SDKD 软件18 线性表及应用
选择题

每一项分别与另一个链表的各项相乘操作次数为 \(N_1\) x \(N_2\)
编程题
7-1 一元多项式的乘法与加法运算 (20 分)
题面

思路
本题除了代码给出的链表版本的解法外,还可以使用数组来解答本题,不过推荐大家首次做此题使用链表的方法来做这样可以练习大家调试代码和编写程序的能力.
多项式相加的操作思路相对简单,就是不断地从两个链表的表头取出元素,然后比较他们的指数大小,如果指数不相同就将指数较大的链接到答案链表的最后,如果指数相同, 那么将他们的系数相加生成一个全新的节点,如果新节点的系数不为零,就将新节点链接到答案链表的最后.
多项式乘法的话,可以将整个乘法操作拆分成多次加法,我们初始化答案链表为空,即我们不断的从A链表的表头取出一个节点,把这个单节点与B链表的乘法结果加到答案链表上,如此一直操作到A链表被取空.
代码
//库函数头文件包含
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <malloc.h>
//函数状态码定义
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define INFEASIBLE -1
#define OVERFLOW -2
typedef struct PolyNode *Polynomial;
struct PolyNode
{
int coef;
int expon;
Polynomial link;
};
void Attach(int c, int e, Polynomial *pRear)
{
Polynomial P;
P = (Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
P->coef = c;
P->expon = e;
P->link = NULL;
(*pRear)->link = P;
*pRear = P;
}
Polynomial ReadPoly()
{
Polynomial P, Rear, tmp;
P = (Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
P->link = NULL;
Rear = P;
int c, e, N;
scanf("%d", &N);
while (N--)
{
scanf("%d %d", &c, &e);
Attach(c, e, &Rear);
}
tmp = P, P = P->link, free(tmp);
return P;
}
Polynomial Add(Polynomial P1, Polynomial P2)
{
int sum;
Polynomial P, Rear, t;
P = (Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
P->link = NULL;
Rear = P;
while (P1 && P2)
{
if (P1->expon == P2->expon)
{
sum = P1->coef + P2->coef;
if (sum != 0)
Attach(sum, P1->expon, &Rear);
P1 = P1->link;
P2 = P2->link;
}
else if (P1->expon > P2->expon)
{
Attach(P1->coef, P1->expon, &Rear);
P1 = P1->link;
}
else
{
Attach(P2->coef, P2->expon, &Rear);
P2 = P2->link;
}
}
while (P1)
{
Attach(P1->coef, P1->expon, &Rear);
P1 = P1->link;
}
while (P2)
{
Attach(P2->coef, P2->expon, &Rear);
P2 = P2->link;
}
Rear->link = NULL;
t = P;
P = P->link;
free(t);
return P;
}
Polynomial Mult(Polynomial P1, Polynomial P2)
{
if (P1 == NULL || P2 == NULL)
return NULL;
Polynomial P, p, p1, p2, t, tmp;
P = (Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
P->link = NULL;
p = P;
p1 = P1;
p2 = P2;
int c, e;
while (p2 != NULL)
{
Attach(p1->coef * p2->coef, p1->expon + p2->expon, &p);
p2 = p2->link;
}
p1 = p1->link;
while (p1 != NULL)
{
p2 = P2;
p = P;
while (p2 != NULL)
{
c = p1->coef * p2->coef;
e = p1->expon + p2->expon;
while (p->link != NULL && p->link->expon > e)
p = p->link;
if (p->link != NULL && p->link->expon == e)
{
if ((p->link->coef + c) != 0)
{
p->link->coef += c;
}
else
{
t = p->link;
p->link = t->link;
free(t);
}
}
else
{
t = (Polynomial)malloc(sizeof(struct PolyNode));
t->coef = c;
t->expon = e;
t->link = p->link;
p->link = t;
p = p->link;
}
p2 = p2->link;
}
p1 = p1->link;
}
tmp = P;
P = P->link;
free(tmp);
return P;
}
void PrintPoly(Polynomial P)
{
int flag = 0;
if (!P)
{
printf("0 0");
return;
}
while (P)
{
if (!flag)
flag = 1;
else
printf(" ");
printf("%d %d", P->coef, P->expon);
P = P->link;
}
}
int main()
{
Polynomial P1, P2, PP, PS;
P1 = ReadPoly();
P2 = ReadPoly();
PP = Mult(P1, P2);
PrintPoly(PP);
printf("\n");
PS = Add(P1, P2);
PrintPoly(PS);
return 0;
}
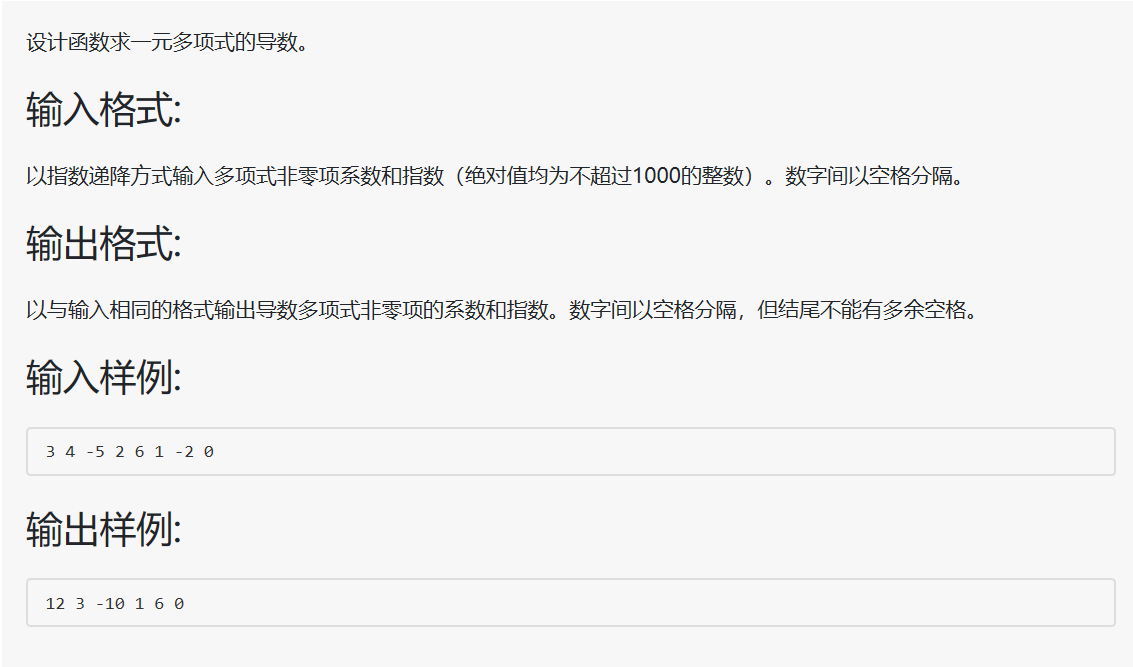
7-2 一元多项式求导 (20 分)
题面
思路
这道题在此提供简单的解法, 当然依然推荐大家使用链表来解, 简单解法的思路就是, 在输入的同时对每一项直接求导, 然后输出即可.
代码
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static final Scanner cin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean flag = true;
while (cin.hasNext()) {
int a = cin.nextInt(), b = cin.nextInt();
int xishu = a * b, zhishu = b - 1;
if (xishu != 0) {
if (flag) flag = false;
else System.out.print(" ");
System.out.print(xishu + " " + zhishu);
}
}
if(flag) System.out.print("0 0");
}
}
7-3 求链式线性表的倒数第K项 (20 分)
题面

