day2&day3——2020牛客暑期多校训练营
day2
B
对于三个点
原点直接带入圆的方程求解得:
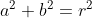
再把另外两个点代入,得:
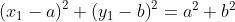
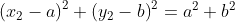
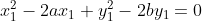

解出a b 统计以此为圆心的圆的个数即可

#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define debug freopen("r.txt","r",stdin) #define mp make_pair #define ri register int using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef double lf; typedef pair<int, int> pii; const int maxn = 5e5+10; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 998244353; const double eps=1e-8; const double PI=acos(-1.0); inline ll read(){ll s=0,w=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')w=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') s=s*10+ch-'0',ch=getchar(); return s*w;} ll qpow(ll p,ll q){return (q&1?p:1)*(q?qpow(p*p%mod,q/2):1)%mod;} int sgn(double x) { if(fabs(x)<eps) return 0; if(x<0) return -1; else return 1; } struct vec{ lf x,y; int num; vec(lf x=0,lf y=0):x(x),y(y){} vec operator-(const vec &b){return vec(x-b.x,y-b.y);} vec operator+(const vec &b){return vec(x+b.x,y+b.y);} vec operator*(lf k){return vec(k*x,k*y);} lf operator ^(const vec &b){return x*b.y-y*b.x;} lf len(){return hypot(x,y);} lf sqr(){return x*x+y*y;} /*截取*/vec trunc(lf k=1){return *this*(k/len());} /*逆时针旋转*/vec rotate(double th){lf c=cos(th),s=sin(th); return vec(x*c-y*s,x*s+y*c);} bool friend operator<(const vec& p1,const vec& p2){ if(sgn(p1.x-p2.x)==-1)return p1.x<p2.x;return p1.y<p2.y; } }p[maxn]; lf cross(vec a,vec b){return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x;}; lf cross(vec a,vec b,vec c){return cross(a-b,b-c);} lf dot(vec a,vec b){return a.x*b.x+a.y*b.y;} bool cmp_xy(const vec &a,const vec &b){return make_pair(a.x,a.y)<make_pair(b.x,b.y);} bool cmp_atan(const vec &a,const vec &b){return atan2(a.x,a.y)<atan2(b.x,b.y);} /*输出*/ostream &operator<<(ostream &o,const vec &v){return o<<'('<<v.x<<','<<v.y<<')';} vec Center(vec p1,vec p2,vec p3) { vec ans; lf a1=p2.x-p1.x,b1=p2.y-p1.y,c1=(a1*a1+b1*b1)/2; lf a2=p3.x-p1.x,b2=p3.y-p1.y,c2=(a2*a2+b2*b2)/2; lf d=a1*b2-a2*b1; ans.x=p1.x+(c1*b2-c2*b1)/d; ans.y=p1.y+(a1*c2-a2*c1)/d; return ans; } map<vec,int> mapp; int maxx,i,j,n; int main() { n=read(); for (i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%lf%lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y); } if (n<=2) { cout<<n<<endl; return 0; } for (i=1;i<=n;i++) { mapp.clear(); for (j=i+1;j<=n;j++) { if (sgn(cross(p[i],p[j]))==0) continue; vec ans=Center(vec(0,0),p[i],p[j]); mapp[ans]++; maxx=max(maxx,mapp[ans]); } } cout<<maxx+1<<endl; return 0; }
C
对于连接着叶子节点的那条边而言,要覆盖此边,其中一个端点必须是叶子节点本身,这样才能够覆盖。
那么对于n个叶子节点而言,要覆盖所有连接它们的边的时候,什么时候次数是最少的呢?
应该为 ⌈n/2⌉,即所有叶子节点之间相连。
而当我们把左叶子节点与右叶子节点相连起来时,所覆盖的路径即是整颗树的路径。

