哈夫曼编码
背景
假如我们要传输一段文本,比如“hello”,怎么办?最容易想到的方法是,直接依次传输每个字符的Unicode,每个字符都用8个比特或以上来传输。这样就需要5*8=40个比特来传输。但是如果我们要传输一段很长的文本怎么办呢?产生的数据量是非常大的,为了节省成本,我们必须要把数据压缩,并且能保证对方接收到压缩的数据可以百分百解读出来原始的信息。
事实上,一段文本中每个字符出现的频率是不同的,比如英文中字母e出现的频率通常是最高的,而z的出现频率要远远低于e。因此可以想到,让出现频率高的字符占用较少的比特。
还是以上面的“hello”为例,因为l出现了2次,而h、e、o只出现了1次,所以l就用1个比特来表示,比如用1来表示,而h、e、o就用2个比特,比如分别用00、11、10来表示,那么“hello”的编码就可以写成这样:
00111110
只需要8个比特,跟前面的40个比特相比,少了80%。
但是,事情发生了转折,当对方接收到这样一个编码的时候就懵逼了,11到底代表两个l呢,还是一个e呢?也就是说,对方通过这段编码,不能还原出原始信息。
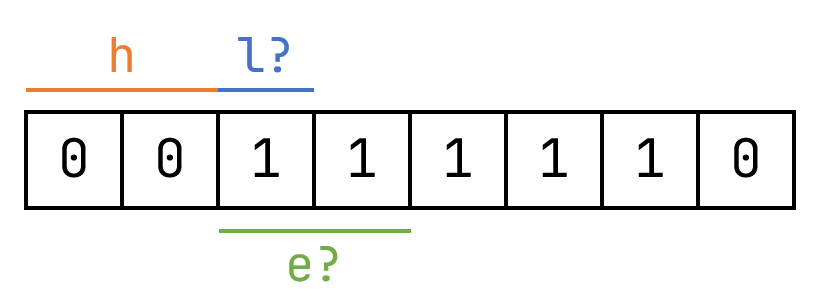
为什么会发生这样的情况呢?原因是因为l的编码1形成了e的编码11的前缀。为了使整个编码没有歧义,需要任何一个字符的编码不能是其余字符编码的前缀,这就是所谓的前缀码(Prefix code)。通俗来讲,假如l的编码是1的话,那么h、e、o的编码不能以1开头,否则的话,e的编码就成了某个其他字符的编码的前缀。
为了满足前缀码的特性,h、e、o的编码可以分别是01、001、000。
那么,整个“hello”字符串的编码就变成了:
0100111000。
这样对方在接收到编码的时候,就可以完美的还原出原始信息了。可以看到,这个编码跟刚才那个编码多了两个比特,但是却换来了无歧义性。
构建二叉树
那怎样去构建这样的前缀码呢?
我们可以构建一棵二叉树,叶节点代表字符,从根节点到叶节点的路径代表比特(规定左0右1),像这样:
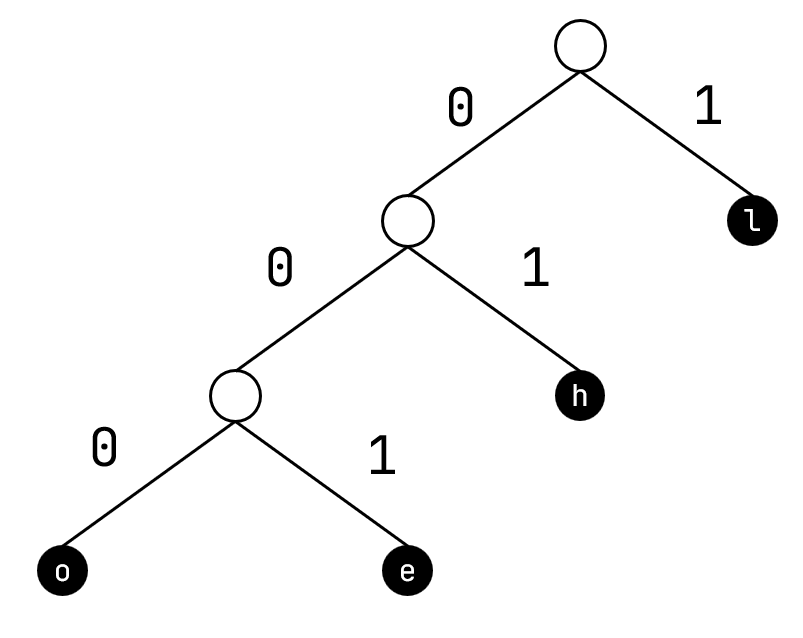
比如从根节点到字母e的路径为“左、左、右”,那么e的编码就为001。
这怎样就能保证整个编码存在前缀码特性呢?证明很简单,如果存在某个字符的编码是其他某个字符的编码的前缀,那么从该节点往下就有路可走,他就不该在叶节点上。
构建最优二叉树
那怎样让二叉树最优化呢?换句话说,怎么样确保出现频率高的字符的路径越短,而出现频率低的字符的路径就越长呢?
