数组中的每个数据元素都是相同的数据类型,数组是由连续的内存位置组成的
常见的数组定义:
第一种:
数据类型 数组名[数组长度]; //这里我们是要自己进行定义赋值的
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[5];
arr[0] = 1;
arr[1] = 2;
for (int i = 0; i < 5;i++) {
cout << arr[i] << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
第二种:
在定义里就给赋值,如果给填充的数字小于数组的长度,没有填充的就自动填充为0
数据类型 数组名[数组长度]={1,2,3};
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[5] = {1,2,3,3};
for (int i = 0; i < 5;i++) {
cout << arr[i] << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
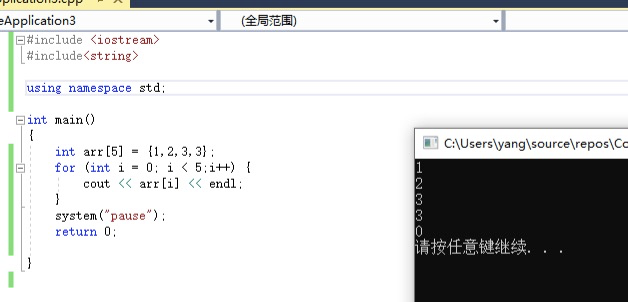
第三种:
数据类型 数组名[]={1,2,3,4};
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[] = {1,2,3,3};
for (int i = 0; i < 5;i++) {
cout << arr[i] << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
一维数组
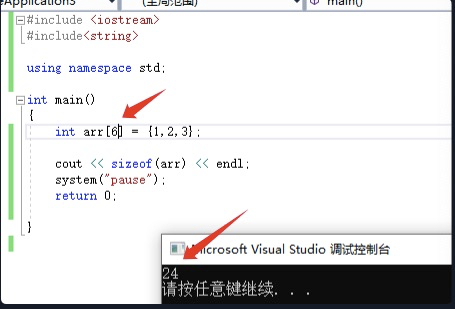
通过数组名统计整个数组占用内存的大小和数量
int整形一个数组占用四个字节,效果如下:
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[6] = {1,2,3};
cout << sizeof(arr) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
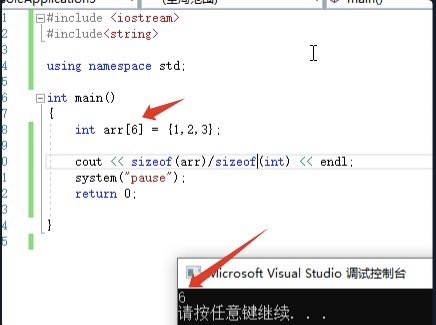
int arr[6] = {1,2,3};
cout << sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
获取数组在内存中的首地址
地址本身其实是16进制的,但可以转换为int,发现int间为4个字字节差,同样也可以发现arr相当于&arr[0],&arr[0]代表的是第一个元素的地址,&就是取这个元素的内存地址,也就是元素的首个地址相当于arr,同样就是&arr[0]
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[5] = {1,2,3};
cout << arr << endl;
cout << (int)arr << endl;
cout << (int)&arr[0] << endl;
cout << (int)&arr[1] << endl;
cout << (int)&arr[2] << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

二维数组
此处列出常见方式,第一种:
数据类型 数组名 [行数][列数]={{a1,a2},{a3,a4}};
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[2][2]=
{
{1,2},
{3,4}
};
system("pause");
return 0;
}
第二种:
数据类型 数组名[行数][列数]={a1,a2,a3,a4};
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[2][2]=
{
1,2,3,4
};
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
cout << arr[i][j] << endl;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
第三种:
数据类型 数组名[][列数]={a1,a2,a3,a4};
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[][2]=
{
1,2,3,4
};
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
cout << arr[i][j] << endl;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
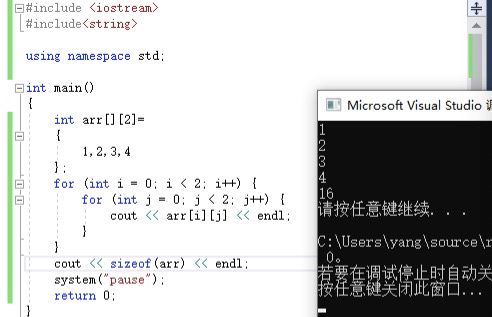
查看二维数组所占用的内存地址
同样此处已知一个int占用4个字节
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[][2]=
{
1,2,3,4
};
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
cout << arr[i][j] << endl;
}
}
cout << sizeof(arr) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
一些数量的获得
获得数组的个数
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[][2]=
{
1,2,3,4
};
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
cout << arr[i][j] << endl;
}
}
cout << sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
获得每行数组的个数
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[][2]=
{
1,2,3,4
};
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
cout << arr[i][j] << endl;
}
}
cout << sizeof(arr[0])/sizeof(int) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
获得详细的行&列
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[][2]=
{
1,2,3,4
};
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
cout << arr[i][j] << endl;
}
}
cout << sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]) << endl;//行数
cout << sizeof(arr[0]) / sizeof(arr[0][0]) << endl;//列数
system("pause");
return 0;
}
获得数组首地址
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[][2]=
{
1,2,3,4
};
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
cout << arr[i][j] << endl;
}
}
cout << (int)arr << endl;
cout << (int)&arr[0] << endl;
cout << (int)&arr[0][0] << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

一维数组基本元素逆置
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[3] = { 1,2,3 };
int length = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int start = 0;
int end = length - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
if (start < end)
{
int tem = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[end];
arr[end] = tem;
start++;
end--;
}
cout << arr[i] << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
二维数组分数分配
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int fenshu[3][3]{
{1,2,3},
{4,5,6},
{7,8,9}
};
string tar[3] = { "a1","a2","a3" };
int sum = 0;
for (int a = 0; a < 3; a++) {
cout << tar[1] << "分数为:";
for (int b = 0; b <= 2; b++) {
sum = sum + fenshu[a][b];
cout << fenshu[a][b] << endl;
}
cout << tar[a] << "总分为:" << sum << endl;
sum = 0;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
联系邮箱:yang_s1r@163.com
博客园地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/Yang34/


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号