msys2环境下为帮助手册Manual建立索引
msys2部署以后,有会有一些文件目录是原生Linux所没有的,比如“根目录”下的mingw32和mingw64路径:
在部署iverilog的时候,发现包名称是带有mingw32/w64的:
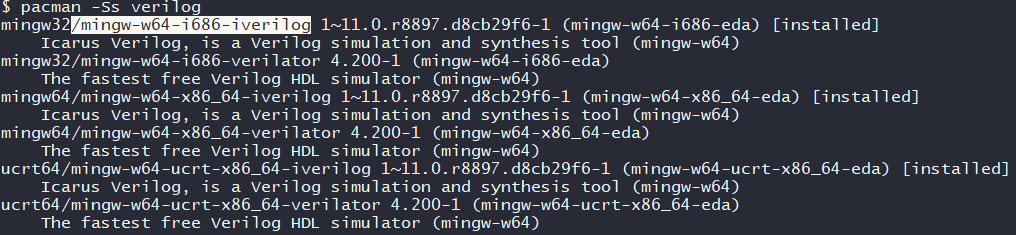
这样的结果是,iverilog编译器和vvp仿真工具都安装在了msys64/mingw32/bin目录下(mingw64和ucrt64类似,放在msys64/mingw64/bin和msys64/ucrt64/bin),而对应的帮助手册(man,System Reference Manual)放在了msys64/mingw32/share/man下,
此时进行手册查询:
man iverilog
会提示找不到手册项:
No manual entry for iverilog
要解决这个问题,需要搞定mandb命令,即Manual Index Database,与之相关的还有manpath命令。
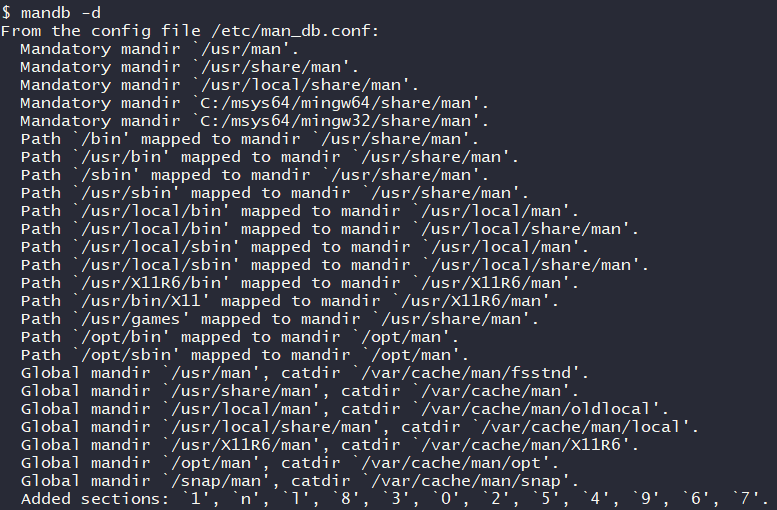
给出mandb(8)的手册内容:
MANDB(8) Manual pager utils MANDB(8) NAME mandb - create or update the manual page index caches SYNOPSIS mandb [-dqsucpt?V] [-C file] [manpath] mandb [-dqsut] [-C file] -f filename ... DESCRIPTION mandb is used to initialise or manually update index database caches. The caches contain information relevant to the current state of the manual page system and the information stored within them is used by the man-db utilities to enhance their speed and functionality. When creating or updating an index, mandb will warn of bad ROFF .so requests, bogus manual page filenames and manual pages from which the whatis cannot be parsed. Supplying mandb with an optional colon-delimited path will override the internal system manual page hierarchy search path, determined from information found within the man-db configuration file. DATABASE CACHES mandb can be compiled with support for any one of the following database types. Name Async Filename ────────────────────────────────────── Berkeley db Yes index.bt GNU gdbm Yes index.db UNIX ndbm No index.(dir|pag) Those database types that support asynchronous updates provide enhanced speed at the cost of possible corruption in the event of unusual termination. In an unusual case where this has occurred, it may be necessary to rerun mandb with the -c option to re-create the databases from scratch. OPTIONS -d, --debug Print debugging information. -q, --quiet Produce no warnings. -s, --no-straycats Do not spend time looking for or adding information to the databases regarding stray cats. -p, --no-purge Do not spend time checking for deleted manual pages and purging them from the databases. -c, --create By default, mandb will try to update any previously created databases. If a database does not exist, it will create it. This option forces mandb to delete previous data‐ bases and re-create them from scratch, and implies --no-purge. This may be necessary if a database becomes corrupt or if a new database storage scheme is introduced in the future. -u, --user-db Create user databases only, even with write permissions necessary to create system databases. -t, --test Perform correctness checks on manual pages in the hierarchy search path. With this option, mandb will not alter existing databases. -f, --filename Update only the entries for the given filename. This option is not for