#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define debug freopen("r.txt","r",stdin) #define mp make_pair #define ri register int using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef pair<int, int> pii; const int maxn = 2e5+10; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 998244353; inline ll read(){ll s=0,w=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')w=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') s=s*10+ch-'0',ch=getchar(); return s*w;} ll qpow(ll p,ll q){return (q&1?p:1)*(q?qpow(p*p%mod,q/2):1)%mod;} vector <int> G[maxn]; int ans[maxn],cnt,du[maxn],u,v,i,n,root; void dfs(int u,int father) { if (du[u]==1) { ans[++cnt]=u; return ; } for (auto v:G[u]) { if (v==father) continue; dfs(v,u); } } int main() { n=read(); for (i=1;i<n;i++) { u=read(),v=read(); du[u]++,du[v]++; G[u].push_back(v); G[v].push_back(u); } for (i=1;i<=n;i++) if (du[i]==2) { root=i; break; } dfs(root,root); cout<<(cnt+1)/2<<endl; if(cnt&1) ans[cnt+1]=ans[cnt]; for (i=1;i<=(cnt+1)/2;i++) { cout<<ans[i]<<" "<<ans[i+(cnt+1)/2]<<endl; } return 0; }
F
二维单调队列
day3
A
有鱼拿鱼,没鱼看是否有饵,没饵判断现在是否有饵来捕鱼,有饵判断现在捕鱼还是拿饵。

#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define debug freopen("r.txt","r",stdin) #define mp make_pair #define ri register int using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef pair<int, int> pii; const int maxn = 2e6+5; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 998244353; inline ll read(){ll s=0,w=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')w=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') s=s*10+ch-'0',ch=getchar(); return s*w;} ll qpow(ll p,ll q){return (q&1?p:1)*(q?qpow(p*p%mod,q/2):1)%mod;} int i,a[maxn],sum,b,n,t; char s[maxn]; int main() { t=read(); while (t--) { n=read(); scanf("%s",s+1); sum=b=0; for (i=1;i<=n;i++) { a[i]=a[i-1]+(s[i]=='0' || s[i]=='1'); } for (i=1;i<=n;i++) { if (s[i]=='0') if (b) sum++,b--; if (s[i]=='1') { if (a[n]-a[i-1]<=b) sum++,b--; else b++; } if (s[i]=='2' || s[i]=='3') sum++; } cout<<sum<<endl; } return 0; }
B
顺序不变,头指针一直在变
C
整个手掌只有最下面的一条长为9的边,则只需要用叉积判断拇指和尾指分别是在这条边的左侧还是右侧即可。

#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define debug freopen("r.txt","r",stdin) #define mp make_pair #define ri register int using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef double lf; typedef pair<int, int> pii; const int maxn = 5e5+10; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 998244353; const double eps=1e-5; const double PI=acos(-1.0); inline ll read(){ll s=0,w=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')w=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') s=s*10+ch-'0',ch=getchar(); return s*w;} ll qpow(ll p,ll q){return (q&1?p:1)*(q?qpow(p*p%mod,q/2):1)%mod;} int sgn(double x) { if(fabs(x)<eps) return 0; if(x<0) return -1; else return 1; } struct vec{ lf x,y; int num; vec(lf x=0,lf y=0):x(x),y(y){} vec operator-(const vec &b){return vec(x-b.x,y-b.y);} vec operator+(const vec &b){return vec(x+b.x,y+b.y);} vec operator*(lf k){return vec(k*x,k*y);} lf operator ^(const vec &b){return x*b.y-y-b.x;} lf len(){return hypot(x,y);} lf sqr(){return x*x+y*y;} /*截取*/vec trunc(lf k=1){return *this*(k/len());} /*逆时针旋转*/vec rotate(double th){lf c=cos(th),s=sin(th); return vec(x*c-y*s,x*s+y*c);} }p[maxn]; lf cross(vec a,vec b){return a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x;}; lf cross(vec a,vec b,vec c){return cross(a-b,b-c);} lf dot(vec a,vec b){return a.x*b.x+a.y*b.y;} bool cmp_xy(const vec &a,const vec &b){return make_pair(a.x,a.y)<make_pair(b.x,b.y);} bool cmp_atan(const vec &a,const vec &b){return atan2(a.x,a.y)<atan2(b.x,b.y);} /*输出*/ostream &operator<<(ostream &o,const vec &v){return o<<'('<<v.x<<','<<v.y<<')';} int t,i,flag; int main() { t=read(); while (t--) { for (i=0;i<20;i++) scanf("%lf%lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y); flag=0; for (i=0;i<20;i++) { if (sgn((p[i]-p[(i+1)%20]).len()-9)==0) { if (cross(p[i],p[(i+1)%20],p[(i+2)%20])>0) if (sgn((p[(i+1)%20]-p[(i+2)%20]).len()-6)==0) flag=1; if (cross(p[i],p[(i+1)%20],p[(i+2)%20])<0) if (sgn((p[(i+1)%20]-p[(i+2)%20]).len()-8)==0) flag=1; } } if (flag==1) cout<<"left"<<endl; else cout<<"right"<<endl; } return 0; }
E
第一种符合条件的序列一定是相邻两个元素的调换。
第二种符合条件的序列由于我们可以将整个序列分为多个4个数的子序列和多个6个数的子序列
对于4个数的子序列,除了相邻两两匹配外,第二小的匹配为a3+a4−a2−a1
对于6个数的子序列,除了相邻两两匹配外,第二小的匹配为a6+a5+a3−a4−a1−a2,那么后续的偶数个的序列可以分为多个4个数和6个数的子序列,此时dp即可。

