RequestMappingHandlerMapping的请求地址映射流程
上篇文章里,我们讲解了RequestMappingHandlerMapping请求地址映射的初始化流程,理解了@Controller和@RequestMapping是如何被加载到缓存中的。
今天我们来进一步学习,在接收到请求时,RequestMappingHandlerMapping是如何进行请求地址映射的。
先放一个类图,在请求地址映射过程中,会依次执行到这些方法:
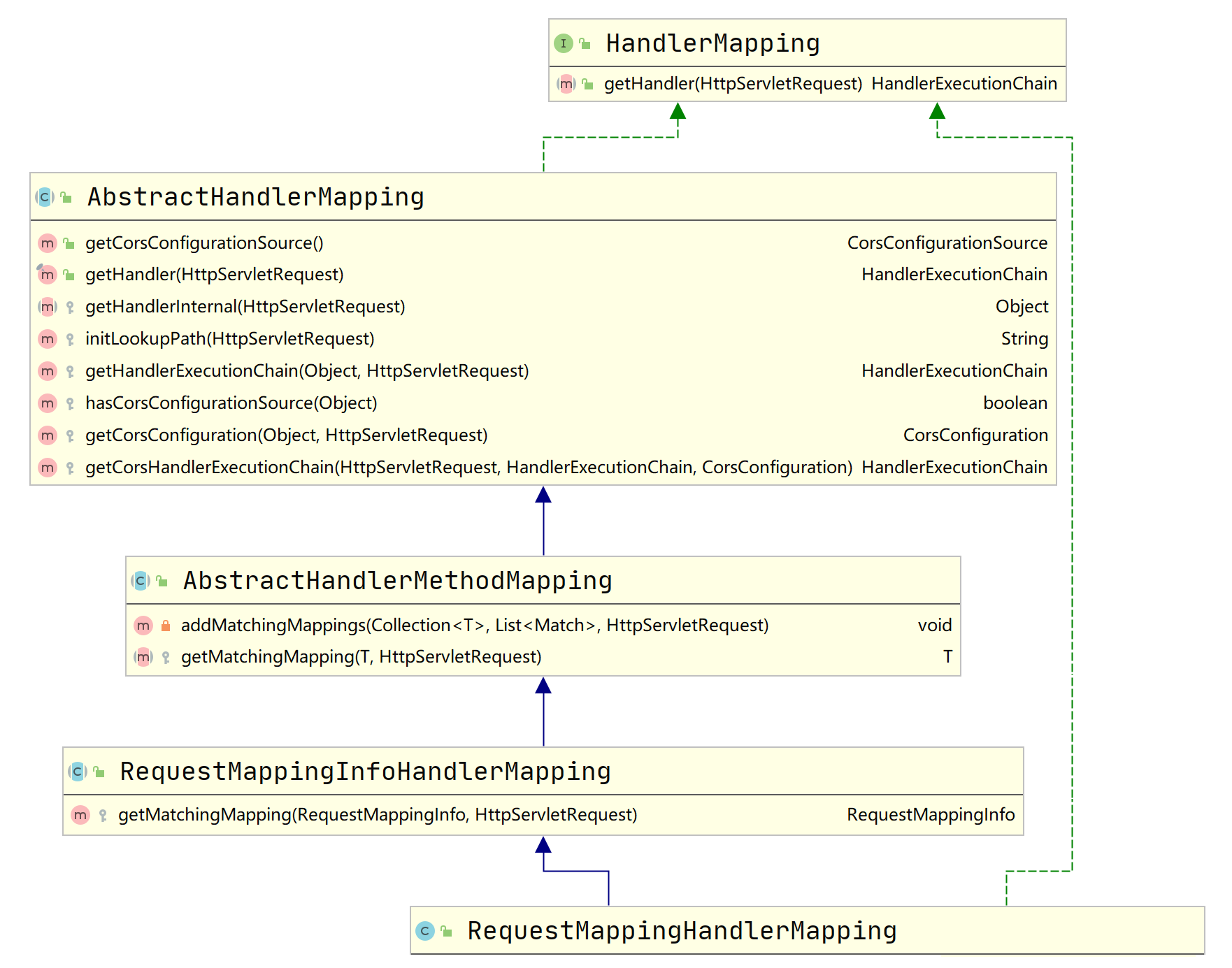
讲解之前,先总结RequestMappingHandlerMapping的请求地址映射流程:
- 获取
handler- 解析
request,获取请求路径path - 根据
path查找pathLookup缓存,获取路径匹配的RequestMappingInfo列表 - 对上述
RequestMappingInfo列表进行筛选,获取条件匹配的RequestMappingInfo列表 - 对上述
RequestMappingInfo列表进行排序,获取匹配度最高的RequestMappingInfo - 根据上述
RequestMappingInfo,获取对应MappingRegistration的HandlerMethod作为handler返回
- 解析
- 创建
HandlerExecutionChain对象 - 添加配置拦截器
- 添加跨域拦截器
1 HandlerMapping
首先,DispatcherServlet会调用HandlerMapping接口的getHandler()方法:
HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
这个方法主要起着规范的作用,DispatcherServlet可以根据这个方法调用所有HandlerMapping实现类进行请求地址映射。
2 AbstractHandlerMapping
AbstractHandlerMapping是所有HandlerMapping的抽象基类,提供了拦截器、排序和默认处理器等功能。
AbstractHandlerMapping是常见HandlerMapping实现类的共同父类,它的核心功能是定义了获取HandlerExecutionChain的基础流程:
- 获取
handler(由实现类定义具体逻辑) - 创建
HandlerExecutionChain,添加拦截器 - 添加跨域拦截器
AbstractHandlerMapping的getHandler()源码如下:
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 1、获取handler
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// Bean name or resolved handler?
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
// Ensure presence of cached lookupPath for interceptors and others
if (!ServletRequestPathUtils.hasCachedPath(request)) {
initLookupPath(request);
}
// 2、创建HandlerExecutionChain,添加拦截器
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);
}
else if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !DispatcherType.ASYNC.equals(request.getDispatcherType())) {
logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());
}
// 3、添加跨域拦截器
if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) || CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration config = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
if (getCorsConfigurationSource() != null) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = getCorsConfigurationSource().getCorsConfiguration(request);
config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(config) : config);
}
if (config != null) {
config.validateAllowCredentials();
}
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
2.1 获取handler
AbstractHandlerMapping通过getHandlerInternal()方法获取handler。
该方法由具体实现类进行实现,如果找到匹配的handler,则会返回该handler;如果没有找到,则会返回null。
具体实现我们会在下文的实现类中进行讲解。
2.2 创建HandlerExecutionChain,添加拦截器
AbstractHandlerMapping通过getHandlerExecutionChain()方法创建HandlerExecutionChain对象,并添加拦截器。源码如下:
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
// 1、创建HandlerExecutionChain对象
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
// 2、添加拦截器
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(request)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}
它会对初始化时配置的拦截器进行遍历:
- 如果是
MappedInterceptor实现类,会根据匹配规则进行判断是否添加。 - 如果不是
MappedInterceptor实现类,会直接添加。
2.3 添加跨域拦截器
添加跨域拦截器分为以下几个步骤:
- 判断是否存在跨域配置,或是否预检请求
- 获取
handler级别的跨域配置 - 获取
HandlerMapping级别的跨域配置 - 整合跨域配置
- 创建并添加跨域拦截器
2.3.1 判断是否存在跨域配置
在AbstractHandlerMapping中,会判断handler是否CorsConfigurationSource的实现类(对于RequestMappingHandlerMapping而言,handler是HandlerMethod类型,所以第一个条件永远是false),以及是否存在HandlerMapping级别的跨域配置源:
protected boolean hasCorsConfigurationSource(Object handler) {
