作业记录(正则表达式提取器&JSON提取器&断言&接口联系&json转Map获取关键字)
1.抓包获取登录、验证通过接口实现
要求:1、使用正则表达式提取器和JSON提取器实现关联;2、必须有断言
1.新增http请求:如下图
2.新增正则表达式提取器
3.新增json提取器
4.新增BeallShell断言
String message="${token}";
if(message == null){
Failure=true;
FailureMessage="断言失败";
}
else{
FailureMessage="断言成功";
}

5.新增JSON断言

6.新增响应断言,检查响应文本是否有token

执行结果:

2.swagerui的接口通过jmeter 完成所有接口的串联(必做)
2.1上传文件接口
2.1.1新增http请求,举例上传图片
对POST使用multipart / form-data,这个选项要勾上(使用multipart选项)//这个现在选不选,都能成功。
文件名称:文件绝对路径+文件名
参数名称:file
mime类型:image/jpeg
注:mime类型需要根据当前文件类型,填写相应的值。

【高级】页签,【实现】改为java


2.通过【姓名、分数、学号】查询学生信息
第一种:在【查询所有学生接口】中,添加BellShell后置处理器,如下图
2.2.2.2.添加【通过name查询学生信息】接口
姓名路径:/findStudentByName/${myname}
分数路径:/findStudentByScore/${myscore}




2:下面都是直接输入值来查询的
2.2、通过姓名查询学生信息
直接输入name值:接口地址:http://localhost:8090/findStudentByName/xiaoqiang


2.3通过分数查询学生信息
直接输入分数,接口地址:http://localhost:8090/findStudentByScore/90


2.4通过学号查询学生信息
接口地址:http://localhost:8090/findStudentByStudentId/002


2.5新增学生
接口地址:http://localhost:8090/studentAdd
{
"className": "3.9",
"courseName": "shuxue",
"email": "huhu@qq.com",
"name": "huhu",
"score": 100,
"sex": "man",
"studentId": "string"
}



2.6通过ID删除一个学生


2.7通过ID查找一个学生信息(studentFindById)
接口地址:http://localhost:8090/studentFindById?id=001


2.8通过ID查找一个学生信息(/studentFindOne/{id})
接口地址:http://localhost:8090/studentFindOne/26


2.9修改学生信息(待做)
2.10查询所有学生
接口地址:http://localhost:8090/students


3.1json转Map获取关键字

代码:
public void testDatezuoye() {
String json="{\"code\":1,\"msg\":\"success\",\"data\":{\"name\":\"pig\",\"age\":\"18\",\"sex\":\"man\",\"hometown\":{\"province\":\"江西省\",\"city\":\"抚州市\",\"county\":\"崇仁县\"}}}";
Map<String,String> parseObject= JSON.parseObject(json,Map.class);
//获取data节点
String data=String.valueOf(parseObject.get("data"));
//获取data集合
Map dataMap = JSON.parseObject(data,Map.class);
//获取hometown集合
Map hometownMap = (Map)dataMap.get("hometown");
//获取province节点
Object province = hometownMap.get("province");
System.out.println(province);
}
3.2关键字对比实现,判断返回的JSON是否相同