这里要引入一个概念,叫“带权路径长度(Weighted path length, WPL)”。给每个节点赋予一个数值,叫做“权”,一个节点的带权路径长度就是从根节点到该节点的路径长度乘上该节点的权值。设叶节点的权值为它在整个字符串中的出现次数,那么我们要做的就是使所有叶节点的带权路径长度之和最小。怎样做到呢?
上个世纪50年代,在麻省理工学院攻读博士学位的哈夫曼(David Albert Huffman)发现了这样一种方法,并证明了这种方法可以使二叉树的所有叶节点的带权路径长度之和最小。这样的二叉树叫做哈夫曼树(Huffman Tree)。
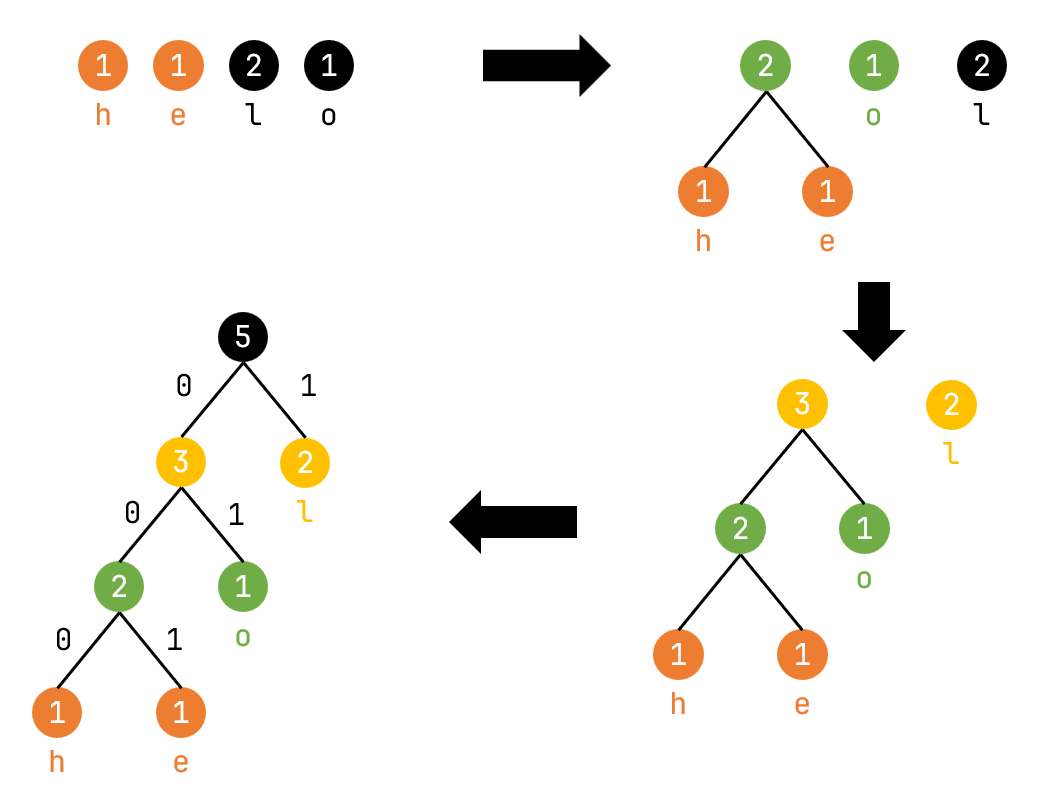
整个过程如下:
- 从n个节点中选出权值最小的2个节点,构建一棵新的二叉树,根节点的权值为这两个节点的权值之和,左右子节点分别为这两个节点。
- 将这两个节点移出去,将新的节点加进来。
- 重复上述步骤,直到只剩下一个节点。
如图所示:
代码实现:
// 定义哈夫曼树节点
struct TreeNode {
size_t weight;
char c;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
// 判断是否为叶节点
bool isLeaf() const {
return left == nullptr && right == nullptr;
}
};
// 该struct用于通过节点指针比较两个节点的权值大小
struct TreeNodeGreater {
bool operator()(TreeNode *lhs, TreeNode *rhs) {
return lhs->weight > rhs->weight;
}
};
// 定义类型别名
// 优先队列(priority_queue)具有先进大(小)出的特性(即队列顶部元素为最大或最小元素),
// 模板参数分别是:存储的类型、底层容器、比较器。
// 这里定义为存储节点指针的先进小出的优先队列。
using TreeNodeQueue = std::priority_queue<TreeNode *, std::vector<TreeNode *>, TreeNodeGreater>;
// 构建哈夫曼树,返回根节点。
TreeNode *buildHuffmanTree(TreeNodeQueue &queue) {
while (queue.size() >= 2) {
auto node1 = queue.top();
queue.pop();
auto node2 = queue.top();
queue.pop();
auto newNode = new TreeNode{node1->weight + node2->weight, 0, node1, node2};
queue.push(newNode);
}
return queue.top();
}
构建编码表
只需深度优先搜索这棵哈夫曼树,遍历到叶节点就加入到哈希表里。
为了方便,这里使用迭代法,具体参见这篇博文。
// vector<bool>是vector模板类的特化,
// 只不过特化成了既不是vector也不存储bool的东西,
// 而是存储比特,是个比特序列,所以正好可以拿来表示字符编码。
using codeMap_t = std::unordered_map<char, std::vector<bool>>;
// 重载流输出运算符
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, std::vector<bool> &bits) {
for (bool bit: bits) {
os << bit;
}
return os;
}
codeMap_t buildCodeMap(TreeNode *root) {
using Path = std::pair<TreeNode *, std::vector<bool>>;
std::stack<Path> pathStack;
codeMap_t codeMap;
pathStack.push({root, {}});
std::cout << "Code Chart:" << std::endl;
while (!pathStack.empty()) {
auto path = pathStack.top();
TreeNode *node = path.first;
auto &bits = path.second;
// 遍历到叶节点就加入到哈希表。
if (node->isLeaf()) {
std::cout << node->c << " : " << bits << std::endl;
codeMap.insert({node->c, bits});
pathStack.pop();
continue;
}
pathStack.pop();
// 将右子节点及路径插入哈希表
if (node->right) {
auto bits1 = bits;
bits1.push_back(true); // 比特序列后面加个1
