ifndef STUDENT_H 2 #define STUDENT_H 3 4 #include <iostream> 5 #include <string> 6 #include <valarray> 7 8 class Student : private std::string,std::valarray 9 { 10 private: 11 typedef std::valarray<double> ArrayDb; //名称的替换 12 std::ostream & arr_out(std::ostream & os) const; //声明私有方法 13 public: 14 Student() : std::string("Null name"), ArrayDb() {} //定义构造函数 15 explicit Student(const std::string & s) : std::string(s), ArrayDb() {} ////定义带一个string参数的构造函数 16 explicit Student(int n) : std::string("Null name"), ArrayDb(n) {} //explicit表示不可以进行隐式转换 ArrayDb(n)表示创建包含n个double数据的集合 17 Student(const std::string & s, int n) : std::string(s),ArrayDb(n) {} 18 Student(const char *str,const double *pd,int n) : std::string(str),ArrayDb(pd,n) {} 19 ~Student() {} 20 21 double Average() const; //返回ArrayDb中数据的平均值 22 double & operator[](int i); //使用Student类对象访问ArrayDb中的数据 23 double operator[](int i) const; //使用Student类对象访问ArrayDb中的数据 24 const std::string & Name() const; //返回数据std::string(类似返回公有继承中的name) 25 26 //friends 27 friend std::istream & operator>>(std::istream & is, const Student & s); //输入一个单词 28 friend std::istream & getline(std::istream & is, const Student & s); //输入一行 29 friend std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os, const Student & s); //输出 30 }; 31 32 #endif

1 /*私有继承Student.cpp*/ 2 #include <iostream> 3 #incldue "Student.h" 4 5 using std::istream; 6 using std::endl; 7 using std::ostream; 8 using std::string; 9 10 /* 11 01)返回ArrayDb中数据的平均值 12 02)私有继承访问基类中的方法 13 */ 14 double Student::Average() const 15 { 16 if(std::valarray<double>::size() > 0) //注意这里的std::valarray<double>也可以换成在h文件中声明的ArrayDb 17 return std::valarray<double>::sum() / std::valarray<double>::size(); //由于私有继承是没有变量名字的,所以只能是这样访问基类方法 18 else 19 return 0; 20 } 21 22 /*使用Student类对象访问ArrayDb中的数据*/ 23 double & Student::operator[](int i) 24 { 25 return ArrayDb::operator[](i); //公有继承中实现方法是直接返回scores[i],但是私有继承必须是调用valarray类中的operator[]()方法 26 } 27 28 /*使用Student类对象访问ArrayDb中的数据*/ 29 double Student::operator[](int i) const 30 { 31 return ArrayDb::operator[](i); 32 } 33 34 /* 35 01)返回数据std::string(类似返回公有继承中的name) 36 02)访问基类对象方法:使用强制转换 37 */ 38 const std::string & Student::Name() const 39 { 40 return (const std::string &) *this; //这里是要返回一个string对象,所以要进行强制转换 41 } 42 43 //友元函数定义 44 45 /*输入一个单词*/ 46 std::istream & Student::operator>>(std::istream & is, const Student & s) 47 { 48 is>>(string &)s; //还是要输入一个单词给string对象啊,所以这里还是要进行强制转换 49 return is; 50 } 51 52 /*输入一行*/ 53 std::istream & Student::getline(std::istream & is, const Student & s) 54 { 55 getline(is,(string &)s); //还是要输入一个单词给string对象啊,所以这里还是要进行强制转换 56 return is; 57 } 58 59 /*输出*/ 60 std::ostream & Student::operator<<(std::ostream & os, const Student & s) 61 { 62 os<<"Scores for "<<(string &)s<<":\n"; 63 arr_out(os); 64 return os; 65 } 66 67 /*定义私有方法*/ 68 std::ostream & Student::arr_out(std::ostream & os) const 69 { 70 int i; 71 int lim = ArrayDb::size(); 72 if(lim != 0) 73 { 74 for(i=0;i<lim;i++) 75 { 76 os << ArrayDb::operator[](i); 77 if(i%5 == 4) 78 os<<endl; //保证每四个数据输出一个换行 79 } 80 } 81 else 82 os << "Empty array" 83 }

1 /*私有继承user_main.cpp*/ 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include "Student.h" 4 5 using std::cin; 6 using std::cout; 7 using std::endl; 8 9 void set(const Student & s,int n); 10 11 const int pupils = 3; 12 const int quizzes = 5; 13 14 int main() 15 { 16 int i; 17 Student ada[pupils] = {Student(quizzes),Student(quizzes),Student(quizzes)}; 18 for(i=0;i<pupils;i++) 19 set(ada[i],quizzes); 20 cout<<"\nStudent List:\n"; 21 for(i=0;i<pupils;i++) 22 cout<<ada[i].Name()<<endl; 23 cout<<"Results:\n"; 24 for(i=0;i<quizzes;i++) 25 { 26 cout<<endl<<ada[i]; //这里的<<ada[i]将会首先调用std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & os,Student & stu)这个函数,在该函数内继续调用arr_out()函数 27 cout<<"average: "<<ada[i].Average()<<endl; 28 } 29 30 cout<<"Done.\n" 31 return 0; 32 } 33 34 void set(const Student & s,int n) 35 { 36 cout << "Please input student name"<<endl; 37 getline(cin,s); //调用对geline()的重载函数 38 cout << "Please input " << n << "quize scores" <<endl; 39 for(int i=0; i<n; i++) 40 cin >> s[i]; //s[i]将调用operator[]()函数 41 while(cin.get() != '\n') 42 continue; 43 }
5、使用using重新定义获得访问权限
01)问题的提出:使用保护继承或者是私有继承时,基类的公有方法将成为保护成员或私有成员,假设要让基类的方法在派生类的外面可用
以下是两种方法:
02)方法一:定义一个使用该基类方法的派生类方法,例如,假设希望Student类能够使用valarray类的sum()方法,可以在Student类中声明
一个sum()方法,然后像下面这样定义:
double Student::sum() const { return std::valarray<double>::sum(); //使用的是私有继承,所以这里要使用私有继承调用基类方法的方式 }
这样Student对象就可以调用Student::sum(),方法为ada.sum(),假如ada是一个Student对象
03)方法二:使用一个using声明来指出派生类可以使用特定的基类方法,可以在Student.h的公有部分加入如下using声明:
class Student : private std::string, private std::valarray { public: using std::valarray<double>::min(); using std::valarray<double>::max(); ... }
假如ada是一个Student对象,那么就可以直接调用min()和max()方法,即ada.min()和ada.max();需要注意的是using声明只适用于私有继承
并不适用于公有继承。
6、多重继承MI
6.1多重继承的引入
本版本重点介绍多重公有继承,其层次结构如下
class Waiter : public Worker {...};
class Singer : public Worker {...};
class SingingWaiter : public Waiter, public Singer {...};
其中Worker是一个基类
注意:本引入涉及到多态