代码如下:
public class JsonMapzuoye {
//判断两个json是否相等
//actual是预期结果,expected是实际结果
public static Boolean isTrue(Object actual,Object expected){
Boolean flag;//定义一个flag变量,类型是boolen,返回值是true或false
if (actual instanceof String){
flag=((String) actual).equals(((String) expected));
//八种基本数据类型分别是:1、4种整数类型(byte、short、int、long);2、2种浮点类型(float、double);
// 3、1种字符类型“char”;4、1种布尔类型“boolean”。
} else if (actual instanceof Boolean){
flag=((Boolean) actual).equals(((Boolean) expected));
} else if (actual instanceof Byte){
flag=((Byte) actual).equals(((Byte) expected));
} else if (actual instanceof Short){
flag=((Short) actual).equals(((Short) expected));
} else if (actual instanceof Integer){
flag=((Integer) actual).equals(((Integer) expected));
} else if (actual instanceof Long){
flag=((Long) actual).equals(((Long) expected));
} else if (actual instanceof Float){
flag=((Float) actual).equals(((Float) expected));
} else if (actual instanceof Double){
flag=((Double) actual).equals(((Double) expected));
} else if (actual instanceof Character){
flag=((Character) actual).equals(((Character) expected));
} else{
JSONObject jsonObject1=JSONObject.parseObject(actual.toString());
JSONObject jsonObject2=JSONObject.parseObject(expected.toString());
String res1=jsonObject1.toString();
String res2=jsonObject2.toString();
flag=res1.equalsIgnoreCase(res2);
}
return flag;
}
//关键字对比
public static Boolean isEquals(Object actual,Object expected){
boolean flag = true;
Map<String,String> map1=JSONObject.parseObject(actual.toString(), Map.class);
Map<String,String> map2=JSONObject.parseObject(expected.toString(),Map.class);