思路
相求长度, 然后找到链表的 (长度+1-K) 项 即可.
代码
//库函数头文件包含
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//函数状态码定义
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define OK 1
#define ERROR -3
#define INFEASIBLE -1
#define OVERFLOW -2
typedef int Status;
typedef int ElemType; //假设线性表中的元素均为整型
typedef struct LNode
{
ElemType data;
struct LNode *next;
} LNode,*LinkList;
Status ListCreate_L(LinkList &L)
{
LNode *rearPtr,*curPtr; //一个尾指针,一个指向新节点的指针
L=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof (LNode));
if(!L)
exit(OVERFLOW);
L->next=NULL; //先建立一个带头结点的单链表
rearPtr=L; //初始时头结点为尾节点,rearPtr指向尾巴节点
while (1) //每次循环都开辟一个新节点,并把新节点拼到尾节点后
{
curPtr=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));//生成新结点
if(!curPtr)
exit(OVERFLOW);
scanf("%d",&curPtr->data);//输入元素值
if(curPtr->data < 0)
break;
curPtr->next=NULL; //最后一个节点的next赋空
rearPtr->next=curPtr;
rearPtr=curPtr;
}
return OK;
}
void ListPrint_L(LinkList &L)
{
//输出单链表
LNode *p=L->next; //p指向第一个元素结点
while(p!=NULL)
{
if(p->next!=NULL)
printf("%d ",p->data);
else
printf("%d",p->data);
p=p->next;
}
}
int Length(LinkList L)
{
if (L == NULL)
return 0;
int cnt = 1;
while (L->next != NULL)
{
cnt++;
L = L->next;
}
return cnt;
}
int FindKth( LinkList L, int K )
{
if(L == NULL || K < 1)
return ERROR;
int cnt = 1;
while(L && cnt < K)
{
cnt++;
L = L -> next;
}
if(L)
return L->data;
else
return ERROR;
}
int main()
{
LinkList L;
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
if(ListCreate_L(L)!= OK)
{
printf("表创建失败!!!\n");
return -1;
}
int len = Length(L->next);
int X = FindKth(L->next, len + 1 - n);
if(X != ERROR)
printf("%d", X);
else
printf("NULL");
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号