1 #ifndef WORKER0_H_ 2 #define WORKER0_H_ 3 4 #include <string> 5 6 /*基类*/ 7 class Worker 8 { 9 private: 10 std::string fullname; 11 long id; 12 public: 13 Worker() : fullname("No one"), id(0L) {} //构造函数定义 14 Worker(const std::string & s, long n) : fullname(s),id(n) {} 15 ~Worker(); 16 virtual void Set(); //声明虚方法,在派生类中可不使用virtual,Set()也会自动成为虚方法 17 virtual void Show() const; 18 }; 19 /*派生类Waiter*/ 20 class Waiter : public Worker 21 { 22 private: 23 int panache; //在Worker类变量的基础上,添加新的变量 24 public: 25 Waiter() : Worker(),panache(0) {} //Worker()使用基类名字来初始化基类变量,将调用不带参数的基类构造函数 26 Waiter(std::string & s,long n, int p=0) : Worker(s,n),panache(p) {} //使用带两个参数的基类构造函数初始化基类变量 27 Waiter(const Worker &wk, int p=0) : Worker(wk),panache(p) {} //使用基类对象来初始化基类变量 28 29 void Set(); //由于在基类中Set()使用的是虚方法,所以在派生类中会自动成为虚方法 30 void Show() const; //同样是自动成为虚方法 31 }; 32 /*派生类Singer*/ 33 class Singer : public Worker 34 { 35 protected: 36 enum {other,alto,contralto,soprano,bass,baritone,tenor}; //定义枚举,other=0,alto=1... 37 enum {Vtype = 7}; 38 private: 39 static char *pv[Vtype]; //声明静态指针数组,并在cpp文件中进行初始化 40 int voice; 41 public: 42 Singer() : Worker(), voice(other) {} //使用不带参数的基类构造函数初始化基类变量 43 Singer(const std::string & s,long n,int v=other) : Worker(s,n),voice(v) {} 44 Singer(const Worker & wk, int v=other) : Worker(wk),voice(v) {} 45 46 void Set(); //由于在基类中Set()使用的是虚方法,所以在派生类中会自动成为虚方法 47 void Show() const; //同样是自动成为虚方法 48 }; 49 50 #endif

1 /*worker0.cpp*/ 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include "worker0.h" 4 5 using std::cin; 6 using std::cout; 7 using std::endl; 8 9 /*基类Worker中的方法实现*/ 10 Worker::~Worker() 11 { 12 13 } 14 15 /*基类输入*/ 16 void Worker::Set() 17 { 18 cout << "Enter woker's name: "; 19 getline(cin,fullname); 20 cout << "Enter worker's ID: "; 21 cin >> id; 22 while(cin.get() != '\n') //一直接收换行符,直到接收到了换行符 23 continue; 24 } 25 26 /*基类输出*/ 27 void Worker::Show() const 28 { 29 cout << "Name: " << fullname <<endl; 30 cout << "Employee ID: " << id <<endl; 31 } 32 33 /*派生类Waiter类方法实现*/ 34 /*派生类Waiter输入*/ 35 void Waiter::Set() 36 { 37 Worker::Set(); //调用基类中的Set()方法,输入基类中的数据 38 cout << "Enter waiter's panche rating: " << endl; 39 cin >> panche; 40 while(cin.get() != '\n') //一直接收换行符,直到接收到了换行符 41 continue; 42 } 43 /*派生类Waiter输出*/ 44 void Waiter::Show() const 45 { 46 cout<<"Category waiter"<<endl; 47 Worker::Show(); //调用基类中的Show()方法 48 cout<<"Panache rating: "<<panche<<endl; 49 } 50 51 /*派生类Singer类方法实现*/ 52 char* Singer::pv[] = {other,alto,contralto,soprano,bass,baritone,tenor};//初始化h文件中的pv指针 53 54 /*派生类Singer输入*/ 55 void Singer::Set() 56 { 57 Worker::Set(); //调用基类方法 58 cout << "Enter number for singer's voice: "; 59 int i; 60 for(i=0;i<Vtypes;i++) 61 { 62 cout<<i<<": "<<pv[i]<<" "; //由于没有换行符,此处用两个空格隔开两个voice类型 63 if(i&4==3) 64 cout<<endl; //每打印四个voice类型输出一个换行符 65 } 66 if(i%4!