Environment体系介绍
1 介绍#
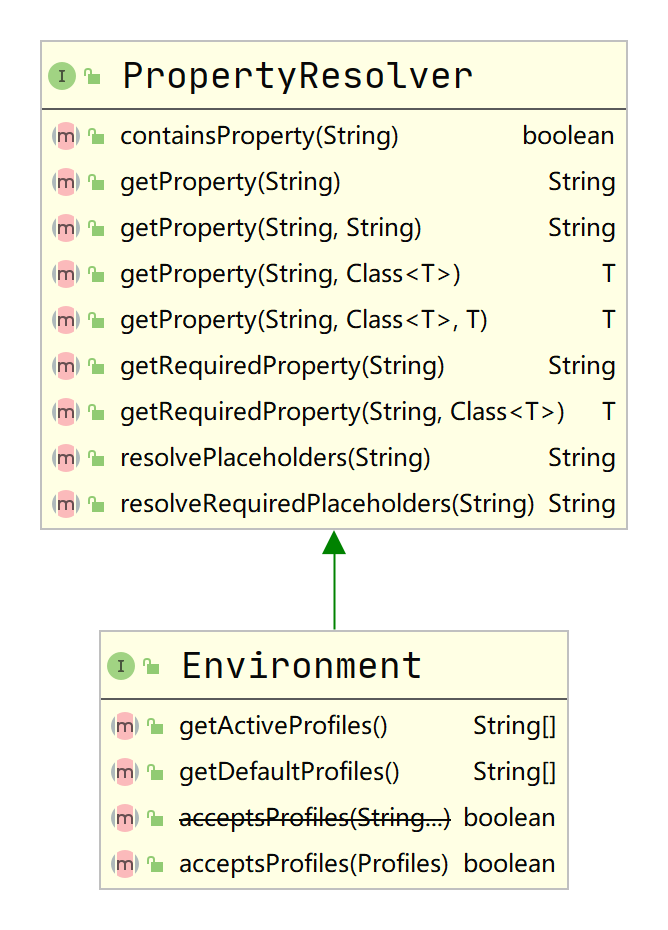
Environment接口表示当前应用的运行时环境,包括profiles环境和properties环境。
profiles是对BeanDefinition逻辑上的分组,每个bean都可以通过@Provile注解指定它所属的profile。在Spring容器注册BeanDefinition时,只会注册当前运行时环境激活的profiles的bean。
properties环境包括propertis文件、JVM变量、系统环境变量、JNDI和servlet上下文参数等。
PropertyResolver提供了对properties环境的操作,Environment接口提供了对profiles环境的操作。
在ApplicationContext实现类作为容器时,可以实现EnvironmentAware接口获取运行时环境:
@Component
public class ComponentA implements EnvironmentAware {
private Environment environment;
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
}
}
这是因为AplicationContext实现类在postProcessBeforeInitialization()阶段,会通过ApplicationContextAwareProcessor#invokeAwareInterfaces()方法执行XxxAware#setXxx()方法:
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
// ……省略
}
也可以通过@Autowired或@Resource直接从AplicationContext中获取environment:
@Component
public class ComponentA implements EnvironmentAware {
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
}
通常不建议直接在应用层使用environment,推荐使用${...}直接引入对应的值:
@Component
public class ComponentA {
@Value("${java.runtime.name}")
private String runtimeName;
}
${...}需要PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer的支持,在Spring Boot中通常会帮我们默认引入:
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public static PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer propertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer() {
return new PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer();
}
}
ConfigurableEnvironment提供了管理profiles和properties环境的基本方法。
在AbstractEnvironment中实现了对profiles和properties环境的基本操作,并通过customizePropertySources()方法使子类可以添加额外自定义配置文件。
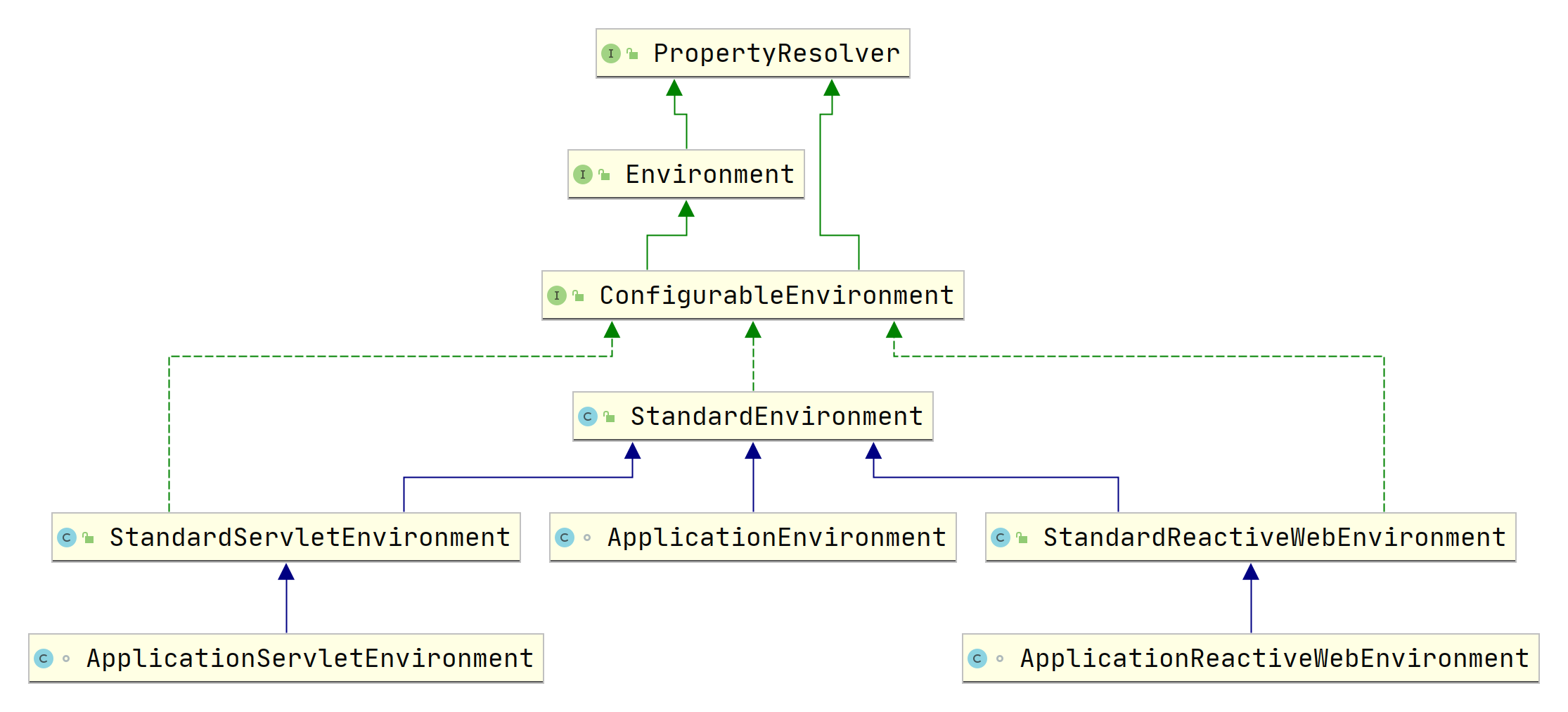
StandardEnvironment、StandardServletEnvironment和StandardReactiveWebEnvironment是Spring为standard应用、Servlet Web应用和Reactive Web应用提供的运行时环境,我们可以根据项目实际情况进行选择。
ApplicationEnvironment、ApplicationServletEnvironment和ApplicationReactiveWebEnvironment则是Spring Boot内置的实现类,专门用于SpringApplication。
2 AbstractEnvironment#
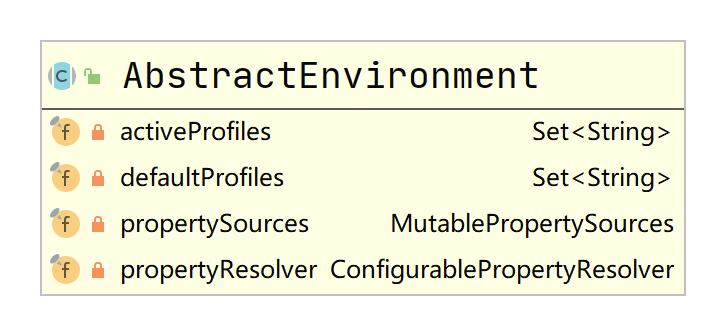
AbstractEnvironment的propetySources保存了配置文件的信息,通过propertyResolver可以从配置文件中获取指定属性值。activeProfiles和defaultProfiles则起着缓存对应配置的作用。
AbstractEnvironment的核心在于它的构造函数,子类在初始化时都会调用这些构造函数进行默认处理。
无参构造函数:
public AbstractEnvironment() {
this(new MutablePropertySources());
}
有参构造函数:
protected AbstractEnvironment(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
this.propertySources = propertySources;
this.propertyResolver = createPropertyResolver(propertySources);
customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}
子类可以通过AbstractEnvironment#customizePropertySources()方法用来添加配置文件:
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
}
在获取配置时,会使用propertyResolver读取配置文件,例如:
public String getProperty(String key) {
return this.propertyResolver.getProperty(key);
}
在获取profiles信息时,则会进行缓存处理,例如:
protected Set<String> doGetActiveProfiles() {
synchronized (this.activeProfiles) {
if (this.activeProfiles.isEmpty()) {
String profiles = doGetActiveProfilesProperty();
if (StringUtils.hasText(profiles)) {
setActiveProfiles(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(
StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(profiles)));
}
}
