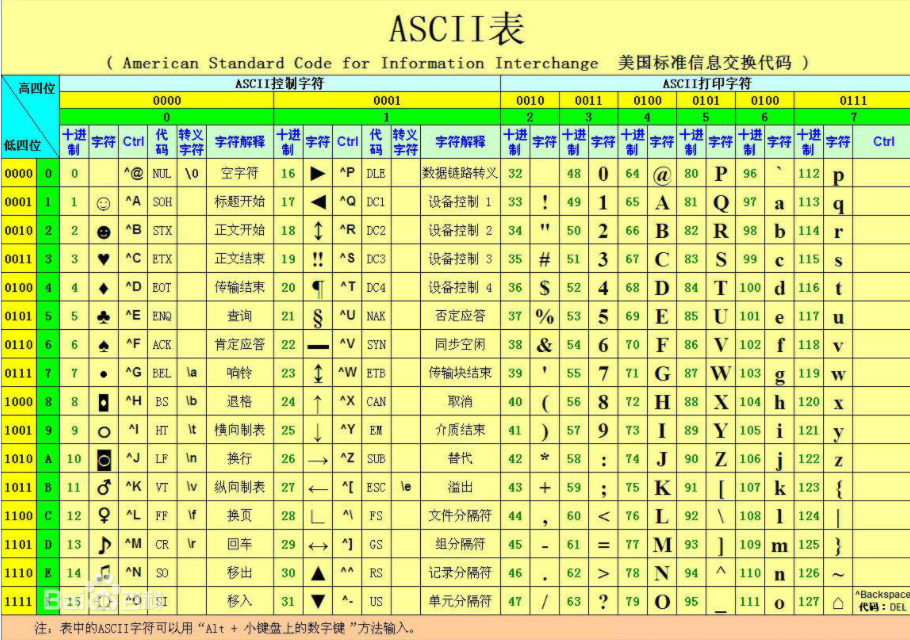
JavaSE01_Day01(中) -字符串常量池、字符串常用API(上)
一、字符串常量池
像周二课程中讲解的字符串创建对象的代码String str = "欢迎同学们来到达内学习!!!",此种创建对象的方式,就是通过字面量创建一个字符串对象,在内存中对于字符串对象进行存储时,JVM会在堆内存中维护一个区域(字符串常量池)进行存储。使用这种方式创建字符串对象可以很好的对于内存资源进行使用,避免多次创建字符串对象堆内存中开辟多块内存地址空间,从而可以避免资源的浪费。当使用这种方案创建字符串对象以后,如果再创建字符串对象的时候,会优先在字符串常量池中查找是否有可以进行复用的资源,如果有责不需要再次创建新的对象,从而达到节约内存资源的效果。

package cn.tedu.str;
/**
* 字符串常量池案例演示
* @author cjn
*/
public class StringDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* Sun公司官方推荐使用字面量的赋值方案对字符串对象进行赋值,
* 而不是推荐使用new运算符调用构造器
* 字面量(固定值)
* Java中的字面量:true、false、null
* 优点:可以复用字符串常量池中的对象,避免资源浪费
*/
String str1 = "123abc";
String str2 = "123abc";
//str1和str2引用是同一块内存地址空间,指向的是同一个对象
System.out.println(str1 == str2);//true
String str3 = "123abc";
//str2和str3引用是同一块内存地址空间,指向的是同一个对象
System.out.println(str2 == str3);//true
String str4 = new String("123abc");//new在堆内存中创建新对象
//str1和str4引用不是同一块内存地址空间,指向的不是同一个对象
System.out.println(str1 == str4);//false
//str4和str5引用不是同一块内存地址空间,指向的不是同一个对象
String str5 = new String("123abc");
System.out.println(str4 == str5);//flase
/*
* 如果希望进行比较两个对象的内容是否相等使用equals方法
* == 是比较两个对象的内存地址是否一致
*/
boolean b = str4.equals(str5);//比较内容
System.out.println(b);//true
}
}
测试结果:
true
true
false
false
true
字符串常见的面试题(背下来)
package cn.tedu.str;
/**
* 字符串常见的面试题案例
* @author cjn
*/
public class StringDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "123abc";
String str2 = "123abc";
//.java文件编译成.class字节码文件的时候会完成字符串拼接:String str3 = "123abc"
//注意:在Eclipse中,将编写后的代码保存后,即完成代码的编译,并不是运行之后才编译!!!
String str3 = "123" + "abc";
System.out.println(str3);//123abc
System.out.println(str1 == str3);//true
//创建一个新的字符串对象:字符串变量+字符串常量池内容--->新创建对象
str1 = str1 + "!!!";
str2 = str2 + "!!!";
//当修改了str2以后,不会影响str1打印的结果
System.out.println(str2);//123abc!!!
System.out.println(str1);//123abc!!!
System.out.println(str1 == str2);//false
String str4 = "123";
//创建了三个对象(之后才会讲),运行时会决定str4的值
String str5 = str4 + "abc";//只有到运行时,才会获取到str4中的内容
System.out.println(str5);//123abc
System.out.println(str1 == str5);//flase
/*
* 单引号和双引号的区别
*/
String str6 = '1' + 23 + "abc";//'1'对应ASCII编码:49
System.out.println(str6);//72abc
}
}
测试结果:
123abc
true
123abc!!!