if (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain) {
handler = ((HandlerExecutionChain) handler).getHandler();
}
return (handler instanceof CorsConfigurationSource || this.corsConfigurationSource != null);
}
而在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping子抽象类中,会进一步判断是否存在handler级别(也就是@CrossOrigin级别)的跨域配置:
protected boolean hasCorsConfigurationSource(Object handler) {
return super.hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler) ||
(handler instanceof HandlerMethod &&
this.mappingRegistry.getCorsConfiguration((HandlerMethod) handler) != null);
}
2.3.2 判断是否是预检请求
org.springframework.web.cors.CorsUtils#isPreFlightRequest:
public static boolean isPreFlightRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
return (HttpMethod.OPTIONS.matches(request.getMethod()) &&
request.getHeader(HttpHeaders.ORIGIN) != null &&
request.getHeader(HttpHeaders.ACCESS_CONTROL_REQUEST_METHOD) != null);
}
2.3.3 获取handler级别跨域配置
在AbstractHandlerMapping中,会判断handler是否CorsConfigurationSource的实现类,从中获取handler级别的跨域配置。对于RequestMappingHandlerMapping而言,handler是HandlerMethod类型,所以第一个条件永远返回null:
protected CorsConfiguration getCorsConfiguration(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
Object resolvedHandler = handler;
if (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain) {
resolvedHandler = ((HandlerExecutionChain) handler).getHandler();
}
if (resolvedHandler instanceof CorsConfigurationSource) {
return ((CorsConfigurationSource) resolvedHandler).getCorsConfiguration(request);
}
return null;
}
在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping子抽象类中,会从mappingRegistry(request-handler缓存)中获取handler级别的跨域配置(在上篇文章中,我们有讲述过RequestMappingHandlerMapping如何缓存@CrossOrigin级别的跨域配置的):
protected CorsConfiguration getCorsConfiguration(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = super.getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
if (handler instanceof HandlerMethod) {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler;
if (handlerMethod.equals(PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH)) {
return AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.ALLOW_CORS_CONFIG;
}
else {
CorsConfiguration corsConfigFromMethod = this.mappingRegistry.getCorsConfiguration(handlerMethod);
corsConfig = (corsConfig != null ? corsConfig.combine(corsConfigFromMethod) : corsConfigFromMethod);
}
}
return corsConfig;
}
2.3.4 获取HandlerMapping级别的跨域配置
从AbstractHandlerMapping的corsConfigurationSource成员变量中,可以获取到HandlerMapping级别的跨域配置,该配置可以通过以下方式添加:
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
// 添加HandlerMapping级别的跨域配置
}
}
2.3.5 整合跨域配置
在整合跨域配置过程中,有三种情况:
- 对于
origins、originPatterns、allowedHeaders、exposedHeaders和methods等列表属性,会获取全部。 - 对于
allowCredentials,会优先获取方法级别的配置。 - 对于
maxAge,会获取最大值。
具体可以查看相关源码:
public CorsConfiguration combine(@Nullable CorsConfiguration other) {
if (other == null) {
return this;
}
// Bypass setAllowedOrigins to avoid re-compiling patterns
CorsConfiguration config = new CorsConfiguration(this);
List<String> origins = combine(getAllowedOrigins(), other.getAllowedOrigins());
List<OriginPattern> patterns = combinePatterns(this.allowedOriginPatterns, other.allowedOriginPatterns);
config.allowedOrigins = (origins == DEFAULT_PERMIT_ALL && !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(patterns) ? null : origins);