=0) 67 cout<<endl; 68 while(cin>>voice && (voice<0 || voice<=Vtypes)) //检查输入的是否为数字,且该数字是否在0和Vtypes之间 69 cout<<"Please enter a value >=0 and <"<<Vtypes<<endl; 70 while(cin.get() != '\n') //一直接收换行符,直到接收到了换行符 71 continue; 72 } 73 74 75 /*派生类Singer输出*/ 76 void Singer::Show() const 77 { 78 cout<<"Category: singer"<<endl; 79 Worker::Show(); 80 cout<<"Voice range: "<<voice<<endl; 81 }

1 /*worktest.cpp*/ 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include "worker0.h" 4 5 const int LIM = 4; 6 int main() 7 { 8 Waiter bob("Bob Apple",314L,5); //创建Waiter类对象fullname=Bob Apple,id=314,panache=5;只是初始化,后面输入会覆盖掉这些初始化内容 9 Singer bev("Beverlly Hills",522L.3); //创建Singer对象 10 Waiter w_temp; 11 Singer s_temp; 12 13 Woeker* pw[LIM] = {&bob,&bev,&w_temp,&s_temp}; //创建基类指针,分别指向Waiter对象和Singer对象 14 15 int i; 16 for(i=0.i<LIm;i++) 17 pw[i]->Set(); // 18 for(i=0;i<LIM;i++) 19 { 20 pw[i]->Show(); 21 std::cout<<std::endl; 22 } 23 return 0; 24 } 25 /* 26 需要注意的是: 27 01)由于Set()和Show()都是虚方法(在基类中定义的是虚方法,所以在派生类中自动会成为虚方法),所以 28 pw[i]->Set();将根据p[i]指向的对象来确定使用那个版本的Set()函数;例如pw[0]=&bob,而bob是Waiter类对象 29 所以pw[0]->Set()将调用Waiter类中的Set()函数;同理pw[1]->Set()将调用Singer类中的Set()方法 30 31 */
注意:
01)worker.h中包括了三个类Worker类(作为基类)、Waiter(派生自Worker类)、Singer类(派生自Worker类)
02)在workerTest.cpp中:由于Set()和Show()都是虚方法(在基类中定义的是虚方法,所以在派生类中自动会成为虚方法),所以
pw[i]->Set();将根据p[i]指向的对象来确定使用那个版本的Set()函数;例如pw[0]=&bob,而bob是Waiter类对象
所以pw[0]->Set()将调用Waiter类中的Set()函数;同理pw[1]->Set()将调用Singer类中的Set()方法
6.2多重继承的问题与改进
假如有如下继承方式:
1 class Worker {...} //作为基类 2 class Waiter : public Worker {...} //Waiter类继承自Worker类 3 class Singer : public Worker {...} //Singer类继承自Worker
如果定义一个类SingingWaiter类,继承Waiter和Singer,即:
class SingingWaiter : public Waiter, public Singer {...}
此时是有问题的:因为Singer和Waiter都继承了一个Worker,所以SingingWaiter中将含有两个Worker类重复的信息,
在使用多态时候,将会出现如下问题;
1 SingingWaiter ed; //声明一个SingingWaiter对象ed 2 Worker *pw = &ed; //基类指针指向SingingWaiter对象,此时会出现二义性
(2020.06.28晚对于ed会出现二义性的解释,当Worker基类指针pw去调用一个虚函数的时候,那么会根据pw指向的对象去判断调用哪个类中的虚函数,此处基类指针pw指向的是SingingWaiter类对象,所以当pw调用一个虚函数的时候,会调用SingingWaiter类中的虚函数,但是如果SingingWaiter类中不存在这个虚函数,那么pw会去找SingingWaiter最近的一个祖先中去找这个虚函数,此时Waiter和Singer都是SingingWaiter最近的祖先(SingingWaiter同时继承了Waiter和Singer),且在Waiter类中和Singer类中都有这个虚函数,那么pw会去调用哪个虚函数?此时就出现了二义性)
由于ed中包含两个Worker对象,所以上式会出现二义性,解决方法;
1 SingingWaiter ed; //声明一个SingingWaiter对象ed 2 Worker *pw1 = (Waiter *)&ed; 3 Worker *pw2 = (Singer *)&ed; //使用强制转换
但是这样会使多态复杂化,此时引入虚基类的概念
6.3虚基类
01)使Worker成为Waiter和Singer虚基类的方法:加关键字virtual
