Service四大组件之一,需要在AndroidMainfest.xml中添加相关配置,运行于后台,不与用户进行交换,没有UI...
配置时可通过《intent-filter.../》元素指定它可被那些Intent启动。
Android系统本身提供了大量的Service组件,可通过这些系统Service来操作Android系统本身。
BroadcastReceiver组件就是一个全局的事件监听器,只不过其用于监听系统发出的BroadCast,通过使用BroadcastReceiver,即可在不同应用程序之间通信。
创建、配置Service操作步骤:
1.定义一个基础Service的子类;
2.在AndroidMainfest.xml中添加配置;
Service与Activity都继承自Context,都可调用Context里定义的如:getResources()、getContentResolver()等方法。
Service也定义了生命周期,方法如下:
| abstract IBinder onBind(Intent intent) | 该方法是Service子类必须实现的方法,该方法返回一个IBinder对象,应用程序可通过该对象与Service组件通信 |
| void oncreate() | 当Service第一次被创建后将立即回调该方法 |
| void onDestory(0 | 当该Service被关闭之前将会回调该方法 |
| void onStartCommand(Intent intent,int flags,int startId) | 该方法的早期版本是void onStart(Intent intent,int startId),每次客户端调用startService(Intent)方法启动该Service时都会回调该方法 |
| boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) | 当该Service上绑定的所有客户端都断开连接时将会回调该方法 |
实例如下:
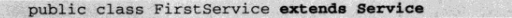

配置如下:

Android系统中运行Service有两种方式:
1.通过Context的startService():通过该方法启动服务,访问者与服务直接没有关联,即使访问者退出了,服务仍然运行——因此Service和访问者直接无法进行通信、数据交换。
2.通过Context的bindService():通过该方法启动服务,访问者与服务绑定在一起,访问者退出,服务也将跟随访问者状态被终止
——如果Service和访问者之间需要进行数据交换或方法调用,则应该使用bindService()和unbindService()方法启动、关闭服务。
启动和停止Service
如下图所示:

