Chamber of Secrets 双端队列广搜BFS 与 SPFA两种解法
Chamber of Secrets
"The Chamber of Secrets has been opened again" — this news has spread all around Hogwarts and some of the students have been petrified due to seeing the basilisk. Dumbledore got fired and now Harry is trying to enter the Chamber of Secrets. These aren't good news for Lord Voldemort. The problem is, he doesn't want anybody to be able to enter the chamber. The Dark Lord is going to be busy sucking life out of Ginny.
The Chamber of Secrets is an n × m rectangular grid in which some of the cells are columns. A light ray (and a basilisk's gaze) passes through the columns without changing its direction. But with some spell we can make a column magic to reflect the light ray (or the gaze) in all four directions when it receives the ray. This is shown in the figure below.
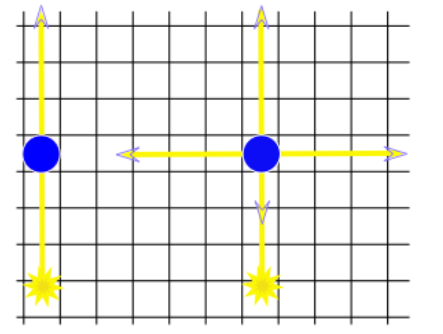
The left light ray passes through a regular column, and the right ray — through the magic column.
The basilisk is located at the right side of the lower right cell of the grid and is looking to the left (in the direction of the lower left cell). According to the legend, anyone who meets a basilisk's gaze directly dies immediately. But if someone meets a basilisk's gaze through a column, this person will get petrified. We know that the door to the Chamber is located on the left side of the upper left corner of the grid and anyone who wants to enter will look in the direction of its movement (in the direction of the upper right cell) from that position.
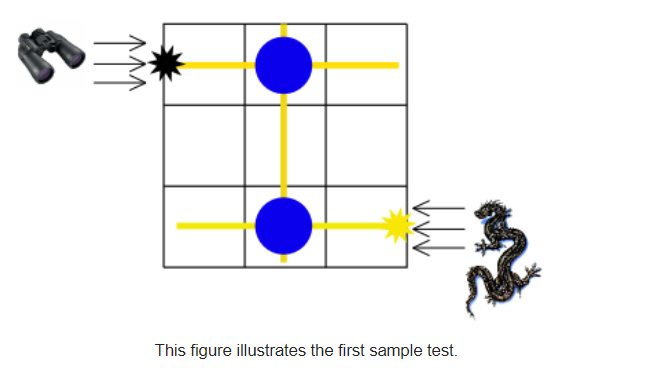
This figure illustrates the first sample test.
Given the dimensions of the chamber and the location of regular columns, Lord Voldemort has asked you to find the minimum number of columns that we need to make magic so that anyone who wants to enter the chamber would be petrified or just declare that it's impossible to secure the chamber.
Input
The first line of the input contains two integer numbers n and m (2 ≤ n, m ≤ 1000). Each of the next n lines contains m characters. Each character is either "." or "#" and represents one cell of the Chamber grid. It's "." if the corresponding cell is empty and "#" if it's a regular column.
Output
Print the minimum number of columns to make magic or -1 if it's impossible to do.
Examples
input
3 3
.#.
...
.#.
output
2
input
4 3
##.
...
.#.
.#.
output
2
Note
The figure above shows the first sample test. In the first sample we should make both columns magic. The dragon figure represents the basilisk and the binoculars represent the person who will enter the Chamber of secrets. The black star shows the place where the person will be petrified. Yellow lines represent basilisk gaze moving through columns.
题意:
给你一个 n * m 的无向图 ,一束激光从左上角(1,1) 向右出发 , 每经过一次 "#" ,你可以选择仍按原方向前进, 或者消耗一次代价,使他向任意方向反射, 问你是否能到达右下角(n,m)并向右射出,如果可以输出最小代价,否则输出-1
思路一:双端BFS
双端BFS适用于 边权为 0 或 1 的搜索, 此题比较有意思的是,我们要存一下,激光的方向.另外 开一个数组p[x][y][dir] 表示当前状态的代价,记得初始化为inf
用双端队列去存 当前激光所在坐标及方向 , 每当我们经过一次'#',我们可以选择操作他反射,并改变他的方向,并使他的 pnow = pfront + 1 ,入队要入尾;
当我们选择不操作他反射时,只需要更新 坐标信息 ,方向和代价均保持不变 ,入队要入头;
见代码
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
void IOS(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
}
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn=5e5+5;
const int inf =0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,m;
char ch[1005][1005];
int p[1005][1005][4];
int dx[4] = {0,1,-1,0};
int dy[4] = {1,0,0,-1};
struct node{
int x,y;
int dir;
// 0 右 1 下 2 上 3 左
}front,now;
bool check(int x,int y)
{
if(x >= 1 && x <= n && y >= 1 && y <= m)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
int bfs()
{
deque<node>dq;
dq.push_back({1,1,0});
p[1][1][0] = 0;
while(!dq.empty())
{
front = dq.front();
dq.pop_front();
int x = front.x;
int y = front.y;
if(x == n && y == m && front.dir == 0)
{
break;
}
if(x == n && y == m && ch[x][y] == '#' && front.dir != 0)
{
p[x][y][0] = p[x][y][front.dir] + 1;
break;
}
//把不操作的放在队首
int xx = x + dx[front.dir];
int yy = y + dy[front.dir];
if(check(xx,yy) && p[xx][yy][front.dir] == inf)
{
now.x = xx;
now.y = yy;
now.dir = front.dir;
p[xx][yy][now.dir] = p[x][y][front.dir];
dq.push_front(now);
}
//操作的放在队尾
if(ch[x][y] == '#')
{
for(int i = 0; i < 4 ; i ++)
{
int xx = x + dx[i];
int yy = y + dy[i];
if(check(xx,yy) && p[xx][yy][i] == inf)
{
now.x = xx;
now.y = yy;
now.dir = i;
p[xx][yy][now.dir] = p[x][y][front.dir] + 1;
dq.push_back(now);
}
}
}
}
if(p[n][m][0] == inf)
return -1;
else
return p[n][m][0];
}
int main(){
memset(p,inf,sizeof(p));
scanf("%d%d",&n , &m);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
{
scanf("%s",ch[i]+1);
}
int t = bfs();
printf("%d\n", t);
return 0;
}
思路二:SPFA() 最短路
以行和列建二分图,如果ch[i][j]=='#',则从i节点到j节点建一条双向边,权值都为1。然后对二分图跑一遍最短路。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
void IOS(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
}
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn=2e6+5;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,m,tol,head[maxn];
int p[maxn];
char ch[1005][1005];
struct node{
int to;
int cost;
int next;
}edge[maxn];
void add(int u,int v,int w)
{
edge[tol].to=v;
edge[tol].cost=w;
edge[tol].next=head[u];
head[u]=tol++;
}
int spfa(int s)
{
queue<int>q;
p[s] = 0;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty())
{
int v=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = head[v]; i != -1 ; i = edge[i].next)
{
node e = edge[i];
if(p[e.to] > p[v] + e.cost)
{
p[e.to] = p[v] + e.cost;
q.push(e.to);
}
}
}
if(p[n] == inf)
return -1;
else
return p[n];
}
int main(){
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
memset(p,inf,sizeof(p));
scanf("%d%d",&n , &m);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
{
scanf("%s",ch[i]+1);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= m ; j ++)
{
if(ch[i][j] == '#')
{
add(i,j+n,1);
add(j+n,i,1);
}
}
}
int t = spfa(1);
printf("%d\n", t);
return 0;
}