1 class Singer :virtual public Worker {...} 2 class Waiter :virtual public Worker {...} //其中virtual和public可以交换次序
然后可以将SingingWaiter定义为:
1 class SingingWaiter : public Singer, public Waiter {...}
此时SIngingWaiter对象只包含Worker对象的一个副本,继承的Singer和Waiter共享一个Worker对象
02)SingingWaiter构造函数的编写方法(主要是如何填充Worker中的数据):
以前的多继承构造函数编写方法:

1 class A //基类 2 { 3 int a; //省略了关键字private 4 public: 5 A(int n=0) : a(n) {} 6 ... 7 }; 8 class B : public A //B继承自A 9 { 10 int b; 11 public: 12 B(int m=0,int n=0) : A(n),b(m) {} //使用基类构造函数A()来填充基类数据 13 ... 14 }; 15 class C : public B //C继承自B 16 { 17 int c; 18 public: 19 C(int q=0,int m=0,int n=0) : B(m,n), c(q); //调用B(int m=0,int n=0)构造函数来填充B类和A类中的数据 20 ... 21 };
C类构造函数只能调用B类的构造函数,而B类构造函数只能调用A类构造函数。在C类构造函数中,将m和n的值传递给B类中的
构造函数,而B类中的构造函数又将n值传递给A类的构造函数,最后初始化自己的值c,这样是可行的。
03)但是如果A是虚基类,那么以上传递方法将不会起作用!!即:
SingingWaiter(const Worker &wk, int p=0,int v=Singer::other) : Waiter(wk,p), Singer(wk,v) {} //存在问题的
存在的问题是,自动传递信息时,将通过两种不同的途径(Singer和Waiter)将wk传递给Worker对象。为避免这种冲突,C++在
基类是虚的时候,禁止通过中间类(Singer和Waiter)将基类数据传递给基类。可以采用如下方式:
SingingWaiter(const Worker & wk, int p=0,int v=Singer::other) : Worker(wk),Waiter(wk,p),Singer(wk,v) {}
上述代码显式的调用虚基类构造函数Worker(const Worker &),对于虚基类,这样做是合法的。
那个方法?
01)问题的提出,假如在SingingWaiter中没有重新定义Show()方法,并试图使用SingingWaiter对象调用Show()方法,即:
1 SingingWaiter newhire("Elise Hawks",2005,6,soprano); 2 newhire.Show(); //会出现二义性,不知道使用那个祖先中的Show()方法
对于单继承来说,如果没有重新定义Show(),则使用最近祖先中的定义;但是对于多继承来说,则会出现二义性
02)解决方法一:可以使用作用域解析运算符,即:
1 SingingWaiter newhire("Elise Hawks",2005,6,soprano); 2 newhire.Singer::Show(); //合法,只有作用域解析运算符来说明要使用Singer类中的Show()f方法
03)解决方法二:最好的方法还是在SingingWaiter中重新定义Show()方法
void SingingWaiter::Show() { Singer::Show(); //但是这种递增方式对SingingWaiter无效,因为它忽略了Wiater类 }
可以使用如下方式进行补救:
void SingingWaiter::Show() { Singer::Show(); //调用了Worker::Show()另外显示自己的私有变量 Wiater::Show(); //调用了Worker::Show()另外显示自己的私有变量 }
然而这一同样会出现问题:这将显示姓名和ID两次,可以提供只显示Worker类变量方式
和只显示Singer类变量、Waiter类变量的三个方法,最后将他们进行组合,即:

1 /*在worker类中定义Data()方法*/ 2 void Worker::Data() const 3 { 4 cout << "Name: " << fullname <<endl; 5 cout << "ID: " << id << endl; 6 } 7 /*在Waiter类中定义Data()方法*/ 8 void Waiter::Data() const 9 { 10 cout << "Panache rating: " << panache <<endl; 11 } 12 /*在Singer类中定义Data()方法*/ 13 void Singer::Data() const 14 { 15 cout << "Vocal range: " << pv[voice] <<endl; 16 } 17 /*在SingingWaiter类中定义Data()方法*/ 18 void SingingWaiter::Data() const 19 { 20 Singer::Data(); 21 Waiter::Data(); 22 } 23 /*在SingingWaiter类中定义Show()方法*/ 24 void SingingWaiter::Show() const 25 { 26 Worker::Data(); //虚基类中的Data()方法 27 Data(); //SingingWaiter类中自己定义的Data()方法 28 }