123abc!!!
false
123abc
false
72abc
二、字符串常用API(上)
2.1获取字符串长度
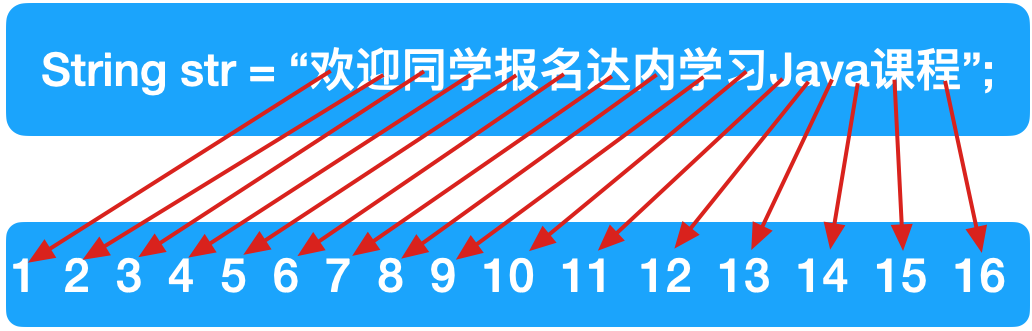
上面图示的数字并不表示下标,而是表示某一个字符是第多少个字符。
package cn.tedu.str;
/**
* 获取字符串长度案例
* length()方法,字符串对象调用length()方法,
* 实际是在对内部维护的字符数组进行取值数组长度
* @author cjn
*/
public class StrLengthDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "欢迎同学报名达内学习Java课程";
System.out.println(str.length());//16
}
}
2.2获取子字符串所在对应字符串的位置

package cn.tedu.str;
/**
* 查找给定子字符串所在当前字符串的位置
* indexOf(String str)
* 查找给定子字符串从给定位置之后出现在目标字符串的位置
* indexOf(String str,int fromIndex)
* 查找给定子字符串最后一次出现的位置
* lastindexOf(String str)
* 如果找到了需要查询的字符串,返回对应的索引位置,否则返回-1
* @author cjn
*/
public class StrIndexOfDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "thinking in java";
//查询给定字符串in第一次在目标字符串中出现的索引位置
int index = str.indexOf("in");
System.out.println("第一次找到in子串的位置索引为:"+index);//2
//从指定的位置(下标从0开始)开始进行查找字符串in出现在目标字符串中的索引位置
index = str.indexOf("in", 4);
System.out.println("从下标4开始找到in子串的位置索引为:"+index);//5
//查找给定字符串in最后一次在目标字符串中出现的索引位置
index = str.lastIndexOf("in");
System.out.println("从字符串最后开始找到in子串的位置索引为:"+index);//9
}
}
测试结果:
第一次找到in子串的位置索引为:2
从下标4开始找到in子串的位置索引为:5
从字符串最后开始找到in子串的位置索引为:9
2.3 从字符串中截取指定的内容
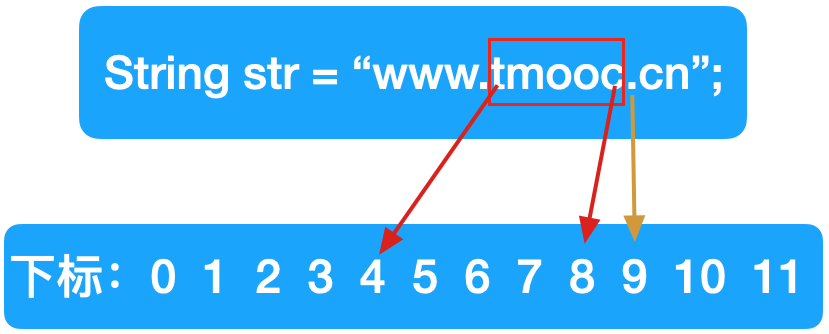
Sun公司规定:截取字符串的时候遵循留前不留后(留头不留尾、含头不含尾)
package cn.tedu.str;
/**
* 截取指定范围内字符串的内容
* substring(开始位置,结束位置)
* 截取原则:留前不留后
* @author cjn
*/
public class StrSubStringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "www.tmooc.cn";
System.out.println("截取前的字符串:"+str);
//截取域名中指定位置的字符串内容:tmooc
String subStr = str.substring(4, 9);
System.out.println("截取后的字符串:"+subStr);
//截取指定起始位置之后的字符串内容:tmooc.cn
subStr = str.substring(4);
System.out.println("截取后的字符串:"+subStr);
}
}
测试结果:
截取前的字符串:www.tmooc.cn
截取后的字符串:tmooc
截取后的字符串:tmooc.cn
2.4去除字符串左右的空格
package cn.tedu.str;
/**
* 字符串去除左右两侧空格案例
* trim()
* @author cjn
*/
public class StrTrimDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = " He llo Wo rld ";
System.out.println("|"+str+"|");
str = str.trim();
System.out.println("|"+str+"|");
//去除字符串中所有的空格内容,实质是字符串内容的替换
str = str.replaceAll(" ", "");
System.out.println("|"+str+"|");
}
}
测试结果:
| He llo Wo rld |
|He llo Wo rld|
|HelloWorld|


