BeanDefinition体系
1 介绍#
BeanDefinition是Spring中非常重要的一个概念。
在Spring启动时,会读取项目中依赖关系的配置(xml文件、groovy文件或注解),将这些依赖关系通过BeanDefinition进行缓存。
在实例化bean时,Spring容器会根据BeanDefinition中的信息进行创建对象、设置属性,也就是我们常说的控制反转(或者依赖注入)。
在缓存BeanDefinition后,实例化bean前,还可以通过BeanFactoryPostProcessor等方式对BeanDefinition进行修改,以此来增强功能(AOP就是通过类似方式实现的)。
因此,我们也可以从这个角度来理解Spring容器:配置文件→BeanDefinition→bean。
2 体系#
BeanDefinition定义了基础的getter/setter方法,用来获取和设置bean的信息。
AbstractBeanDefinition提取了bean的通用信息:
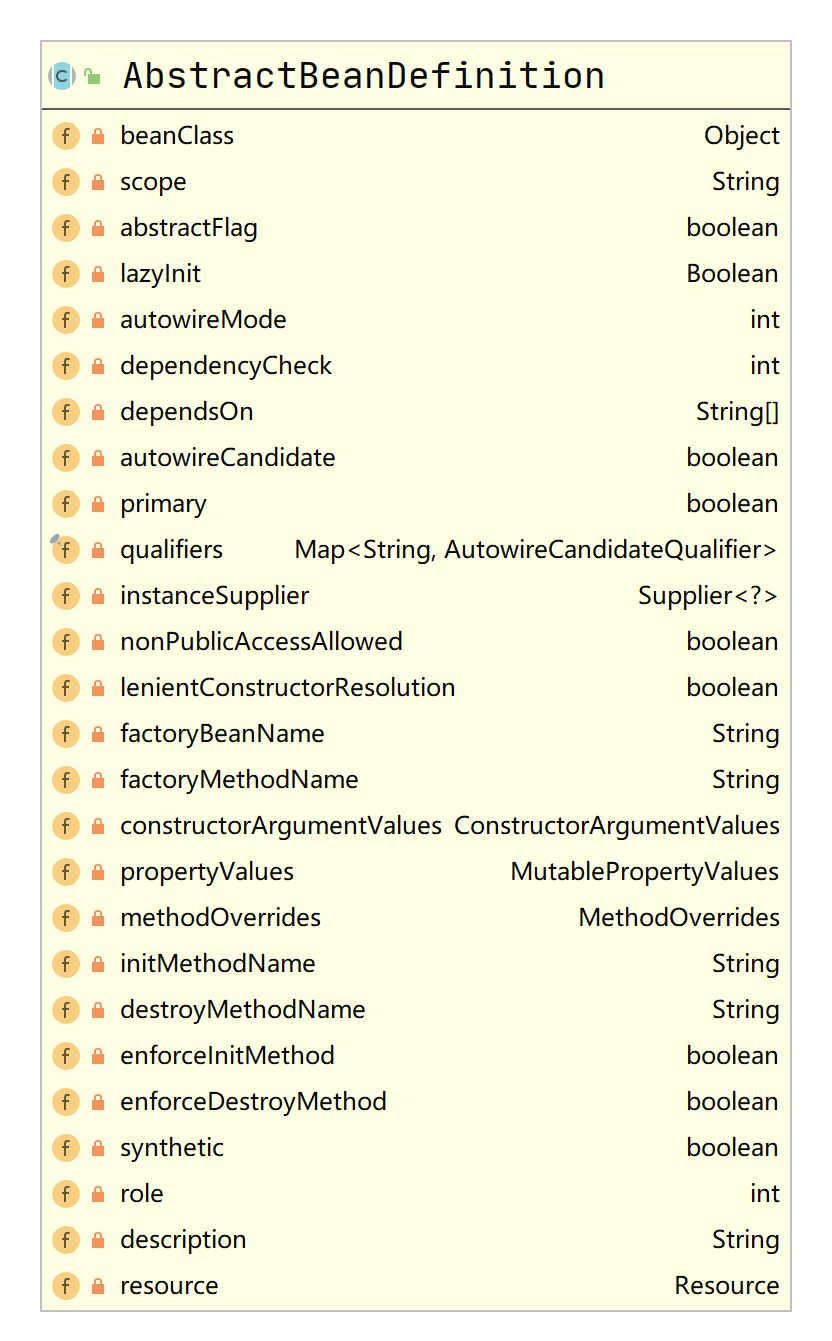
RootBeanDefinition保存了bean的完整信息以及实例化状态,Spring容器会根据RootBeanDefinition进行创建对象和设置属性:

Spring容器在读取xml文件、groovy文件和注解等配置信息时,会首先通过GenericBeanDefinition来保存,它主要在AbstractBeanDefinition的基础上定义了bean配置的父子关系:
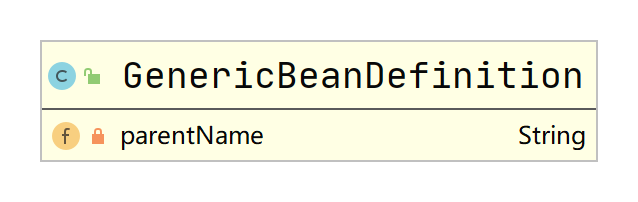
在Spring容器实例化bean时,会对GenericBeanDefinition进行一个merge操作,将其完整信息保存到RootBeanDefinition中进行后续实例化。
对于不同形式的配置文件,可能会使用对应的GenericBeanDefinition子类进行保存额外信息。例如,AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader用AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition保存,ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner使用ScannedGenericBeanDefinition保存。
3 典型使用#
3.1 AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader#
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader在注册类对象时,会创建AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition对象保存依赖关系。
AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader#doRegisterBean():
private <T> void doRegisterBean(Class<T> beanClass,
@Nullable String name,
@Nullable Class<? extends Annotation>[] qualifiers,
@Nullable Supplier<T> supplier,
@Nullable BeanDefinitionCustomizer[] customizers) {
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition abd = new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(beanClass);
if (this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(abd.getMetadata())) {
return;
}
abd.setInstanceSupplier(supplier);
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(abd);
abd.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = (name != null ? name : this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(abd, this.registry));
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(abd);
if (qualifiers != null) {
for (Class<? extends Annotation> qualifier : qualifiers) {
if (Primary.class == qualifier) {
abd.setPrimary(true);
}
else if (Lazy.class == qualifier) {
abd.setLazyInit(true);
}
else {
abd.addQualifier(new AutowireCandidateQualifier(qualifier));
}
}
}
if (customizers != null) {
for (BeanDefinitionCustomizer customizer : customizers) {
customizer.customize(abd);
}
}
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(abd, beanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
3.2 ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner#
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner在注册类对象时,会创建ScannedGenericBeanDefinition对象保存依赖关系。
ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider#scanCandidateComponents():
private Set<BeanDefinition> scanCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>();
try {
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX +
resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + '/' + this.resourcePattern;
Resource[] resources = getResourcePatternResolver().getResources(packageSearchPath);
boolean traceEnabled = logger.isTraceEnabled();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
for (Resource resource : resources) {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Scanning " + resource);
}
try {
MetadataReader metadataReader = getMetadataReaderFactory().getMetadataReader(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) {
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader);
