C#:Event
概念介绍
事件的定义
事件:某些重要的发生的事情。
角色:具备通知能力的类或对象。通知能力是事件发生的效果。
使用:多个角色之间通过事件通知/响应进行信息传递。因此有效的事件都包含某些特定参数。C#将现实中的此类行为抽象为事件模型(Event Model)。
事件行为与SomeIP的Service Discovery服务发现机制类似,都具备发布/订阅/处理的具体过程,您也可以按照SomeIP的SD机制间接理解。
事件模型的组成部分
根据定义,将事件模型的组成的部分可以划分为5个:事件的拥有者、事件成员、事件的响应者、事件处理器、事件订阅。
拥有者:Event Source,事件的产生方,事件不会主动发生,都是由拥有者内部逻辑触发的。
成员:Event,主要有方法成员、属性成员。
响应者:Event Subscriber,事件的响应方,产生方自身也可能是响应方。
处理器:Event Handler,是响应者的一个方法成员,一般是一个委托实例或者具体方法名。
订阅:Subscribe,事件发生的第一步。
上面的成员概念不是很清楚的话,可以参考下图代码,在代码中会有更好的理解。注意:事件模型的五个成员可以有不同的组合方法。
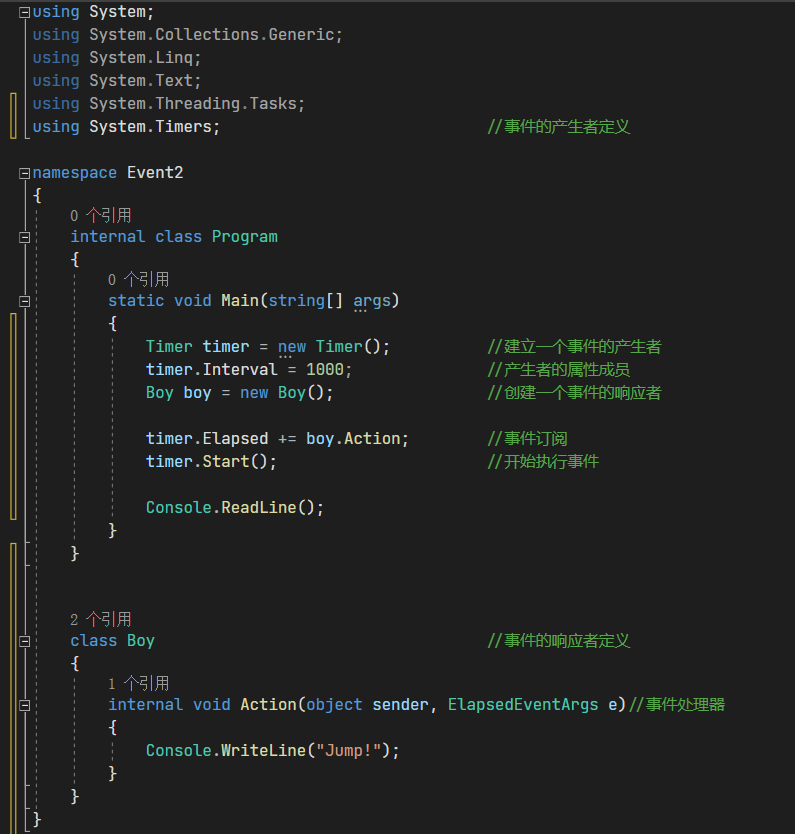
事件的使用
时间的使用我们一般都是使用事件的完全体:产生者+响应者+事件处理器+成员+订阅,但是五个组成也有不同的组成结构。
场景1:事件的产生者和响应者独立
查看代码
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Timers; //事件的产生者定义 namespace Event2 { internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Timer timer = new Timer(); //建立一个事件的产生者 timer.Interval = 1000; //产生者的属性成员 Boy boy = new Boy(); //创建事件的响应者1 Girl girl = new Girl(); //创建事件的响应者2 timer.Elapsed += boy.Action; //事件订阅1 timer.Elapsed += girl.Action; //事件订阅2 timer.Start(); //开始执行事件 Console.ReadLine(); } } class Boy //事件的响应者1定义 { internal void Action(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e)//事件处理器 { Console.WriteLine("Jump!"); } } class Girl //事件的响应者2定义 { internal void Action(object sender, ElapsedEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine("Sing!"); } } }
场景2:事件的产生者也是事件的响应者
查看代码
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms; //事件的产生者定义 namespace Event2 { internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Form form = new Form(); //创建一个事件的产生者 Controller controller = new Controller(form);//创建一个事件的响应者 form.ShowDialog(); } } class Controller//事件的响应者定义 { private Form form;//事件的拥有者 public Controller(Form form) { if (form != null) { this.form = form; this.form.Click += this.FormClicked;//事件订阅 } } private void FormClicked(object sender, EventArgs e)//事件处理器 { this.form.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString(); } } }
场景3:事件的响应者包含了事件的产生者
查看代码
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace Event2 { internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { MyForm myForm = new MyForm(); myForm.ShowDialog(); } } class MyForm:Form { private TextBox textbox; private Button button;//事件的拥有者是事件的响应者的一个成员 public MyForm() //事件的响应者 { this.textbox = new TextBox(); this.button = new Button(); this.button.Top = 100; this.button.Width = 100; this.button.Height = 100; this.button.Text = "Button"; this.Controls.Add(this.textbox); this.Controls.Add(this.button); this.button.Click += this.ButtonCliked;//事件订阅,事件的拥有者是Button } private void ButtonCliked(object sender, EventArgs e)//处理器 { this.textbox.Text = "Hello,world!"; } } }
场景3:事件的继承使用
查看代码
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Windows.Forms; namespace Event2 { internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Myform myform = new Myform(); myform.Click += myform.FormClick; myform.ShowDialog(); } } class Myform : Form { internal void FormClick(object sender, EventArgs e) { this.Text = DateTime.Now.ToString(); } } }
本文来自博客园,作者:{张一默},转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/YiMo9929/p/17731236.html





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)