config.allowedOriginPatterns = patterns;
config.setAllowedMethods(combine(getAllowedMethods(), other.getAllowedMethods()));
config.setAllowedHeaders(combine(getAllowedHeaders(), other.getAllowedHeaders()));
config.setExposedHeaders(combine(getExposedHeaders(), other.getExposedHeaders()));
Boolean allowCredentials = other.getAllowCredentials();
if (allowCredentials != null) {
config.setAllowCredentials(allowCredentials);
}
Long maxAge = other.getMaxAge();
if (maxAge != null) {
config.setMaxAge(maxAge);
}
return config;
}
2.3.6 创建并添加跨域拦截器
在这一步,对于预检请求,会创建HandlerExecutionChain;对于普通请求,会创建CorsInterceptor拦截器,并添加到首位:
protected HandlerExecutionChain getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(HttpServletRequest request,
HandlerExecutionChain chain, @Nullable CorsConfiguration config) {
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = chain.getInterceptors();
return new HandlerExecutionChain(new PreFlightHandler(config), interceptors);
}
else {
chain.addInterceptor(0, new CorsInterceptor(config));
return chain;
}
}
3 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping是HandlerMethod请求映射的抽象基类,它的getHandlerInternal()方法定义了请求地址映射的核心流程:
- 解析请求路径
- 根据请求地址查找
HandlerMethod
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getHandlerInternal:
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 1、解析请求地址
String lookupPath = initLookupPath(request);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
// 2、根据请求地址查找HandlerMethod
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
3.1 解析请求路径
解析请求路径过程会获取当前请求的接口地址路径。
简单来说,会去除请求地址开头的contextPaht。例如在application.properties配置contextPath如下:
server.servlet.context-path=/context-path
此时,请求/context-path/test地址,经过initLookPath()方法处理,会返回/test为实际请求路径。
实际上,这也很容易理解。因为在RequestMappingHandlerMapping初始化pathLookup映射缓存时,就没有将contextPath考虑在内,那么在实际处理请求时,当然也要把contextPath去掉。
解析请求路径的作用也是为了方便直接从pathLookup映射缓存中获取对应的RequestMappingInfo信息。
AbstractHandlerMapping#initLookupPath源码如下:
protected String initLookupPath(HttpServletRequest request) {
if (usesPathPatterns()) {
request.removeAttribute(UrlPathHelper.PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
RequestPath requestPath = ServletRequestPathUtils.getParsedRequestPath(request);
String lookupPath = requestPath.pathWithinApplication().value();
return UrlPathHelper.defaultInstance.removeSemicolonContent(lookupPath);
}
else {
return getUrlPathHelper().resolveAndCacheLookupPath(request);
}
}
3.2 根据请求路径查找HandlerMethod
在AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#lookupHandlerMethod方法中,会按如下步骤获取HandlerMethod:
- 根据请求路径从
pathLookup映射缓存查找对应的RequestMappingInfo列表。 - 根据
RequestMappingInfo从registry缓存中获取对应的MappingRegistration列表。 - 根据当前
request,对MappingRegistration列表按匹配度进行排序。 - 从中取匹配度最高的
HandlerMethod进行返回。
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#lookupHandlerMethod源码如下:
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath);
if (directPathMatches != null) {
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), matches, request);
}
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (matches.size() > 1) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
matches.sort(comparator);
bestMatch = matches.get(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);
}
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
for (Match match : matches) {
if (match.hasCorsConfig()) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
