C#:Delagate(委托)
概念介绍
C++/C函数指针
C#委托是C/C++中 函数指针的升级版。C++函数指针本质是一串32位/64位的地址,函数指针是指向函数的指针,可以借此指针调用函数,也可以用指针指向另一个函数。函数指针举例如下:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; typedef int (*cal)(int a, int b);//函数指针:返回值类型+指针名称+参数列表 int Add(int a, int b);//函数声明 int main(void) { cal funtion11 = &Add;//函数指针指向ADD函数,也可以指向其他函数 int sum = funtion11(1,2); cout << "FUNCIOTN IS "<<sum << endl; } int Add(int a, int b) { int result = a + b; return result; }
可以看出函数指针可以指向任何符合定义类型的函数。这是一种间接调用方式。
直接调用:直接调用函数名。
间接调用:通过函数函数指针调用函数。
C#委托
为什么委托是函数指针的升级版?
委托的声明和调用类似于函数指针,并且C#是基于C++设计的,因此委托是函数指针的升级版。
C#基本的委托有两种:Action、Func,这无须开发者自己定义。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Delegate { internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Calculater Calculater = new Calculater(); Action action = new Action(Calculater.Report);//Action委托指向无返回值的report方法 action();//间接调用 Func<int/*返回值类型*/, int/*函数参数1*/, int/*函数参数2*/> func = new Func<int, int, int>(Calculater.Add);//Function委托指向有返回值的函数 int result = func(1,2); Console.WriteLine(result); } } class Calculater { public void Report() => Console.WriteLine("Hello world!"); public int Add(int a, int b) { int result =a + b; return result; } } }
如何自定义委托?
委托实际是一种类,您可以执行以下语句,结果返回True。另外,如果您使用的是VS Code开发,可以看到Action与Func的颜色为水蓝色,这代表一种数据类型。
Type type = typeof(Action);
既然是类,这代表开发者可以自定义委托。举例如下:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Delegate { public delegate int/*返回值类型*/ Calc(int a/*参数1*/, int b/*参数2*/);//自定义委托 internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Calculater Calculater = new Calculater(); Calc calc = new Calc(Calculater.Add);//新建委托 int res = calc(1,2); Console.WriteLine(res); } } class Calculater { public int Add(int a, int b) { int result =a + b; return result; } } }
- 自定义委托返回的数据类型必须和指向的函数一致。
- 自定义委托的参数个数和数据类型必须和指向的函数一致。
- 委托的声明必须声明在名称空间中,和其他类同级。
委托的一般使用
C#委托意义同C++函数指针的意义,一般都是将委托当作参数传递给另一个方法。有Template方法和CallBack方法两种。
Template方法