pathStack.push({node->right, bits1});
}
// 将左子节点及路径插入哈希表
if (node->left) {
auto bits0 = bits;
bits0.push_back(false); // 比特序列后面加个0
pathStack.push({node->left, bits0});
}
}
return codeMap;
}
将整个字符串进行编码
这个没啥可说的,直接上代码
std::vector<bool> encode(std::string &message, codeMap_t &codeMap) {
std::vector<bool> bits;
for (char c: message) {
std::vector<bool> &code = codeMap.at(c);
bits.insert(bits.end(), code.begin(), code.end());
}
return bits;
}
从编码中还原信息
从根节点开始,按照左0右1的原则不断向下走,遇到叶节点就认为还原了一个字符,并回到根节点。
std::string decode(std::vector<bool> &code, TreeNode *root) {
std::string message;
TreeNode *current = root;
for (bool bit: code) {
current = bit ? current->right : current->left;
if (current->isLeaf()) {
message.append(1, current->c);
current = root;
}
}
return message;
}
完整代码
#include <unordered_map>
#include <string>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <iostream>
struct TreeNode {
size_t weight;
char c;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
bool isLeaf() const {
return left == nullptr && right == nullptr;
}
};
struct TreeNodeGreater {
bool operator()(TreeNode *lhs, TreeNode *rhs) {
return lhs->weight > rhs->weight;
}
};
using TreeNodeQueue = std::priority_queue<TreeNode *, std::vector<TreeNode *>, TreeNodeGreater>;
using countMap_t = std::unordered_map<char, size_t>;
using codeMap_t = std::unordered_map<char, std::vector<bool>>;
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream &os, std::vector<bool> &bits) {
for (bool bit: bits) {
os << bit;
}
return os;
}
countMap_t buildCountMap(const std::string &message) {
countMap_t freq;
for (char c : message) {
if (!freq.count(c)) {
freq.insert({c, 0});
}
freq.at(c)++;
}
return freq;
}
TreeNodeQueue buildQueue(const countMap_t &map) {
TreeNodeQueue queue;
for (auto &pair : map) {
char c = pair.first;
size_t freq = pair.second;
auto node = new TreeNode{freq, c, nullptr, nullptr};
queue.push(node);
}
return queue;
}
TreeNode *buildHuffmanTree(TreeNodeQueue &queue) {
while (queue.size() >= 2) {
auto node1 = queue.top();
queue.pop();
auto node2 = queue.top();
queue.pop();
auto newNode = new TreeNode{node1->weight + node2->weight, 0, node1, node2};
queue.push(newNode);
}
return queue.top();
}
codeMap_t buildCodeMap(TreeNode *root) {