for (Map.Entry< String,String>map:map1.entrySet()){
String key=map.getKey();
Object value1=map1.get(key);
Object value2=map2.get(key);
if(!isTrue(value1,value2)){
flag=false;
break;
}
}
return flag;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
String str1="{\"code\":1,\"msg\":\"success\",\"data\":{\"name\":\"pig\",\"age\":\"18\",\"sex\":\"man\",\"hometown\":{\"province\":\"江西省\",\"city\":\"抚州市\",\"county\":\"崇仁县\"}}}";
String str2="{\"code\":11,\"msg\":\"success\",\"data\":{\"name\":\"pig\",\"age\":\"18\",\"sex\":\"man\",\"hometown\":{\"province\":\"江西省\",\"city\":\"抚州市\",\"county\":\"崇仁县\"}}}";
System.out.println(isEquals(str1,str2));
}
}
课上案例练习:
1、jmeter【正则表达式提取器】
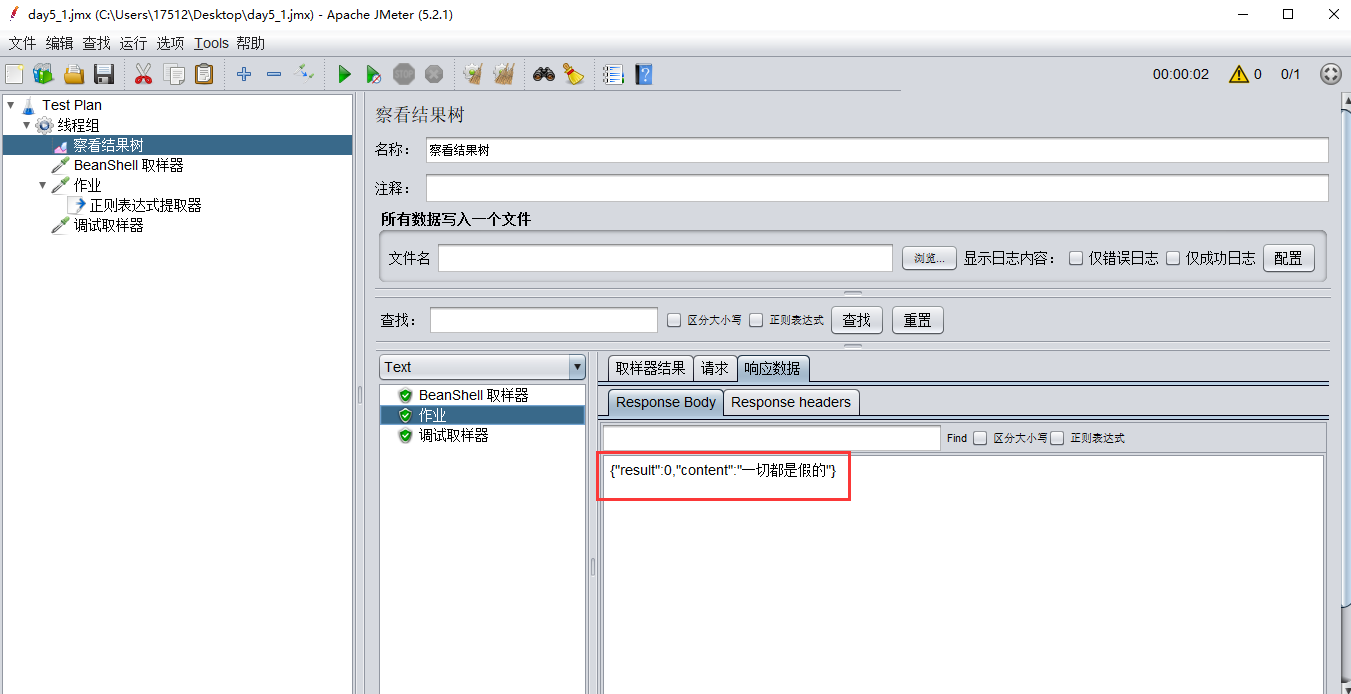
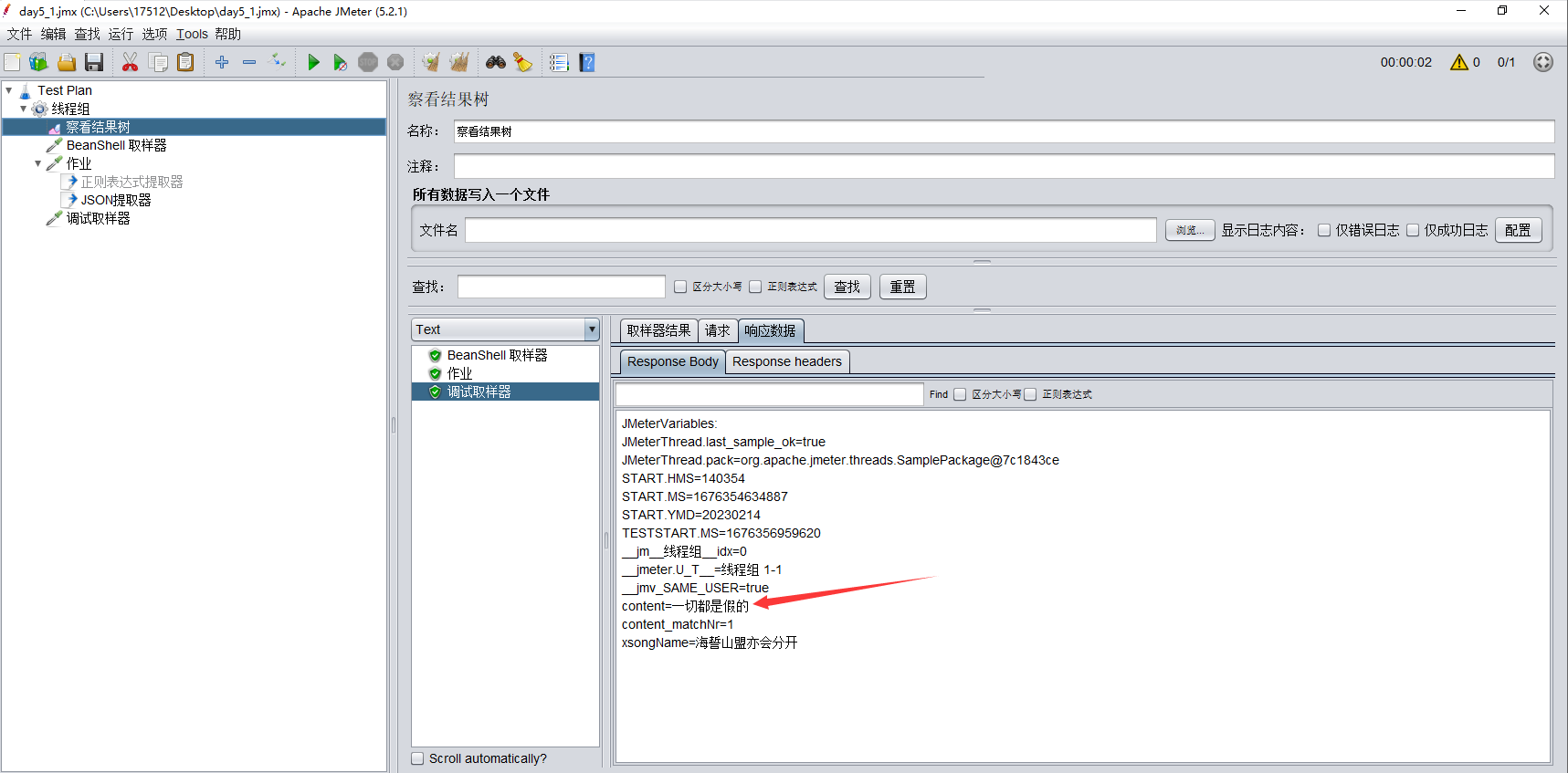
1.1例如下图http接口,执行后,返回信息是:{"result":0,"content":"一切都是假的"}
1.2作业右键菜单--【添加--后置处理器--正则表达式提取器】