#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define debug freopen("r.txt","r",stdin) #define mp make_pair #define ri register int using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef pair<int, int> pii; const int maxn = 2e5+5; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 998244353; inline ll read(){ll s=0,w=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')w=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') s=s*10+ch-'0',ch=getchar(); return s*w;} ll qpow(ll p,ll q){return (q&1?p:1)*(q?qpow(p*p%mod,q/2):1)%mod;} int t,n,i; ll dp[maxn],a[maxn],sum; int main() { t=read(); while (t--) { n=read(); for (i=1;i<=n;i++) { a[i]=read(); } sort(a+1,a+1+n); sum=0; for (i=1;i<=n;i+=2) sum+=(a[i+1]-a[i]); dp[4]=a[3]+a[4]-a[1]-a[2]; dp[6]=a[3]+a[5]+a[6]-a[1]-a[2]-a[4]; dp[8]=a[3]-a[2]+a[4]-a[1]+a[7]-a[6]+a[8]-a[5]; for (i=10;i<=n;i+=2) { dp[i]=min(dp[i-6]+a[i]-a[i-2]+a[i-1]-a[i-4]+a[i-3]-a[i-5],dp[i-4]+a[i]-a[i-2]+a[i-1]-a[i-3]); } cout<<sum+dp[n]<<endl; } return 0; }
G
list的神奇应用,在进行把一个点集都并在另一个点集的操作的时候,可以直接应用list里面的splice。

#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define debug freopen("r.txt","r",stdin) #define mp make_pair #define ri register int using namespace std; typedef long long ll; typedef pair<int, int> pii; const int maxn = 8e5+5; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 998244353; inline ll read(){ll s=0,w=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')w=-1;ch=getchar();} while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9') s=s*10+ch-'0',ch=getchar(); return s*w;} ll qpow(ll p,ll q){return (q&1?p:1)*(q?qpow(p*p%mod,q/2):1)%mod;} int f[maxn],t,i,n,m,x,y,q,u; int find(int x) { if (x!=f[x]) f[x]=find(f[x]); return f[x]; } list<int> G[maxn]; int main() { t=read(); while (t--) { n=read(),m=read(); for (i=0;i<n;i++) { f[i]=i; G[i].clear(); } while (m--) { x=read(),y=read(); G[x].push_back(y); G[y].push_back(x); } q=read(); while (q--) { u=read(); if (u!=find(u)) continue; list<int> s; for (auto v:G[u]) { x=find(v); if (x==u) continue; else f[x]=u; s.splice(s.end(),G[x]); } swap(s,G[u]); } for (i=0;i<n;i++) cout<<find(i)<<" "; cout<<endl; } return 0; }