using Path = std::pair<TreeNode *, std::vector<bool>>;
std::stack<Path> pathStack;
codeMap_t codeMap;
pathStack.push({root, {}});
std::cout << "Code Chart:" << std::endl;
while (!pathStack.empty()) {
auto path = pathStack.top();
TreeNode *node = path.first;
auto &bits = path.second;
if (node->isLeaf()) {
std::cout << node->c << " : " << bits << std::endl;
codeMap.insert({node->c, bits});
pathStack.pop();
continue;
}
pathStack.pop();
if (node->right) {
auto bits1 = bits;
bits1.push_back(true);
pathStack.push({node->right, bits1});
}
if (node->left) {
auto bits0 = bits;
bits0.push_back(false);
pathStack.push({node->left, bits0});
}
}
return codeMap;
}
std::vector<bool> encode(std::string &message, codeMap_t &codeMap) {
std::vector<bool> bits;
for (char c: message) {
std::vector<bool> &code = codeMap.at(c);
bits.insert(bits.end(), code.begin(), code.end());
}
return bits;
}
std::string decode(std::vector<bool> &code, TreeNode *root) {
std::string message;
TreeNode *current = root;
for (bool bit: code) {
current = bit ? current->right : current->left;
if (current->isLeaf()) {
message.append(1, current->c);
current = root;
}
}
return message;
}
void release(TreeNode *node) {
if (node->left) {
release(node->left);
}
if (node->right) {
release(node->right);
}
delete node;
}
int main() {
std::string message;
std::cout << "Input message: " << std::endl;
std::getline(std::cin, message);
auto originalSize = message.size() * 8;
std::cout << "Size of message: " << originalSize << " bits" << std::endl;
auto countMap = buildCountMap(message);
auto nodeQueue = buildQueue(countMap);
auto root = buildHuffmanTree(nodeQueue);
auto codeMap = buildCodeMap(root);
auto code = encode(message, codeMap);
auto compressedSize = code.size();
std::cout << "Encode result: " << std::endl
<< code << std::endl
<< "Size: " << compressedSize << " bits" << std::endl
<< "compress ratio: " << (long double)compressedSize * 100 / originalSize << '%' << std::endl;
auto decodedMessage = decode(code, root);
std::cout << "Decode result: " << std::endl << decodedMessage << std::endl;
release(root);
return 0;
}
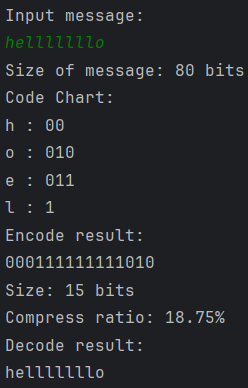
测试:
本文来自博客园,作者:YVVT_Real,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/YWT-Real/p/16770527.html