sbd.setSource(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Identified candidate component class: " + resource);
}
candidates.add(sbd);
}
else {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Ignored because not a concrete top-level class: " + resource);
}
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not matching any filter: " + resource);
}
}
}
catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored non-readable " + resource + ": " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to read candidate component class: " + resource, ex);
}
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("I/O failure during classpath scanning", ex);
}
return candidates;
}
3.3 AbstractBeanFactory#
AbstractBeanFactory在实例化bean时,首先会将GenericBeanDefinition合并成RootBeanDefinition。
AbstractBeanFactory#getMergedBeanDefinition():
protected RootBeanDefinition getMergedBeanDefinition(
String beanName, BeanDefinition bd, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBd)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
synchronized (this.mergedBeanDefinitions) {
RootBeanDefinition mbd = null;
RootBeanDefinition previous = null;
// Check with full lock now in order to enforce the same merged instance.
if (containingBd == null) {
mbd = this.mergedBeanDefinitions.get(beanName);
}
if (mbd == null || mbd.stale) {
previous = mbd;
if (bd.getParentName() == null) {
// Use copy of given root bean definition.
if (bd instanceof RootBeanDefinition) {
mbd = ((RootBeanDefinition) bd).cloneBeanDefinition();
}
else {
mbd = new RootBeanDefinition(bd);
}
}
else {
// Child bean definition: needs to be merged with parent.
BeanDefinition pbd;
try {
String parentBeanName = transformedBeanName(bd.getParentName());
if (!beanName.equals(parentBeanName)) {
pbd = getMergedBeanDefinition(parentBeanName);
}
else {
BeanFactory parent = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parent instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory) {
pbd = ((ConfigurableBeanFactory) parent).getMergedBeanDefinition(parentBeanName);
}
else {
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(parentBeanName,
"Parent name '" + parentBeanName + "' is equal to bean name '" + beanName +
"': cannot be resolved without a ConfigurableBeanFactory parent");
}
}
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(bd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Could not resolve parent bean definition '" + bd.getParentName() + "'", ex);
}
// Deep copy with overridden values.
mbd = new RootBeanDefinition(pbd);
mbd.overrideFrom(bd);
}
// Set default singleton scope, if not configured before.
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(mbd.getScope())) {
mbd.setScope(SCOPE_SINGLETON);
}
// A bean contained in a non-singleton bean cannot be a singleton itself.
// Let's correct this on the fly here, since this might be the result of // parent-child merging for the outer bean, in which case the original inner bean // definition will not have inherited the merged outer bean's singleton status. if (containingBd != null && !containingBd.isSingleton() && mbd.isSingleton()) {
mbd.setScope(containingBd.getScope());
}
// Cache the merged bean definition for the time being
// (it might still get re-merged later on in order to pick up metadata changes) if (containingBd == null && isCacheBeanMetadata()) {
this.mergedBeanDefinitions.put(beanName, mbd);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
copyRelevantMergedBeanDefinitionCaches(previous, mbd);
}
return mbd;
}
}



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· DeepSeek在M芯片Mac上本地化部署
· 葡萄城 AI 搜索升级:DeepSeek 加持,客户体验更智能