general use; it is used internally by man when it has been compiled with the MAN_DB_UPDATES option and finds that a page is out of date. It implies -p and disables -c and -s. -C file, --config-file=file Use this user configuration file rather than the default of ~/.manpath. -?, --help Show the usage message, then exit. --usage Print a short usage message and exit. -V, --version Show the version, then exit. EXIT STATUS 0 Successful program execution. 1 Usage, syntax, or configuration file error. 2 Operational error. 3 A child process failed. DIAGNOSTICS The following warning messages can be emitted during database building. <filename>: whatis parse for page(sec) failed An attempt to extract whatis line(s) from the given <filename> failed. This is usually due to a poorly written manual page, but if many such messages are emitted it is likely that the system contains non-standard manual pages which are incompatible with the man-db whatis parser. See the WHATIS PARSING section in lexgrog(1) for more in‐ formation. <filename>: is a dangling symlink <filename> does not exist but is referenced by a symbolic link. Further diagnostics are usually emitted to identify the <filename> of the offending link. <filename>: bad symlink or ROFF `.so' request <filename> is either a symbolic link to, or contains a ROFF include request to, a non existent file. <filename>: ignoring bogus filename The <filename> may or may not be a valid manual page but its name is invalid. This is usually due to a manual page with sectional extension <x> being put in manual page section <y>. <filename_mask>: competing extensions The wildcard <filename_mask> is not unique. This is usually caused by the existence of both a compressed and uncompressed version of the same manual page. All but the most recent are ignored. FILES /etc/man_db.conf man-db configuration file. /var/cache/man/index.(bt|db|dir|pag) An FHS compliant global index database cache. Older locations for the database cache included: /usr/man/index.(bt|db|dir|pag) A traditional global index database cache. /var/catman/index.(bt|db|dir|pag) An alternate or FSSTND compliant global index database cache. SEE ALSO lexgrog(1), man(1), manpath(5), catman(8) The WHATIS PARSING section formerly in this manual page is now part of lexgrog(1). AUTHOR Wilf. (G.Wilford@ee.surrey.ac.uk). Fabrizio Polacco (fpolacco@debian.org). Colin Watson (cjwatson@debian.org). BUGS https://savannah.nongnu.org/bugs/?group=man-db 2.9.4 2021-02-08 MANDB(8)
manpath命令对man索引建立的说明是:
MANPATH(1) Manual pager utils MANPATH(1) NAME manpath - determine search path for manual pages SYNOPSIS manpath [-qgdc?V] [-m system[,...]] [-C file] DESCRIPTION If $MANPATH is set, manpath will simply display its contents and issue a warning. If not, manpath will determine a suitable manual page hierarchy search path and display the re‐ sults. The colon-delimited path is determined using information gained from the man-db configuration file – (/etc/man_db.conf) and the user's environment. OPTIONS -q, --quiet Do not issue warnings. -d, --debug Print debugging information. -c, --catpath Produce a catpath as opposed to a manpath. Once the manpath is determined, each path element is converted to its relative catpath. -g, --global Produce a manpath consisting of all paths named as "global" within the man-db configuration file. -m system[,...], --systems=system[,...] If this system has access to other operating system's manual hierarchies, this option can be used to include them in the output of manpath. To include NewOS's manual page hierarchies use the option -m NewOS. The system specified can be a combination of comma delimited operating system names. To include the native operating system's manual page hierarchies, the system name man must be included in the argument string. This option will override the $SYSTEM environment variable. -C file, --config-file=file Use this user configuration file rather than the default of ~/.manpath. -?, --help Print a help message and exit. --usage Print a short usage message and exit. -V, --version Display version information. ENVIRONMENT MANPATH If $MANPATH is set, manpath displays its value rather than determining it on the fly. If $MANPATH is prefixed by a colon, then the value of the variable is appended to the list determined from the content of the configuration files. If the colon comes at the end of the value in the variable, then the determined list is appended to the content of the variable. If the value of the variable contains a double colon (::), then the determined list is inserted in the middle of the value, between the two colons. SYSTEM If $SYSTEM is set, it will have the same effect as if it had been specified as the argument to the -m option. FILES /etc/man_db.conf man-db configuration file. SEE ALSO apropos(1), man(1), whatis(1) AUTHOR Wilf. (G.Wilford@ee.surrey.ac.uk). Fabrizio Polacco (fpolacco@debian.org). Colin Watson (cjwatson@debian.org). BUGS https://savannah.nongnu.org/bugs/?group=man-db 2.9.4 2021-02-08 MANPATH(1)
这里需要搞清楚的是:mandb命令会为文档内容建立索引,建立索引的过程需要依据MANPATH环境变量和/etc/man_db.conf文件中的设定,具体规则是:
如果MANPATH环境变量存在,那么mandb会从MANPATH的路径中寻找内容、建立索引;

如果MANPATH环境变量不存在,那么mandb会从/etc/man_db.conf中找到对MANPATH的描述建立索引。(-d选项表示Debug,打印调试信息)
另外要注意的是,/etc/profile文件也设定了MANPATH的路径:

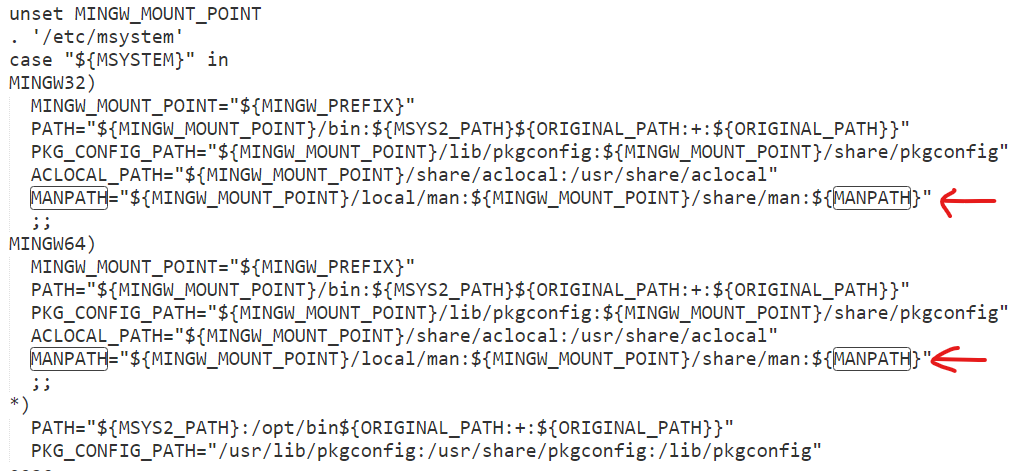
这里为iverilog建立索引的办法是:在/etc/man_db.conf以外的地方清除MANPATH变量,在/etc/man_db.conf里面指定mandb搜索的路径:
在/etc/profile文件末尾进行unset清除操作:
unset MANPATH
在/etc/man_db.conf文件中,为MANPATH添加目录,诸如:
MANDATORY_MANPATH /usr/local/share/man MANDATORY_MANPATH C:/msys64/mingw64/share/man MANDATORY_MANPATH C:/msys64/mingw32/share/man
MANDATORY表示必须搜索的绝对路径(?)
保存文件,更新变量:
source /etc/profile
最后更新man索引:
mandb -c
现在有了iverilog、iverilog-vpi和vvp的手册。