由于保护成员只可以在本类内和子类内被访问,在其他文件中不可以被访问,所以可以将以上的Data()全部声明为类中的保护成员。
6.4虚基类与二义性
01)使用非虚基类时:如果一个类从不同的类中继承了两个或更多的同名函数(数据或方法),则使用该
成员名的时候,如果没有用类名进行限定,将会导致二义性。
02)使用虚基类时:如果一个类从不同的类中继承了两个或更多的同名函数(数据或方法),则使用该
成员名的时候,如果没有用类名进行限定,将不一定会导致二义性,如果某个名称优先于其他所有名称
,则使用它时,即使不适用限定符,也不会导致二义性。
03)一个成员名如何优先于另一个成员们呢?派生类中的名称优先于直接或间接祖先类中相同名称,例如:

1 class B //作为基类 2 { 3 public: 4 short q(); 5 ... 6 }; 7 class C : virtual public B /使B成为虚基类 8 { 9 public: 10 long q(); //由于C继承B,所以C中的q()优先于B中的q() 11 int omg(); 12 }; 13 class D : public C 14 { 15 ... 16 }; 17 class E :virtual public B 18 { 19 private: 20 int omg(); 21 ... 22 }; 23 class F : public D, public E 24 { 25 q(); //这里使用的是C中的q()方法;因为只有B和C中有q()方法,而C中的优先于B中的q()方法 26 //而D继承自C,C继承自B 27 omg(); //由于C中有omg()方法,E中也有;但是C不是E的基类,且E也不是C的基类,所以C和E中的omg()方法无法比较有限性 28 //这里调用omg()将会导致二义性 29 ... 30 };
7、类模板
7.1类模板简单实现
01)由于模板不是函数,它们不可单独编译,因此模板必须和实例化(即实现)一起使用,为此最简单的方法就是将所有模板信息放入一个头文件中
02)模板的具体实现成为实例化或具体化,即将int、string、double等替换Type
03)每个函数定义都需要使用项目的模板声明template <class Type> 打头
04)类限定符Stack::改为Stack<Type>::
05)如果在类声明中定义了方法(内联定义),则可以省略模板前缀和类限定符。
由于[]的优先级比--高,所以在执行item = items[--top]的时候,先将items[top]的值赋给item,后将top的值自减1
类声明+类方法定义的h文件:

1 #ifndef STACKTP_H_ 2 #define STACKTP_H_ 3 4 /* 5 01)下面的type只说明Type是一个通用类型说明符,并不是类,在使用时将用实际类型替换它 6 02)Type被称为泛型标识符 7 */ 8 template <class Type> //关键字template告诉编译器将要创建一个模板,其中class可用typename替换 Tyoe为任意取的名字,实际会被int、string等代替 9 class Stack 10 { 11 private: 12 enum {MAX = 10}; //使用枚举创建常量 13 Type items[MAX]; //使用模板中的Type创建数组 14 int top; 15 public: 16 Stack(); //声明构造函数 17 bool isempty(); 18 bool isfull(); 19 bool push(const Type & item); //入栈 20 bool pop(Type & item); //出栈,由于是使用的引用,故在item的变化和传入的实参一起变化(即形参和实参一起变化) 21 }; 22 23 /* 24 01)由于模板不是函数,它们不可单独编译,因此模板必须和实例化(即实现)一起使用,为此最简单的方法就是将所有模板信息放入一个头文件中 25 02)模板的具体实现成为实例化或具体化,即将int、string、double等替换Type 26 03)每个函数定义都需要使用项目的模板声明template <class Type> 打头 27 04)类限定符Stack::改为Stack<Type>:: 28 05)如果在类声明中定义了方法(内联定义),则可以省略模板前缀和类限定符。 29 */ 30 template <class Type> //模板前缀 31 Stack<Type>::Stack() 32 { 33 top = 0; 34 } 35 36 /*判断栈是否为空*/ 37 template <class Type> 38 bool Stack<Type>::isempty() 39 { 40 return top == 0; //若top=0则返回true 41 } 42 43 /*判断栈是否已满*/ 44 template <class Type> 45 bool Stack<Type>::isfull() 46 { 47 return top == MAX; //若top=MAX则返回true 48 } 49 50 /*入栈*/ 51 template <class Type> 52 bool Stack<Type>::push(const Type & item) 53 { 54 if (top < MAX) 55 { 56 items[top++] = item; //将传入的参数传入items数组(栈),并将top自加1 57 return true; 58 } 59 else 60 return false; 61 } 62 63 /* 64 01)出栈 65 02)由于[]的优先级比--高,所以在执行item = items[--top]的时候,先将items[top]的值赋给item,后将top的值自减1 66 02)由于--top是先修改后使用,故pop(po)中 67 */ 68 template <class Type> 69 bool Stack<Type>::pop(Type & item) 70 { 71 if (top > 0) 72 { 73 item = items[--top]; //将数组items(栈)中的参数传给item,同时主函数中的实参也会更新 74 return true; 75 } 76 else 77 return false; 78 } 79 80 #endif