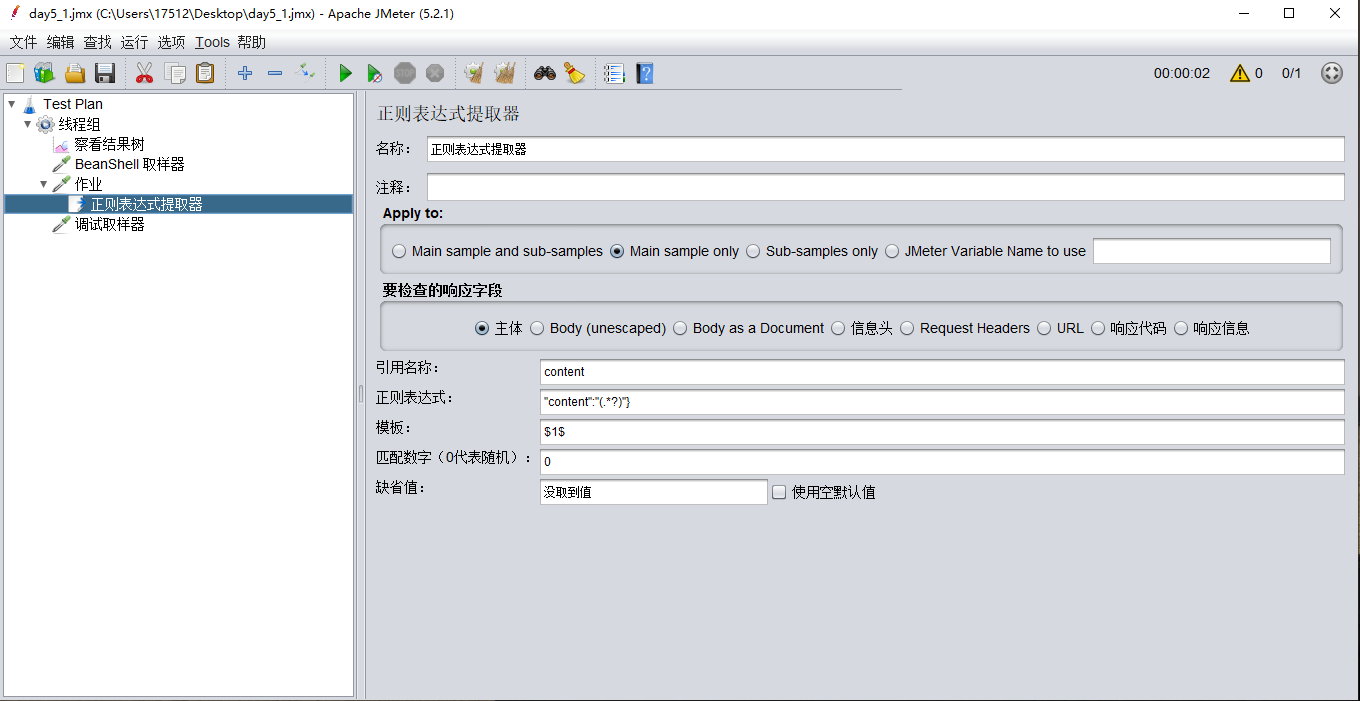
例如我们要取到content的值
引用名称:content
正则表达式:(.*?),把值前面的"content":"放在()括号前面,把"}放在括号后面,如下图。
模板:$1$
匹配数值:0(注:这里填1的话,是精准匹配,填0就是把所有可能的数据都返回出来,能更好的看到调试的结果)
缺省值:没有取到值
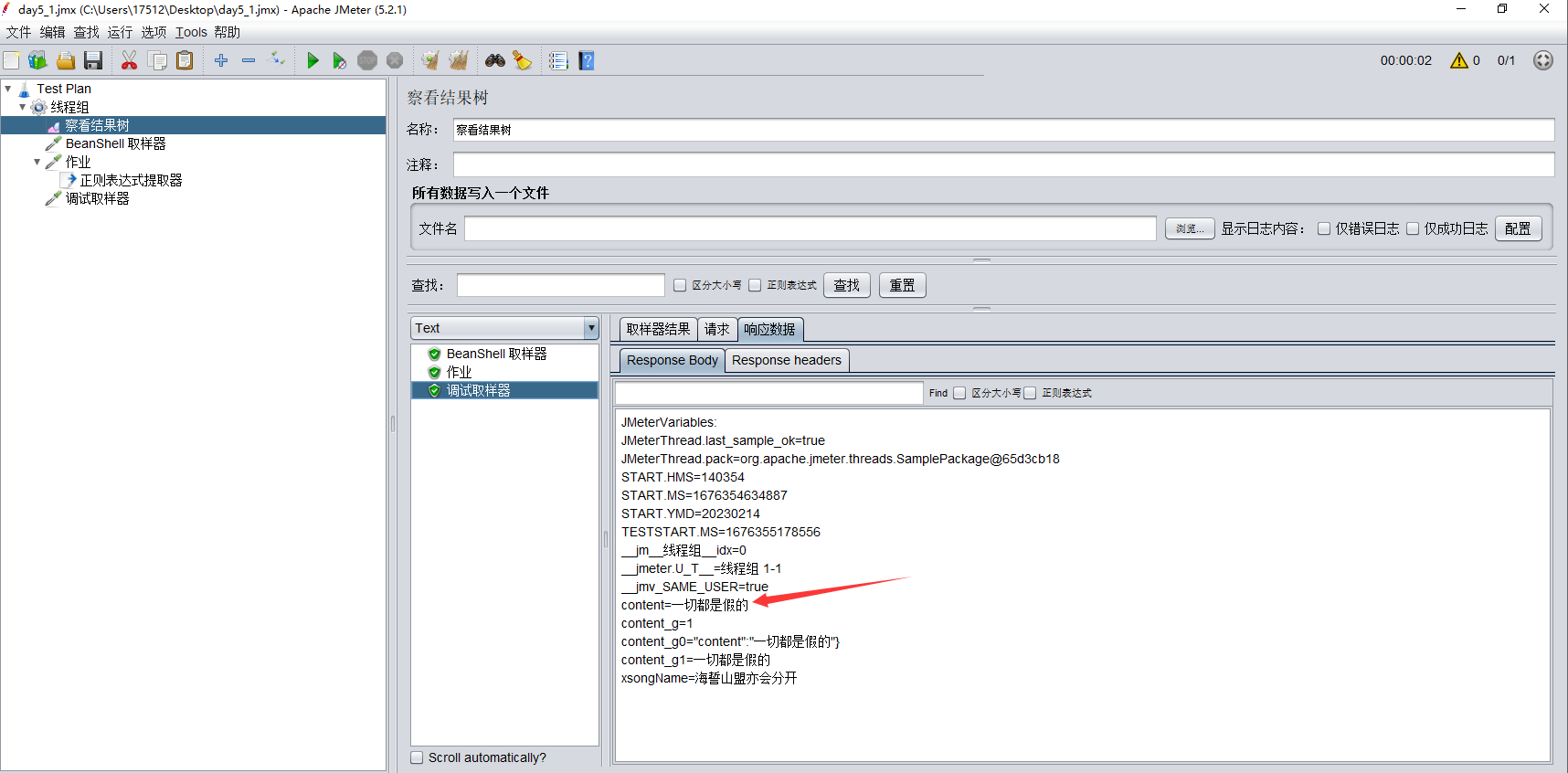
1.3添加【调试取样器】
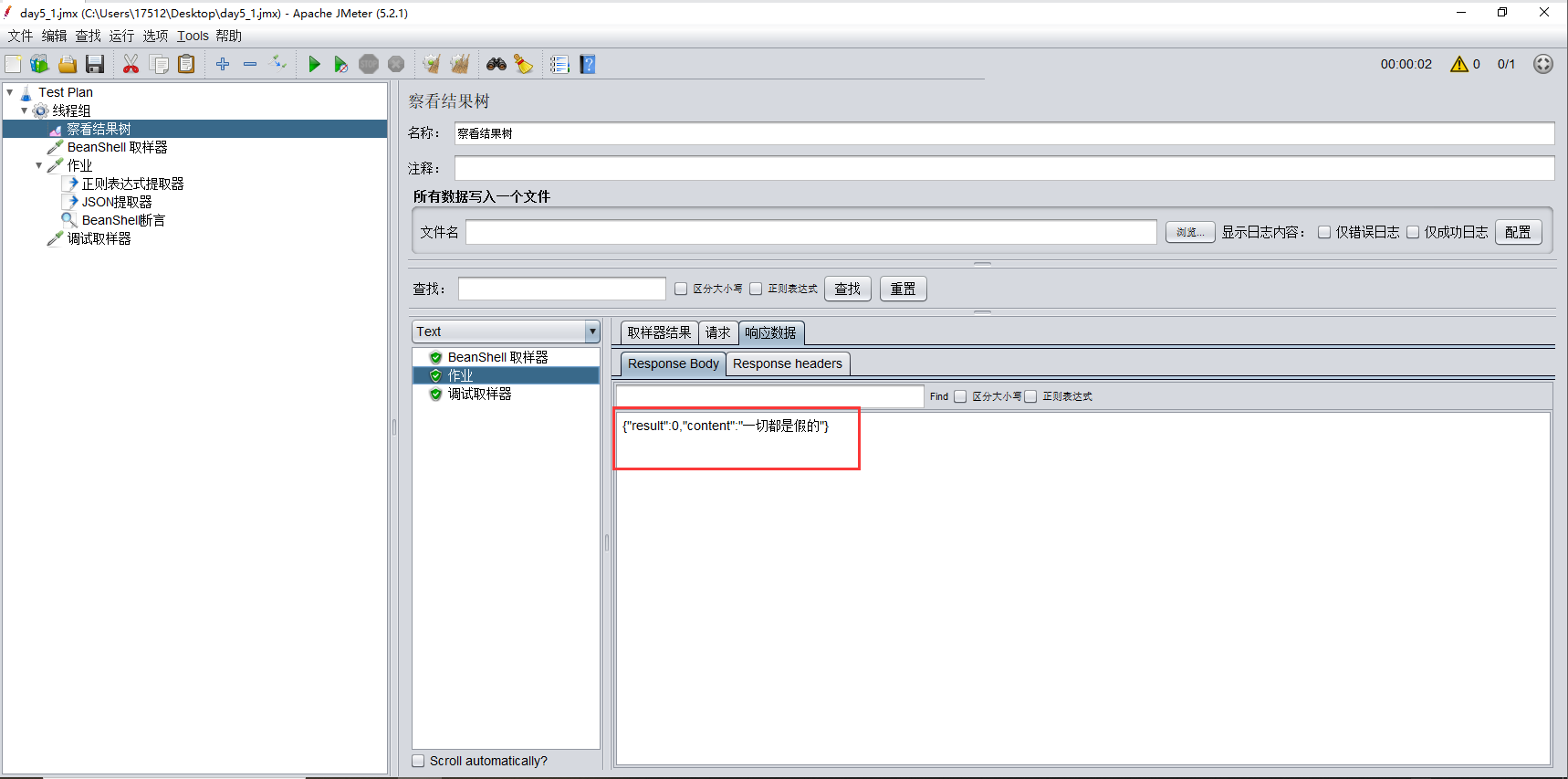
执行后,看到【察看结果树--调试取样器】中,content字段已经取到值了
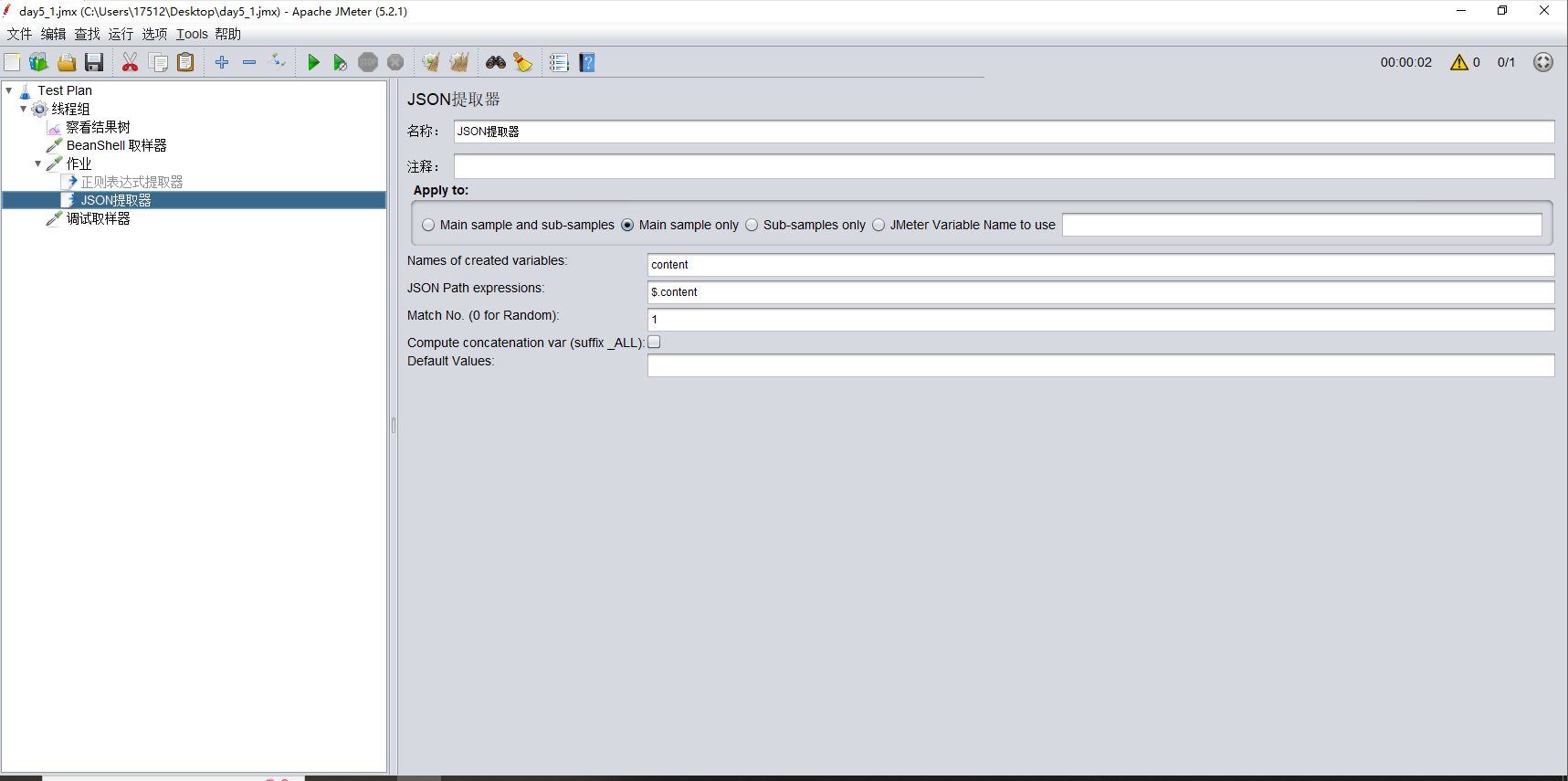
2.JSON提取器,配置如下图
$符号是对象的意思
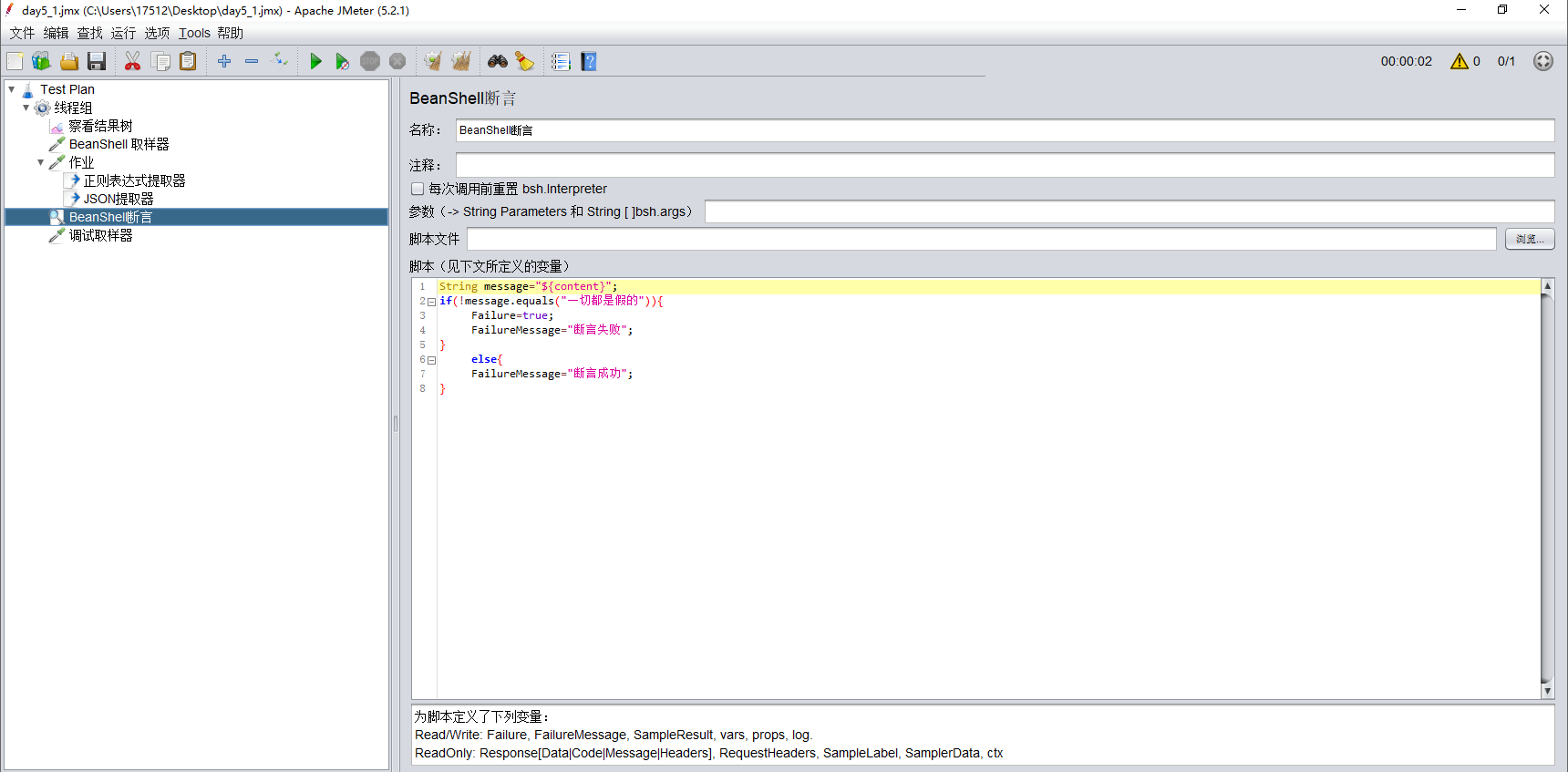
3、beanShell断言
String message="${content}";
if(!message.equals("一切都是假的")){
Failure=true;
FailureMessage="断言失败";
}
else{
FailureMessage="断言成功";
}
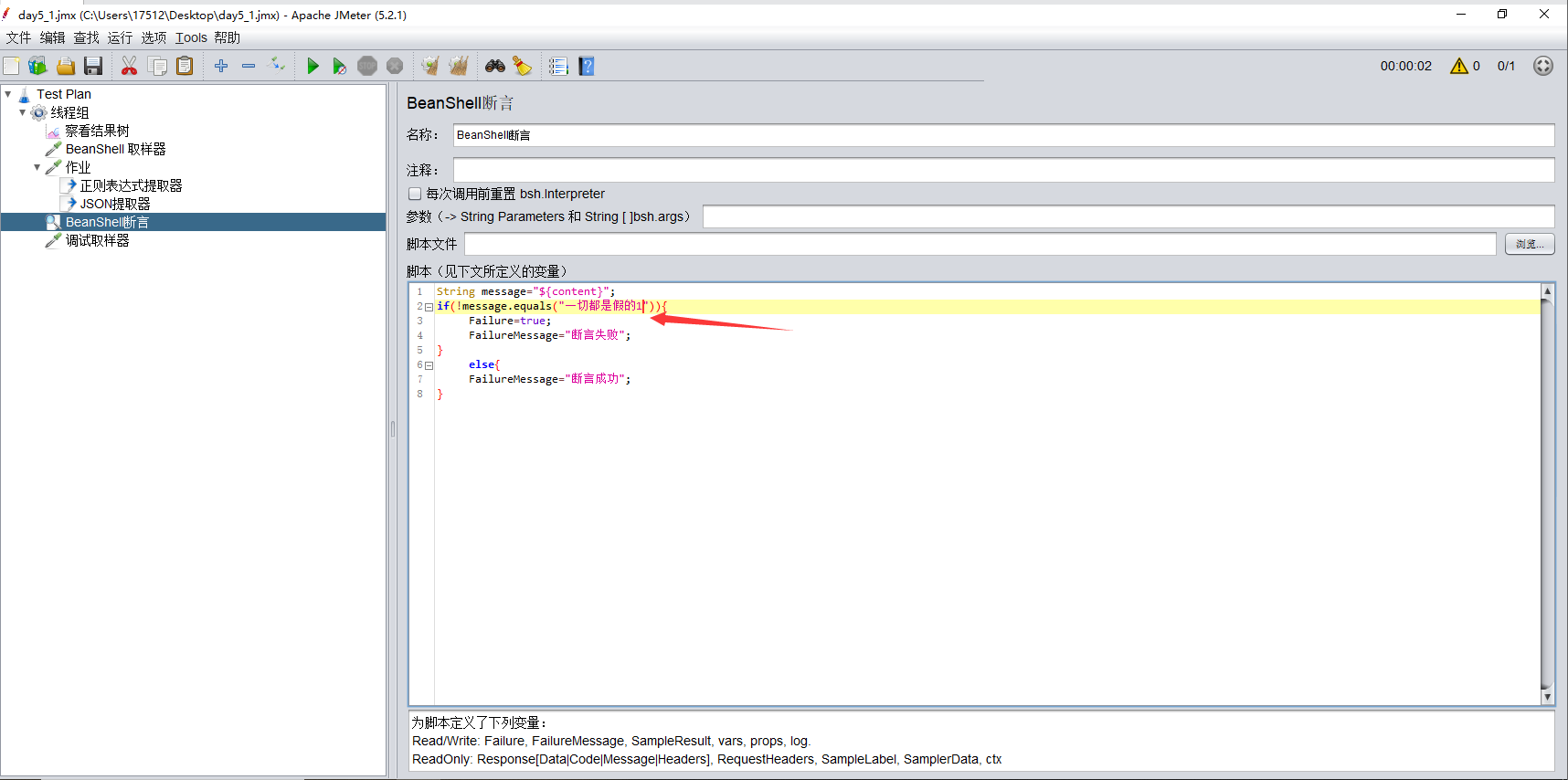
执行后,察看结果树没有报错就行
如下图:如果不一致,就返回断言失败
json转map获取关键字:
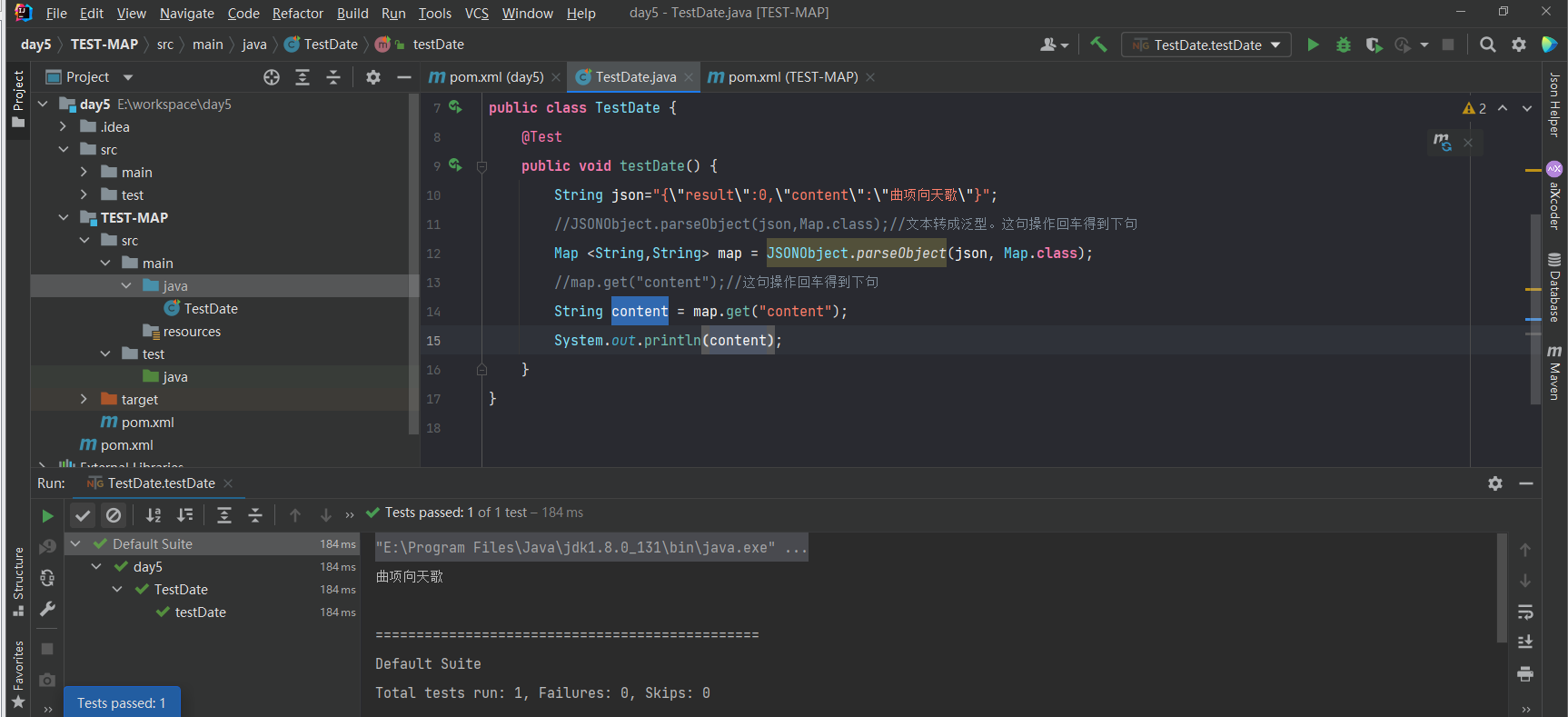
方法内代码如下:
public void testDate() {
String json="{\"result\":0,\"content\":\"曲项向天歌\"}";