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Delegate { public delegate int Calc(int a, int b);//自定义委托 internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();//创建一个产品工厂 WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();//创建一个包装工厂 //创建委托 Func<Product/*返回值类型*/> fun1 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeCake/*满足返回值类型的方法*/); //将委托作为参数输入给包装工厂 Box box1 = wrapFactory.WarpProduct(fun1);//输入指向产品的委托 Console.WriteLine( box1.Product.name); } } class Product//产品制作 { public string name { get; set; } } class Box//包装盒制作 { public Product Product { get; set; } } class ProductFactory//蛋糕生产 { public Product MakeCake() { Product product = new Product(); product.name = "Da_Li_Yuan"; return product; } } class WrapFactory //产品包装 { public Box WarpProduct(Func<Product> getProduct)/*委托作为函数参数,意味着必须输入一个指向产品的委托*/ { Box box = new Box(); Product product = getProduct();//调用委托 box.Product = product; return box; } } }
上述这种方法就是模板方法:调用通用的外部方法,有返回值。只要满足Func<Product> getProduct,都可以传入方法。
CallBack方法
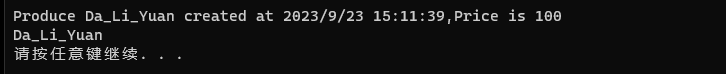
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Runtime.Remoting.Messaging; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace Delegate { public delegate int Calc(int a, int b);//自定义委托 internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();//创建一个产品工厂 WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();//创建一个包装工厂 Logger logger = new Logger(); Func<Product/*返回值类型*/> fun1 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeCake/*满足返回值类型的方法*/); Action<Product> log1 = new Action<Product>(logger.Log); Box box1 = wrapFactory.WarpProduct(fun1,log1);//输入指向产品的委托,输入log函数 Console.WriteLine( box1.Product.name); } } class Logger//记录程序的运行状态 { public void Log(Product product) { Console.WriteLine("Produce {0} created at {1},Price is {2}",product.name,DateTime.UtcNow,product.Price); } } class Product//产品制作 { public string name { get; set; } public double Price { get; set; } } class Box//包装盒制作 { public Product Product { get; set; } } class ProductFactory//蛋糕生产 { public Product MakeCake() { Product product = new Product(); product.name = "Da_Li_Yuan"; product.Price = 100; return product; } } class WrapFactory //产品包装 { public Box WarpProduct(Func<Product> getProduct,Action<Product> logCallBack)/*委托作为函数参数,意味着必须输入一个指向产品的委托*/ { Box box = new Box(); Product product = getProduct();//调用委托 if(product.Price>=50) logCallBack.Invoke(product); box.Product = product; return box; } } }
上述方法就是回调方法:调用指定的外部方法,无返回值。比如这里的log。
注意事项
- 委托是一种方法级别的高度耦合,使用时请慎之又慎!