return this.activeProfiles;
}
}
AbstractEnvironment#getSystemProperties()方法可以获取系统配置信息:
public Map<String, Object> getSystemProperties() {
try {
return (Map) System.getProperties();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
return (Map) new ReadOnlySystemAttributesMap() {
@Override
@Nullable
protected String getSystemAttribute(String attributeName) {
try {
return System.getProperty(attributeName);
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
return null;
}
}
};
}
}
AbstractEnvironment#getSystemEnvironment()方法可以获取系统环境信息:
public Map<String, Object> getSystemEnvironment() {
if (suppressGetenvAccess()) {
return Collections.emptyMap();
}
try {
return (Map) System.getenv();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
return (Map) new ReadOnlySystemAttributesMap() {
@Override
@Nullable
protected String getSystemAttribute(String attributeName) {
try {
return System.getenv(attributeName);
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
return null;
}
}
};
}
}
3 StandardEnvironment#
StandardEnvironment通过customizePropertySources()方法添加了systemEnvironment和systemProperties环境变量:
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(
new PropertiesPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
propertySources.addLast(
new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}
3.1 StandardServletEnvironment#
StandardServletEnvironment通过customizePropertySources()方法添加了servletConfigInitParams、servletContextInitParams和jndiProperties配置文件:
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
if (jndiPresent && JndiLocatorDelegate.isDefaultJndiEnvironmentAvailable()) {
propertySources.addLast(new JndiPropertySource(JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
}
super.customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}
3.2 StandardReactiveWebEnvironment#
StandardReactiveWebEnvironment使用着StandardEnvironment原本的功能:
public class StandardReactiveWebEnvironment extends StandardEnvironment implements ConfigurableReactiveWebEnvironment {
public StandardReactiveWebEnvironment() {
super();
}
protected StandardReactiveWebEnvironment(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
super(propertySources);
}
}
3.3 ApplicationXxxEnvironment#
ApplicationEnvironment、ApplicationServletEnvironment和ApplicationReactiveEnvironment除了继承对应StandardXxxEnvironment的功能外,主要的变化是重写了createPropertyResolver()方法,使用ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertyResolver对象作为propertyResolver:
protected ConfigurablePropertyResolver createPropertyResolver(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
return ConfigurationPropertySources.createPropertyResolver(propertySources);
}
4 典型案例#
4.1 ConditionEvaluator#
在AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader或ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner中初始化conditionEvaluator时,都会创建environment对象:
private static Environment getOrCreateEnvironment(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
if (registry instanceof EnvironmentCapable) {
return ((EnvironmentCapable) registry).getEnvironment();
}
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
4.2 ApplicationContext#
AbstractApplicationContext提供了createEnvironment()方法,不同子类可能有不同的实现。