//JSONObject.parseObject(json,Map.class);//文本转成泛型。这句操作回车得到下句
Map <String,String> map = JSONObject.parseObject(json, Map.class);
//map.get("content");
String content = map.get("content");
System.out.println(content);
关键字对比实现,判断返回的JSON是否相同
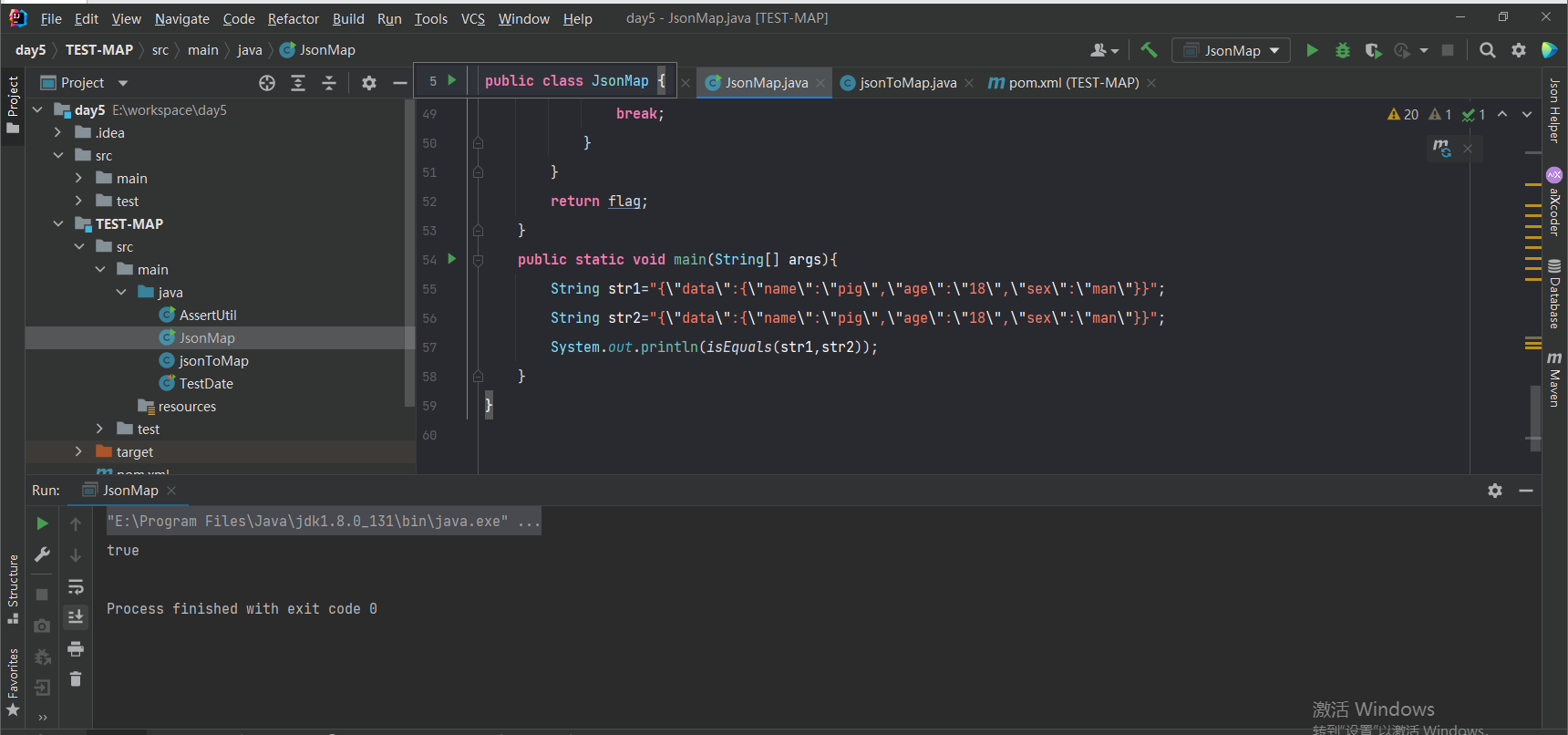
方法内代码如下:
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import java.util.Map;
public class JsonMap {
//判断两个json是否相等
//actual是预期结果,expected是实际结果
public static Boolean isTrue(Object actual,Object expected){
boolean flag;//定义一个flag变量,类型是boolen,返回值是true或false
if (actual instanceof String){
flag=((String) actual).equals(((String) expected));
//八种基本数据类型分别是:1、4种整数类型(byte、short、int、long);2、2种浮点类型(float、double);
// 3、1种字符类型“char”;4、1种布尔类型“boolean”。
} else if (actual instanceof Boolean){
flag=((Boolean) actual).equals(((Boolean) expected));