}
}
else {
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.getHandlerMethod().getMethod();
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
}
request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.getHandlerMethod());
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
return bestMatch.getHandlerMethod();
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
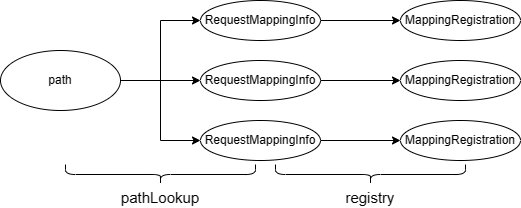
3.2.1 查找pathLookup缓存
在RequestMappingHandlerMapping请求地址映射的初始化过程中,会将@RequestMapping中的信息缓存到pathLookup中,其中该注解的请求路径作为key,该注解的各属性封装成RequestMappingInfo作为值。
需要注意的是,pathLookup的类型是MultiValueMap<String, T>,这里的T就是RequestMappingInfo。
pathLookup的底层数据结构实际上是path-List<RequestMappingInfo>,这是因为请求路径不是接口的唯一指标,还包括请求头、请求方法等信息。
所以,一个请求地址实际上可能映射着多个HandlerMethod。
例如,我们可以定义如下接口:
@RestController
public class SamePathController {
@GetMapping("/samePath")
public String get() {
return "get";
}
@PostMapping("/samePath")
public String post() {
return "post";
}
}
此时,GET localhost:8080/samePath和POST localhost:8080/samePath可以分别请求到对应的接口。
回到AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getHandlerInternal源码,此时通过请求路径可以获取多个RequestMappingInfo:
List<RequestMappingInfo> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByDirectPath(lookupPath);
3.2.2 查找registry缓存
在RequestMappingHandlerMapping请求地址映射的初始化过程中,会将接口的详细信息缓存到registry中,将上述RequestMappingInfo作为key,将RequestMappingInfo和HanlderMethod等信息装成MappingRegistration作为值。
registry的类型是Map<T, MappingRegistration<T>>,这里的T指的是RequestMappingInfo。
需要注意的是,由于RequestMappingInfo根据接口的@RequestMapping信息进行构造,如果存在@RequestMapping信息完全相同的多个接口,项目是无法启动的。
因此,RequestMappingInfo可以唯一定位到该接口,即RequestMappingInfo和MappingRegistration是一一对应的。我们也可以将RequestMappingInfo等效于实际接口。
我们可以总结一下pathLookup和registry缓存的关系:
回到AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#getHandlerInternal源码:
if (directPathMatches != null) {
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().keySet(), matches, request);
}
存在两种情况:
- 如果在
pathLookup缓存中找到对应List<RequestMappingInfo>,会进一步从该列表中查找更加匹配的RequestMappingInfo,并根据该RequestMapping从registry缓存中找到对应的MappingRegistration,封装成Match对象返回。 - 如果在
pathLookup缓存中没有找到对应List<RequestMappingInfo>,会遍历registry缓存中的所有key,从中查找更加匹配的RequestMappingInfo,并根据该RequestMapping从registry缓存中找到对应的MappingRegistration,封装成Match对象返回。
具体流程对应的AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#addMatchingMappings源码如下:
private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) {
for (T mapping : mappings) {
T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request);
if (match != null) {
matches.add(new Match(match, this.mappingRegistry.getRegistrations().get(mapping)));
}
}
}
查找更加匹配的RequestMappingInfo对应的是RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping#getMatchingMapping方法:
protected RequestMappingInfo getMatchingMapping(RequestMappingInfo info, HttpServletRequest request) {
return info.getMatchingCondition(request);
}
RequestMappingInfo#getMatchingCondition方法会对请求的methods、params、consumes、produces以及path进行校验,只有所有条件通过才会返回该RequestMappingInfo,否则会返回null。具体源码如下:
public RequestMappingInfo getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
RequestMethodsRequestCondition methods = this.methodsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (methods == null) {
return null;
}
ParamsRequestCondition params = this.paramsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (params == null) {
