关于锁的8个问题
问题一:下面代码先执行打电话还是发短信 发短信
public class A { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Phone phone = new Phone(); // 锁的存在 new Thread(()->{ try { phone.sendmsg(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"A").start(); // 休息1s TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); new Thread(()->{ phone.call(); },"B").start(); } } @SuppressWarnings("all") class Phone { // synchronized锁的对象是方法的调用者 // 两个方法用的是同一个锁,谁先拿到谁执行 public synchronized void sendmsg() throws InterruptedException { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); System.out.println("发短信"); } public synchronized void call() { System.out.println("打电话"); } }

问题二---如果变为两个对象,下面代码先执行打电话还是发短信? 打电话
public class A { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Phone phone1 = new Phone(); Phone phone2 = new Phone(); // 锁的存在 new Thread(()->{ try { phone1.sendmsg(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"A").start(); // 休息1s TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); new Thread(()->{ phone2.call(); },"B").start(); } } @SuppressWarnings("all") class Phone { // synchronized锁的对象是方法的调用者 // 两个方法用的是同一个锁,谁先拿到谁执行 public synchronized void sendmsg() throws InterruptedException { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); System.out.println("发短信"); } public synchronized void call() { System.out.println("打电话"); } }

问题三---增加普通方法,先打印发短信还是hello?
public class B { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Phone2 phone = new Phone2(); new Thread(()->{ try { phone.sendmsg(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"A").start(); // 休息1s TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); new Thread(()->{ phone.hello(); },"B").start(); } } @SuppressWarnings("all") class Phone2 { // synchronized锁的对象是方法的调用者 // 两个方法用的是同一个锁,谁先拿到谁执行 public synchronized void sendmsg() throws InterruptedException { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); System.out.println("发短信"); } public synchronized void call() { System.out.println("打电话"); } // 这里没有锁,不是同步方法,不受锁的影响 public void hello() { System.out.println("hello"); } }

问题四---用不同对象去调用发短信和hello方法,执行结果?
public class B { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Phone2 phone1 = new Phone2(); Phone2 phone2 = new Phone2(); new Thread(()->{ try { phone1.sendmsg(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"A").start(); // 休息1s TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); new Thread(()->{ phone2.hello(); },"B").start(); } } @SuppressWarnings("all") class Phone2 { public synchronized void sendmsg() throws InterruptedException { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); System.out.println("发短信"); } public synchronized void call() { System.out.println("打电话"); } // 这里没有锁,不是同步方法,不受锁的影响 public void hello() { System.out.println("hello"); } }

解释同上
问题5---当加了static关键字之后,执行结果是怎样的?
public class C { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Phone3 phone = new Phone3(); new Thread(()->{ try { phone.sendmsg(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"A").start(); // 休息1s TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); new Thread(()->{ phone.call(); },"B").start(); } } @SuppressWarnings("all") // phone3只有唯一的一个class对象 phone3.class(全局唯一) class Phone3 { // synchronized锁的对象是方法的调用者 // 两个方法用的是同一个锁,谁先拿到谁执行 // static 静态方法,类一加载就有了,class 模板 // 此时锁的就是class public static synchronized void sendmsg() throws InterruptedException { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); System.out.println("发短信"); } public static synchronized void call() { System.out.println("打电话"); } }

问题6---当加了static关键字来修饰之后,用两个不同对象来调用,执行结果又是怎样?
public class C { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 两个对象,但此时锁的是class,不关对象事。 // 两个对象的class类模板只有一个 Phone3 phone1 = new Phone3(); Phone3 phone2 = new Phone3(); new Thread(()->{ try { phone1.sendmsg(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"A").start(); // 休息1s TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); new Thread(()->{ phone2.call(); },"B").start(); } } @SuppressWarnings("all") // phone3只有唯一的一个class对象 phone3.class(全局唯一) class Phone3 { // synchronized锁的对象是方法的调用者 // 两个方法用的是同一个锁,谁先拿到谁执行 // static 静态方法,类一加载就有了,class 模板 // 此时锁的就是class public static synchronized void sendmsg() throws InterruptedException { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); System.out.println("发短信"); } public static synchronized void call() { System.out.println("打电话"); } }
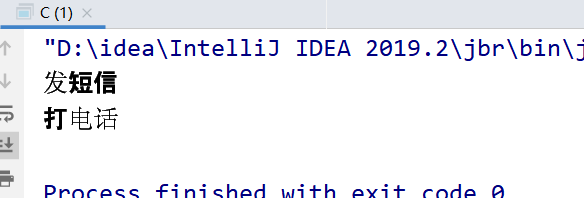
问题7--普通同步方法和静态同步方法放一起,执行顺序是怎样的?
public class D { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Phone4 phone = new Phone4(); new Thread(()->{ try { phone.sendmsg(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"A").start(); // 休息1s TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); new Thread(()->{ phone.call(); },"B").start(); } } @SuppressWarnings("all") // phone3只有唯一的一个class对象 phone3.class(全局唯一) class Phone4 { // 静态同步方法 public static synchronized void sendmsg() throws InterruptedException { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); System.out.println("发短信"); } // 普通同步方法 public synchronized void call() { System.out.println("打电话"); } }
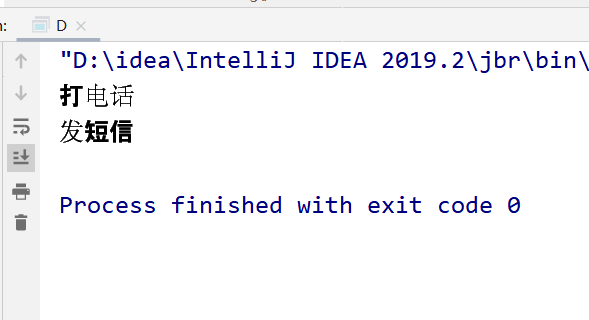
分析:

问题8:两个不同对象来调用,结果又是怎样?
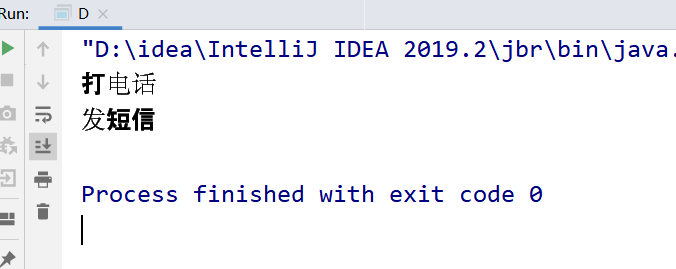
public class D { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Phone4 phone1 = new Phone4(); Phone4 phone2 = new Phone4(); new Thread(()->{ try { phone1.sendmsg(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } },"A").start(); // 休息1s TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); new Thread(()->{ phone2.call(); },"B").start(); } } @SuppressWarnings("all") // phone3只有唯一的一个class对象 phone3.class(全局唯一) class Phone4 { // 静态同步方法 public static synchronized void sendmsg() throws InterruptedException { TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4); System.out.println("发短信"); } // 普通同步方法 public synchronized void call() { System.out.println("打电话"); } }
结果:
posted on 2021-06-08 14:40 Love&Share 阅读(62) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 从HTTP原因短语缺失研究HTTP/2和HTTP/3的设计差异
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~