} else if (actual instanceof Byte){
flag=((Byte) actual).equals(((Byte) expected));
} else if (actual instanceof Short){
flag=((Short) actual).equals(((Short) expected));
} else if (actual instanceof Integer){
flag=((Integer) actual).equals(((Integer) expected));
} else if (actual instanceof Long){
flag=((Long) actual).equals(((Long) expected));
} else if (actual instanceof Float){
flag=((Float) actual).equals(((Float) expected));
} else if (actual instanceof Double){
flag=((Double) actual).equals(((Double) expected));
} else if (actual instanceof Character){
flag=((Character) actual).equals(((Character) expected));
} else{
JSONObject jsonObject1=JSONObject.parseObject(actual.toString());
JSONObject jsonObject2=JSONObject.parseObject(expected.toString());
String res1=jsonObject1.toString();
String res2=jsonObject2.toString();
flag=res1.equalsIgnoreCase(res2);
}
return flag;
}
//关键字对比
public static Boolean isEquals(Object actual,Object expected){
boolean flag = true;
Map<String,String> map1=JSONObject.parseObject(actual.toString(), Map.class);
Map<String,String> map2=JSONObject.parseObject(expected.toString(),Map.class);
for (Map.Entry< String,String>map:map1.entrySet()){
String key=map.getKey();
Object value1=map1.get(key);
Object value2=map2.get(key);
if(!isTrue(value1,value2)){
flag=false;
break;
}
}
return flag;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
String str1="{\"data\":{\"name\":\"pig\",\"age\":\"18\",\"sex\":\"man\"}}";
String str2="{\"data\":{\"name\":\"pig\",\"age\":\"18\",\"sex\":\"man\"}}";
System.out.println(isEquals(str1,str2));
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号