使用类模板:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <cctype> 4 #include "stacktp.h" 5 6 using std::string; 7 using std::cin; 8 using std::cout; 9 using std::endl; 10 11 /* 12 01)模板类对象的创建方法: 13 Stack<int> st1; //使用int替换模板中所有的Type 14 Stack<string> st2; 15 */ 16 int main() 17 { 18 Stack<string> st; //将Stack类中的Type使用string替换,并创建Stack对象st,st为模板类对象 19 char ch; 20 string po; 21 cout << "please enter A to add a purchase order,\n" 22 << "P to process a puurchase order, or Q to quit." << endl; 23 while (cin >> ch && std::toupper(ch) != 'Q') //注:toupper(ch)将ch字符转换为大写 24 { 25 while (cin.get() != '\n') 26 continue; //一直接收换行符 27 if (!std::isalpha(ch)) //isalpha(ch)判断ch是否为英文字母,若是则返回非0 28 { 29 cout << '\a'; //发出蜂鸣声 30 continue; //返回while循环 31 } 32 switch (ch) 33 { 34 case 'A': 35 case 'a': 36 cout << "Enter a purchase order to add: "; 37 cin >> po; 38 if (st.isfull()) 39 cout << "栈已满!" << endl; 40 else 41 st.push(po); //将po入栈 42 break; 43 case 'p': 44 case 'P': 45 if (st.isempty()) 46 cout << "栈已空!" << endl; 47 else 48 { 49 st.pop(po); //将po出栈,并更新po;因为po为被指向的引用,会随着形参的改变而改变 50 cout << "purchase order #" << po << " popped" << endl; 51 break; 52 } 53 } 54 cout << "please enter A to add a purchase order,\n" 55 << "P to process a puurchase order, or Q to quit." << endl; 56 } 57 cout << "Bye!" << endl; 58 system("pause"); 59 return 0; 60 }
执行结果:

7.2栈指针
需要参考int**表示一个二维数组方法:https://www.cnblogs.com/YiYA-blog/p/11456085.html
另外此程序也展示了类对象可以直接用直接访问运算符(点)来访问自己的私有数据
栈中存储的是指针(字符串的首地址)

1 #ifndef STACKTP1_H_ 2 #define STACKTP1_H_ 3 4 template <class Type> 5 class Stack 6 { 7 private: 8 enum {SIZE = 10}; //默认栈大小 9 int stacksize; 10 Type * items; //栈 Type用char*替换后,即char** items;创建指向指针的指针,但是一旦用new给items分配空间之后,就items就可以指代一个二维数组 11 int top; 12 public: 13 explicit Stack(int ss = SIZE); //构造函数,因为该构造函数只含有一个参数,需要使用explicit关闭隐式转换 14 Stack(const Stack & st); //声明复制构造函数 15 ~Stack() { delete[] items; } //由于是要将Type声明为char *,所以需要加上[] 16 bool isempty() { return top == 0; } 17 bool isfull() { return top == stacksize; } 18 bool push(const Type & item); 19 bool pop(Type & item); 20 Stack & operator=(const Stack & st); 21 }; 22 23 /*含有一个int型参数的构造函数*/ 24 template <class Type> 25 Stack<Type>::Stack(int ss) : stacksize(ss), top(0) 26 { 27 items = new Type[stacksize]; //给items分配空间,当Type=char*时,items = new char*[stacksize]即创建一个数组,数组内全是指针 