AbstractApplicationContext#createEnvironment():
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext#createEnvironment():
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
}
AnnotationConfigReactiveWebApplicationContext#createEnvironment():
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
return new StandardReactiveWebEnvironment();
}
GenericReactiveWebApplicationContext#createEnvironment():
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
return new StandardReactiveWebEnvironment();
}
GenericWebApplicationContext#createEnvironment():
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
}
StaticWebApplicationContext#createEnvironment():
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
}
4.3 SpringApplication#
SpringApplication是Spring Boot的启动类,它会使用SpringApplication#prepareEnvironment()方法创建environment:
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// 根据webApplicationType创建不同类型的environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 设置conversionService,根据args修改propertySources和profiles
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// 添加configurationProperties配置
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 执行监听器:添加额外配置文件
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
// 将defaultProperties配置移到末尾
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
Assert.state(!environment.containsProperty("spring.main.environment-prefix"),
"Environment prefix cannot be set via properties.");
// 将environment绑定到SpringApplication中
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = convertEnvironment(environment);
}
// 将configurationProperties配置移到首位
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
SpringApplication#getOrCreateEnvironment()会根据webApplicationType创建不同的Environment对象:
private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() {
if (this.environment != null) {
return this.environment;
}
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
return new ApplicationServletEnvironment();
case REACTIVE:
return new ApplicationReactiveWebEnvironment();
default:
return new ApplicationEnvironment();
}
}
listeners.environmentPrepared()方法会调用到EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener#onApplicationEvent()方法,进行不同阶段的处理:
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
// 准备阶段
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
// 准备完成
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent();
}
// 失败
if (event instanceof ApplicationFailedEvent) {
onApplicationFailedEvent();
}
}
在准备阶段,会调用不同的EnvironmentPostProcessor的postProcessEnvironment()方法进行处理:
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = event.getEnvironment();
SpringApplication application = event.getSpringApplication();
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : getEnvironmentPostProcessors(application.getResourceLoader(),
event.getBootstrapContext())) {
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(environment, application);
}
}
其中,ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor会获取application.properties等的信息。



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· DeepSeek在M芯片Mac上本地化部署
· 葡萄城 AI 搜索升级:DeepSeek 加持,客户体验更智能