return null;
}
HeadersRequestCondition headers = this.headersCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (headers == null) {
return null;
}
ConsumesRequestCondition consumes = this.consumesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (consumes == null) {
return null;
}
ProducesRequestCondition produces = this.producesCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (produces == null) {
return null;
}
PathPatternsRequestCondition pathPatterns = null;
if (this.pathPatternsCondition != null) {
pathPatterns = this.pathPatternsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (pathPatterns == null) {
return null;
}
}
PatternsRequestCondition patterns = null;
if (this.patternsCondition != null) {
patterns = this.patternsCondition.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (patterns == null) {
return null;
}
}
RequestConditionHolder custom = this.customConditionHolder.getMatchingCondition(request);
if (custom == null) {
return null;
}
return new RequestMappingInfo(this.name, pathPatterns, patterns,
methods, params, headers, consumes, produces, custom, this.options);
}
通常情况下,通过这种判断可以筛选出唯一一个对应的RequestMappingInfo,除非是我们定义的接口比较特殊。
例如,我们定义接口如下:
@RestController
public class SamePathController {
@RequestMapping(value = "samePath", method = {RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST})
public String getAndPost() {
return "getAndPost";
}
@PostMapping("/samePath")
public String post() {
return "post";
}
}
此时,请求GET localhost:8080/samePath,可以筛选出来唯一一个定位到getAndPost()接口的RequestMappingInfo;请求POST localhost:8080/samePath,值可以筛选出两个分别定义到getAndPost()和post()方法的RequestMappingInfo,因为它们的规则都满足条件,需要进一步筛选。
3.2.3 按匹配度排序
通常情况下,通过上述步骤可以筛选出唯一一个RequestMappingInfo。
但是也有可能定义出条件重叠的接口(不推荐),此时会筛选出多个RequestMappingInfo。此时,需要根据某种规则进行匹配度排序。
RequestMappingInfo对于匹配度排序的规则是:
- 比较
methods、params和headers等条件的长度:越短越具体,匹配度越高。 - 长度相等时,比较其他特殊规则:例如
methods包含HEAD方法的匹配度高。
具体实现源码在RequestMappingInfo#compareTo:
public int compareTo(RequestMappingInfo other, HttpServletRequest request) {
int result;
// Automatic vs explicit HTTP HEAD mapping
if (HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(request.getMethod())) {
result = this.methodsCondition.compareTo(other.getMethodsCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
}
result = getActivePatternsCondition().compareTo(other.getActivePatternsCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
result = this.paramsCondition.compareTo(other.getParamsCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
result = this.headersCondition.compareTo(other.getHeadersCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
result = this.consumesCondition.compareTo(other.getConsumesCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
result = this.producesCondition.compareTo(other.getProducesCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
// Implicit (no method) vs explicit HTTP method mappings
result = this.methodsCondition.compareTo(other.getMethodsCondition(), request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
result = this.customConditionHolder.compareTo(other.customConditionHolder, request);
if (result != 0) {
return result;
}
return 0;
}
3.2.4 获取匹配度最高的HandlerMethod
通过上述步骤,我们最终获取到匹配度最高的RequestMappingInfo,直接取对应MappingRegistration的HandlerMethod成员变量返回即可。