注意:
每当Service被创建时回调onCreate()方法,每次Service被启动时会回调onStart(),多次启动一个已有的Service组件将不会再回调onCreate(),但每次启动时都会回调onStart()。
绑定本地Service并与之通信
Context的bindService方法的完整方法签名为:bindService(Intent service,ServiceConnection conn,int flags):
service——该参数通过Intent指定要启动的服务;
ServiceConnection ——该参数是一个ServiceConnection对象,该对象用于监听访问者与Service之间的连接情况。
当访问者与Service之间连接成功时将回调该ServiceConnection对象的onServiceConnected(ComponetName name,IBinder binder)方法;
当访问者与Service之间断开连接时将回调该ServiceConnection对象的onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name)方法。
flags——指定绑定时是否自动创建Service(如果Service还未创建)。该参数可指定为0(不自动创建)或BIND_AUTO_CREATE(自动创建)。
1.注意到ServiceConnection对象的onServiceConnected方法中有一个IBinder对象,该对象即可实现与被绑定Service之间的通信。
2.当开发Service类时,该Service类必须提供一个IBinder binder(Intent intent)方法,在绑定本地Service的情况下,onBind(Intent intent)方法返回的IBinder对象将会传给ServiceConnection对象里的
onSeviceConnected(ComponentName name ,IBinder binder)方法的service参数,这样访问者就可通过该IBinder对象与Service进行通信。
注意:实际上开发时通常会采用继承Binder(IBinder的实现类)的方式实现自己的IBinder对象。
实例如下:
布局文件==》
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@drawable/photo12"
android:gravity="center_horizontal|center_vertical"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnBinder"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="binder"
android:textSize="25dp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnUnBinder"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:text="unbinder"
android:textSize="25dp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnServiceStatus"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:text="service status"
android:textSize="25dp" />
</LinearLayout>
AndroidMainfest.xml==>
添加
<service android:name="com.example.myservice1.BindService">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.myservice1.MainActivity"/>
</intent-filter>
</service>
代码实现==》
package com.example.myservice1;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Binder;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class BindService extends Service
{
private Integer count = 0;
private boolean quit;
// 定义onBinder方法所返回的对象
private MyBinder binder = new MyBinder();
// 通过继承Binder来实现IBinder类f
public class MyBinder extends Binder
{
public int getCount()
{
// 获取Service的运行状态:count
return count;
}
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent)
{
System.out.println("Service is Binded");
Log.i("swg", "Service is Binded");
return binder;
}
@Override
public void onCreate()
{
super.onCreate();
System.out.println("Service is onCreate");
Log.i("swg", "Service is onCreate");
// 启动一条线程、动态地修改count状态值
new Thread()
{
@Override
public void run()
{
while (!quit)
{
try
{
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
count++;
}
}
}.start();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy()
{
super.onDestroy();
System.out.println("Service is onDestroy");
Log.i("swg", "Service is onDestroyed");
this.quit = true;
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent)
{
System.out.println("Service is onUnbind");
Log.i("swg", "Service is onUnbind");
// return super.onUnbind(intent);
return true;
}
}
package com.example.myservice1;
import com.example.myservice1.BindService.MyBinder;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
@SuppressLint("ShowToast")
public class MainActivity extends Activity
{
BindService.MyBinder binder;
final String TAG = "com.example.myservice1.MainActivity";
private ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection()
{
// 当Activity与服务连接成功时回调该方法
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service)
{
System.out.println("-------------Service is onServiceConnected-------------");
Log.i("swg", "-------------Service is onServiceConnected-------------");
// 获取Service的onBind方法所返回的MyBinder对象
binder = (MyBinder) service;
}
// 当Activity与服务断开连接时回调该方法
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name)
{
System.out.println("-------------Service is onServiceDisconnected-------------");
Log.i("swg", "-------------Service is onServiceDisconnected-------------");
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button btnBinder = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.btnBinder);
Button btnUnBinder = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.btnUnBinder);
Button btnServiceStatus = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.btnServiceStatus);
btnBinder.setOnClickListener(new MyButtonClick());
btnUnBinder.setOnClickListener(new MyButtonClick());
btnServiceStatus.setOnClickListener(new MyButtonClick());
}
private class MyButtonClick implements OnClickListener
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction(TAG);
try
{
switch (v.getId())
{
case R.id.btnBinder:
Log.i("swg", "-------------onClick is btnBinder-------------");
bindService(intent, conn, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);// 绑定时自动创建服务
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Service btnBinder success", 3000)
.show();
break;
case R.id.btnUnBinder:
Log.i("swg", "-------------onClick is btnUnBinder-------------");
unbindService(conn);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Service btnUnBinder success", 3000)
.show();
break;
case R.id.btnServiceStatus:
Log.i("swg", "-------------onClick is btnServiceStatus-------------");
// 获取并显示Service的count值
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Service count==" + binder.getCount(), 5000)
.show();
break;
}
} catch (Exception e)
{
//Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Service error==" + e.getMessage(), 5000).show();
return;
}
}
}
}
运行效果:
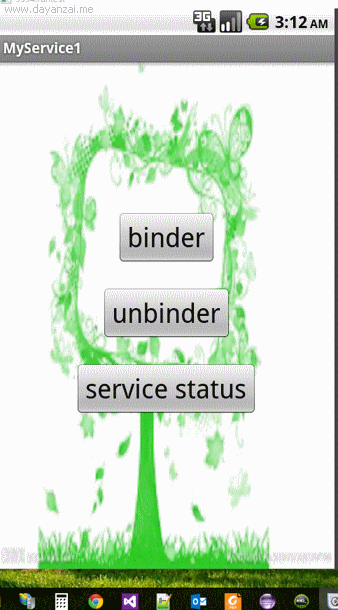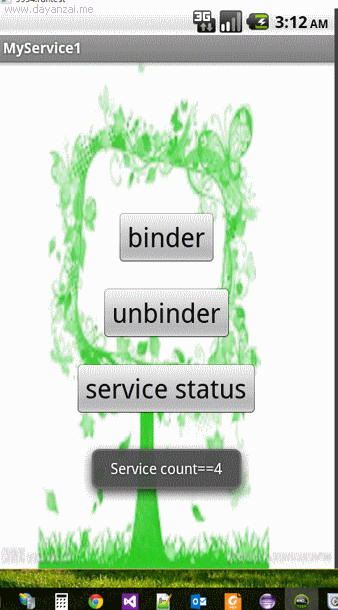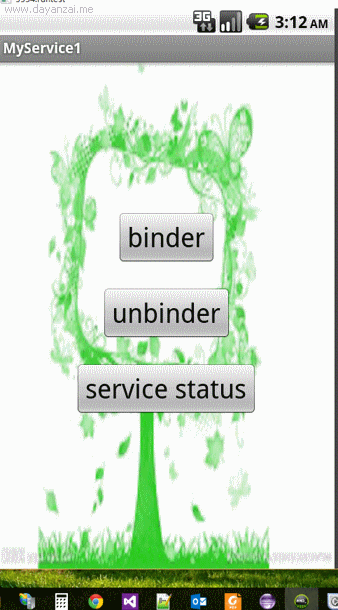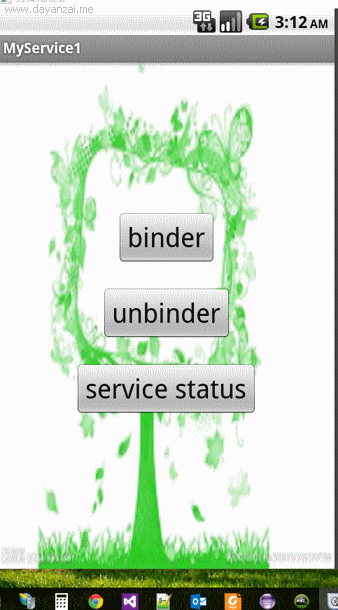
注意:对于Service的onBind()所返回的IBinder对象来说,其可被当成该Service组件所返回的回调对象,Service允许客户端通过该IBinder对象访问
Service内部的数据,这样即可实现客户端与Service之间的通信。
与多次调用startService()启动Service不同的是,多次调用bindService()并不会重复执行绑定;
前者,启动一次服务,系统就会调用一次服务的onStart(),后者,系统只会调用onBind()方法一次。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号