- 委托使可读性降低,debug难度增加
- 委托和多线程,异步调用,委托回调纠缠在一起时,请慎之又慎!
- 委托使用不当将导致内存泄漏和性能下降。
委托的高级使用
多播委托
多播委托指一个委托内部包含有多个委托/方法。单播委托指一个 委托只委托一个方法。
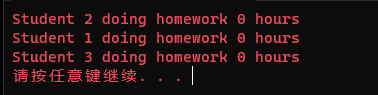
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace AdvancedDelegate { internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Student student1 = new Student() {Id = 1,Color = ConsoleColor.Yellow}; Student student2 = new Student() { Id = 2, Color = ConsoleColor.Green }; Student student3 = new Student() { Id = 3, Color = ConsoleColor.Red }; ; Action action1 = new Action(student1.DoHomeWork); Action action2 = new Action(student2.DoHomeWork); Action action3 = new Action(student3.DoHomeWork); //单播委托:一个委托进行执行 action1(); action2(); action3(); //多播委托:一个委托封装多个委托的方式,执行的顺序按照封装的顺序 action1 += action2; action1 += action3; action1(); } } public class Student { public int Id { get; set; } public ConsoleColor Color { get; set; } public void DoHomeWork() { for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { Console.ForegroundColor = this.Color; Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homework {1} hours", this.Id, i); Thread.Sleep(200); } } } }
多播采用+进行委托包含。
异步与同步调用
线程与进程:一个Main函数/代码文件就是一个进程,一个进程可以包含多个进程。
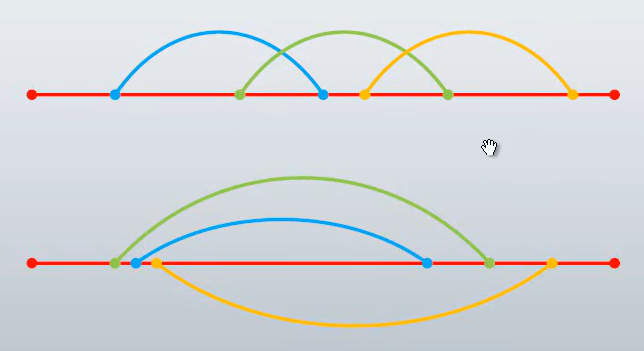
同步调用:顺序执行,多个线程接力跑。同步=单线程=串行。线程会互相影响。
异步调用:同时执行,多个线程同时跑 。异步=多线程=并行。线程不会互相影响。
同步调用
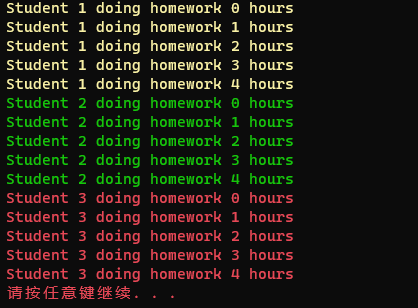
static void Main(string[] args) { Student student1 = new Student() {Id = 1,Color = ConsoleColor.Yellow}; Student student2 = new Student() { Id = 2, Color = ConsoleColor.Green }; Student student3 = new Student() { Id = 3, Color = ConsoleColor.Red }; ; Action action1 = new Action(student1.DoHomeWork); Action action2 = new Action(student2.DoHomeWork); Action action3 = new Action(student3.DoHomeWork); //直接同步调用 student1.DoHomeWork(); student2.DoHomeWork(); student3.DoHomeWork(); //间接同步调用(单播),单播委托就是同步调用 action1(); action2(); action3(); //间接同步调用(多播),多播委托也是同步调用 action1 += action2; action1 += action3; action1(); //主线程继续做其他的事情 //.... .... }
异步调用
隐式异步指使用委托的Begininvoke,显式异步指Thread开辟线程。
隐式异步调用即委托采用Delegate.BeginInvoke(AsyncCallback callback,object object)方法执行,使用此方法时程序将开辟一个线程来执行委托。
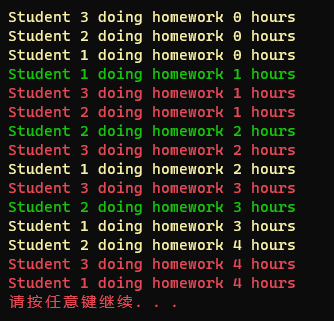
static void Main(string[] args) { Student student1 = new Student() {Id = 1,Color = ConsoleColor.Yellow}; Student student2 = new Student() { Id = 2, Color = ConsoleColor.Green }; Student student3 = new Student() { Id = 3, Color = ConsoleColor.Red }; ; Action action1 = new Action(student1.DoHomeWork); Action action2 = new Action(student2.DoHomeWork); Action action3 = new Action(student3.DoHomeWork); ////隐式异步调用 action1.BeginInvoke(null, null); action1.BeginInvoke(null, null); action1.BeginInvoke(null, null); } }
可以看出,三个委托不会互相等待,并且打印出了不同的颜色,这是因为异步调用时三个委托都在同时访问前景色,导致颜色一致,只有采用线程锁才可以解决此问题。
显示异步采用Thread自定义线程。
internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Student student1 = new Student() {Id = 1,Color = ConsoleColor.Yellow}; Student student2 = new Student() { Id = 2, Color = ConsoleColor.Green }; Student student3 = new Student() { Id = 3, Color = ConsoleColor.Red }; //显示异步调用方式1 Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(student1.DoHomeWork)); Thread thread2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(student2.DoHomeWork)); Thread thread3 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(student3.DoHomeWork)); thread1.Start(); thread2.Start(); thread3.Start(); } }
显示异步调用也可采用task进行,但是要包含using System.Threading.Tasks
internal class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Student student1 = new Student() {Id = 1,Color = ConsoleColor.Yellow}; Student student2 = new Student() { Id = 2, Color = ConsoleColor.Green }; Student student3 = new Student() { Id = 3, Color = ConsoleColor.Red }; ; //显示异步调用方式2 Task task1 = new Task(student1.DoHomeWork); Task task2 = new Task(student2.DoHomeWork); Task task3 = new Task(student3.DoHomeWork); task1.Start(); task2.Start(); task3.Start(); } }

综上:
- 直接同步调用:直接调用方法名。
- 间接同步调用:将方法委托,然后调用委托名。
- 隐式(间接)异步调用:将方法委托,然后使用委托的
BeginInvoke方法。 - 显式(直接)异步调用:使用
Thread/Task直接给方法定义线程,然后调用Task名。 - 单播委托与多播委托:单播委托只委托一个方法,多播委托为一个委托
+其他委托。委托调用都是间接调用。 - 可以使用接口来替代委托,这部分后续再写。
附
我们可以看一段糟糕的代码: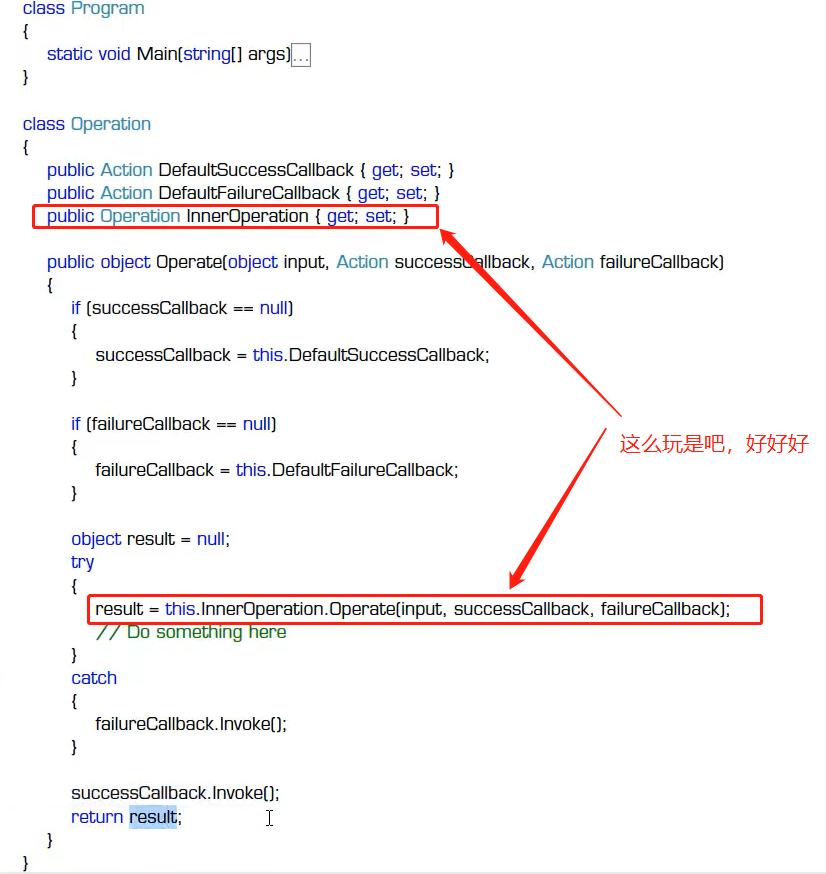
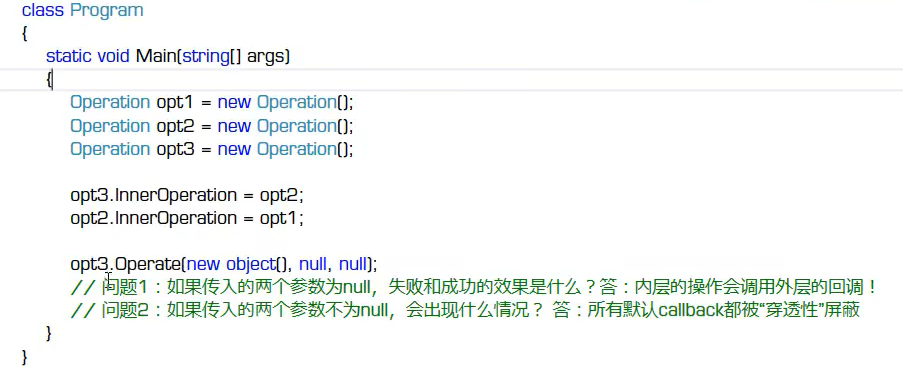
是不是感觉还好?只是进行了一次套用,那我再拿出如下代码,阁下如何应对?
本文来自博客园,作者:{张一默},转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/YiMo9929/p/17725413.html






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)