28 } 29 30 /* 31 01)含有一个Stack类对象引用参数的构造函数 32 02)items = new Type[stacksize];给items分配空间,当Type=char*时,items = new char*[stacksize]即创建一个数组,数组内全是指针 33 */ 34 template <class Type> 35 Stack<Type>::Stack(const Stack & st) 36 { 37 stacksize = st.stacksize; //使用类对象直接访问自己本身的私有数据 38 top = st.top; //使用类对象直接访问自己本身的私有数据 39 items = new Type[stacksize]; //Type用char*替换后,即items = new char*[stacksize]创建一个数组,内全为指针 40 for (int i = 0; i < top; i++) 41 { 42 items[i] = st.items[i]; 43 } 44 } 45 46 /*入栈*/ 47 template <class Type> 48 bool Stack<Type>::push(const Type & item) 49 { 50 if (top < stacksize) 51 { 52 items[top++] = item; 53 return true; 54 } 55 else 56 return false; 57 } 58 59 /*出栈*/ 60 template <class Type> 61 bool Stack<Type>::pop(Type & item) 62 { 63 if (top > 0) 64 { 65 item = items[--top]; 66 return true; 67 } 68 else 69 return false; 70 } 71 72 /* 73 01)对=的重载函数定义 74 02)注意:函数返回类型为Stack类引用时,返回类型在声明中可以直接写Stack & ,但是在定义中必须使用Stack<Type> & 75 03)返回类型为类引用,如果在类中可以使用Stack,但是在类外必须使用Stack<Type> 76 04)一下代码使用了深复制 77 */ 78 template <class Type> 79 Stack<Type> & Stack<Type>::operator=(const Stack & st) 80 { 81 if (this == &st) 82 return *this; 83 delete[] items; 84 stacksize = st.stacksize; 85 top = st.top; 86 items = new Type[stacksize]; 87 for (int i = 0; i < top; i++) 88 items[i] = st.items[i]; 89 return *this; 90 } 91 92 #endif

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdlib> 3 #include <ctime> 4 #include "stacktp1.h" 5 6 using std::cin; 7 using std::cout; 8 using std::endl; 9 const int Num = 10; 10 11 int main() 12 { 13 std::srand(std::time(0)); 14 cout << "please enter atck size: "; 15 int stacksize; 16 cin >> stacksize; 17 18 Stack<const char*> st(stacksize); //隐式的调用含一个int行参数的Stack类构造函数创建对象st,其中h文件中所有Type用char*代替 19 20 //创建指针数组 21 const char* in[Num] = { 22 "1: Hank Gilgaeh", "2: Kiki Ishtar", 23 "3: Wolfang Kibble", "4: Ian Flagranti", 24 "5: Betty Rocker", "6: Ports Koop", 25 "7: Joy Almondo", "8: Xavertie Paprika", 26 "9: Juan Moora", "10: Misha Mache" 27 }; 28 const char* out[Num]; //编译打印输出 29 30 int processed = 0; 31 int nextin = 0; 32 while (processed < Num) 33 { 34 if (st.isempty()) //栈只有第一次执行的时候是空的,之后就是有内容在里面,不是空也不是满的状态 35 st.push(in[nextin++]); //以指针的形式入栈,即栈中存储的是一个字符串的地址 36 else if (st.isfull()) //当达到主程序中输入的stacksize之后,栈就达到了满的状态,然后执行第一个else if,之后就有达到了不满要也不空的状态 37 st.pop(out[processed++]); 38 else if (std::rand() % 2 && nextin < Num) //执行下面两句的几率各为50% 39 st.push(in[nextin++]); 40 else 41 st.pop(out[processed++]); 42 } 43 for (int i = 0; i < Num; i++) 44 cout << out[i] << endl; 45 system("pause"); 46 return 0; 47 48 }
执行结果:






