每日4道算法题——第014天

目录
1、三维形体投影面积
在 n x n 的网格 grid 中,我们放置了一些与 x,y,z 三轴对齐的 1 x 1 x 1 立方体。
每个值 v = grid[i][j] 表示 v 个正方体叠放在单元格 (i, j) 上。
现在,我们查看这些立方体在 xy 、yz 和 zx 平面上的投影。
投影 就像影子,将 三维 形体映射到一个 二维 平面上。从顶部、前面和侧面看立方体时,我们会看到“影子”。
返回 所有三个投影的总面积 。
示例 1:
输入:[[1,2],[3,4]]
输出:17
解释:这里有该形体在三个轴对齐平面上的三个投影(“阴影部分”)。
示例 2:输入:grid = [[2]]
输出:5
示例 3:输入:[[1,0],[0,2]]
输出:8
class Solution {
public int projectionArea(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
int xyArea = 0, yzArea = 0, zxArea = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int yzHeight = 0, zxHeight = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
xyArea += grid[i][j] > 0 ? 1 : 0;
yzHeight = Math.max(yzHeight, grid[j][i]);
zxHeight = Math.max(zxHeight, grid[i][j]);
}
yzArea += yzHeight;
zxArea += zxHeight;
}
return xyArea + yzArea + zxArea;
}
}2、救生艇
给定数组 people 。people[i]表示第 i 个人的体重 ,船的数量不限,每艘船可以承载的最大重量为 limit。
每艘船最多可同时载两人,但条件是这些人的重量之和最多为 limit。
返回 承载所有人所需的最小船数 。
示例 1:
输入:people = [1,2], limit = 3
输出:1
解释:1 艘船载 (1, 2)
示例 2:输入:people = [3,2,2,1], limit = 3
输出:3
解释:3 艘船分别载 (1, 2), (2) 和 (3)
示例 3:输入:people = [3,5,3,4], limit = 5
输出:4
解释:4 艘船分别载 (3), (3), (4), (5)
class Solution {
public int numRescueBoats(int[] people, int limit) {
int ans = 0;
Arrays.sort(people);
int light = 0, heavy = people.length - 1;
while (light <= heavy) {
if (people[light] + people[heavy] <= limit) {
++light;
}
--heavy;
++ans;
}
return ans;
}
}3、索引处的解码字符串
给定一个编码字符串 S。请你找出 解码字符串 并将其写入磁带。解码时,从编码字符串中 每次读取一个字符 ,并采取以下步骤:
如果所读的字符是字母,则将该字母写在磁带上。
如果所读的字符是数字(例如 d),则整个当前磁带总共会被重复写 d-1 次。
现在,对于给定的编码字符串 S 和索引 K,查找并返回解码字符串中的第 K 个字母。示例 1:
输入:S = "leet2code3", K = 10
输出:"o"
解释:
解码后的字符串为 "leetleetcodeleetleetcodeleetleetcode"。
字符串中的第 10 个字母是 "o"。
示例 2:输入:S = "ha22", K = 5
输出:"h"
解释:
解码后的字符串为 "hahahaha"。第 5 个字母是 "h"。
示例 3:输入:S = "a2345678999999999999999", K = 1
输出:"a"
解释:
解码后的字符串为 "a" 重复 8301530446056247680 次。第 1 个字母是 "a"。
class Solution {
public String decodeAtIndex(String S, int K) {
long size = 0;
int N = S.length();
// Find size = length of decoded string
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
char c = S.charAt(i);
if (Character.isDigit(c))
size *= c - '0';
else
size++;
}
for (int i = N-1; i >= 0; --i) {
char c = S.charAt(i);
K %= size;
if (K == 0 && Character.isLetter(c))
return Character.toString(c);
if (Character.isDigit(c))
size /= c - '0';
else
size--;
}
throw null;
}
}4、细分图中的可到达结点
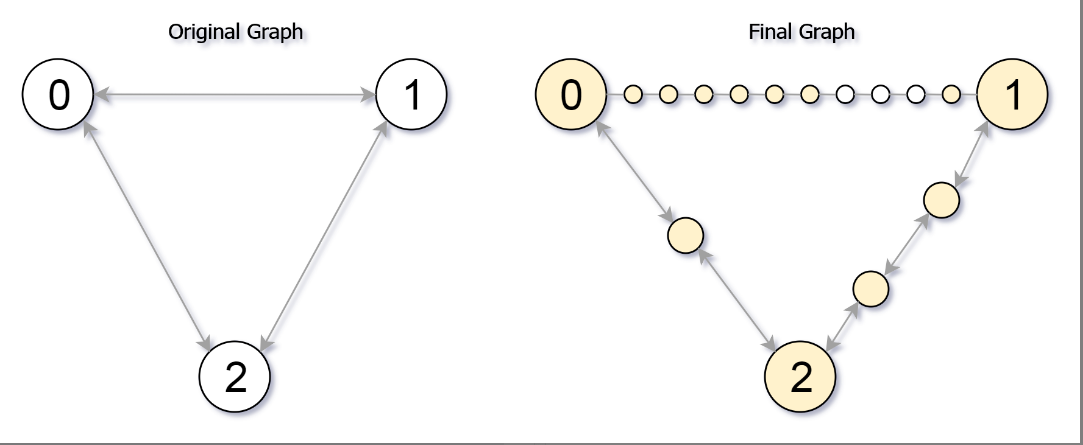
给你一个无向图(原始图),图中有 n 个节点,编号从 0 到 n - 1 。你决定将图中的每条边 细分 为一条节点链,每条边之间的新节点数各不相同。
图用由边组成的二维数组 edges 表示,其中 edges[i] = [ui, vi, cnti] 表示原始图中节点 ui 和 vi 之间存在一条边,cnti 是将边 细分 后的新节点总数。注意,cnti == 0 表示边不可细分。
要 细分 边 [ui, vi] ,需要将其替换为 (cnti + 1) 条新边,和 cnti 个新节点。新节点为 x1, x2, ..., xcnti ,新边为 [ui, x1], [x1, x2], [x2, x3], ..., [xcnti+1, xcnti], [xcnti, vi] 。
现在得到一个 新的细分图 ,请你计算从节点 0 出发,可以到达多少个节点?如果节点间距离是 maxMoves 或更少,则视为 可以到达 。
给你原始图和 maxMoves ,返回 新的细分图中从节点 0 出发 可到达的节点数 。
示例 1:
输入:edges = [[0,1,10],[0,2,1],[1,2,2]], maxMoves = 6, n = 3
输出:13
解释:边的细分情况如上图所示。
可以到达的节点已经用黄色标注出来。
示例 2:输入:edges = [[0,1,4],[1,2,6],[0,2,8],[1,3,1]], maxMoves = 10, n = 4
输出:23
示例 3:输入:edges = [[1,2,4],[1,4,5],[1,3,1],[2,3,4],[3,4,5]], maxMoves = 17, n = 5
输出:1
解释:节点 0 与图的其余部分没有连通,所以只有节点 0 可以到达。
class Solution {
public int reachableNodes(int[][] edges, int M, int N) {
Map<Integer, Map<Integer, Integer>> graph = new HashMap();
for (int[] edge: edges) {
int u = edge[0], v = edge[1], w = edge[2];
graph.computeIfAbsent(u, x->new HashMap()).put(v, w);
graph.computeIfAbsent(v, x->new HashMap()).put(u, w);
}
PriorityQueue<ANode> pq = new PriorityQueue<ANode>(
(a, b) -> Integer.compare(a.dist, b.dist));
pq.offer(new ANode(0, 0));
Map<Integer, Integer> dist = new HashMap();
dist.put(0, 0);
Map<Integer, Integer> used = new HashMap();
int ans = 0;
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
ANode anode = pq.poll();
int node = anode.node;
int d = anode.dist;
if (d > dist.getOrDefault(node, 0)) continue;
// Each node is only visited once. We've reached
// a node in our original graph.
ans++;
if (!graph.containsKey(node)) continue;
for (int nei: graph.get(node).keySet()) {
// M - d is how much further we can walk from this node;
// weight is how many new nodes there are on this edge.
// v is the maximum utilization of this edge.
int weight = graph.get(node).get(nei);
int v = Math.min(weight, M - d);
used.put(N * node + nei, v);
// d2 is the total distance to reach 'nei' (nei***or) node
// in the original graph.
int d2 = d + weight + 1;
if (d2 < dist.getOrDefault(nei, M+1)) {
pq.offer(new ANode(nei, d2));
dist.put(nei, d2);
}
}
}
// At the end, each edge (u, v, w) can be used with a maximum
// of w new nodes: a max of used[u, v] nodes from one side,
// and used[v, u] nodes from the other.
// [We use the encoding (u, v) = u * N + v.]
for (int[] edge: edges) {
ans += Math.min(edge[2], used.getOrDefault(edge[0] * N + edge[1], 0) +
used.getOrDefault(edge[1] * N + edge[0], 0) );
}
return ans;
}
}
class ANode {
int node, dist;
ANode(int n, int d) {
node = n;
dist = d;
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号